Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Torsional Stressed Spring
Torsional Stressed Spring
Uploaded by
mahmoudOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Torsional Stressed Spring
Torsional Stressed Spring
Uploaded by
mahmoudCopyright:
Available Formats
Ahmed El-Bialy
Torsion Spring
What is the torsion spring ?
A torsion spring is a spring that works by torsion or twisting ; that is , a flexible elastic object
that stores mechanical energy when it is twisted. When it is twisted , it exerts a force (actually
torque) in the opposite direction , proportional to the amount (angle) it is twisted .
How does a torsion spring work ?
torsion spring are helical springs that exert a torque or rotary force. ... They offer resistance to
twist or rotationally applied force. Depending on the application, torsion springs can be
designed to work in a clockwise or counter-clockwise rotation, thus determining the direction
of the wind .
What are the uses of springs ?
The energy you use isn't lost : most of it is stored as potential energy in the spring. Release a
stretched spring and you can use it to do work for you.
Are torsion springs better than extension Springs ?
Torsion springs are sturdier and last longer. Torsion springs do cost more, but generally last
between 15,000 and 20,000 cycles, whereas extension springs last up to 10,000 cycles .
what are the types of torsion spring ?
A torsion bar is a straight bar of metal or rubber that is subjected to twisting (shear stress)
about its axis by torque applied at its ends. A more delicate form used in sensitive instruments,
called a torsion fiber consists of a fiber of silk, glass, or quartz under tension, that is twisted
about its axis. The other type, a helical torsion spring, is a metal rod or wire in the shape of a
helix (coil) that is subjected to twisting about the axis of the coil by sideways forces (bending
moments) applied to its ends, twisting the coil tighter. This terminology can be confusing
because in a helical torsion spring the forces acting on the wire are actually bending stresses,
not torsional (shear) stresses .
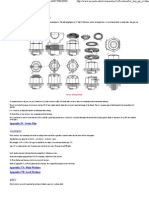
Standard Torsion Springs
1- Selection :-
First choose material type and helix. Next, select a range
of wire diameter that you think may be appropriate.
Finally, select the amount of deflection you expect to have
in the application.
2- load
This is the direct force applied at a given radius. Torque can be converted to load by the formula
given below.
Load (P) =Torque/Radius
3- Tolerances
Torque: 10%
Diameter: 5%
4- Torque
Torque values shown are at the degree of deflection listed for each spring. To find the
torque values for any other position simply use a direct proportion of the required
position divided by the listed position position, i.e. if the torque is listed as .500 in-lbs at
180 degrees deflection, what is the torque at 90 degrees?
( 90 deg / 180 deg ) x 500 in-lb = 0.250 in-lb
You might also like
- Kobelev Vladimir Durability of SpringsDocument291 pagesKobelev Vladimir Durability of Springsаримотома аримотомаNo ratings yet
- The Book of Basic Machines: The U.S. Navy Training ManualFrom EverandThe Book of Basic Machines: The U.S. Navy Training ManualRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- DME Unit 5 Springs PDFDocument51 pagesDME Unit 5 Springs PDFsachinroy8638No ratings yet
- Notes Unit 5 SHAIKH SIR NOTESmsbte Engg Info WebsiteDocument12 pagesNotes Unit 5 SHAIKH SIR NOTESmsbte Engg Info Websitebot armyNo ratings yet
- Design of Springs (Course-Notes)Document112 pagesDesign of Springs (Course-Notes)mOchONo ratings yet
- Spring DesignDocument112 pagesSpring Designchshbt80% (5)
- Helical Spring DesignDocument47 pagesHelical Spring DesignHKHKBOOKS100% (1)
- KCG College of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering Ce 6306-Strength of Materials (Sem: 3) Question Bank For Unit 3Document3 pagesKCG College of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering Ce 6306-Strength of Materials (Sem: 3) Question Bank For Unit 3adamodaraNo ratings yet
- MD SpringDocument19 pagesMD Springiftikhar ahmedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ShaftsDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Shaftsसुमित शर्माNo ratings yet
- MM 3rd Lab ReportDocument9 pagesMM 3rd Lab ReportIbrahim AfridiNo ratings yet
- Design of Springs PDFDocument54 pagesDesign of Springs PDFDhruv PancholiNo ratings yet
- TorsionDocument18 pagesTorsionBhupesh GoyalNo ratings yet
- Design of Helical and Leaf SpringsDocument92 pagesDesign of Helical and Leaf Springs208W1A1027Sec-A LINGAMANENI KOWSHIKNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Torsion - 2015Document38 pagesLecture 6 - Torsion - 2015imranjamiNo ratings yet
- Dme Short Answer QuestionsDocument16 pagesDme Short Answer QuestionsAbinandh VNo ratings yet
- Machine DesignDocument26 pagesMachine Designrajasekar21No ratings yet
- ME-603 SpringsDocument15 pagesME-603 Springskanaktanu54No ratings yet
- Dme Unit V (17.11.22)Document16 pagesDme Unit V (17.11.22)sathiaNo ratings yet
- AMSM Module 4Document27 pagesAMSM Module 4Shaji EtNo ratings yet
- ME374 - Module 4 (Updated)Document36 pagesME374 - Module 4 (Updated)VinNo ratings yet
- Design of Power ScrewsDocument45 pagesDesign of Power Screwssbkulk100% (1)
- Designofspring 190916095639Document16 pagesDesignofspring 190916095639ManojKumar MNo ratings yet
- CE8395 Solid MechanicsDocument4 pagesCE8395 Solid Mechanics26 MaheshkannanNo ratings yet
- Power ScrewsDocument45 pagesPower Screwsmuhammad hamzaNo ratings yet
- Closed Coiled Helical Springs Subjected To Axial LoadsDocument6 pagesClosed Coiled Helical Springs Subjected To Axial LoadsSnehasish Ishar100% (1)
- UNIT 3 Torsion and SpringDocument4 pagesUNIT 3 Torsion and Springl8o8r8d8s8i8v8100% (1)
- Steel ColumnDocument33 pagesSteel Columnelect aksNo ratings yet
- Sanjivani K. B. P. Polytechnic Kopargaon: Department of MechatronicsDocument35 pagesSanjivani K. B. P. Polytechnic Kopargaon: Department of MechatronicsChaitanya YengeNo ratings yet
- ME374 Module 2Document57 pagesME374 Module 2Christian Breth BurgosNo ratings yet
- Report of Spring Making Machine (1) (Repaired)Document42 pagesReport of Spring Making Machine (1) (Repaired)Ankit Mistry100% (2)
- Helical Springs - Design and SelectionDocument2 pagesHelical Springs - Design and SelectionCarlos Ediver Arias RestrepoNo ratings yet
- Design of SpringsDocument116 pagesDesign of SpringsIvica GNo ratings yet
- 5 Module 3 - Design of Mechanical Springs 17-05-2023Document79 pages5 Module 3 - Design of Mechanical Springs 17-05-2023aditya.d2021No ratings yet
- Springs 6Document53 pagesSprings 6Gaurav JiwnaniNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Notes - Engineering Level 3 CtechDocument11 pagesUnit 3 Notes - Engineering Level 3 CtechHadley PeckNo ratings yet
- Shaft DesignDocument16 pagesShaft DesignOgunsina AdebayoNo ratings yet
- ME374P1C2 - Exercise 5 - GuditoDocument49 pagesME374P1C2 - Exercise 5 - GuditoDessa GuditoNo ratings yet
- SpringsDocument12 pagesSpringssangei2093No ratings yet
- Torsion LectureDocument91 pagesTorsion LectureY o oNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Lab Manual (Repaired)Document32 pagesEngineering Mechanics Lab Manual (Repaired)sher shahNo ratings yet
- Design For ShaftDocument60 pagesDesign For ShaftMarlNo ratings yet
- Torsion Pendulum IDocument2 pagesTorsion Pendulum Ig.odbayar2021No ratings yet
- Kom Unit 5 NotesDocument94 pagesKom Unit 5 NotesParkunam RandyNo ratings yet
- Irjet V5i10168 PDFDocument6 pagesIrjet V5i10168 PDFRahul GargNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 TorsionDocument24 pagesLecture 3 TorsionJacob BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Shaft DesignDocument71 pagesChapter One Shaft DesignhaymanotNo ratings yet
- Som QBDocument6 pagesSom QB123rtyNo ratings yet
- SpringsDocument11 pagesSpringsDharmin MirajkarNo ratings yet
- Helical Spring RevisedDocument5 pagesHelical Spring RevisedJubaer RabbyNo ratings yet
- Definition For SpringDocument18 pagesDefinition For SpringamanpurushothNo ratings yet
- Technical Paper-Turbine Vibration NathDocument5 pagesTechnical Paper-Turbine Vibration NathHimansu GoswamiNo ratings yet
- SPRINGSDocument16 pagesSPRINGSPHANI RAJA RAONo ratings yet
- Springs NotesDocument9 pagesSprings NotesP DargopatilNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsFrom EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNo ratings yet
- LRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronFrom EverandLRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronNo ratings yet
- Locking Devices, Keys, Springs, Rivets and WeldingDocument13 pagesLocking Devices, Keys, Springs, Rivets and WeldingSrinath SaiNo ratings yet
- Thesis - Ishan Aggarwal - New Word PDFDocument67 pagesThesis - Ishan Aggarwal - New Word PDF1105456No ratings yet
- Moving The TeethDocument117 pagesMoving The TeethThirunavukkarasu Srinivasan100% (2)
- Design of Helical Compression Spring Used in PRVs of Gas Pipe-Lines SystemDocument31 pagesDesign of Helical Compression Spring Used in PRVs of Gas Pipe-Lines SystemHisham ShehadehNo ratings yet
- Feeder Tunnel DesignDocument71 pagesFeeder Tunnel DesignAkshay DuggalNo ratings yet
- Spring Wind UpDocument8 pagesSpring Wind UpAvinashRaiNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document30 pagesModule 5Vishwa VardhanNo ratings yet
- Helical SpringDocument7 pagesHelical SpringSalam Albaradie100% (4)
- Machine Drawing Is The Art of Representation of An Object by Systematic Lines On A PaperDocument79 pagesMachine Drawing Is The Art of Representation of An Object by Systematic Lines On A PaperAvinash KambleNo ratings yet
- Is 7907 1 2004 PDFDocument30 pagesIs 7907 1 2004 PDFAnisVisuNo ratings yet
- 1700 Animated 3Document143 pages1700 Animated 3Aquino MiguelNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Final Draft Portfolio VersionDocument8 pagesUnit 2 Final Draft Portfolio Versionapi-252159248No ratings yet
- IPhO 2010 Exp Problem 1Document4 pagesIPhO 2010 Exp Problem 1Paul DonayreNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Hydraulic Zigzag Bending MachineDocument5 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Hydraulic Zigzag Bending MachineeshwariNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Notes: Hookes LawDocument12 pagesForm 2 Notes: Hookes LawReg Ulus100% (1)
- Spiral Cylindrical Torsion SpringsDocument16 pagesSpiral Cylindrical Torsion SpringsSuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Energy, Energy Transfer, and General Energy Analysis: Prof. Dr. Ali PINARBAŞIDocument48 pagesEnergy, Energy Transfer, and General Energy Analysis: Prof. Dr. Ali PINARBAŞItaha haiderNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Elements 2 Marks - 5 UnitsDocument20 pagesDesign of Machine Elements 2 Marks - 5 UnitsArjun Arumugaswamy100% (4)
- Power Generation by Foot Step Method - Rack and PinionDocument13 pagesPower Generation by Foot Step Method - Rack and Pinionprem53100% (2)
- Helical SpringsDocument31 pagesHelical SpringsKiranNo ratings yet
- Gerak HarmoniDocument13 pagesGerak HarmoniNella Sri PujirahayuNo ratings yet
- 10.1. Spring Design (Formulas and Problems)Document2 pages10.1. Spring Design (Formulas and Problems)Melvin MhdsNo ratings yet
- 33 13FDocument86 pages33 13FGNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Machines-1Document4 pagesDynamics of Machines-1Akshay BondadeNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 TorsionDocument51 pagesChapter-3 TorsionNaimur Asif BornoNo ratings yet
- 64217Document28 pages64217amdevaNo ratings yet
- Design of SpringsDocument116 pagesDesign of SpringsIvica GNo ratings yet
- ON SUGAR CANE BUD CHIPPER Update-1Document17 pagesON SUGAR CANE BUD CHIPPER Update-1விக்னேஷ் வரன்No ratings yet
- Compression Spring Calculator (Load Based DesignDocument4 pagesCompression Spring Calculator (Load Based DesignabasakNo ratings yet