Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gillespie 4 e
Gillespie 4 e
Uploaded by
Swathi Uday0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
226 views3 pagesEconomics
Original Title
Gillespie4e
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEconomics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
226 views3 pagesGillespie 4 e
Gillespie 4 e
Uploaded by
Swathi UdayEconomics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Gillespie: Foundations of Economics 4e
Put into practice and end of chapter review questions
Chapter 19
Review questions
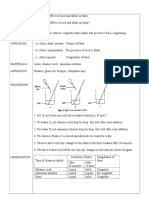
1. What is shown by aggregate demand?
Total planned expenditure on final goods and services in an economy in a
given time period.
2. What is shown by aggregate supply?
Total planned output of final goods and services in an economy in a given
time period.
3. How might an increase in the aggregate demand affect the equilibrium
price and output in the economy?
If aggregate supply is upward sloping it should lead to an increase in
equilibrium price and output.
4. Explain two factors that might cause an outward shift of the aggregate
supply curve.
An increase in the quantity of resources.
An improvement in the quality of resources.
5. Why might the aggregate supply be price inelastic?
If the economy is near full capacity then price changes may have relatively
little effect on the quantity supplied.
6. Explain two supply-side policies to promote growth.
Investment in training.
Improving the workings of the labour market.
Increase investment in capital and technology.
7. Explain two demand-side policies to promote growth.
Reduce direct taxation to encourage consumption spending to boost demand.
Andrew Gillespie, 2016. All rights reserved.
Gillespie: Foundations of Economics 4e
Increased government spending to boost demand.
8. Explain why Keynesians think aggregate supply is price elastic.
If the economy is significantly below full employment there will be
underutilised resources and capacity. This means output can increase
relatively easily if prices rise.
9. Explain why Classical economists think aggregate supply is price
inelastic.
If the economy is at full employment then an increase in price cannot easily
increase output and so supply is price inelastic.
10. Should demand-side policies always be used rather than supply-side
policies when a government intervenes in an economy?
It depends on the position of the economy- how close or far from full
employment it is and the effectiveness of different policies.
Put into practice questions
1. Explain why aggregate supply might be price inelastic.
The economy is near full capacity.
2. Explain why aggregate supply might be price elastic.
Economy is well below its capacity e.g. high levels of unemployment.
3. Show the effect of a decrease in aggregate demand on the equilibrium
price level in the economy and the quantity; assume that aggregate
supply is relatively price inelastic.
A fall in price and quantity; most of the effect is on price.
4. Show the effect of an increase in aggregate supply on the equilibrium
price and quantity. Assume that aggregate demand is relatively price
inelastic.
A fall in price and an increase in quantity. Most of the effect will be on price.
5. Explain the difference between demand-side policies and supply-side
policies using diagrams.
Demand side policies focus on influencing aggregate demand.
Andrew Gillespie, 2016. All rights reserved.
Gillespie: Foundations of Economics 4e
Supply side policies focus on influencing aggregate supply.
6. Imagine the components of aggregate demand are:
Consumption 500 billion
Investment 100 billion
Government spending 200 billion
Import spending 150 billion
Total aggregate demand 900 billion
What is the value of export spending? Explain your answer.
AD= C+I+G+X-M
900=500+100+200+?-150
Exports = 250 billion
7. All things being equal which could have caused the price level to have
fallen from P1 to P2?
a. a fall in interest rates. No.
b. a fall in exports. Yes this reduces aggregate demand.
c. a fall in production costs. No.
d. a fall in taxation rates. No.
Andrew Gillespie, 2016. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Tor - Mba Project - Walls Trikes Research - 1Document10 pagesTor - Mba Project - Walls Trikes Research - 1Hoorain KapadiaNo ratings yet
- The Sugarcube Sc-1 Mini: SweetvinylDocument2 pagesThe Sugarcube Sc-1 Mini: SweetvinylTaeMinKimNo ratings yet
- HTC160 Individual Assignment Foie GrasDocument13 pagesHTC160 Individual Assignment Foie GrasNurul DianahNo ratings yet
- Advanced Taxation Tutorial 4Document15 pagesAdvanced Taxation Tutorial 4kk k100% (1)
- Img 0004Document4 pagesImg 0004velavanNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Bahasa Inggeris Skema Kertas 2 Set BDocument5 pages2.4 Bahasa Inggeris Skema Kertas 2 Set BWnhannan Mohamad67% (3)
- Marketing Research ProposalDocument21 pagesMarketing Research Proposalsyu dinNo ratings yet
- Tajuk-Tajuk Penting Kertas 2 & 3 Biologi SPMDocument67 pagesTajuk-Tajuk Penting Kertas 2 & 3 Biologi SPMCaryn YeapNo ratings yet
- FFT Aura Fence Installation Manual v1.1.2Document104 pagesFFT Aura Fence Installation Manual v1.1.2Usman Zouque100% (2)
- Study of Marketing Mix of Maruti Suzuki - BBA Marketing Summer Training Project Report PDFDocument95 pagesStudy of Marketing Mix of Maruti Suzuki - BBA Marketing Summer Training Project Report PDFRj Bîmålkümãr75% (4)
- Reflective JournalDocument12 pagesReflective JournalNur asyikin SamsudiNo ratings yet
- Peka Form 5 2 (Exp No 1.3)Document3 pagesPeka Form 5 2 (Exp No 1.3)Naguib Zakaria100% (4)
- Chapter 5 - Capital Structure and Cost of CapitalDocument12 pagesChapter 5 - Capital Structure and Cost of CapitalTAN YUN YUNNo ratings yet
- 2020 F4 SCIENCE NOTES KSSM CHAPTER 4 6aDocument1 page2020 F4 SCIENCE NOTES KSSM CHAPTER 4 6aWani MesraNo ratings yet
- Aa025 Tutorial Answer Topic 7 AcmcDocument28 pagesAa025 Tutorial Answer Topic 7 Acmccjeipin123No ratings yet
- 2 KKIP (Slide Presentation)Document42 pages2 KKIP (Slide Presentation)Chin Thau WuiNo ratings yet
- English Form 4/5Document16 pagesEnglish Form 4/5Kannagi RajaNo ratings yet
- BM Contoh Karangan SPMDocument108 pagesBM Contoh Karangan SPMVeronicaNo ratings yet
- Study at Home For Secondary School Pupils 2020Document27 pagesStudy at Home For Secondary School Pupils 2020Jee Razali100% (1)
- SWOT Analysis Nasi Lemak DatinDocument1 pageSWOT Analysis Nasi Lemak Datinhakimu90No ratings yet
- What Is The Best Way For Teenagers To Stay Fit andDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Best Way For Teenagers To Stay Fit andQiao XinNo ratings yet
- React 2.0 Module JPN PerakDocument166 pagesReact 2.0 Module JPN PerakKureen FreddieNo ratings yet
- Universiti Teknologi Mara Final Examination: Confidential LW/APR 2010/LAW436/119Document4 pagesUniversiti Teknologi Mara Final Examination: Confidential LW/APR 2010/LAW436/119Hairulanuar SuliNo ratings yet
- ECO211Document11 pagesECO211Mia KulalNo ratings yet
- Soalan PpumDocument7 pagesSoalan PpumkiranaNo ratings yet
- Nota Sejarah Tingkatan 5 Bab 1 - KEMUNCULAN DAN PERKEMBANGAN NASIONALISME DI ASIA TENGGARADocument13 pagesNota Sejarah Tingkatan 5 Bab 1 - KEMUNCULAN DAN PERKEMBANGAN NASIONALISME DI ASIA TENGGARAJonathan HoNo ratings yet
- Boombastic Words ModulDocument20 pagesBoombastic Words Moduldavina100% (1)
- c5 Carbon Compounds f5Document19 pagesc5 Carbon Compounds f5Rui Er LiewNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 11 Preparation of Financial Statements (Q)Document6 pagesTutorial 11 Preparation of Financial Statements (Q)lious liiNo ratings yet
- SM025 Chapter 10 2018Document15 pagesSM025 Chapter 10 2018siti aisyahNo ratings yet
- FIN242 REPORT Group 3Document32 pagesFIN242 REPORT Group 3Izzat FarhanNo ratings yet
- Exercise Am015 Topic 1 UpsDocument3 pagesExercise Am015 Topic 1 UpsHafeszDean 860% (1)
- Peka Report Experiment 4.8 Effects of Acid and Alkali On LatexDocument2 pagesPeka Report Experiment 4.8 Effects of Acid and Alkali On LatexHOOI PHING CHANNo ratings yet
- Modern Math Form 4 (Mind Map)Document11 pagesModern Math Form 4 (Mind Map)Farieysha Binti Rohzi.No ratings yet
- C. Compilation of MUET Writting QuestionsDocument4 pagesC. Compilation of MUET Writting Questionsmuhamad habilNo ratings yet
- Course Information: 1.0 COURSE LEARNING OUTCOMES Upon Completion of This Course, Students Should BeDocument2 pagesCourse Information: 1.0 COURSE LEARNING OUTCOMES Upon Completion of This Course, Students Should BeaisyahNo ratings yet
- Bab 4 T4 Jirim Dan Bahan (Guru)Document14 pagesBab 4 T4 Jirim Dan Bahan (Guru)LeeKee100% (1)
- Q&A Section A AA025 - Lecturer EditionDocument40 pagesQ&A Section A AA025 - Lecturer EditionSyirleen Adlyna Othman100% (1)
- 294 Latihan Intensif PT3 2019 Sains PDFDocument23 pages294 Latihan Intensif PT3 2019 Sains PDFNorulfarrah binti Jaafar Teb3092No ratings yet
- Modul KPS SAINS SPMDocument54 pagesModul KPS SAINS SPMHuda WahabNo ratings yet
- Accounting 2 Second EditionDocument152 pagesAccounting 2 Second EditionFatin AinaNo ratings yet
- Bahagian BDocument6 pagesBahagian BNik ZakiahNo ratings yet
- Modul Pintas Tingkatan 5 Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM 2018 Skema Jawapan Matematik Tambahan Kertas 1 3472/1Document5 pagesModul Pintas Tingkatan 5 Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM 2018 Skema Jawapan Matematik Tambahan Kertas 1 3472/1allycat97No ratings yet
- Maf151 Chapter 3Document63 pagesMaf151 Chapter 3Aiman Zikry bin AzmiNo ratings yet
- F4 Physics Paper 3 Section B Experiments PDFDocument7 pagesF4 Physics Paper 3 Section B Experiments PDFahbingNo ratings yet
- Bio PBL 1Document13 pagesBio PBL 1Wee DarcyNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Answer SchemeDocument3 pagesTest 1 Answer SchemeNorazilah YunusNo ratings yet
- Tuisyen BiDocument134 pagesTuisyen BiwanieNo ratings yet
- Bahan Sintetik Dalam Industri: Synthetic Materials in IndustryDocument11 pagesBahan Sintetik Dalam Industri: Synthetic Materials in IndustrySunSuriaNo ratings yet
- (Soalan) 8 Koleksi Soalan Komsas NovelDocument22 pages(Soalan) 8 Koleksi Soalan Komsas NovelNoor Amira Rosli40% (5)
- Physics FolioDocument11 pagesPhysics FolioNadiah ChenNo ratings yet
- Analysis and List of Experiments For Biology SPM Paper 3Document2 pagesAnalysis and List of Experiments For Biology SPM Paper 3Adrian Jonathan Louis100% (1)
- Modul Analisis Fizik Merbau Miri SPM 2014 SkemaDocument5 pagesModul Analisis Fizik Merbau Miri SPM 2014 SkemaCikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- ECO415Document4 pagesECO415lohlinda25No ratings yet
- MRSM 2018 - JawapanDocument14 pagesMRSM 2018 - JawapanbeaveralterNo ratings yet
- Tuto5 BKAL DoneDocument8 pagesTuto5 BKAL DoneThe Four Incredible Hulks100% (1)
- Modul Semarak Bahasa Melayu SPM (Kertas 1 & 2) Penampang, Sabah 2021 SoalanDocument144 pagesModul Semarak Bahasa Melayu SPM (Kertas 1 & 2) Penampang, Sabah 2021 Soalannur liyana100% (1)
- BAB 3 Chapter Math ConsumerDocument3 pagesBAB 3 Chapter Math ConsumerJiah Mohd DaudNo ratings yet
- Koleksi Trial 2017 Paper 123Document176 pagesKoleksi Trial 2017 Paper 123shahidaNo ratings yet
- Nota Biologi Tingkatan 4 BAB 3Document12 pagesNota Biologi Tingkatan 4 BAB 3Firas Muhammad50% (4)
- Questions Teka TekiDocument3 pagesQuestions Teka TekiSyaifulHabibNo ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF Macroeconomics 9th Edition Boyes Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument39 pagesInstant Download PDF Macroeconomics 9th Edition Boyes Solutions Manual Full Chaptertalibheyley6100% (5)
- Full Macroeconomics 9Th Edition Boyes Solutions Manual Online PDF All ChapterDocument39 pagesFull Macroeconomics 9Th Edition Boyes Solutions Manual Online PDF All Chapterstevenjordan961980100% (5)
- Macroeconomics 9th Edition Boyes Solutions ManualDocument16 pagesMacroeconomics 9th Edition Boyes Solutions Manualgrainnematthew7cr3xy100% (34)
- IndiaDocument49 pagesIndiaSwathi UdayNo ratings yet
- Session 1 MISDocument30 pagesSession 1 MISSwathi UdayNo ratings yet
- Obtain The Initial Basic Feasible Solution by All Three Method and Optimal Solution byDocument1 pageObtain The Initial Basic Feasible Solution by All Three Method and Optimal Solution bySwathi UdayNo ratings yet
- How Businesses Use Information Systems-1Document10 pagesHow Businesses Use Information Systems-1Swathi UdayNo ratings yet
- Graphical Techniques 2015 AssignemntDocument2 pagesGraphical Techniques 2015 AssignemntSwathi UdayNo ratings yet
- 4thh Quarter Pre TestDocument1 page4thh Quarter Pre TestAlona Camino100% (2)
- Chinese Class Survey (Completed)Document4 pagesChinese Class Survey (Completed)Yibing ZhangNo ratings yet
- The First Lesson Plan ShapesDocument2 pagesThe First Lesson Plan Shapesapi-374751355No ratings yet
- ResumeDocument3 pagesResumejohn DaqueNo ratings yet
- Inbound 5129053772572461691Document17 pagesInbound 5129053772572461691LaksndNo ratings yet
- Maria Margaretha: Personal DetailDocument3 pagesMaria Margaretha: Personal DetailncocikaNo ratings yet
- Assembly 1Document21 pagesAssembly 1MOHIT PANTNo ratings yet
- Liebert - CRV Series Air Conditioner User Manual: V1.4 Revision Date May 28, 2012 BOM 31011886Document79 pagesLiebert - CRV Series Air Conditioner User Manual: V1.4 Revision Date May 28, 2012 BOM 31011886Dam Ngoc KienNo ratings yet
- Annual Procurement Plan-AppDocument6 pagesAnnual Procurement Plan-AppJonas MapacpacNo ratings yet
- 151-Enablon Orm - Permit To WorkDocument2 pages151-Enablon Orm - Permit To WorkRishikesh GunjalNo ratings yet
- 202221JSA (Job Safety Analysis) and HIRARC (Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment and Risk Control)Document7 pages202221JSA (Job Safety Analysis) and HIRARC (Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment and Risk Control)Khairulz AnuarNo ratings yet
- Workplace ViolenceDocument383 pagesWorkplace ViolenceAmeni Hlioui ChokriNo ratings yet
- Martin Luther 1st ThesisDocument6 pagesMartin Luther 1st Thesisrzaeetief100% (2)
- Rohit K ADocument13 pagesRohit K Awlv rajNo ratings yet
- 12h Identification Des Pieces Service BrakeDocument3 pages12h Identification Des Pieces Service BrakeaniriNo ratings yet
- Extraefi - Co.Uk Reset Problems: Ms1-Extra and Ms2-ExtraDocument8 pagesExtraefi - Co.Uk Reset Problems: Ms1-Extra and Ms2-Extraasser_salehNo ratings yet
- Sony Kdl32!37!40s5600 Chassis Ex2n-PeppermintDocument57 pagesSony Kdl32!37!40s5600 Chassis Ex2n-Peppermintvideoson100% (1)
- Father Absence and Self EsteemDocument40 pagesFather Absence and Self EsteemAlexandra BobeșNo ratings yet
- Lab 1.1 - 1.1.7 Lab - Basic Switch ConfigurationDocument13 pagesLab 1.1 - 1.1.7 Lab - Basic Switch ConfigurationHeng PhinNo ratings yet
- Viichy France and The Resistance Culture & IdeologyDocument301 pagesViichy France and The Resistance Culture & IdeologyandybgNo ratings yet
- Error Analysis in Physics PDFDocument2 pagesError Analysis in Physics PDFKrystal0% (1)
- Assignment Rubric Template 8.17.21Document3 pagesAssignment Rubric Template 8.17.21Aris Kendell BungabongNo ratings yet
- 40 HasanatDocument4 pages40 HasanatMuhammad KhanNo ratings yet
- Ielts Reading Test 40Document8 pagesIelts Reading Test 40Samarth BajajNo ratings yet
- Capacitor Placement Replacement Control in Large-Scale Distribution Systems by A GA-Based Two-Stage AlgorithmDocument7 pagesCapacitor Placement Replacement Control in Large-Scale Distribution Systems by A GA-Based Two-Stage AlgorithmKishore Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- S&D Market AnalysisDocument26 pagesS&D Market AnalysisMitali KNo ratings yet