Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Iron Overload in Transfusion-Dependent
Iron Overload in Transfusion-Dependent
Uploaded by
IrenaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Iron Overload in Transfusion-Dependent
Iron Overload in Transfusion-Dependent
Uploaded by
IrenaCopyright:
Available Formats
H E M A T O L O G Y C L I N I C
Iron overload in transfusion-dependent
thalassemia
Introduction organs that are most commonly affected by iron
Hemoglobin is a protein that plays an important role in overload in transfusion-dependent thalassemia.
the structure and the stability of red blood cells. As a result, excess iron is deposited in different
Hemoglobin is also important for carrying oxygen body organs causing (1) heart dysfunction and
throughout the body. Thalassemia is a chronic con- failure, (2) liver disease, cirrhosis, and cancer, and
dition caused by a defective gene resulting in a (3) endocrine disease, such as growth
reduced amount of hemoglobin and fewer red blood abnormalities.
cells than normal. This inherited condition results in
anemia that may need regular blood transfusions for Symptoms and signs
survival. With the frequent transfusions, iron, which As the symptoms and signs of iron overload are not
is found in red blood cell products, accumulates in sufficiently sensitive and specific, thalassemic
the body and gets deposited in different organs, patients should be monitored early on after the
such as the heart, liver, and endocrine glands. Iron onset of transfusion therapy for the development of
overload is a condition that could be treated by medi- transfusional iron overload. Symptoms and signs
cations called iron chelators. Your physician can help related to iron overload may include hyperpigmenta-
you choose the best iron chelator for your condition. tion (dark skin), which is a late and rare finding.
Other symptoms and signs of iron overload are
Cause those related to the end organ damage that
The major cause of iron overload in transfusion- happens from iron deposition in the different organs.
dependent thalassemia is the high intake of iron Heart dysfunction due to iron overload usually
found in red blood cell products. The human body presents as shortness of breath on exertion and
does not have an effective means to get rid of increased lower extremity swelling. Cardiac arrhythmias can
iron load because of blood transfusions. In addition, a present as palpitations, loss of consciousness
state of chronic anemia stimulates dietary iron absorp- (syncope), or sudden cardiac death.
tion through the gut. However, this amount of iron Patients with liver disease may present with an
remains minor as compared to the amount accumu- enlarged liver (hepatomegaly), an enlarged spleen
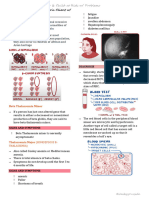
lated from frequent transfusions. Figure 1 shows the (splenomegaly), or an abdominal fluid accumulation
Figure 1 Major mechanism of iron overload in transfusion-dependent thalassemia. As shown in the figure, the major cause of iron
overload in transfusion-dependent thalassemia is the excessive accumulation of transfusional iron that is deposited in the different
organs leading to different complications such as heart failure and arrhythmias, liver disease, and endocrine gland dysfunction.
© W. S. Maney & Son Ltd 2015
DOI 10.1179/1024533215Z.000000000365 Hematology 2015 VOL. 20 NO. 5 311
H E M A T O L O G Y C L I N I C
Table 1 Characteristics of different iron chelators
Deferoxamine Deferiprone Deferasirox
How is it administered? Under the skin By mouth (orally) By mouth, dispersed in
(subcutaneously) water (orally)
Through the vein
(intravenously)
How many times a day should I Usually daily over 8–24 hours Three times daily Once daily
take it?
What should my doctor and I Hearing abnormalities Gastrointestinal disturbances Gastrointestinal
watch for when I am on disturbances
treatment? Visual abnormalities Decrease in white blood cell count Increase in serum
(neutropenia/agranulocytosis) creatinine
Infections or reactions at the Joint pain Increase in liver
site of the infusion enzymes
Delay in bone growth Increase in liver enzymes Skin rash
Liver failure
Kidney failure
(ascites). Jaundice is also common in thalassemia regimen that is both convenient to you and effective
and may be worsened by liver dysfunction. in reducing iron overload. Your physician will also
Endocrine disease presents as slow growth in counsel you on how to follow up with blood and
children. Absence of menstrual periods (amenor- urine tests, in addition to other investigations, to
rhea), loss of libido, and erectile dysfunction may monitor for side effects.
be a symptom of endocrine dysfunction due to
iron overload. Polyuria and polydipsia may be pre- Outlook
senting symptoms of hyperglycemia due to pan- Most guidelines agree that iron chelation therapy
creatic iron deposition. should be started after the cumulative transfusion
of 10–20 units of packed red blood cells or when
Tests serum ferritin is greater than 1000 ng/mL. With ade-
Serum ferritin remains a valuable means to assess quate screening and treatment, complications and
iron overload. However, this method is not the mortality related to iron overload are significantly
most reliable among the available tools as serum delayed and improved.
ferritin may fluctuate with inflammation.
Liver iron load can be assessed using a liver biopsy, Additional resources
which is an invasive and technically demanding pro- You may find many resources online, but the most
cedure. Therefore, the most widely used method for valuable are the following:
reliable assessment of liver iron load is magnetic res-
(1) The Thalassaemia International Federation:
onance imaging (MRI) for the measuring liver iron
http://www.thalassaemia.org.cy/
concentration. However, MRI assessment of liver iron
(2) The Center for Disease Control and Prevention:
concentration is expensive and may be unavailable
http://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/thalassemia/
in certain areas where thalassemia is prevalent. (3) Cooley’s Anemia Foundation: http://www
Heart iron load can be measured using specific .thalassemia.org/learn-about-thalasse
MRI techniques, the T2* or R2*. mia/about-thalassemia/
(4) The Curriculum in Iron Metabolism and
Treatment options Related Disorders: European Society of
There are different iron chelators available for use in Haematology: http://www.ironcurriculum
treating iron overload secondary to blood transfu- .esh.org/
sions. Table 1 explains the characteristics of the
different iron chelators. The oldest agent is deferox-
amine, an iron chelator that should be administered Antoine Saliba, Ali Taher
intravenously (through the vein) or subcutaneously Department of Internal Medicine, Division of
(under the skin). The two other chelators are deferi- Hematology/Oncology, American University of
prone and deferasirox each with unique character- Beirut, Lebanon
istics and side effects. Deferiprone is taken three Correspondence to: Ali Taher, Naef K. Basile
times daily while deferasirox is a once-daily medi- Cancer Institute, American University of Beirut
cation. Your physician will discuss with you the Medical Center, Building 56, 5th floor, Cairo Street,
side effects and the benefits of each of these iron PO Box 11-0236, Riad El Solh 1107 2020, Beirut,
chelators. Your physician will tailor a chelation Lebanon. Email: ataher@aub.edu.lb
312 Hematology 2015 VOL. 20 NO. 5
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- A Critical Perspective On Trophic Feeding.1Document2 pagesA Critical Perspective On Trophic Feeding.1IrenaNo ratings yet
- Childhood MedulloblastmaDocument17 pagesChildhood MedulloblastmaIrenaNo ratings yet
- 10 - 258sepsis Neonatorum Awitan DiniDocument4 pages10 - 258sepsis Neonatorum Awitan DiniIrenaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Jurnal Junior Stase RespirologiDocument44 pagesTugas Jurnal Junior Stase RespirologiIrenaNo ratings yet
- Rickets Not Just A Disase Caused Deficiency Vitamin DDocument6 pagesRickets Not Just A Disase Caused Deficiency Vitamin DIrenaNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Rickets Around The World An UpdateDocument16 pagesNutritional Rickets Around The World An UpdateIrenaNo ratings yet
- Idiopatic SyringomyeliaDocument9 pagesIdiopatic SyringomyeliaIrenaNo ratings yet
- Haematology Theory PDFDocument4 pagesHaematology Theory PDFasankandessNo ratings yet
- Hubungan Kepatuhan Transfusi Darah Dan Kelasi Besi Dengan Kualitas Hidup Anak ThalasemiaDocument7 pagesHubungan Kepatuhan Transfusi Darah Dan Kelasi Besi Dengan Kualitas Hidup Anak ThalasemiaIntan SariNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging Versus Serum Iron Status As Diagnostic Tools For Pituitary Iron Overload in Children With Beta ThalassemiaDocument13 pagesMagnetic Resonance Imaging Versus Serum Iron Status As Diagnostic Tools For Pituitary Iron Overload in Children With Beta ThalassemiaAbdurrahman HasanuddinNo ratings yet
- To Study Effectiveness of Deferasirox, An Oral Iron Chelator in Blood Transfusion Dependent Pediatric Thalassemia PatientsDocument7 pagesTo Study Effectiveness of Deferasirox, An Oral Iron Chelator in Blood Transfusion Dependent Pediatric Thalassemia PatientsIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- MCQ of HematologyDocument37 pagesMCQ of Hematologyalemante92% (13)
- Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation: PediatricDocument8 pagesBiology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation: PediatricMichael John AguilarNo ratings yet
- Clinical Study: Piya Rujkijyanont, Chalinee Monsereenusorn, Pimpat Manoonphol, and Chanchai TraivareeDocument9 pagesClinical Study: Piya Rujkijyanont, Chalinee Monsereenusorn, Pimpat Manoonphol, and Chanchai Traivareejungkat unguNo ratings yet
- نسخة 12- Lecture Hematological DisordersDocument12 pagesنسخة 12- Lecture Hematological DisordersRoxe BroNo ratings yet
- Family Medicine Clerkship Logbook G3 FinalDocument76 pagesFamily Medicine Clerkship Logbook G3 FinalMohammed AlomarNo ratings yet
- A Project Proposal: Shri Jalaram Arogya Seva Trust HospitalDocument29 pagesA Project Proposal: Shri Jalaram Arogya Seva Trust HospitalSHREE SWAMINARAYAN AYURVEDIC COLLEGE GUJARATNo ratings yet
- MHD Exam 6 MaterialDocument179 pagesMHD Exam 6 Materialnaexuis5467100% (1)
- Anemias ChartDocument14 pagesAnemias ChartM Patel100% (2)
- RefatllariDocument46 pagesRefatllariDhiren KapuparaNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Finals L10 1Document18 pagesNCM 109 Finals L10 1Leigh Angelika Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Aplastic Anemia: Kevin NonesDocument71 pagesAplastic Anemia: Kevin NonesNolan CabralNo ratings yet
- Medication ThalassemiaDocument3 pagesMedication ThalassemiaDivya ToppoNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in Genetics and Common Genetic DisordersDocument88 pagesBasic Concepts in Genetics and Common Genetic Disordersannu panchalNo ratings yet
- Disease Chart I3-1 (Emmeline)Document20 pagesDisease Chart I3-1 (Emmeline)ivankcurryNo ratings yet
- Adrian Hardec Nasdal Modul 6 LBM 2Document9 pagesAdrian Hardec Nasdal Modul 6 LBM 2Rizqon Yassir KuswondoNo ratings yet
- ThalassemiaDocument93 pagesThalassemiaHafdzi MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Longitudinal Case-Riska Munggaran (UNPAD) 2Document19 pagesLongitudinal Case-Riska Munggaran (UNPAD) 2Pramadio Bambang NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of The Thalassemias - UpToDateDocument52 pagesClinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of The Thalassemias - UpToDatesushi37No ratings yet
- Ma. Angelika Nicole C. Lopez 08-06-18 MD1Y1-8Document2 pagesMa. Angelika Nicole C. Lopez 08-06-18 MD1Y1-8John Lord CalasinNo ratings yet
- 7 Genetic DisordersDocument36 pages7 Genetic DisordersPrem ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Physiological C-WPS OfficeDocument15 pagesPhysiological C-WPS OfficeGwagsiGlennNo ratings yet
- MRCPass Notes For MRCP 1 - HEMATOLOGYDocument9 pagesMRCPass Notes For MRCP 1 - HEMATOLOGYsabdali100% (1)
- 5 Hemolytic AnemiaDocument72 pages5 Hemolytic Anemiacoosa liquorsNo ratings yet
- Journal 1Document13 pagesJournal 1Nur Ajiyanti 'anthi' SabirinaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Anemia InternasionalDocument8 pagesJurnal Anemia InternasionalmeldhaNo ratings yet
- Quiz PediatricsDocument56 pagesQuiz PediatricsMedShare87% (39)