Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Inquiry Based Lesson Pythagorean Theorem
Inquiry Based Lesson Pythagorean Theorem
Uploaded by
api-384985442Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- G.gmd.4 Lesson Plan-Identifying Three-Dimensional Figures by Rotating Two-Dimensional FiguresDocument4 pagesG.gmd.4 Lesson Plan-Identifying Three-Dimensional Figures by Rotating Two-Dimensional FiguresWan FaizNo ratings yet
- Find The Distance Between The PointsDocument7 pagesFind The Distance Between The PointsMarie LouNo ratings yet
- Edu 650 - Week 5 Final ProjectDocument5 pagesEdu 650 - Week 5 Final Projectapi-259186679No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Parallel Lines Cut by A TransversalDocument2 pagesLesson Plan Parallel Lines Cut by A Transversalapi-534095936No ratings yet
- Number and Quantity Functions: Sequences Function NotationDocument2 pagesNumber and Quantity Functions: Sequences Function NotationAdit GhosalkarNo ratings yet
- Sat Math Hard Practice QuizDocument18 pagesSat Math Hard Practice QuizTongton Friend100% (2)
- Chapter 4 Deductive GeometryDocument34 pagesChapter 4 Deductive GeometryEric Mooi100% (1)
- Lesson Plan: The Importance of Pythagoras TheoremDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: The Importance of Pythagoras TheoremJoseph OluwasegunNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Questions and CuesDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Questions and Cuesapi-341104695No ratings yet
- Guided Notes Pythagorean Theorem 1Document4 pagesGuided Notes Pythagorean Theorem 1api-470562131No ratings yet
- Classroom Demographic Profile: Standards-Aligned Lesson Plan TemplateDocument8 pagesClassroom Demographic Profile: Standards-Aligned Lesson Plan TemplateJ JohnsonNo ratings yet
- 8 Grade Practice Test Objective 1.1aDocument29 pages8 Grade Practice Test Objective 1.1aV-academy Maths0% (1)
- Ell ChecklistfillableDocument2 pagesEll Checklistfillableapi-332482522No ratings yet
- Gifted and Talented PresentationDocument24 pagesGifted and Talented Presentationapi-379088385No ratings yet
- 513 Pythagorean Worked ExamplesDocument15 pages513 Pythagorean Worked Exampleskris_meslerNo ratings yet
- Math g8 m7 Teacher Materials PDFDocument340 pagesMath g8 m7 Teacher Materials PDFAce MariscalNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan GuideDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Guidex0rth0rnNo ratings yet
- LPP First DraftDocument9 pagesLPP First Draftapi-250867541100% (1)
- Identify Desired Results (Stage 1) Content Standards: Title of Unit Grade Level Curriculum Area Time Frame Developed byDocument7 pagesIdentify Desired Results (Stage 1) Content Standards: Title of Unit Grade Level Curriculum Area Time Frame Developed byapi-283548263No ratings yet
- Pythagorean THM LPDocument6 pagesPythagorean THM LPapi-270322298No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Trig RatiosDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Trig RatiosNazimul GhanieNo ratings yet
- Pythagoras TheoremDocument12 pagesPythagoras TheoremYeahNo ratings yet
- 5e Lesson PlanDocument2 pages5e Lesson PlanShiela May CacalNo ratings yet
- Sample UnitDocument5 pagesSample Unitapi-281594404No ratings yet
- Digital Unit Plan TemplateDocument3 pagesDigital Unit Plan TemplateNshanZeitounianNo ratings yet
- LessonplanfinalDocument17 pagesLessonplanfinalapi-347695796No ratings yet
- Surface AreaDocument36 pagesSurface AreaMary Belle Peraren Estores100% (1)
- L2-Apply P. T.: 8th Grade Unit 3: Geometric Applications of ExponentsDocument10 pagesL2-Apply P. T.: 8th Grade Unit 3: Geometric Applications of Exponentsapi-295961633No ratings yet
- 04-MCPT Pyth ParticipantDocument22 pages04-MCPT Pyth ParticipantEmmanuel K AnimNo ratings yet
- Differentiated Lessons 8th GradeDocument4 pagesDifferentiated Lessons 8th Gradeapi-245618331No ratings yet
- Label The Sides and Fill in The Blanks!Document4 pagesLabel The Sides and Fill in The Blanks!Alexandra KeresztesNo ratings yet
- Lesson NotebookDocument14 pagesLesson Notebookapi-242207724No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Day 1 of Similar Figures: Teachers: Bethany ConradDocument6 pagesLesson Plan: Day 1 of Similar Figures: Teachers: Bethany Conradapi-193730631No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Guide: TE 407 - Fall 2007 1/10 08.27.07Document10 pagesLesson Plan Guide: TE 407 - Fall 2007 1/10 08.27.07api-283548263No ratings yet
- Latex of Area of A Triangle Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesLatex of Area of A Triangle Lesson Planapi-326746305No ratings yet
- Grade 9 Measurement - Area Lesson PlanDocument30 pagesGrade 9 Measurement - Area Lesson Plannegus russellNo ratings yet
- How Long Are My Sides?Document4 pagesHow Long Are My Sides?Alexandra KeresztesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3-Angles of TrianglesDocument5 pagesLesson 3-Angles of Trianglesapi-269787508No ratings yet
- Unit Plan Ed 331Document20 pagesUnit Plan Ed 331api-271061830No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Pythagorean TheoremDocument3 pagesLesson Plan - Pythagorean TheoremEric StottNo ratings yet
- Geo 2 4Document3 pagesGeo 2 4rmullen82No ratings yet
- Area of CirclesDocument6 pagesArea of CirclesliahliahliahNo ratings yet
- Eugenetalbot En453 Ten Day Unit PlanDocument20 pagesEugenetalbot En453 Ten Day Unit Planapi-304800863No ratings yet
- ResearchDocument7 pagesResearchapi-269301109No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Sequence of LearningDocument5 pagesUnit 3 Sequence of Learningapi-258500655No ratings yet
- Pythagorean Theorem 3Document8 pagesPythagorean Theorem 3Molly FrantzNo ratings yet
- Geometry Observation Lesson For Area and PerimeterDocument20 pagesGeometry Observation Lesson For Area and Perimeterapi-234842570No ratings yet
- Distance Formula LPDocument2 pagesDistance Formula LPapi-270322298No ratings yet
- Weeblyisosceles 2Document10 pagesWeeblyisosceles 2api-273150759No ratings yet
- CCSS - Math.Content - HSG.SRT.C.8: Lesson Plan Candidate: Subject(s) : Grade Level(s) : DateDocument2 pagesCCSS - Math.Content - HSG.SRT.C.8: Lesson Plan Candidate: Subject(s) : Grade Level(s) : Dateapi-324346015No ratings yet
- But Wait, You Can Make It Easier! Multiply!Document4 pagesBut Wait, You Can Make It Easier! Multiply!Alexandra KeresztesNo ratings yet
- Coteaching Strategy LessonDocument11 pagesCoteaching Strategy Lessonapi-548203401No ratings yet
- Triangle Inequality Theorem Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesTriangle Inequality Theorem Lesson PlanManilyn SuarezNo ratings yet
- En 408 Geometry Unit MapDocument2 pagesEn 408 Geometry Unit Mapapi-253882035No ratings yet
- 6th Graph Geometric FiguresDocument2 pages6th Graph Geometric Figuresapi-253021879No ratings yet
- Discovering The Area Formula For TrianglesDocument4 pagesDiscovering The Area Formula For TrianglesPanagiotis SotiropoulosNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Feb 8th-11thDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Feb 8th-11thapi-272841990No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesLesson PlanMGPagaduanNo ratings yet
- Digital Camera Assignment WordDocument4 pagesDigital Camera Assignment Wordapi-309168612No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Math 3Document11 pagesLesson Plan For Math 3api-692048029No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument19 pagesLesson Planapi-549572509No ratings yet
- An Alternative Approach To Alternate AnglesDocument17 pagesAn Alternative Approach To Alternate AnglesFani TNo ratings yet
- Grade9 Week12Document6 pagesGrade9 Week12Shamsa AwaisNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 3-Final-RevisedDocument3 pagesLesson Plan 3-Final-Revisedapi-234882491No ratings yet
- 8-2 Notes GeometryDocument2 pages8-2 Notes GeometryNoah BlautNo ratings yet
- Volley BallDocument8 pagesVolley Ballapi-385746668No ratings yet
- Crop Circle Theorems: Their Proofs and Relationship To Musical NotesDocument16 pagesCrop Circle Theorems: Their Proofs and Relationship To Musical NotesRisto PirovskiNo ratings yet
- Christine - Cover Letter - The Orchard HideoutDocument2 pagesChristine - Cover Letter - The Orchard Hideoutapi-458139452No ratings yet
- GR 12 2020 Mathematics Paper 1 - Topic Revision QuestionsDocument52 pagesGR 12 2020 Mathematics Paper 1 - Topic Revision Questionssunday simwandaNo ratings yet
- Triplet ProjectDocument4 pagesTriplet ProjectAKSHITHAJELLANo ratings yet
- Right Angle TrigonometryDocument4 pagesRight Angle Trigonometryarg456No ratings yet
- Anticipation Guide Rob WollerDocument1 pageAnticipation Guide Rob WollerRob WollerNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument26 pagesTrigonometryDwayne TraceyNo ratings yet
- Nazca MysteriesDocument17 pagesNazca MysteriesJah BillahNo ratings yet
- App Inventor. Examples. Tutorials. Games. Codes BlocksDocument23 pagesApp Inventor. Examples. Tutorials. Games. Codes BlocksFernandoNo ratings yet
- Piping Isometrics What Is An Isometric - C H A P T e R 13Document38 pagesPiping Isometrics What Is An Isometric - C H A P T e R 13Cleyton L. AlvesNo ratings yet
- Math Sem-1 Objective QuestionsDocument68 pagesMath Sem-1 Objective QuestionsAyaan NawazNo ratings yet
- UPCAT Mathematics Answer Key Set 2Document10 pagesUPCAT Mathematics Answer Key Set 2Irishmae HervasNo ratings yet
- b9 Maths Wk5Document4 pagesb9 Maths Wk5MOHAMMED ABDULNo ratings yet
- Mathematics "History of MathemeticiansDocument30 pagesMathematics "History of MathemeticiansDHANo ratings yet
- HL Portfolio WorkDocument76 pagesHL Portfolio WorkFadi AyyoubNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry SolutionsDocument3 pagesTrigonometry Solutionsscribd-in-actionNo ratings yet
- Demo PythagoreanDocument5 pagesDemo PythagoreanJacquelyne Bocoya TenebroNo ratings yet
- CuboctahedronDocument16 pagesCuboctahedronapi-310888850No ratings yet
- Copy Lines & PlanesDocument17 pagesCopy Lines & Planeskembara08No ratings yet
- Pythagorean Theorem: 5000 B.C. and Other Philosophical FantasiesDocument91 pagesPythagorean Theorem: 5000 B.C. and Other Philosophical FantasiesDini Putri UtamiNo ratings yet
- Similarity of TrianglesDocument38 pagesSimilarity of TrianglesunikxocizmNo ratings yet
- Expt 1 - PHY433-430 - PHET Simulation - Vector - Oct 2020 PDFDocument7 pagesExpt 1 - PHY433-430 - PHET Simulation - Vector - Oct 2020 PDFNurul AtikaNo ratings yet
- PythagoreanTheoremWorksheet 2Document3 pagesPythagoreanTheoremWorksheet 2yetriNo ratings yet
- Squares and Square RootsDocument41 pagesSquares and Square RootsSuchit singh F 30No ratings yet
Inquiry Based Lesson Pythagorean Theorem
Inquiry Based Lesson Pythagorean Theorem
Uploaded by
api-384985442Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Inquiry Based Lesson Pythagorean Theorem
Inquiry Based Lesson Pythagorean Theorem
Uploaded by
api-384985442Copyright:
Available Formats
Lesson Plan
General Topic of Lesson and Concepts and Procedures to be Used:
The purpose of this lesson is for students to discover and prove the Pythagorean Theorem. This would be a two
day lesson when taught to my students. This is an 8th grade topic.
The NJSLL for this lesson is 8.G.B Understand and apply the Pythagorean Theorem, with concentration on sub-
strands 6 and 7.
8.G.B.6 - Explain a proof of the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse.
8.G.B.7 - Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to determine unknown side lengths in right triangles in real world
and mathematical problems in two and three dimensions.
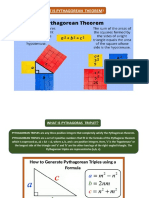
Students will investigate the Pythagorean Theorem using a puzzle to find that the sum of the areas of the
squares on the legs of a right triangle is equal to the area of the square on the hypotenuse. Students will then
collect data about the areas of squares on the sides of a right triangle. They use patterns in their data to confirm
that the sum of the areas of the two smaller squares equals the area of the largest square. Students are then
introduced to this idea in symbolic form: If a and b are the lengths of the legs of a right triangle, and c is the
length of the hypotenuse, then a2 + b2 = c2.
Mathematics Goals: (Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs):
Students will be able to solve for the unknown measurement in any given right triangle.
Students will be able to justify the relationship between the legs and hypotenuse of any right triangle.
Procedures and Materials:
Enactive (Concrete/Motor) Mode Materials and Procedures Students will investigate an 11 Piece puzzle and
try to fit the pieces into two frames. They must use all of the pieces. The pieces consist of 3 squares and 8
equal right triangles. Once students have fit the pieces into the frames they will make conjectures about the
relationship between the sides of the right triangle and the area of the squares. The goal is for the students to
see that the square root of each square represents one side of the triangle.
Iconic (Pictorial) Mode Materials and Procedures Students will be given two right triangles that are drawn on a dot
grids. They will construct the squares on each side of the triangle. Students will then find the area of the squares and
the corresponding side lengths. Students will organize their data in a table and then draw conclusions about the
relationship between the sum of the area of the squares. The goal is for students to discover that the sum of the area
of the two smaller squares is equal to the area of the largest square.
Symbolic (Written or Oral) Mode Materials and Procedures Students will be asked to analyze the patterns
from the two previous activities to create a rule that can be used for any right triangle. The goal is for students
to develop a2 + b2 = c2.
Assessment of Learning Outcomes Students will complete an exit ticket requiring them to solve for the
unknown side of a right triangle.
You might also like
- G.gmd.4 Lesson Plan-Identifying Three-Dimensional Figures by Rotating Two-Dimensional FiguresDocument4 pagesG.gmd.4 Lesson Plan-Identifying Three-Dimensional Figures by Rotating Two-Dimensional FiguresWan FaizNo ratings yet
- Find The Distance Between The PointsDocument7 pagesFind The Distance Between The PointsMarie LouNo ratings yet
- Edu 650 - Week 5 Final ProjectDocument5 pagesEdu 650 - Week 5 Final Projectapi-259186679No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Parallel Lines Cut by A TransversalDocument2 pagesLesson Plan Parallel Lines Cut by A Transversalapi-534095936No ratings yet
- Number and Quantity Functions: Sequences Function NotationDocument2 pagesNumber and Quantity Functions: Sequences Function NotationAdit GhosalkarNo ratings yet
- Sat Math Hard Practice QuizDocument18 pagesSat Math Hard Practice QuizTongton Friend100% (2)
- Chapter 4 Deductive GeometryDocument34 pagesChapter 4 Deductive GeometryEric Mooi100% (1)
- Lesson Plan: The Importance of Pythagoras TheoremDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: The Importance of Pythagoras TheoremJoseph OluwasegunNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Questions and CuesDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Questions and Cuesapi-341104695No ratings yet
- Guided Notes Pythagorean Theorem 1Document4 pagesGuided Notes Pythagorean Theorem 1api-470562131No ratings yet
- Classroom Demographic Profile: Standards-Aligned Lesson Plan TemplateDocument8 pagesClassroom Demographic Profile: Standards-Aligned Lesson Plan TemplateJ JohnsonNo ratings yet
- 8 Grade Practice Test Objective 1.1aDocument29 pages8 Grade Practice Test Objective 1.1aV-academy Maths0% (1)
- Ell ChecklistfillableDocument2 pagesEll Checklistfillableapi-332482522No ratings yet
- Gifted and Talented PresentationDocument24 pagesGifted and Talented Presentationapi-379088385No ratings yet
- 513 Pythagorean Worked ExamplesDocument15 pages513 Pythagorean Worked Exampleskris_meslerNo ratings yet
- Math g8 m7 Teacher Materials PDFDocument340 pagesMath g8 m7 Teacher Materials PDFAce MariscalNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan GuideDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Guidex0rth0rnNo ratings yet
- LPP First DraftDocument9 pagesLPP First Draftapi-250867541100% (1)
- Identify Desired Results (Stage 1) Content Standards: Title of Unit Grade Level Curriculum Area Time Frame Developed byDocument7 pagesIdentify Desired Results (Stage 1) Content Standards: Title of Unit Grade Level Curriculum Area Time Frame Developed byapi-283548263No ratings yet
- Pythagorean THM LPDocument6 pagesPythagorean THM LPapi-270322298No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Trig RatiosDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Trig RatiosNazimul GhanieNo ratings yet
- Pythagoras TheoremDocument12 pagesPythagoras TheoremYeahNo ratings yet
- 5e Lesson PlanDocument2 pages5e Lesson PlanShiela May CacalNo ratings yet
- Sample UnitDocument5 pagesSample Unitapi-281594404No ratings yet
- Digital Unit Plan TemplateDocument3 pagesDigital Unit Plan TemplateNshanZeitounianNo ratings yet
- LessonplanfinalDocument17 pagesLessonplanfinalapi-347695796No ratings yet
- Surface AreaDocument36 pagesSurface AreaMary Belle Peraren Estores100% (1)
- L2-Apply P. T.: 8th Grade Unit 3: Geometric Applications of ExponentsDocument10 pagesL2-Apply P. T.: 8th Grade Unit 3: Geometric Applications of Exponentsapi-295961633No ratings yet
- 04-MCPT Pyth ParticipantDocument22 pages04-MCPT Pyth ParticipantEmmanuel K AnimNo ratings yet
- Differentiated Lessons 8th GradeDocument4 pagesDifferentiated Lessons 8th Gradeapi-245618331No ratings yet
- Label The Sides and Fill in The Blanks!Document4 pagesLabel The Sides and Fill in The Blanks!Alexandra KeresztesNo ratings yet
- Lesson NotebookDocument14 pagesLesson Notebookapi-242207724No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Day 1 of Similar Figures: Teachers: Bethany ConradDocument6 pagesLesson Plan: Day 1 of Similar Figures: Teachers: Bethany Conradapi-193730631No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Guide: TE 407 - Fall 2007 1/10 08.27.07Document10 pagesLesson Plan Guide: TE 407 - Fall 2007 1/10 08.27.07api-283548263No ratings yet
- Latex of Area of A Triangle Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesLatex of Area of A Triangle Lesson Planapi-326746305No ratings yet
- Grade 9 Measurement - Area Lesson PlanDocument30 pagesGrade 9 Measurement - Area Lesson Plannegus russellNo ratings yet
- How Long Are My Sides?Document4 pagesHow Long Are My Sides?Alexandra KeresztesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3-Angles of TrianglesDocument5 pagesLesson 3-Angles of Trianglesapi-269787508No ratings yet
- Unit Plan Ed 331Document20 pagesUnit Plan Ed 331api-271061830No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Pythagorean TheoremDocument3 pagesLesson Plan - Pythagorean TheoremEric StottNo ratings yet
- Geo 2 4Document3 pagesGeo 2 4rmullen82No ratings yet
- Area of CirclesDocument6 pagesArea of CirclesliahliahliahNo ratings yet
- Eugenetalbot En453 Ten Day Unit PlanDocument20 pagesEugenetalbot En453 Ten Day Unit Planapi-304800863No ratings yet
- ResearchDocument7 pagesResearchapi-269301109No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Sequence of LearningDocument5 pagesUnit 3 Sequence of Learningapi-258500655No ratings yet
- Pythagorean Theorem 3Document8 pagesPythagorean Theorem 3Molly FrantzNo ratings yet
- Geometry Observation Lesson For Area and PerimeterDocument20 pagesGeometry Observation Lesson For Area and Perimeterapi-234842570No ratings yet
- Distance Formula LPDocument2 pagesDistance Formula LPapi-270322298No ratings yet
- Weeblyisosceles 2Document10 pagesWeeblyisosceles 2api-273150759No ratings yet
- CCSS - Math.Content - HSG.SRT.C.8: Lesson Plan Candidate: Subject(s) : Grade Level(s) : DateDocument2 pagesCCSS - Math.Content - HSG.SRT.C.8: Lesson Plan Candidate: Subject(s) : Grade Level(s) : Dateapi-324346015No ratings yet
- But Wait, You Can Make It Easier! Multiply!Document4 pagesBut Wait, You Can Make It Easier! Multiply!Alexandra KeresztesNo ratings yet
- Coteaching Strategy LessonDocument11 pagesCoteaching Strategy Lessonapi-548203401No ratings yet
- Triangle Inequality Theorem Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesTriangle Inequality Theorem Lesson PlanManilyn SuarezNo ratings yet
- En 408 Geometry Unit MapDocument2 pagesEn 408 Geometry Unit Mapapi-253882035No ratings yet
- 6th Graph Geometric FiguresDocument2 pages6th Graph Geometric Figuresapi-253021879No ratings yet
- Discovering The Area Formula For TrianglesDocument4 pagesDiscovering The Area Formula For TrianglesPanagiotis SotiropoulosNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Feb 8th-11thDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Feb 8th-11thapi-272841990No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesLesson PlanMGPagaduanNo ratings yet
- Digital Camera Assignment WordDocument4 pagesDigital Camera Assignment Wordapi-309168612No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Math 3Document11 pagesLesson Plan For Math 3api-692048029No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument19 pagesLesson Planapi-549572509No ratings yet
- An Alternative Approach To Alternate AnglesDocument17 pagesAn Alternative Approach To Alternate AnglesFani TNo ratings yet
- Grade9 Week12Document6 pagesGrade9 Week12Shamsa AwaisNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 3-Final-RevisedDocument3 pagesLesson Plan 3-Final-Revisedapi-234882491No ratings yet
- 8-2 Notes GeometryDocument2 pages8-2 Notes GeometryNoah BlautNo ratings yet
- Volley BallDocument8 pagesVolley Ballapi-385746668No ratings yet
- Crop Circle Theorems: Their Proofs and Relationship To Musical NotesDocument16 pagesCrop Circle Theorems: Their Proofs and Relationship To Musical NotesRisto PirovskiNo ratings yet
- Christine - Cover Letter - The Orchard HideoutDocument2 pagesChristine - Cover Letter - The Orchard Hideoutapi-458139452No ratings yet
- GR 12 2020 Mathematics Paper 1 - Topic Revision QuestionsDocument52 pagesGR 12 2020 Mathematics Paper 1 - Topic Revision Questionssunday simwandaNo ratings yet
- Triplet ProjectDocument4 pagesTriplet ProjectAKSHITHAJELLANo ratings yet
- Right Angle TrigonometryDocument4 pagesRight Angle Trigonometryarg456No ratings yet
- Anticipation Guide Rob WollerDocument1 pageAnticipation Guide Rob WollerRob WollerNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument26 pagesTrigonometryDwayne TraceyNo ratings yet
- Nazca MysteriesDocument17 pagesNazca MysteriesJah BillahNo ratings yet
- App Inventor. Examples. Tutorials. Games. Codes BlocksDocument23 pagesApp Inventor. Examples. Tutorials. Games. Codes BlocksFernandoNo ratings yet
- Piping Isometrics What Is An Isometric - C H A P T e R 13Document38 pagesPiping Isometrics What Is An Isometric - C H A P T e R 13Cleyton L. AlvesNo ratings yet
- Math Sem-1 Objective QuestionsDocument68 pagesMath Sem-1 Objective QuestionsAyaan NawazNo ratings yet
- UPCAT Mathematics Answer Key Set 2Document10 pagesUPCAT Mathematics Answer Key Set 2Irishmae HervasNo ratings yet
- b9 Maths Wk5Document4 pagesb9 Maths Wk5MOHAMMED ABDULNo ratings yet
- Mathematics "History of MathemeticiansDocument30 pagesMathematics "History of MathemeticiansDHANo ratings yet
- HL Portfolio WorkDocument76 pagesHL Portfolio WorkFadi AyyoubNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry SolutionsDocument3 pagesTrigonometry Solutionsscribd-in-actionNo ratings yet
- Demo PythagoreanDocument5 pagesDemo PythagoreanJacquelyne Bocoya TenebroNo ratings yet
- CuboctahedronDocument16 pagesCuboctahedronapi-310888850No ratings yet
- Copy Lines & PlanesDocument17 pagesCopy Lines & Planeskembara08No ratings yet
- Pythagorean Theorem: 5000 B.C. and Other Philosophical FantasiesDocument91 pagesPythagorean Theorem: 5000 B.C. and Other Philosophical FantasiesDini Putri UtamiNo ratings yet
- Similarity of TrianglesDocument38 pagesSimilarity of TrianglesunikxocizmNo ratings yet
- Expt 1 - PHY433-430 - PHET Simulation - Vector - Oct 2020 PDFDocument7 pagesExpt 1 - PHY433-430 - PHET Simulation - Vector - Oct 2020 PDFNurul AtikaNo ratings yet
- PythagoreanTheoremWorksheet 2Document3 pagesPythagoreanTheoremWorksheet 2yetriNo ratings yet
- Squares and Square RootsDocument41 pagesSquares and Square RootsSuchit singh F 30No ratings yet