Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CT: They Are Sharply Circumscribed and Lobulated Mass That Abuts The Dura. The
CT: They Are Sharply Circumscribed and Lobulated Mass That Abuts The Dura. The
Uploaded by
Joni KurniawanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CT: They Are Sharply Circumscribed and Lobulated Mass That Abuts The Dura. The
CT: They Are Sharply Circumscribed and Lobulated Mass That Abuts The Dura. The
Uploaded by
Joni KurniawanCopyright:
Available Formats
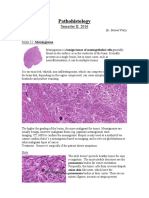
BAHAN Radiologi meningioma
Clinical Overview: Meningioma is the
most common extraaxial brain tumor.
They represent 20% of all primary brain
tumors. They are most common in adults
and are usually asymptomatic. They can
arise in a radiation field many years after
irradiation.
As in this case, 5% are atypical and 1%
are malignant, having a much worse
prognosis.
CT: They are sharply circumscribed and lobulated mass that abuts the dura. The
are extraaxial thus forming an obtuse angle to the dura. This is a key observation in
making the diagnosis because they are the most common extraaxial brain mass.
Furethermore, the obtuse angle to the dura can be associated with a "dural tail" sign
which is highly suggestive of a meningioma differentiating it from other extraaxial
mass like a schwannoma (figure 1). On unenhanced CT, most of the time they are
denser than brain. 20% have calcifications. It enhances very brightly and
occasionally have a non-enhancing necrotic center. The amount of surrounding
edema varies. There is hyperostotic or osteolytic bony reaction in 20% of the cases.
CT can be 95% sensitive with contrast and 85% without contrast.
MRI: Finding are characteristic of extraaxial masses: 1. CSF/vascular cleft
betweeen the mass and brain (figure 1) 2. displacement of gray-white matter
interface around mass.
T1 - iso or slightly hypointense relative to cortex
You might also like
- KMKP 2 BookDocument499 pagesKMKP 2 BookgigaslayerxNo ratings yet
- CNS Congenital AnomaliesDocument74 pagesCNS Congenital AnomaliesMoh DrhusseinyNo ratings yet
- Spinal Meningioma: DR Frank Gaillard View Revision HistoryDocument3 pagesSpinal Meningioma: DR Frank Gaillard View Revision HistoryRia SulistianaNo ratings yet
- Meningioma GreenbergDocument15 pagesMeningioma GreenbergRavanno Fanizza HarahapNo ratings yet
- SDL 8 Intracranial Space Occupying LesionDocument5 pagesSDL 8 Intracranial Space Occupying LesionJonathan YeohNo ratings yet
- MeningiomaDocument7 pagesMeningiomaLili HapverNo ratings yet
- Seizure, Headaches, and Right Hemiparesis: R M. B Iii, MDDocument2 pagesSeizure, Headaches, and Right Hemiparesis: R M. B Iii, MDcazecageNo ratings yet
- MeningiomaDocument19 pagesMeningiomaRavanno Fanizza HarahapNo ratings yet
- Intramedullary Spinal Cord Tumors: Clinical PresentationDocument15 pagesIntramedullary Spinal Cord Tumors: Clinical Presentationmetasoniko81No ratings yet
- Department of Internal Medicine,: Prof WBP Matuja Muhas/MnhDocument31 pagesDepartment of Internal Medicine,: Prof WBP Matuja Muhas/MnhDanyu KibuguluNo ratings yet
- Linee GuidaDocument7 pagesLinee GuidaDPNo ratings yet
- Pineal TumorDocument88 pagesPineal TumorHima AlamrieNo ratings yet
- Meningioma ArtikelDocument1 pageMeningioma ArtikelnabilaNo ratings yet
- Tumors of The Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesTumors of The Nervous SystemRituNo ratings yet
- Cerebellopontine Angle TumoursDocument11 pagesCerebellopontine Angle TumoursIsmail Sholeh Bahrun MakkaratteNo ratings yet
- WK II WikiDocument4 pagesWK II Wikiapi-174496267No ratings yet
- Presentation and Management of Intracranial Space Occupying Lesions (Icsol)Document66 pagesPresentation and Management of Intracranial Space Occupying Lesions (Icsol)heruNo ratings yet
- PEDTRIC SURGERY Dr. Isabedra - PDF Notes - 201702082201Document25 pagesPEDTRIC SURGERY Dr. Isabedra - PDF Notes - 201702082201deevonc100% (1)
- Brain TumorsDocument78 pagesBrain Tumorsnarswiponshistoryan100% (3)
- Brain TumorDocument26 pagesBrain TumorreginNo ratings yet
- Ventricular LesionsDocument76 pagesVentricular LesionsIslam AghouryNo ratings yet
- Tumors of The Nervous SystemDocument45 pagesTumors of The Nervous SystemIsaac MwangiNo ratings yet
- Brain TumorDocument9 pagesBrain TumorSara SabirNo ratings yet
- Posterior Fossa Metastases: Are There Pathognomonic MRI Features?Document2 pagesPosterior Fossa Metastases: Are There Pathognomonic MRI Features?Ira TadikaNo ratings yet
- BRAINTUMORSDocument2 pagesBRAINTUMORSkarenmstamNo ratings yet
- The Radiology Assistant Brain Tumor - Systematic Approach PDFDocument29 pagesThe Radiology Assistant Brain Tumor - Systematic Approach PDFMichael DeanNo ratings yet
- Braintumor 160822132617Document39 pagesBraintumor 160822132617krishnasreeNo ratings yet
- 10.1016@B978 0 323 47674 4.00063 3Document75 pages10.1016@B978 0 323 47674 4.00063 3ana claraNo ratings yet
- Skull Base Tumors PDFDocument20 pagesSkull Base Tumors PDFhimadriNo ratings yet
- A Meningioma Is ADocument20 pagesA Meningioma Is ASherry KingNo ratings yet
- Reti No Blast OmaDocument54 pagesReti No Blast OmaSaviana Tieku100% (1)
- Cranio Pha Ryn Gio MaDocument3 pagesCranio Pha Ryn Gio MaSerious LeoNo ratings yet
- Foramen Magnum Meningioma: A Rare Case Report: Haradhan Deb Nath Kanak Kanti Barua Shahnewaj Bari Hafizul AminDocument5 pagesForamen Magnum Meningioma: A Rare Case Report: Haradhan Deb Nath Kanak Kanti Barua Shahnewaj Bari Hafizul AminSham SundarNo ratings yet
- Journal of Child Neurology: Topical Review: A Review of Leptomeningeal Metastases in PediatricsDocument10 pagesJournal of Child Neurology: Topical Review: A Review of Leptomeningeal Metastases in PediatricsNurvia AndrianiNo ratings yet
- Sol IntracranialDocument76 pagesSol IntracranialPanduRespatiNo ratings yet
- Conjunctival Pigmented LesionsDocument0 pagesConjunctival Pigmented LesionsBhartendu Agarwal0% (1)
- ScriptDocument8 pagesScriptChristian Edward MacabaliNo ratings yet
- Brain TumorDocument15 pagesBrain TumorA Farid WajdyNo ratings yet
- Brain Tumors: Primary BTDocument5 pagesBrain Tumors: Primary BTMohamed Al-zichrawyNo ratings yet
- Mcfaline Figueroa2018Document9 pagesMcfaline Figueroa2018Kang LimbaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Meningiomas: A Pictorial ReviewDocument10 pagesMagnetic Resonance Imaging of Meningiomas: A Pictorial ReviewKevin EdroNo ratings yet
- Tumours of The Central Nervous System: FM Brett MD., FrcpathDocument57 pagesTumours of The Central Nervous System: FM Brett MD., FrcpathRerendhutNo ratings yet
- Agarwal 2016Document51 pagesAgarwal 2016Daniel Alfredo Tenorio GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Neuroma - PagesDocument2 pagesAcoustic Neuroma - Pagespeter-5No ratings yet
- 2017 - Paul Tahalele - Brain TumourDocument49 pages2017 - Paul Tahalele - Brain TumourVincentius Michael WilliantoNo ratings yet
- Brain TumorsDocument30 pagesBrain TumorsDagmawi BahiruNo ratings yet
- DR - Ign Purna Putra, Sps (K)Document64 pagesDR - Ign Purna Putra, Sps (K)Sheryl ElitaNo ratings yet
- Brain Cancer: by Cara KlingamanDocument16 pagesBrain Cancer: by Cara KlingamanLouis FortunatoNo ratings yet
- Caring For An Adult With A Malignant Primary BrainDocument6 pagesCaring For An Adult With A Malignant Primary Brainkayla sheppardNo ratings yet
- Brain Tumors: ReviewDocument9 pagesBrain Tumors: ReviewsarabisimonaNo ratings yet
- Medical Progress: Rain UmorsDocument10 pagesMedical Progress: Rain UmorsMoan JosNo ratings yet
- Brain Tumours: Clinical FeaturesDocument3 pagesBrain Tumours: Clinical FeaturesOber Sánchez100% (1)
- Intramedullary Spinal Cord TumorsDocument7 pagesIntramedullary Spinal Cord TumorsmutalimNo ratings yet
- Tumours of The Central Nervous System: FM Brett MD., FrcpathDocument57 pagesTumours of The Central Nervous System: FM Brett MD., FrcpathDrGasnasNo ratings yet
- Brain TumorsDocument34 pagesBrain TumorsbenedictusNo ratings yet
- Brain Cancer: by Cara KlingamanDocument16 pagesBrain Cancer: by Cara Klingamanrenu_gang1552No ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Brain TumorDocument9 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment of Brain TumorCharan TejaNo ratings yet
- Primary Brain TumorDocument33 pagesPrimary Brain Tumoriura echin100% (2)
- Botond Pathohisto Semester II Red PDFDocument108 pagesBotond Pathohisto Semester II Red PDFVeres ZsuzsiNo ratings yet
- Living with a Brain Tumor: Dr. Peter Black's Guide to Taking Control of Your TreatmentFrom EverandLiving with a Brain Tumor: Dr. Peter Black's Guide to Taking Control of Your TreatmentRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)