Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Plumbing Is Any System That Conveys Fluids For A Wide Range of
Plumbing Is Any System That Conveys Fluids For A Wide Range of
Uploaded by
Joseph BelisarioOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Plumbing Is Any System That Conveys Fluids For A Wide Range of
Plumbing Is Any System That Conveys Fluids For A Wide Range of
Uploaded by
Joseph BelisarioCopyright:
Available Formats
Plumbing is any system that conveys fluids for a wide range of
applications. Plumbing uses pipes, valves, plumbing fixtures, tanks, and
other apparatuses to convey fluids.[1] Heating and
cooling (HVAC), waste removal, and potable water delivery are among
the most common uses for plumbing, but it is not limited to these
applications. The word derives from the Latin for lead, plumbum, as the
first effective pipes used in the Roman era were lead pipes.
In the developed world, plumbing infrastructure is critical to public
health and sanitation. Boilermakers and pipefitters are not plumbers,
although they work with piping as part of their trade, but their work can
include some plumbing
Plumbing includes all of the water supply and water waste lines. When
the home's foundation is built, a plumber runs a supply line from the
street through the foundation wall or the slab. From that point, they run
the lines that supply water to the home to rooms where sinks, bathtubs,
showers and other fixtures will be installed.
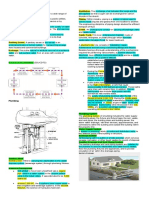
Copper piping is the traditional material most often used for water
supply lines, although some plastic piping materials are gaining
popularity and code approval. This diagram shows the path of the water
to the fixtures, as well as the path for waste water from the fixtures
through the drain waste vent pipes (DWV), and away from the home.
The drain waste vent pipe is part of a home's plumbing system that is
specifically used to carry waste water down and away from the home,
and allows sewer gases to be pushed out through the roof. Drain waste
vent pipes are typically plastic.
You might also like
- Plumbing ReportDocument29 pagesPlumbing ReportJohn Orland67% (3)
- PlumbingDocument19 pagesPlumbingJefford C. ObañaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PlumbingDocument18 pagesIntroduction To PlumbingJerico Ancheta86% (7)
- Plumbing 010Document79 pagesPlumbing 010Lyka Jane MercadoNo ratings yet
- PlumbingDocument5 pagesPlumbingmico alilayaNo ratings yet
- Masonry AND Concrete Works: "Plumbing System in Relation To Masonry" & "Plumbing Terms"Document7 pagesMasonry AND Concrete Works: "Plumbing System in Relation To Masonry" & "Plumbing Terms"mitch willyNo ratings yet
- Plumbing: Plumbing Is The System of Pipes, Drains Fittings, Valves, Valve Assemblies, and Devices Installed in ADocument1 pagePlumbing: Plumbing Is The System of Pipes, Drains Fittings, Valves, Valve Assemblies, and Devices Installed in ALGCPNo ratings yet
- Final Building UtiDocument18 pagesFinal Building UtiJalenmoriena PerezNo ratings yet
- Reaserch PaperDocument5 pagesReaserch PaperJohn Michael PascuaNo ratings yet
- Plumbing System: Prepared By: Group 7Document56 pagesPlumbing System: Prepared By: Group 7Glenn Midel Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- History: Drinking Pipes Tubing Plumbing Fixtures Plumber Piping Water Heaters Backflow PreventersDocument6 pagesHistory: Drinking Pipes Tubing Plumbing Fixtures Plumber Piping Water Heaters Backflow PreventersAnabelaVillaflorPendonNo ratings yet
- Tle q4 M1to3Document12 pagesTle q4 M1to3Syrart's Digitally Art'sNo ratings yet
- 1 Plumbing DefinitionDocument18 pages1 Plumbing DefinitionVikram DhabaleNo ratings yet
- Plumbing PortfolioDocument32 pagesPlumbing PortfolioAllan DeGuzman Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Plumbing Plans PDFDocument24 pagesChapter 20 Plumbing Plans PDFmimahmoud50% (2)
- 2 - Plumbing Definition and HistoryDocument19 pages2 - Plumbing Definition and HistoryMark Danilo CastilloNo ratings yet
- University of Gondar Institute of Technology Department of CotmDocument39 pagesUniversity of Gondar Institute of Technology Department of CotmYasichalew sefinehNo ratings yet
- Draft Sanitary and Plumbing Layout and DetailsDocument11 pagesDraft Sanitary and Plumbing Layout and DetailsRonelyn Tuliao Bueno Daniel100% (1)
- Plumbing: Prepared By: Ma. Sofia M. Gutierrez Beed 2-FDocument14 pagesPlumbing: Prepared By: Ma. Sofia M. Gutierrez Beed 2-FSOFIA GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Plumbing Is Any System That ConveysDocument1 pagePlumbing Is Any System That ConveysNina KatrinaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Plumbing Level 1 Rev 2Document10 pagesIntroduction To Plumbing Level 1 Rev 2Florence KisengeseNo ratings yet
- Plumbing Engineering: Design & EstimateDocument24 pagesPlumbing Engineering: Design & EstimateGintokiNo ratings yet
- PlumbingDocument11 pagesPlumbingTeodoro Miguel Carlos IsraelNo ratings yet
- Plumbing ResearchDocument4 pagesPlumbing ResearchJohn Renier AureadaNo ratings yet
- Plumbing Key AnswerDocument7 pagesPlumbing Key AnswerStanley Scott ArroyoNo ratings yet
- Plumbing-Water-System-Review (3B) PDFDocument22 pagesPlumbing-Water-System-Review (3B) PDFJhyneJazarenoAtutuboNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Hand Outs A.Y 2023 2024Document39 pagesGrade 7 Hand Outs A.Y 2023 2024Ryan Joseph BalmacedaNo ratings yet
- Interior Service SystemsDocument177 pagesInterior Service Systemsprashantkothari2002No ratings yet
- Hot Water Supply System MaterialsDocument4 pagesHot Water Supply System MaterialsVarunPatyalNo ratings yet
- Plumbing: Plumbing Is Any System That ConveysDocument58 pagesPlumbing: Plumbing Is Any System That Conveysstallone21No ratings yet
- QualifiedDocument25 pagesQualifiednatiz addisNo ratings yet
- Plumbing ModuleDocument14 pagesPlumbing ModuleJoseph CoralesNo ratings yet
- IndustrialArts Group5 PlumbingDocument6 pagesIndustrialArts Group5 Plumbingsrain092No ratings yet
- ME 428 Building Drainage SystemDocument11 pagesME 428 Building Drainage SystemJorwel Vincent E. VillalunaNo ratings yet
- Civil Technology - Topic 4Document14 pagesCivil Technology - Topic 4Zyla Balandra SorillaNo ratings yet
- TLE - PlumbingDocument20 pagesTLE - PlumbingsaglebalNo ratings yet
- GROUP 3 Solid WasteDocument20 pagesGROUP 3 Solid WastePhilip jhon T. IcaroNo ratings yet
- Notes in TleDocument110 pagesNotes in TlejhezelfrancostNo ratings yet
- PlumbingDocument1 pagePlumbingCri S TelNo ratings yet
- Part I - Sanitation and DrainageDocument25 pagesPart I - Sanitation and DrainagemariyaNo ratings yet
- Plumbing Technology Materials: Prepared by Patrick Macharia KivutiDocument8 pagesPlumbing Technology Materials: Prepared by Patrick Macharia KivutiPatrick MachariaNo ratings yet
- PLUMBING SYSTEM-WPS OfficeDocument10 pagesPLUMBING SYSTEM-WPS OfficeLea MaligsayNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Basic Plumbing SystemsDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Basic Plumbing SystemsSunKing Majestic Allaah100% (1)
- BuDocument2 pagesBuMARVEL SHOWSNo ratings yet
- Prelim-Reviewer-Utilities 2 (Plumbing)Document3 pagesPrelim-Reviewer-Utilities 2 (Plumbing)andromeda21233No ratings yet
- Plumbing Materials, Traps, Ventilation, Fixtures and InstallationDocument3 pagesPlumbing Materials, Traps, Ventilation, Fixtures and InstallationAldea ChanNo ratings yet
- Presentation 006 - The-Waste-and-Soil-Pipe-Report-Group-4Document17 pagesPresentation 006 - The-Waste-and-Soil-Pipe-Report-Group-4Mark Angelo Teodoro (Teodee)No ratings yet
- Sewage: Sullage: Plumbing/Drainage System: Sewer: Soil PipeDocument2 pagesSewage: Sullage: Plumbing/Drainage System: Sewer: Soil PipeMuhammad Nouman KhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PlumbingDocument52 pagesIntroduction To PlumbingDiane de OcampoNo ratings yet
- Plumbing PDFDocument266 pagesPlumbing PDFReaksmey BinNo ratings yet
- Plumbing PDFDocument70 pagesPlumbing PDFGiesyvel CaparosoNo ratings yet
- L-2 Housedrainage SystemDocument69 pagesL-2 Housedrainage SystemLumbini DuddeNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 ReviewerDocument5 pagesExam 1 ReviewerGriffin GarciaNo ratings yet
- Written R. PlumbingDocument5 pagesWritten R. PlumbingRia LopezNo ratings yet
- Harme, Jaylord Z. Assignment Engineering Utilities 2ce-1Document22 pagesHarme, Jaylord Z. Assignment Engineering Utilities 2ce-1Jaylord HarmeNo ratings yet
- Generalized Skeletal Disease, Has Emerged As A Major Health Problem Affecting Middle Aged and Older IndividualsDocument1 pageGeneralized Skeletal Disease, Has Emerged As A Major Health Problem Affecting Middle Aged and Older IndividualsJoseph BelisarioNo ratings yet
- Estimates QTY Unit Unit Cost Material Cost Clearing and Grubbing EarthworksDocument4 pagesEstimates QTY Unit Unit Cost Material Cost Clearing and Grubbing EarthworksJoseph BelisarioNo ratings yet
- Earthquakeanalysis rc2Document9 pagesEarthquakeanalysis rc2Joseph BelisarioNo ratings yet
- FEM LoadCombi DFDocument25 pagesFEM LoadCombi DFJoseph BelisarioNo ratings yet