Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mechanics
Mechanics
Uploaded by
BhanuOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mechanics
Mechanics
Uploaded by
BhanuCopyright:
Available Formats
5/15/2014
WRC MECHANICA
ENGLISH | Bhanu Timalsena
PHYSIC ~1~
Mechanics
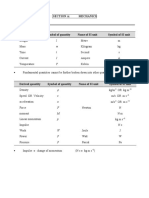
Fundamental physical quantities
Physical quantities not depending on other quantities are
fundamental quantities & their units are k\a fundamental
unities.
CGS, MKS, & FPS system have only 3 fundamental quantities
while SI system has 7.
Fundamental Unties Symbol Reference element
quantities
Length Meter M Krypton-86
Mass Kilogram Kg Platinum-iridium cylinder
(90%+10%)
Time Second S Caesium-133
Temperature Kelvin K
Current Ampere A
Luminous Candela Cd
intensity
Amount of Mole Mol Carbon-12
substance
Units
1 shake=10-8sec
1 barn=10-28m2
1 parsec= 3.26 light year
1 light year=9.45*1015m
1 Astronomical unit (AU)=1.5*1011m
1 metric tonne =10 quintal=10000 kg
1 feet=0.3048m
1 Chandrasekher limit=1.4 Ms (Where Ms is mass of sun)
1 A0=10-10m
BY: BHANU TIMAKLSENA
PHYSIC ~2~
1 X-ray unit=10-13m
1 torr=1mm of Hg=133.3 Pa
Dimensionless quantities [M0L0T0]
1. Relative density 8. Magnetic susceptibility
2. Angle and solid angle 9. Electric susceptibility
3. Strain 10. Dielectric constant
4. Poisson’s ratio 11. Relative permeability
5. Refractive index 12. Relative permittivity
6. Mechanical eqvt. of heat 13. Coefficient of friction
7. Emissivity 14. Loudness
Quantities having identical dimension
Quantities Dimension
Frequency, Angular frequency, [Mo L0 T-1]
Angular velocity, Velocity gradient
Angular momentum, modulus of [M L2 T-1]
elasticity, Energy density
Pressure, Stress, Modulus of [M L-1 T-2]
elasticity, Energy density
Work, Energy, Torque [M L2 T2]
BY: BHANU TIMAKLSENA
PHYSIC ~3~
Thermal capacity, Water equivalent, [ML2 T-2 K-1 ]
Boltzmann constant
Electric field strength equivalent, [M L T-3 A-1]
potential gradient
Electric potential, Potential [M L2 T-3 A-1]
difference and Emf
Force, Thrust, Weight, Energy [M LT-2]
gradient
L/R=√𝐋𝐂=RC =Dimensions of time [T]
Surface Tension, Surface energy, [MT-2]
Spring constant, Force gradient
PV = nRT = qV =Ll2 =
𝐪^𝟐
=Vlt [ML2 T2]
𝐂
=V2C=Dimensions of work
Physical Dimensions S.I. Unit
quantity
From Mechanics
Acceleration [M0 L T-2 ] Ms-2
Force [M L T-2] Kg ms-2
Linear momentum [M L T-1] Kg ms-1
BY: BHANU TIMAKLSENA
PHYSIC ~4~
Impulse [M L T-1] Kg ms-1
Work or Energy [M L2 T-2] Kg m2s-2
Power [M L2 T-3] Kg m2s-3
Presser or stress [M L-1 T-2] Kg m-1s-2
Strain [M0 L0 T0} No unit
Elastic modulus [M L-1 T-2] Nm-2
Angular [M0 L0 T0] Rad
displacement
Angular velocity [M0 L0 T-1] Rad s-1
Frequency [M0 L0 T-1] Hz
Angular [M0 L0 T-2] Rad s-2
acceleration
Momentum of [M L2 T0] Kg m2
inertia
Surface tension [M L0 T-2] Nm-1
Force constant [M L0 T-2] Nm-1
Angular [M L2 T-1] J-s
momentum
Gravitational [M-1 L3 T-2] Kg-1m3s-2
constant
Velocity gradient [M0 L0 T-1] s-1
Coefficient of [M L-1 T-1] Kgm-1s-1
viscosity
Gravitational [M0 L T-2] N/kg
intensity
Gravitational [M L2 T-2] J/kg
potential
BY: BHANU TIMAKLSENA
PHYSIC ~5~
Plank’s constant [M L2 T-1] J-s
From Heat
Heat energy [M L2 T-2] J
Specific heat [L2 T-2]K-1] Jkg-1°𝑪
Latent heat [M0 L2 T-2] J-kg-1
Thermal [M L T-3 K1] Kilocal m-1s-1°𝒄-1
conductivity
BY: BHANU TIMAKLSENA
You might also like
- The List of Dimensional Formula. A Useful Handout.Document5 pagesThe List of Dimensional Formula. A Useful Handout.vikramkhatri478% (151)
- Base Quantity Name Symbol: Fundamentals of Mechanical EngineeringDocument39 pagesBase Quantity Name Symbol: Fundamentals of Mechanical Engineeringlukhman100% (1)
- Ta35 Libro de PartesDocument620 pagesTa35 Libro de Partesestefaniacs100% (1)
- 01 42 13 - Abbreviations and SymbolsDocument4 pages01 42 13 - Abbreviations and SymbolsshauhramNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Physics and Measurement Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadDocument8 pagesJEE Main Physics and Measurement Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadGIRIDHARAN MURUGANNo ratings yet
- General Physics I NoteDocument9 pagesGeneral Physics I NoteAyuba oveyNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument145 pagesPhysicsSS NDANo ratings yet
- Physics Notes Class 11 CHAPTER 2 UNITS AND MEASUREMENTS PDFDocument7 pagesPhysics Notes Class 11 CHAPTER 2 UNITS AND MEASUREMENTS PDFLYF WITH AK KUMAR67% (3)
- Mole ObjectiveDocument26 pagesMole ObjectiveDevil WalkerNo ratings yet
- SI UnitsDocument8 pagesSI UnitsRoy VeseyNo ratings yet
- Final-01PE Units, Dimensions and Errors in Measurement - DocDocument10 pagesFinal-01PE Units, Dimensions and Errors in Measurement - Docnavidnazar12028No ratings yet
- Physical Quantities, Units and DimensionsDocument12 pagesPhysical Quantities, Units and Dimensionsdavid ama100% (1)
- Dimensional Analysis NotesDocument7 pagesDimensional Analysis Notes32 - VEDANSH JAISWALNo ratings yet
- Ashes of Love ?Document4 pagesAshes of Love ?Aadyasha PandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 NotesDocument8 pagesChapter 2 NotesSatyam YadavNo ratings yet
- A Units & DimensionsDocument19 pagesA Units & Dimensionsf20230069No ratings yet
- Easurements: Course: Diploma Subject: Applied Science Physics Unit: IDocument28 pagesEasurements: Course: Diploma Subject: Applied Science Physics Unit: Ipankaj baviskarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - 240Document13 pagesChapter 1 - 240Nurul AinNo ratings yet
- Class Xi MaterialDocument316 pagesClass Xi MaterialShlok MishraNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Analysis and SimilitudeDocument25 pagesDimensional Analysis and Similitudejllama20004321No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On PHY 101Document7 pagesLecture Notes On PHY 101Ezenwaka Eucharia100% (2)
- Fluid Mechanics Lecture 5Document19 pagesFluid Mechanics Lecture 5Muhammad ShahayarNo ratings yet
- Units, Dimensions Error AnalysisDocument25 pagesUnits, Dimensions Error AnalysisVishal KumarNo ratings yet
- FLUID MECHANICS (MEE 414) LECTURE NOTE (New)Document46 pagesFLUID MECHANICS (MEE 414) LECTURE NOTE (New)Sampson UsangNo ratings yet
- One Candela Is The Luminous Intensity in Perpendicular Direction of A Surface ofDocument6 pagesOne Candela Is The Luminous Intensity in Perpendicular Direction of A Surface ofydsrajuNo ratings yet
- Class11 MathsDocument6 pagesClass11 Mathsansuman9901No ratings yet
- Gravimetric Analysis (PDFDrive)Document167 pagesGravimetric Analysis (PDFDrive)ChilaNo ratings yet
- STPM Physic FormulaDocument4 pagesSTPM Physic FormulaWee Soon ChaiNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document53 pagesModule 1Alias SimounNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Points To RememberDocument8 pagesChapter 1 Points To RememberSaksham YadavNo ratings yet
- Units and MeasurementDocument4 pagesUnits and Measurementsonu kumarNo ratings yet
- Formulae - 2Document35 pagesFormulae - 2A.BensonNo ratings yet
- The List of Dimensional Formula A Useful HandoutDocument5 pagesThe List of Dimensional Formula A Useful Handoutrakibul islam100% (6)
- Units and Dimmension Important MaterialDocument11 pagesUnits and Dimmension Important MaterialAMARENDRA SINo ratings yet
- M T L T N I I: Physical Quantity Unit SymbolDocument3 pagesM T L T N I I: Physical Quantity Unit SymbolMark ArceNo ratings yet
- 1.2 UnitsDocument24 pages1.2 UnitsHerman HermanNo ratings yet
- Units & DimensionsDocument6 pagesUnits & DimensionsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Stucor Ce3391 deDocument141 pagesStucor Ce3391 deAnish KumarNo ratings yet
- 3238-Article Text-5879-1-10-20180104Document140 pages3238-Article Text-5879-1-10-20180104Maharajan McsNo ratings yet
- Cha01sec41 PDFDocument10 pagesCha01sec41 PDFAnonymous wczzN84ONo ratings yet
- Unidades y Dimensiones PDFDocument17 pagesUnidades y Dimensiones PDFISRAELNo ratings yet
- Besaran, Satuan, Dan Pengukuran Dalam FisikaDocument4 pagesBesaran, Satuan, Dan Pengukuran Dalam FisikaRhasyah R. SanjayaNo ratings yet
- All Dimensional Formula List PDF Free Download PDF HunterDocument5 pagesAll Dimensional Formula List PDF Free Download PDF HunterSarthak Kamli100% (1)
- All Dimensional Formula List PDF Free Download PDF HunterDocument5 pagesAll Dimensional Formula List PDF Free Download PDF HunterIrangaMadhuhansi SellahewaNo ratings yet
- Units and Dimensions of Class 11 Physics - PWDocument10 pagesUnits and Dimensions of Class 11 Physics - PWsoumojitg16No ratings yet
- 3.units and MeasurementsDocument15 pages3.units and MeasurementsNiranjan V SNo ratings yet
- International UnitsDocument10 pagesInternational Unitspilas_nikolaNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document2 pagesSheet 1gfhgjhkjNo ratings yet
- Draft Concise Summary 2018Document6 pagesDraft Concise Summary 2018Edgar TreviñoNo ratings yet
- Oil Field Trainee TestDocument102 pagesOil Field Trainee TesteditinggroNo ratings yet
- SSC Mts Ex: Studymaterialfor GenralawarenessDocument6 pagesSSC Mts Ex: Studymaterialfor GenralawarenessSubhajit DasNo ratings yet
- CSEC Physics - Definitions and FormulaeDocument39 pagesCSEC Physics - Definitions and FormulaeA.Benson100% (1)
- Physical Quantities, Standards and Units PDFDocument6 pagesPhysical Quantities, Standards and Units PDFARAVINDNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics Notes Chapter 1 Studyguide360Document24 pagesClass 11 Physics Notes Chapter 1 Studyguide360Allmagicalme YTNo ratings yet
- Fluid (F)Document13 pagesFluid (F)Muhammad HiwaNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Boiler EfficiencyDocument14 pagesCalculation of Boiler EfficiencyBharat Choksi100% (1)
- Zoo Architecture - Animal / Visitor / Management Friendly Designs, Presentation at The SAZARC Fourth Annual Meeting, Colombo, December 1-7, 2003Document3 pagesZoo Architecture - Animal / Visitor / Management Friendly Designs, Presentation at The SAZARC Fourth Annual Meeting, Colombo, December 1-7, 2003greyNo ratings yet
- Impeller Trim For PumpDocument9 pagesImpeller Trim For PumpkasiNo ratings yet
- Gypsum Blocks - Definitions, Requirements and Test Methods: British Standard Bs en 12859:2001Document38 pagesGypsum Blocks - Definitions, Requirements and Test Methods: British Standard Bs en 12859:2001AA0809No ratings yet
- Consulting - Specifying Engineer - NFPA 20 - Fire Pump Design 1Document15 pagesConsulting - Specifying Engineer - NFPA 20 - Fire Pump Design 1HSEI Jatim - NSU 2020No ratings yet
- Flashing 580iDocument3 pagesFlashing 580ikirananneNo ratings yet
- VSP Final ReportDocument53 pagesVSP Final ReportAnand GautamNo ratings yet
- Bu 80Document34 pagesBu 80laurent.nouvelNo ratings yet
- Brun&Beslier (1996) Mantle ExhumationDocument13 pagesBrun&Beslier (1996) Mantle ExhumationClarisse FernandesNo ratings yet
- CV Rizaljs Indonesia PDFDocument18 pagesCV Rizaljs Indonesia PDFHumairah AnandaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry Lab 2Document7 pagesInorganic Chemistry Lab 2apple75% (4)
- Mohan ResumeDocument4 pagesMohan ResumeRamesh NaiduNo ratings yet
- Ultrafit PL 1Document20 pagesUltrafit PL 1Vijay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1: 1.0 Over View of ProjectDocument10 pagesChapter - 1: 1.0 Over View of ProjectsunilkumareceNo ratings yet
- Synerquest 2014 Annual Calendar of DOLE-prescribed CoursesDocument3 pagesSynerquest 2014 Annual Calendar of DOLE-prescribed CoursesrobinrubinaNo ratings yet
- Using Boss Tone Studio For Me-25Document12 pagesUsing Boss Tone Studio For Me-25felipe herreraNo ratings yet
- MaxxForce11 13SpecCardDocument2 pagesMaxxForce11 13SpecCardJohn MkCito KINo ratings yet
- L80 - Continental AlloysDocument1 pageL80 - Continental AlloysHans CohnNo ratings yet
- Causes and Prevention of Paint Failure PDFDocument14 pagesCauses and Prevention of Paint Failure PDFsenthilkumarNo ratings yet
- GN-253CW Service ManualDocument38 pagesGN-253CW Service Manualdanielradu270% (1)
- Din en Iso 3822-1 - enDocument27 pagesDin en Iso 3822-1 - enDaniel GrobNo ratings yet
- Underground ConduitsDocument25 pagesUnderground ConduitsAbdul AzimNo ratings yet
- Kernel Internals Student NotesDocument404 pagesKernel Internals Student Notesnaveednad2003556100% (1)
- RD-M972 RD-M972: XTR Rear DerailleurDocument1 pageRD-M972 RD-M972: XTR Rear DerailleurJonah HexNo ratings yet
- Engine Control Module (ECM), Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Guide - PV776-890469121Document82 pagesEngine Control Module (ECM), Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Guide - PV776-890469121Jose HernandezNo ratings yet
- Constraint Effect in Fracture - What Is ItDocument10 pagesConstraint Effect in Fracture - What Is ItSoupramanien KathirvelouNo ratings yet
- Desch PSC3 Base MibDocument24 pagesDesch PSC3 Base MibAlejandro Rubio ReyesNo ratings yet
- F607OTSFP Válvula de Compuerta NibcoDocument1 pageF607OTSFP Válvula de Compuerta NibcoAlberth Rojas CastellanosNo ratings yet