Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Signalling Lodish Cbib
Cell Signalling Lodish Cbib
Uploaded by
Shreyas Dhuliya0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views3 pagesThe document summarizes several major types of cell signaling pathways:
1. Ligand-gated ion channels signal by localized changes in membrane potential or cytosolic calcium levels upon ligand binding.
2. G protein-coupled receptors activate second messenger pathways or linked ion channels upon ligand binding via associated G proteins.
3. Receptor serine/threonine kinases directly activate cytosolic transcription factors like Smad.
4. Cytokine receptors also activate STAT transcription factors or other pathways like MAPK or PI3K.
Original Description:
The file is prepared for students to remember cell signalling pathways
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes several major types of cell signaling pathways:
1. Ligand-gated ion channels signal by localized changes in membrane potential or cytosolic calcium levels upon ligand binding.
2. G protein-coupled receptors activate second messenger pathways or linked ion channels upon ligand binding via associated G proteins.
3. Receptor serine/threonine kinases directly activate cytosolic transcription factors like Smad.
4. Cytokine receptors also activate STAT transcription factors or other pathways like MAPK or PI3K.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views3 pagesCell Signalling Lodish Cbib
Cell Signalling Lodish Cbib
Uploaded by
Shreyas DhuliyaThe document summarizes several major types of cell signaling pathways:
1. Ligand-gated ion channels signal by localized changes in membrane potential or cytosolic calcium levels upon ligand binding.
2. G protein-coupled receptors activate second messenger pathways or linked ion channels upon ligand binding via associated G proteins.
3. Receptor serine/threonine kinases directly activate cytosolic transcription factors like Smad.
4. Cytokine receptors also activate STAT transcription factors or other pathways like MAPK or PI3K.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
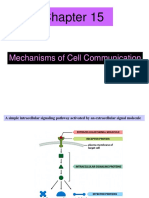
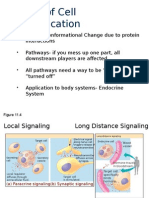
Cell signalling - CBIB syllabus
Ligand-gated ion channels Ligands: Neurotransmitters (e.g., acetylcholine,
glutamate), cGMP, physical stimuli (e.g., touch,
stretching), IP3 (receptor in ER membrane)
Receptors: Four or five subunits with a
homologous segment in each subunit lining the
ion channel
Signal transduction: (1) Localized change in
membrane potential due to ion influx, (2)
elevation of cytosolic Ca2+
G protein–coupled receptors Ligands: Epinephrine, glucagon, serotonin,
vasopressin, ACTH, adenosine, and many
others (mammals); odorant molecules, light;
mating factors (yeast)
Receptors: Seven transmembrane helices;
cytosolic domain associated with a membrane-
tethered trimeric G protein
Signal transduction: (1) Second-messenger
pathways involving cAMP or IP3/DAG; (2)
linked ion channels; (3) MAP kinase pathway
TGF receptors Ligands: Transforming growth factor
superfamily (TGF , BMPs), activin, inhibins
(mammals); Dpp (Drosophila)
Receptors: Intrinsic protein serine/threonine
kinase activity in cytosolic domain (type I and
II)
Signal transduction: Direct activation of
cytosolic Smad transcription factors
Cytokine receptors Ligands: Interferons, erythropoietin, growth
hormone, some interleukins (IL-2, IL-4), other
cytokines
Receptors: Single transmembrane helix;
conserved multi- strand fold in extracellular
domain; JAK kinase associated with
intracellular domain
Signal transduction: (1) Direct activation of
cytosolic STAT transcription factors; (2) PI-3
kinase pathway; (3) IP3/DAG pathway; (4) Ras-
MAP kinase pathway
Receptor guanylyl cyclases Ligands: Atrial natriuretic factor and related
peptide hormones
Receptor: Single transmembrane helix; intrinsic
guanylate cyclase activity in cytosolic domain
Signal transduction: Generation of cGMP
Receptor tyrosine kinases Ligands: Insulin, epidermal growth factor
(EGF), fibroblast growth factor (FGF),
neurotrophins, other growth factors
Receptor: Single transmembrane helix; intrinsic
protein tyrosine kinase activity in cytosolic
domain
Signal transduction: (1) Ras–MAP kinase
pathway; (2) IP3/DAG pathway; (3) PI-3 kinase
pathway
Signalling via regulated proteolysis
Wnt pathway Ligands: Secreted Wnt (mammals); Wg
(Drosophila)
Receptors: Frizzled (Fz) with seven
transmembrane helices; associated membrane-
bound LDL receptor–related protein (Lrp)
required for receptor activity
Signal transduction: Assembly of multiprotein
complex at membrane that inhibits the
proteasome-mediated proteolysis of cytosolic -
catenin transcription factor, resulting in its
accumulation
Hedgehog (Hh) pathway Ligands: Cell-tethered Hedgehog
Receptors: Binding of Hh to Patched (Ptc),
which has 12 transmembrane helices; activation
of signaling from Smoothened (Smo), with 7
transmembrane helices Signal transduction:
Proteolytic release of a transcriptional activator
from multiprotein complex in the cytosol
Notch/Delta pathway Ligands: Membrane-bound Delta or Serrate
protein
Receptors: Extracellular subunit of Notch
receptor noncovalently associated with
transmembrane-cytosolic subunit
Signal transduction: Intramembrane proteolytic
cleavage of receptor transmembrane domain
with release of cytosolic segment that functions
as co-activator for nuclear trascription factors
NF- B pathways Ligands: Tumor necrosis factor (TNF- ),
interleukin 1 (mammals); Spätzle (Drosophila)
Receptors: Various in mammals; Toll and Toll-
like receptors in Drosophila
Signal transduction: Phosphorylation-
dependent degradation of inhibitor protein with
release of active NF- B transcription factor
(Dorsal in Drosophila) in the cytosol
For Introduction and more details and figures refer Lodish, berkly.
You might also like
- JEHLE RENY Solutions To Selected ExercisesDocument38 pagesJEHLE RENY Solutions To Selected ExercisesSyed Yusuf Saadat100% (7)
- Cell Communication: Biology 5ADocument6 pagesCell Communication: Biology 5APuron RahmanNo ratings yet
- Biology 230 - Molecules and Cells: TermsDocument12 pagesBiology 230 - Molecules and Cells: TermsAman SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Cellular CommunicationDocument51 pagesCellular CommunicationBerslan ArslanNo ratings yet
- Cell Signalling 1.2 2017Document61 pagesCell Signalling 1.2 2017PutriNo ratings yet
- BC0103 ch13Document93 pagesBC0103 ch13oreaNo ratings yet
- Komunikasi Antar SelDocument39 pagesKomunikasi Antar SelMOCHILNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcome 7Document3 pagesLearning Outcome 7Anj DeograciasNo ratings yet
- Heldin2002 - Signal Transduction: OverviewDocument7 pagesHeldin2002 - Signal Transduction: Overview7cmym76z2jNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document26 pagesLecture 5BlaNo ratings yet
- 4.24.34.4 Signal TransductionDocument35 pages4.24.34.4 Signal TransductionbloodredrosalinaNo ratings yet
- 1 2 Receptor Tyrosine Kinases 2021Document44 pages1 2 Receptor Tyrosine Kinases 2021Bilakovics NoemiNo ratings yet
- CH1131 - Biomolecular Engineering - Week 5 - Signaling - Sep 08 15 2015Document29 pagesCH1131 - Biomolecular Engineering - Week 5 - Signaling - Sep 08 15 2015joshuaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Signal: Hormone 1: Biosignaling (WEEK 2)Document27 pagesChemical Signal: Hormone 1: Biosignaling (WEEK 2)Fenny Aulia SugianaNo ratings yet
- Cell Communication - DADocument66 pagesCell Communication - DAMuhammad Ardiansyah MNo ratings yet
- neurotransmittersNSlectures HDocument67 pagesneurotransmittersNSlectures Hapi-3784483No ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Cell CommunicationDocument51 pagesMechanisms of Cell CommunicationSujanNo ratings yet
- 5 Cell SignallingDocument19 pages5 Cell Signallingharshit khareNo ratings yet
- Multicellular Organisms Have BIG Communication Problems: Hey You - Divide Now!!! Oi! We Need Some Glucose!Document73 pagesMulticellular Organisms Have BIG Communication Problems: Hey You - Divide Now!!! Oi! We Need Some Glucose!kevin andrewNo ratings yet
- GenomicsDocument38 pagesGenomicsBiplabendu DandapatNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ReceptorsDocument24 pagesIntroduction To ReceptorsFyqa QamarNo ratings yet
- BiosignallingDocument16 pagesBiosignallingAsmaa HatemNo ratings yet
- Biosel Ke 7Document99 pagesBiosel Ke 7Rena PurnamaNo ratings yet
- 1.signal - Transduction Med 1Document16 pages1.signal - Transduction Med 1Ragdha MehdawiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document40 pagesChapter 3Mutiara KataNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Cell Communications - 20234Document35 pagesChapter 3 - Cell Communications - 20234afeeqrashidNo ratings yet
- 1 Cell CommunicationDocument33 pages1 Cell CommunicationKaye Macauba CentinoNo ratings yet
- Mouse (Mus Musculus)Document4 pagesMouse (Mus Musculus)Jhestine AbayanNo ratings yet
- Translation and Proteins: The Products of TranscriptionDocument10 pagesTranslation and Proteins: The Products of TranscriptionRenz L. SalumbreNo ratings yet
- Signal TransductionDocument30 pagesSignal Transductionpalak100% (1)
- Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Biosignaling: Prof. Yong Tae KwonDocument86 pagesMolecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Biosignaling: Prof. Yong Tae KwonJon QNo ratings yet
- Chapt09 Lecture 2019-SDocument45 pagesChapt09 Lecture 2019-SPaulNo ratings yet
- 3.komunikasi Sel Feb19Document45 pages3.komunikasi Sel Feb19Faizah Abdullah Djawas100% (1)
- Cell Signaling Signal TransductionDocument7 pagesCell Signaling Signal TransductionArslan AliNo ratings yet
- 10 25 2006 LifescienceDocument51 pages10 25 2006 Lifescienceapi-3696530No ratings yet
- Intro To Hormones - Dr. Magat FINALDocument8 pagesIntro To Hormones - Dr. Magat FINALneutralmindNo ratings yet
- Claudia Gonzalez Lima 2020Document76 pagesClaudia Gonzalez Lima 2020Ann LourieNo ratings yet
- Kuliah VIII - Sistem Endokrin - KKPMT IIDocument50 pagesKuliah VIII - Sistem Endokrin - KKPMT IIRae SenaNo ratings yet
- 1P - Physio - Cell Physiology 3&4 - 1BDocument8 pages1P - Physio - Cell Physiology 3&4 - 1Burvashi rao rajputNo ratings yet
- Transcriptional & Chromatin RegulationDocument11 pagesTranscriptional & Chromatin RegulationClaraNo ratings yet
- Cell CommDocument17 pagesCell CommShashank Shekhar SinghNo ratings yet
- Cell Signaling 1 Lecture Notes 9:7:16Document45 pagesCell Signaling 1 Lecture Notes 9:7:16Ahmed FarhanNo ratings yet
- Innate 2005 AbDocument93 pagesInnate 2005 AbAnonymous wVgEAr6No ratings yet
- Enzyme Linked Receptors LectureDocument52 pagesEnzyme Linked Receptors LectureJason PastisNo ratings yet
- FarmakodinamikDocument44 pagesFarmakodinamikHarri HardiNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Gene Expression RevDocument81 pagesEukaryotic Gene Expression RevHanaNo ratings yet
- Group 4: The Mouse 4 - Biology - 8 Members: Basilio, M., Canlas, C., Enriquez, C., Gutierrez, T., Jurilla, J., Pua Phee, M. & Wahab, DDocument4 pagesGroup 4: The Mouse 4 - Biology - 8 Members: Basilio, M., Canlas, C., Enriquez, C., Gutierrez, T., Jurilla, J., Pua Phee, M. & Wahab, DAudreyNo ratings yet
- Señalización Molecular: Julio Hilario VargasDocument43 pagesSeñalización Molecular: Julio Hilario VargasAndrew Emilio Castillo PachecoNo ratings yet
- 4-Farmacodinamia OWC2017Document19 pages4-Farmacodinamia OWC2017Sam VargasNo ratings yet
- Tirosin Kinase Receptor (RTK)Document8 pagesTirosin Kinase Receptor (RTK)Nur Afra YsNo ratings yet
- Cell Communication 1Document10 pagesCell Communication 1api-277471896No ratings yet
- Cell Signaling - The Components of Signaling PathwaysDocument31 pagesCell Signaling - The Components of Signaling Pathwaysk10 Lớp Dinh DưỡngNo ratings yet
- Cell Surface Receptors: G-Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCR)Document37 pagesCell Surface Receptors: G-Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCR)Ahmed FarhanNo ratings yet
- Biosignaling Biosignaling Biosignaling BiosignalingDocument48 pagesBiosignaling Biosignaling Biosignaling BiosignalingAG KhanNo ratings yet
- The Genetic Code and Transcription: Flow of Genetic InformationDocument10 pagesThe Genetic Code and Transcription: Flow of Genetic InformationRenz L. SalumbreNo ratings yet
- TMP 559 FDocument12 pagesTMP 559 FFrontiersNo ratings yet
- 2019 - Identification of Betamethasone-Regulated Target Genes and Cell Pathways in Fetal Rat Lung Mesenchymal FibroblastsDocument17 pages2019 - Identification of Betamethasone-Regulated Target Genes and Cell Pathways in Fetal Rat Lung Mesenchymal Fibroblastsgrazi_rNo ratings yet
- SignallingDocument74 pagesSignallingAshrafNo ratings yet
- Cell Signaling: Protocols & Applications Guide Rev. 9/06Document22 pagesCell Signaling: Protocols & Applications Guide Rev. 9/06Fidiya Septi Kusma WardaniNo ratings yet
- The Effector Molecules of Innate ResponseDocument8 pagesThe Effector Molecules of Innate Responseratnesh gautamNo ratings yet
- Presented By:: Civil Engineerin GDocument23 pagesPresented By:: Civil Engineerin GChuckMañoscaNo ratings yet
- Samson Feeder Aumund Ds.a.ifrDocument52 pagesSamson Feeder Aumund Ds.a.ifrNicolas Recio Fdez-TresguerresNo ratings yet
- Rabindranath & ScienceDocument9 pagesRabindranath & ScienceProf. (Dr) Ananda M Ghosh.No ratings yet
- Lichfield Sutton Coldfield Birmingham Long Bridge RedditchDocument4 pagesLichfield Sutton Coldfield Birmingham Long Bridge RedditchLouisMichaelNo ratings yet
- Project Report 1Document57 pagesProject Report 1Juan Julio BadaracoNo ratings yet
- Smell Tech PPT - 115345Document16 pagesSmell Tech PPT - 115345srilekhaNo ratings yet
- BIMxDocument20 pagesBIMxlentiNo ratings yet
- FIR Design MintedDocument6 pagesFIR Design MintedGajendra PaikraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Simvastatin)Document2 pagesDrug Study (Simvastatin)Julianne Jeaven Bumanglag LimNo ratings yet
- 01-01-2021 GOC2 English ADocument39 pages01-01-2021 GOC2 English APrabhakar BandaruNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2007: GCE Biology (8040/9040)Document12 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2007: GCE Biology (8040/9040)Fathmath MohamedNo ratings yet
- Problems of Dyeing Polyester With Disperse DyesDocument1 pageProblems of Dyeing Polyester With Disperse DyesrashidtexNo ratings yet
- 1 Grap TutB AnswerDocument13 pages1 Grap TutB AnswerPang Hua TanNo ratings yet
- PV 2Document6 pagesPV 2Vijay YerrojuNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Transformation Agency (ATA) Office of Human ResourceDocument2 pagesAgricultural Transformation Agency (ATA) Office of Human ResourceRedwanNo ratings yet
- AQUAVARI - Kinetic Air Valve WeightsDocument47 pagesAQUAVARI - Kinetic Air Valve WeightssandeshNo ratings yet
- Bhs Inggris A - SoalDocument9 pagesBhs Inggris A - SoalKhaerul AnamNo ratings yet
- Environmental DeterminismDocument7 pagesEnvironmental DeterminismSafdar HussainNo ratings yet
- English Grade 3Document269 pagesEnglish Grade 3Berhanu AlemuNo ratings yet
- Home Cmplab HTML Bbs Data Pds0085 1Document9 pagesHome Cmplab HTML Bbs Data Pds0085 1呂昕儒No ratings yet
- Interview For DomRAC TechnicianDocument5 pagesInterview For DomRAC TechnicianAldrine LatorreNo ratings yet
- 2017 Fall ME501 06 VectorCalculusDocument95 pages2017 Fall ME501 06 VectorCalculusAfaq AhmedNo ratings yet
- ER420 - MS of G.I Pipe Crossing - r0Document12 pagesER420 - MS of G.I Pipe Crossing - r0Wr ArNo ratings yet
- 2021 Sustainability ReportDocument101 pages2021 Sustainability ReportGrupo DOCStore Brasil LtdaNo ratings yet
- Journal of Nutrition CollegeDocument6 pagesJournal of Nutrition CollegeNur HikmahNo ratings yet
- Test 14 - Science and Technology - II - QPDocument24 pagesTest 14 - Science and Technology - II - QPsachinstinNo ratings yet
- JACM - Volume 1 - Issue 1 - Pages 10-16Document7 pagesJACM - Volume 1 - Issue 1 - Pages 10-16Raksha AroraNo ratings yet
- Metrado de Explanaciones (Metrex) : Material Suelto Roca Suelta Roca FijaDocument56 pagesMetrado de Explanaciones (Metrex) : Material Suelto Roca Suelta Roca FijaWashington CairaNo ratings yet
- Combined Cooling, Heating and Power: A Review: Article in PressDocument37 pagesCombined Cooling, Heating and Power: A Review: Article in Pressali rahimiNo ratings yet