Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Body Sistem Palmonary/Respiratori: Human Respiratory Process
Body Sistem Palmonary/Respiratori: Human Respiratory Process
Uploaded by
Putri Revany ElvinCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Human Breathing SystemDocument5 pagesThe Human Breathing SystemHarry Cianne Luther Sayon100% (1)
- Respiration (Part 1)Document15 pagesRespiration (Part 1)Jessie Clarinda JoyceNo ratings yet
- Breathing and RespirationDocument30 pagesBreathing and Respirationhamzahazard527No ratings yet
- Presentation 4Document15 pagesPresentation 4achsanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Respiratory SystemDocument33 pagesChapter 13 - Respiratory SystemCess Abad AgcongNo ratings yet
- Meri Bing Tugas RespiratoryDocument4 pagesMeri Bing Tugas RespiratoryNona MeyNo ratings yet
- Sistem Respirasi-Isti AnindyaDocument18 pagesSistem Respirasi-Isti AnindyaSindia MirnaNo ratings yet
- HBVHB B HBGVGHBDocument9 pagesHBVHB B HBGVGHBbaneNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Respiratory SystemDocument42 pagesAnatomy of The Respiratory Systempsidra456No ratings yet
- Animalphysio2nd 180428184330Document28 pagesAnimalphysio2nd 180428184330environmentalgyanNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System of Human Body FactsDocument12 pagesThe Respiratory System of Human Body FactsjulianneboloronNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Ventilation Report DraftDocument3 pagesPulmonary Ventilation Report DraftPrincess OlarteNo ratings yet
- Review of Respiratory PhysiologyDocument53 pagesReview of Respiratory PhysiologyMiftahul IfahNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System OkDocument36 pagesRespiratory System Okakselerasi10No ratings yet
- Module 9 Lesson 5Document21 pagesModule 9 Lesson 5Faatoots FatsNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System 8Document32 pagesRespiratory System 8Naanmatha PuspanathanNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesPhysiology of Respiratory SystemAngelica Joan SorianoNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 5 PDFDocument5 pagesLecture - 5 PDFDavid JokerNo ratings yet
- Ppt-Grade 9 - Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesPpt-Grade 9 - Respiratory SystemEdralyn Panes VillacrucisNo ratings yet
- University of Guyana School of Medicine Med 1106 - Physiology I DR Kalima ThompsonDocument66 pagesUniversity of Guyana School of Medicine Med 1106 - Physiology I DR Kalima ThompsonKNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: (A Written Report)Document16 pagesRespiratory System: (A Written Report)hellofrom theothersideNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument31 pagesRespiratory SystemMark Jhosua Austria GalinatoNo ratings yet
- Tarea de InglesDocument6 pagesTarea de InglesCesia Sinaí TrejoNo ratings yet
- Funda LecDocument5 pagesFunda LecJoannalyn FlordelizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17Document10 pagesChapter 17Yash Singh 11th BNo ratings yet
- Ingles Medico Ii - Clase 3: Vocabulary of Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesIngles Medico Ii - Clase 3: Vocabulary of Respiratory SystemAgustín Bravo ArreyesNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Breathing 2023Document17 pagesPhysiology of Breathing 2023ErickTéquizNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Respiration: Course Code: BBS01T1008 Course Name: Biology For EngineersDocument15 pagesPhysiology of Respiration: Course Code: BBS01T1008 Course Name: Biology For EngineersDivya TripathyNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument17 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasesArjun ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument56 pagesRespiratory SystemLorenz PasensyosoNo ratings yet
- Respiration & BreathingDocument18 pagesRespiration & BreathingKristal CampbellNo ratings yet
- RespiratoryDocument20 pagesRespiratoryBon BonselNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 BioDocument18 pagesChapter 11 BioRylee LNo ratings yet
- RespiratoryDocument249 pagesRespiratoryBulborea MihaelaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Anatomy Physiology and Dse DefinitionDocument4 pagesRespiratory Anatomy Physiology and Dse Definitionmiss RN100% (2)
- 14788physiology Respiration Lecture 1 - RRS BlockDocument11 pages14788physiology Respiration Lecture 1 - RRS BlockHsay AyitehgNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Anatomy of Respiratory Organs and Their FunctionsDocument6 pagesRespiratory System: Anatomy of Respiratory Organs and Their FunctionsRishabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance)Document17 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance)Michelle Gliselle Guinto MallareNo ratings yet
- Gr. 9 Science LM (AG)Document33 pagesGr. 9 Science LM (AG)Aizalonica GalangNo ratings yet
- Therespiratorysystem Grade 9Document19 pagesTherespiratorysystem Grade 9ClarkBautistaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument54 pagesRespiratory SystemALYZZA JANE BUNANo ratings yet
- Hercor CollegeDocument7 pagesHercor CollegeRodrinerBillonesNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 - Respiratory System 2021Document36 pagesTopic 7 - Respiratory System 2021Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyMarie Cris SorianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.1Document22 pagesChapter 1.1ieya_yNo ratings yet
- BIO 2701 Lecture Notes Exchange With The EnvironmentDocument11 pagesBIO 2701 Lecture Notes Exchange With The EnvironmentDorothy MayakaNo ratings yet
- Nota Ringkas Sains Bab 1 RespirasiDocument6 pagesNota Ringkas Sains Bab 1 RespirasiZuraina ShaharomNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument20 pagesRespiration in OrganismsAdityaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Nose and Nasal CavityDocument8 pagesRespiratory System: Nose and Nasal CavityJasper AlbuferaNo ratings yet
- Power Point Breathing SystemDocument17 pagesPower Point Breathing SystemI love ochinchinNo ratings yet
- Gray's Anatomy of The Human BodyDocument18 pagesGray's Anatomy of The Human BodyShinigami AmnerrorNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Gas Exchange in HumansDocument4 pagesCH 11 Gas Exchange in HumansPranitha RaviNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and Human Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesDiffusion and Human Respiratory SystemPriscilla AshwiniNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesRespiratory SystemayuNo ratings yet
- PDBreathing and Exchange of Gases Class 11 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 17FDocument15 pagesPDBreathing and Exchange of Gases Class 11 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 17Fgandhitirth147No ratings yet
- Respiatory (Histo) SubtitlesDocument17 pagesRespiatory (Histo) SubtitlesIsai Rivera-Sto DomingoNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 The Respiratory System: Learning OutcomesDocument9 pagesUnit 7 The Respiratory System: Learning OutcomesDeolita BadiangNo ratings yet
- Askep Sistem PernapasanDocument12 pagesAskep Sistem Pernapasanirlin ritiNo ratings yet
- How Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandHow Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
Body Sistem Palmonary/Respiratori: Human Respiratory Process
Body Sistem Palmonary/Respiratori: Human Respiratory Process
Uploaded by
Putri Revany ElvinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Body Sistem Palmonary/Respiratori: Human Respiratory Process
Body Sistem Palmonary/Respiratori: Human Respiratory Process
Uploaded by
Putri Revany ElvinCopyright:
Available Formats
BODY SISTEM
PALMONARY/RESPIRATORI
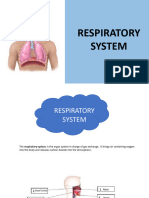
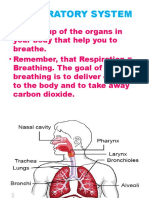
The respiratory system (called also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological
system consisting of specificorgans and structures used for the process of respiration in
organism. The respiratory system is involved in the intake andex change of oxygen and carbon
dioxide between an organism and the environment.
Sistem pernapasan (disebut juga aparatus pernapasan, sistem ventilasi) adalah sistem biologis
yang terdiri dari organ tertentu dan struktur yang digunakan untuk proses respirasi pada sebuah
organisme. Sistem pernapasan terlibat dalam intake dan pertukaran oksigen dan karbon
dioksida antara organisme dan lingkungan.
Humans need oxygen supplied continuously to the process of cell respiration, and remove excess
carbon dioxide as a toxic waste product of the process. Pertukatan between oxygen gas with
carbon dioxide is done in order to continue the process of cell respiration. Oxygen is needed for
cell respiration process is derived from the atmosphere
Manusia membutuhkan suply oksigen secara terus-menerus untuk proses respirasi sel, dan
membuang kelebihan karbondioksida sebagai limbah beracun produk dari proses tersebut.
Pertukatan gas antara oksigen dengan karbondioksida dilakukan agar proses respirasi sel terus
berlangsung. Oksigen yang dibutuhkan untuk proses respirasi sel ini berasal dari atmosfer,
Oxygen into the body through the intermediary of a respirator that is outside. In humans, the
alveoli are found in lung function as a surface for gas exchange.
Oksigen masuk kedalam tubuh melalui perantaraan alat pernapasan yang berada di luar. Pada
manusia, alveolus yang terdapat di paru-paru berfungsi sebagai permukaan untuk tempat
pertukaran gas.
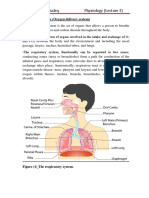
Human Respiratory Process
The course of the Breathing Air
1. Air enters through the nostrils
2. past the nasopharynx
3. pass oral farink
4. past the glottis
5. entry into the trachea
6. entry into the trachea called branching bronchus
7. entered into branching bronchi called bronchioles
8. Air ends at the end of the bronchus in the form of bubbles, called alveoli
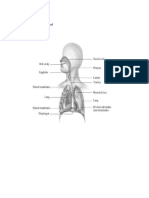
The order of the respiratory tract are as follows: the nasal cavity> faring> trachea> bronchus>
lungs (bronchioles and alveoli).
The process of respiration in humans begins from the nose. The air is sucked in when breathing
in (inspiration) usually enter through the nostrils (nares) left and right other than through the
mouth.
After passing through the nasal cavity, air enters the upper esophagus (Naro-pharinx) and then
down to the next entry throat (larynx).
Once through the throat, air enters the trachea or trachea, from there forwarded to the channel
named bronchus or bronchi. The bronchial tubes consist of several branching levels and
eventually have in the alveoli in the lungs.
The air will be absorbed through the alveoli into the capillaries which then flowed into the
pulmonary vein or pulmonary vein. Gas oxygen taken up by the blood. From there, the blood
will be poured into the left atrium of the heart and so on.
Proses Pernapasan Manusia
Ringkasan jalannya Udara Pernapasan:
1. Udara masuk melalui lubang hidung
2. melewati nasofaring
3. melewati oral farink
4. melewati glotis
5. masuk ke trakea
6. masuk ke percabangan trakea yang disebut bronchus
7. masuk ke percabangan bronchus yang disebut bronchiolus
8. udara berakhir pada ujung bronchus berupa gelembung yang disebut alveolus
Urutan saluran pernapasan adalah sebagai berikut: rongga hidung > faring > trakea > bronkus >
paru-paru (bronkiolus dan alveolus).
Proses pernapasan pada manusia dimulai dari hidung. Udara yang diisap pada waktu menarik
nafas (inspirasi) biasanya masuk melalui lubang hidung (nares) kiri dan kanan selain melalui
mulut.
Setelah melewati rongga hidung, udara masuk ke kerongkongan bagian atas (naro-pharinx) lalu
kebawah untuk selanjutnya masuk tenggorokan (larynx).
Setelah melalui tenggorokan, udara masuk ke batang tenggorok atau trachea, dari sana diteruskan
ke saluran yang bernama bronchus atau bronkus. Saluran bronkus ini terdiri dari beberapa tingkat
percabangan dan akhirnya berhubungan di alveolus di paru-paru.
Udara yang diserap melalui alveoli akan masuk ke dalam kapiler yang selanjutnya dialirkan ke
vena pulmonalis atau pembuluh balik paru-paru. Gas oksigen diambil oleh darah. Dari sana
darah akan dialirkan ke serambi kiri jantung dan seterusnya.
Types of Breathing In Humans
1. breathing Chest
Chest breathing is breathing that involves muscle antartulang ribs. The mechanism can
be distinguished as follows.
a. Inspiration phase
The muscles between the ribs (external intercostalis muscle) to contract -> raised ribs
(flat position) -> The lungs inflate -> air pressure in the lungs become smaller than
the outside air pressure -> air into lungs.
b. expiratory phase
The muscles between the ribs of relaxation -> rib decreases -> lungs shrink -> air
pressure in the lungs is greater than the outside air pressure -> the air out of the
lungs.
2. Abdominal breathing
Abdominal breathing is breathing that involves the muscles of the diaphragm. The
mechanism can be distinguished as follows.
a. Inspiration phase
diafragma contract -> into a horizontal position of the curved -> lungs inflate -> air
pressure in the lung is smaller than the outside air pressure -> the inlet air
b. expiratory phase
diafragma muscle relaxation -> position of the horizontal back arched -> lungs
deflating -> air pressure in the lungs more Besas than the outside air pressure -> the
air out of the lungs.
Jenis-Jenis Pernapasan Pada Manusia
1. Pernapasan Dada
Pernapasan dada adalah pernapasan yang melibatkan otot antartulang rusuk.
Mekanismenya dapat dibedakan sebagai berikut.
a. Fase inspirasi
Otot antar tulang rusuk (muskulus intercostalis eksternal) berkontraksi --> tulang rusuk
terangkat (posisi datar) --> Paru-paru mengembang --> tekanan udara dalam paru-paru
menjadi lebih kecil dibandingkan tekanan udara luar --> udara luar masuk ke paru-paru.
b. Fase ekspirasi
Otot antar tulang rusuk relaksasi --> tulang rusuk menurun --> paru-paru menyusut -->
tekanan udara dalam paru-paru lebih besar dibandingkan dengan tekanan udara luar -->
udara keluar dari paru-paru.
2. Pernapasan Perut
Pernapasan perut adalah pernapasan yang melibatkan otot diafragma. Mekanismenya
dapat dibedakan sebagai berikut.
a. Fase inspirasi
sekat rongga dada (diafraghma) berkontraksi --> posisi dari melengkung menjadi
mendatar --> paru-paru mengembang --> tekanan udara dalam paru-paru lebih kecil
dibandingkan tekanan udara luar --> udara masuk
b. Fase ekspirasi.
otot diafraghma relaksasi --> posisi dari mendatar kembali melengkung --> paru-paru
mengempis --> tekanan udara di paru-paru lebih besas dibandingkan tekanan udara luar --
> udara keluar dari paru-paru.
You might also like
- The Human Breathing SystemDocument5 pagesThe Human Breathing SystemHarry Cianne Luther Sayon100% (1)
- Respiration (Part 1)Document15 pagesRespiration (Part 1)Jessie Clarinda JoyceNo ratings yet
- Breathing and RespirationDocument30 pagesBreathing and Respirationhamzahazard527No ratings yet
- Presentation 4Document15 pagesPresentation 4achsanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Respiratory SystemDocument33 pagesChapter 13 - Respiratory SystemCess Abad AgcongNo ratings yet
- Meri Bing Tugas RespiratoryDocument4 pagesMeri Bing Tugas RespiratoryNona MeyNo ratings yet
- Sistem Respirasi-Isti AnindyaDocument18 pagesSistem Respirasi-Isti AnindyaSindia MirnaNo ratings yet
- HBVHB B HBGVGHBDocument9 pagesHBVHB B HBGVGHBbaneNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Respiratory SystemDocument42 pagesAnatomy of The Respiratory Systempsidra456No ratings yet
- Animalphysio2nd 180428184330Document28 pagesAnimalphysio2nd 180428184330environmentalgyanNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System of Human Body FactsDocument12 pagesThe Respiratory System of Human Body FactsjulianneboloronNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Ventilation Report DraftDocument3 pagesPulmonary Ventilation Report DraftPrincess OlarteNo ratings yet
- Review of Respiratory PhysiologyDocument53 pagesReview of Respiratory PhysiologyMiftahul IfahNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System OkDocument36 pagesRespiratory System Okakselerasi10No ratings yet
- Module 9 Lesson 5Document21 pagesModule 9 Lesson 5Faatoots FatsNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System 8Document32 pagesRespiratory System 8Naanmatha PuspanathanNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesPhysiology of Respiratory SystemAngelica Joan SorianoNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 5 PDFDocument5 pagesLecture - 5 PDFDavid JokerNo ratings yet
- Ppt-Grade 9 - Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesPpt-Grade 9 - Respiratory SystemEdralyn Panes VillacrucisNo ratings yet
- University of Guyana School of Medicine Med 1106 - Physiology I DR Kalima ThompsonDocument66 pagesUniversity of Guyana School of Medicine Med 1106 - Physiology I DR Kalima ThompsonKNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: (A Written Report)Document16 pagesRespiratory System: (A Written Report)hellofrom theothersideNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument31 pagesRespiratory SystemMark Jhosua Austria GalinatoNo ratings yet
- Tarea de InglesDocument6 pagesTarea de InglesCesia Sinaí TrejoNo ratings yet
- Funda LecDocument5 pagesFunda LecJoannalyn FlordelizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17Document10 pagesChapter 17Yash Singh 11th BNo ratings yet
- Ingles Medico Ii - Clase 3: Vocabulary of Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesIngles Medico Ii - Clase 3: Vocabulary of Respiratory SystemAgustín Bravo ArreyesNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Breathing 2023Document17 pagesPhysiology of Breathing 2023ErickTéquizNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Respiration: Course Code: BBS01T1008 Course Name: Biology For EngineersDocument15 pagesPhysiology of Respiration: Course Code: BBS01T1008 Course Name: Biology For EngineersDivya TripathyNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument17 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasesArjun ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument56 pagesRespiratory SystemLorenz PasensyosoNo ratings yet
- Respiration & BreathingDocument18 pagesRespiration & BreathingKristal CampbellNo ratings yet
- RespiratoryDocument20 pagesRespiratoryBon BonselNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 BioDocument18 pagesChapter 11 BioRylee LNo ratings yet
- RespiratoryDocument249 pagesRespiratoryBulborea MihaelaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Anatomy Physiology and Dse DefinitionDocument4 pagesRespiratory Anatomy Physiology and Dse Definitionmiss RN100% (2)
- 14788physiology Respiration Lecture 1 - RRS BlockDocument11 pages14788physiology Respiration Lecture 1 - RRS BlockHsay AyitehgNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Anatomy of Respiratory Organs and Their FunctionsDocument6 pagesRespiratory System: Anatomy of Respiratory Organs and Their FunctionsRishabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance)Document17 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance)Michelle Gliselle Guinto MallareNo ratings yet
- Gr. 9 Science LM (AG)Document33 pagesGr. 9 Science LM (AG)Aizalonica GalangNo ratings yet
- Therespiratorysystem Grade 9Document19 pagesTherespiratorysystem Grade 9ClarkBautistaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument54 pagesRespiratory SystemALYZZA JANE BUNANo ratings yet
- Hercor CollegeDocument7 pagesHercor CollegeRodrinerBillonesNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 - Respiratory System 2021Document36 pagesTopic 7 - Respiratory System 2021Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyMarie Cris SorianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.1Document22 pagesChapter 1.1ieya_yNo ratings yet
- BIO 2701 Lecture Notes Exchange With The EnvironmentDocument11 pagesBIO 2701 Lecture Notes Exchange With The EnvironmentDorothy MayakaNo ratings yet
- Nota Ringkas Sains Bab 1 RespirasiDocument6 pagesNota Ringkas Sains Bab 1 RespirasiZuraina ShaharomNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument20 pagesRespiration in OrganismsAdityaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Nose and Nasal CavityDocument8 pagesRespiratory System: Nose and Nasal CavityJasper AlbuferaNo ratings yet
- Power Point Breathing SystemDocument17 pagesPower Point Breathing SystemI love ochinchinNo ratings yet
- Gray's Anatomy of The Human BodyDocument18 pagesGray's Anatomy of The Human BodyShinigami AmnerrorNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Gas Exchange in HumansDocument4 pagesCH 11 Gas Exchange in HumansPranitha RaviNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and Human Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesDiffusion and Human Respiratory SystemPriscilla AshwiniNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesRespiratory SystemayuNo ratings yet
- PDBreathing and Exchange of Gases Class 11 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 17FDocument15 pagesPDBreathing and Exchange of Gases Class 11 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 17Fgandhitirth147No ratings yet
- Respiatory (Histo) SubtitlesDocument17 pagesRespiatory (Histo) SubtitlesIsai Rivera-Sto DomingoNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 The Respiratory System: Learning OutcomesDocument9 pagesUnit 7 The Respiratory System: Learning OutcomesDeolita BadiangNo ratings yet
- Askep Sistem PernapasanDocument12 pagesAskep Sistem Pernapasanirlin ritiNo ratings yet
- How Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandHow Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet