Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vii. Drug Study Drug Mechanism of Action
Vii. Drug Study Drug Mechanism of Action
Uploaded by
Rifa'atul Mahmudah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
381 views7 pagesCycloserine is an antibiotic used to treat tuberculosis. It works by blocking the growth of the bacterial cell wall. It is used in combination with other medications to treat TB when treatment with other medicines has not been effective. Common side effects include anxiety, confusion, dizziness, and irritability. Nurses should monitor for side effects and ensure patients do not drink alcohol while taking cycloserine due to drug interactions.
Ethambutol is an antibiotic used with other medications to treat tuberculosis and prevent spreading the infection. It works by obstructing formation of the mycolic acid cell wall. Common side effects include loss of appetite, vomiting, numbness and tingling. Nurses should monitor for signs of infection
Original Description:
Original Title
VII._DRUG_STUDY_DRUG_MECHANISM_OF_ACTION.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCycloserine is an antibiotic used to treat tuberculosis. It works by blocking the growth of the bacterial cell wall. It is used in combination with other medications to treat TB when treatment with other medicines has not been effective. Common side effects include anxiety, confusion, dizziness, and irritability. Nurses should monitor for side effects and ensure patients do not drink alcohol while taking cycloserine due to drug interactions.
Ethambutol is an antibiotic used with other medications to treat tuberculosis and prevent spreading the infection. It works by obstructing formation of the mycolic acid cell wall. Common side effects include loss of appetite, vomiting, numbness and tingling. Nurses should monitor for signs of infection
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
381 views7 pagesVii. Drug Study Drug Mechanism of Action
Vii. Drug Study Drug Mechanism of Action
Uploaded by
Rifa'atul MahmudahCycloserine is an antibiotic used to treat tuberculosis. It works by blocking the growth of the bacterial cell wall. It is used in combination with other medications to treat TB when treatment with other medicines has not been effective. Common side effects include anxiety, confusion, dizziness, and irritability. Nurses should monitor for side effects and ensure patients do not drink alcohol while taking cycloserine due to drug interactions.
Ethambutol is an antibiotic used with other medications to treat tuberculosis and prevent spreading the infection. It works by obstructing formation of the mycolic acid cell wall. Common side effects include loss of appetite, vomiting, numbness and tingling. Nurses should monitor for signs of infection
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
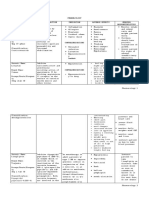
VII.
DRUG STUDY
DRUG MECHANISM OF ACTION INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS ADVERSE EFFECTS NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Cycloserine is an antibiotic. Treating tuberculosis (TB) Hypersensitivity More common Be aware that oral
GENERIC NAME: It works by blocking the in the lungs and other Alcohol use solution contains
CYCLOSERINE growth of the bacterial cell places in the body Renal dysfunction, Anxiety alcohol and shouldn’t
wall. (including the kidneys) confusion be administered to
severe
BRAND NAME: dizziness patient who drinks
when treatment with other History of seizure drowsiness heavily or has a
SEROMYCIN medicines has not been disorder, mental increased irritability history of alcohol
effective. Cycloserine depression, severe increased dependence.
CLASSIFICATION: should be used in anxiety or psychosis restlessness Don’t add water to
ANTI-TUBECULAR AGENT combination with other mental depression oral solution because
medicines. It may also be muscle twitching or itwill alter drug’s
ROUTE:
used to treat certain trembling effectiveness.
ORAL
urinary tract infections. nervousness Avoid giving oral
nightmares cyclosporine with
DOSAGE: other mood or grape-fruit juice,
.
250mg, 2 TABLETS mental changes which may raise
speech problems trough
FREQUENCY: thoughts of suicide level,increasing risk of
ONCE A DAY nephrotoxicity.
Less common Monitor blood
pressure, especially in
Convulsions (seizures) patients with a
numbness, tingling, history of
burning pain, or hypertension,because
weakness in the drug can worsen this
hands or feet condition.Expect to
skin rashes decrease dosage if
hypertension
develops
DRUG STUDY
DRUG MECHANISM OF ACTION INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS ADVERSE EFFECTS NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Ethambutol is bacteriostatic Ethambutol eliminates Contraindicated in patients Loss of appetite Assess patient for
GENERIC NAME: against actively growing TB certain bacteria that cause who are known to be Upset stomach infection
MYAMBUTOL bacilli, it works by tuberculosis (TB). It is used hypersensitive to this drug. Vomiting (appearance of
obstructing the formation with other medicines to It is also contraindicated in Numbness and wounds, sputum, VS,
BRAND NAME: of cell wall. Mycolic acids treat tuberculosis and to patients with known optic tingling in the urine and stool and
ETHAMBUTOL attach to the 5′-hydroxyl prevent you from giving the neuritis unless clinical hands or fee WBC.) at beginning
groups of D-arabinose infection to others. judgment determines that Optic neuritis and during therapy.
CLASSIFICATION:
residues of arabinogalactan it may be used. Ethambutol blurring of vision Obtain specimens
ANTI-TUBERCULAR AGENT
and form mycolyl- hydrochloride is before initiating
ROUTE: arabinogalactan- contraindicated in patients therapy. Take drug
ORAL peptidoglycan complex in who are unable to as indicated.
the cell wall. It disrupts appreciate and report visual Not to be given to
DOSAGE: arabinogalactan synthesis side ettects or changes in children 6 years
400mg, 3 TABLETS by inhibiting the enzyme vision (eg, young children, below due to optic
arabinosyl transferase. unconscious patients). neuritis
FREQUENCY: Disruption of the Provide
ONCE A DAY arabinogalactan synthesis supplemental
inhibits the formation of vitamin A. if not
this complex and leads to contraindicated
increased permeability of
the cell wall.
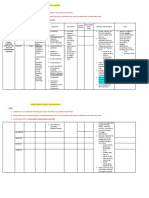
DRUG STUDY
DRUG MECHANISM OF ACTION INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS ADVERSE EFFECTS NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
The severe or irreversible Review dosing
GENERIC NAME: Prothionamide is clinically Prothionamide is taken as Prothionamide is adverse effects of schedule and
PROTHIONAMIDE effective in the treatment part of a treatment contraindicated in Prothionamide, which give prescribed length of
of TB; the precise regimen, usually involving conditions like Hepatic rise to further therapy with patient.
BRAND NAME: mechanisms of action 5 medicines, to treat MDR disease,General complications include Liver Emphasize to patient
NO BRANDS AVAILABLE that treatment will be
remain unknown, but a TB. It has the same active dose,Chronic resistant damage, Hepatitis, GI
lengthy and that the
cell-based activation substances and cross vaginal candidiasis. dysfunction.
CLASSIFICATION: entire course of
method causes an resistance with Prothionamide produces treatment must be
ANTI-TUBERCULAR AGENT
inhibiting complex. ethionamide; Leprosy. potentially life-threatening completed to avoid
effects which include relapse or
ROUTE:
Convulsions, Hepatitis. development of
ORAL
which are responsible for resistance.
the discontinuation of Advise patient to take
DOSAGE:
Prothionamide therapy. each dose with food
250mg, 3 TABLETS
The symptomatic adverse to prevent or reduce
reactions produced by GI adverse reactions.
FREQUENCY:
Prothionamide are more or Instruct patient to
ONCE A DAY
less tolerable and if they report the following
to health care
become severe, they can
provider: intolerable
be treated GI adverse reactions,
symptomatically, these changes in thinking or
include Sleepiness, mood, dizziness,
Headache, Insomnia, blurred vision or loss
Depression, Paresthesias. of vision, with or
without eye pain.
DRUG STUDY
DRUG MECHANISM OF ACTION INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS ADVERSE EFFECTS NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Assess patient if
GENERIC NAME: Pyridoxine is required for This medication is a Hypersensitivity; Patients Severe allergic reactions he/she has any
PYRIDOXINE VITAMIN B6 the proper function of vitamin, prescribed for the with Heart disease (rash; hives; itching; known allergies.
sugars, fats, and proteins in treatment and prevention difficulty breathing; Educate patient
BRAND NAME: the body. It is also required of vitamin B6 deficiency. It tightness in the chest; with the side effects
NO BRAND AVAILABLE for the proper growth and is important for the swelling of the mouth, of the drug and
development of the brain, breakdown of protein, fats, face, lips, or tongue); contact his/her
CLASSIFICATION:
nerves, skin, and many and carbohydrates from decreased sensation of physician
VITAMINS
other parts of the body. foods. touch, temperature, or immediately if he
Pyridoxine is also used to vibration; loss of experiences severe
ROUTE:
overcome certain harmful coordination; numbness of allergic reactions.
ORAL
side effects related to the feet or around the Stress importance
DOSAGE: radiation treatment and mouth; numbness or of compliance and
50mg, 2 TABLETS treatment with tingling of the skin. of good nutrition if
medications such as drug is prescribed
FREQUENCY: mitomycin, procarbazine, for maintenance
ONCE A DAY cycloserine, fluorouracil, therapy to prevent
hydrazine, isoniazid, recurrence of
penicillamine, and deficiency.
vincristine. Carefully monitor
patient’s diet.
Excessive protein
intake increases
daily pyridoxine
requirements.
DRUG STUDY
DRUG MECHANISM OF ACTION INDICATION Contraindication ADVERSE REACTION NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Levofloxacin is a broad-spectrum Levofloxacin is used to treat Hypersensitivity to the Most Common: Tell patient to take
GENERIC NAME: antibiotic that is active against infections of the sinuses, skin, drug, tendon drug as prescribed if
nausea or
LEVOFLOXACIN both Gram-positive and Gram- lungs, ears, airways, bones, and disorders,epilepsy. signs and symptoms
negative bacteria. Like all joints caused by susceptible Used cautiously in vomiting, disappear.
quinolones, it functions by bacteria. Levofloxacin also is patients with history of diarrhea, headache, and Advised patient to take
BRAND NAME: inhibiting the two type frequently used to treat urinary Seizure disorders or constipation. drug with plenty of
AMESOL IItopoisomerase enzymes, infections, including those other CNS diseases fluids and to space
Less common side effects include
namely DNA resistant to other antibiotics, as such as cerebral antacids sucralfate in
CLASSIFICATION: gyrase and topoisomerase well as prostatitis (infection of difficulty sleeping,
atherosclerosis. products containing
ANTIBACTERIAL, IV.[51] Topoisomerase IV is the prostate). Levofloxacin is Used cautiously and dizziness, iron and zinc.
FLURUOQUINOLONE necessary to separate DNA that effective in treating with dosage abdominal pain, Tell patient to take oral
has been replicated (doubled) infectious diarrhea caused byE. adjustment in patients rash, solution 1 hour before
prior to bacterial cell division. coli, Campylobacter jejuni, with renal impairment. or 2 hours after eating.
ROUTE: abdominal gas, and
With the DNA not being and Shigella bacteria. Safety and Instruct patient to stop
ORAL separated, the process is Levofloxacin also can be used to itching.
effectiveness of drugs drug and notify
stopped, and the bacterium treat various obstetric in children younger Rare allergic reactions have prescriber if rash or
DOSAGE: cannot divide. DNA gyrase, on infections, including mastitis than age 18 and in been described, such as: other signs and
the other hand, is responsible (infection of the pregnant and bf symptoms of
250mg, 2 TABLETS hives and
for supercoiling the DNA, so that breast). Inhalational women. hypersensitivity
it will fit in the newly formed anthrax exposure also is treated anaphylaxis (shock).
develop.
FREQUENCY: cells. Both mechanisms amount with levofloxacin. Instruct patient to
ONCE A DAY to killing the bacterium, that is, notify prescriber of
levofloxacin acts as loose stools or
a bactericide.[52] diarrhea.
DRUG STUDY
DRUG MECHANISM OF ACTION INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS ADVERSE EFFECTS NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Is indicated for the initial Severe hepatic damage; More common Emphasize need to be
GENERIC NAME: Pyrazinamide is a prodrug that treatment of active tuberculosis acute gout. Pain in large and small joints compliant with regimen
PYRAZINAMIDE stops the growth in adult and children when Used cautiously in
combine with other tuberculous patients with diabetes Rare and that doses should
of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. agents. It is also indicated after mellitus, renal failure or Loss of appetite
BRAND NAME: not be missed.
treatment failure with other gouts.
NO BRANDS AVAILABLE Pyrazinamide diffuses into M. Explain that long-term
primary drugs in any form of pain and swelling of joints,
tuberculosis, where the active tuberculosis. therapy (6 mo to 2 yr)
CLASSIFICATION: Pyrazinamide should only be especially big toe, ankle, and
enzyme pyrazinamidase converts will be necessary.
ANTI-TUBERCULAR AGENT used in conjuction with other knee
pyrazinamide to the active effective anti tuberculous Instruct patient to
form pyrazinoic acid. Under agents. tense, hot skin over affected report the following
ROUTE:
ORAL acidic conditions, the pyrazinoic joints symptoms to health
acid that slowly leaks out care provider: fever;
unusual tiredness or
DOSAGE: converts to the protonated
weakness loss of appetite;
50mg, 2 TABLETS conjugate acid, which is thought malaise; nausea and
to diffuse easily back into the yellow eyes or skin
FREQUENCY: vomiting; darkened
ONCE A DAY bacilli and accumulate. The net Rare urine; yellowish skin or
effect is that more pyrazinoic Itching eye discoloration; pain
acid accumulates inside the or swelling joints.
skin rash
bacillus at acid pH than at Advise patient to avoid
neutral pH. intake of alcoholic
beverages and alcohol-
containing products.
You might also like
- Drug StudyDocument21 pagesDrug StudyRemedios Bandong100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Multiple MyelomaDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Multiple MyelomaRifa'atul Mahmudah100% (1)
- Aspirin: Generic NameDocument4 pagesAspirin: Generic NameGwww BabababaNo ratings yet
- GanciclovirDocument3 pagesGanciclovirRosher Deliman JanoyanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: (Celecoxib)Document11 pagesDrug Study: (Celecoxib)Princess Brigitte R. PATE�ANo ratings yet
- Nifedipine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesNifedipine Drug StudyMary Shane MoraldeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CapDocument5 pagesDrug Study - CapABARAJNo ratings yet
- Tinidazole Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTinidazole Drug StudyEmagra AzilNo ratings yet
- Check The Physician's Observe and Follow The 14 Warn The Mother AboutDocument2 pagesCheck The Physician's Observe and Follow The 14 Warn The Mother AboutJust nowNo ratings yet
- A Drug Study On MISOPROSTOLDocument6 pagesA Drug Study On MISOPROSTOLAlexandrea MayNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyAisha LakibulNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AtropineDocument3 pagesDrug Study AtropineAerron Severus Secano ShuldbergNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Acute Aspirin ToxicityDocument1 pageGeneric Name: Acute Aspirin ToxicityShermayne Mallapre HernandezNo ratings yet
- Drug CelexaDocument1 pageDrug CelexaSrkocher100% (1)
- Drug Study: Loop DiureticDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Loop DiureticNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument10 pagesDrugsRebecca JolieNo ratings yet
- Dolan Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDolan Drug StudyLian Robbie BautistaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Buscopan)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Buscopan)marielleNo ratings yet
- Francis Peteros Drug Study 2 BetamethasoneDocument8 pagesFrancis Peteros Drug Study 2 BetamethasoneFrancis PeterosNo ratings yet
- VILLAMIN - Drug StudyDocument4 pagesVILLAMIN - Drug StudyAzizah VillaminNo ratings yet
- Lasix - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLasix - Drug StudyRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Complete Albendazole Information From DrugsDocument4 pagesComplete Albendazole Information From DrugselephantynoseNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage/Frequency/ Timing/Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesName of Drug Dosage/Frequency/ Timing/Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitieskyleNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug Studymegreen GamingNo ratings yet
- BuscopanDocument2 pagesBuscopancen janber cabrillosNo ratings yet
- Activity 6 - Drug StudyDocument14 pagesActivity 6 - Drug StudyAl-Mujib TanogNo ratings yet
- MetherginDocument2 pagesMetherginOtan Cuison100% (1)
- RifampinDocument3 pagesRifampinZenit DjajaNo ratings yet
- MisoprostolDocument3 pagesMisoprostolMichael Aditya LesmanaNo ratings yet
- Promethazine (Phenergan)Document1 pagePromethazine (Phenergan)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Lyrica (Pregabalin)Document2 pagesLyrica (Pregabalin)Laromac RolandNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyryanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CefradoxilDocument13 pagesDrug Study - CefradoxilJohara G'naid0% (1)
- BeclomethasoneDocument2 pagesBeclomethasoneDiane Bonita HerreraNo ratings yet
- Kremil S Drug StudyDocument1 pageKremil S Drug StudyDivine LavaNo ratings yet
- DUPHASTON Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDUPHASTON Drug StudyAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- CefadroxilDocument2 pagesCefadroxilArvie AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Lui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionDocument1 pageLui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionMagdayao Romamea100% (1)
- DORMICUMDocument1 pageDORMICUMArian Rose100% (1)
- MethergineDocument2 pagesMetherginebdumaranNo ratings yet
- Drugs, Amlodipine, Cefuroxime, Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrugs, Amlodipine, Cefuroxime, Drug StudyKevin Sam AguirreNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Metronidazole (Flagyl)Document1 pageDrug Study - Metronidazole (Flagyl)Jule SantoyaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MethergineDocument2 pagesDrug Study MethergineJahmil DulatreNo ratings yet
- Cephalexin Drug Study RNpedia ComDocument2 pagesCephalexin Drug Study RNpedia ComKatyana Cesar100% (1)
- Medication Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Drug Reaction GenericDocument1 pageMedication Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Drug Reaction GenericTrisha CayabyabNo ratings yet
- MetamucilDocument1 pageMetamucilSheri490No ratings yet
- MG Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMG Drug StudySandra MedinaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesName of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesNemo Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Tramadol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTramadol Drug StudyTipey Segismundo0% (1)
- Clotrimazole Cream Lotion Solution Dusting PowderDocument4 pagesClotrimazole Cream Lotion Solution Dusting Powderedy744No ratings yet
- Ditropan Drug CardDocument2 pagesDitropan Drug CardBenNo ratings yet
- Gentamicin Pedia Drug StudyDocument3 pagesGentamicin Pedia Drug StudyGong AllenaNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone Sodium Drug StudyDocument1 pageCeftriaxone Sodium Drug StudyMelissa Marie CustodioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HepatitisDocument7 pagesDrug Study HepatitisKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Tamoxifen NolvadexDocument1 pageTamoxifen NolvadexAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- GENTIMICINDocument1 pageGENTIMICINVinzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study...Document5 pagesDrug Study...Ezra Dizon ManzanoNo ratings yet
- CHN Drug StudyDocument17 pagesCHN Drug StudyEdmel Pamplona DuquesaNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Drug StudyDocument18 pagesDrug StudyJinky Nacar DomingoNo ratings yet
- Selectively: Inhibitors Inhibit Serotonin Reuptake and Elicit An Antidepressan T ResponseDocument2 pagesSelectively: Inhibitors Inhibit Serotonin Reuptake and Elicit An Antidepressan T ResponseDanii LuvNo ratings yet
- AAN 204 - Online Class - Requirement 6Document2 pagesAAN 204 - Online Class - Requirement 6Rifa'atul MahmudahNo ratings yet
- The Program Proposal - DiabetesDocument11 pagesThe Program Proposal - DiabetesRifa'atul Mahmudah100% (2)
- EINC ReviewDocument14 pagesEINC ReviewRifa'atul MahmudahNo ratings yet
- Heart Catheterization & AngioplastyDocument25 pagesHeart Catheterization & AngioplastyRifa'atul MahmudahNo ratings yet
- Exercise Stress Test: Presented By: Ns. Rifa'atul MahmudahDocument14 pagesExercise Stress Test: Presented By: Ns. Rifa'atul MahmudahRifa'atul MahmudahNo ratings yet
- We Care House FixDocument24 pagesWe Care House FixRifa'atul MahmudahNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Multiple Myeloma OkDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Multiple Myeloma OkRifa'atul MahmudahNo ratings yet
- IT FractureDocument42 pagesIT FractureRifa'atul MahmudahNo ratings yet
- Soal KasusDocument1 pageSoal KasusRifa'atul MahmudahNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Bone DiseaseDocument27 pagesMetabolic Bone DiseaseRifa'atul MahmudahNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan I Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term GoalDocument11 pagesNursing Care Plan I Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term GoalRifa'atul MahmudahNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Table OkDocument29 pagesDrug Study Table OkRifa'atul Mahmudah100% (1)
- Business Plan Shradded Snakehead FishDocument16 pagesBusiness Plan Shradded Snakehead FishRifa'atul MahmudahNo ratings yet
- Pathway DMDocument3 pagesPathway DMRifa'atul MahmudahNo ratings yet
- Nursing As Caring TheoryDocument9 pagesNursing As Caring TheoryRifa'atul MahmudahNo ratings yet
- Healthy and Smart Teenagers ProposalDocument31 pagesHealthy and Smart Teenagers ProposalRifa'atul MahmudahNo ratings yet
- Middle Range Theory of CaringDocument14 pagesMiddle Range Theory of CaringRifa'atul MahmudahNo ratings yet
- By: Eirene Eunike Meidiana Gaghauna & Rifa'Atul MahmudahDocument30 pagesBy: Eirene Eunike Meidiana Gaghauna & Rifa'Atul MahmudahRifa'atul MahmudahNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Molecular Genetics: January 2015Document24 pagesEssentials of Molecular Genetics: January 2015lavomo-simangoNo ratings yet
- Nejmoa 2312117Document14 pagesNejmoa 2312117Carlos SteccaNo ratings yet
- EHS Awareness (EHS Tips For Harmattan Season) - Ghana - Feb W7, 2020Document12 pagesEHS Awareness (EHS Tips For Harmattan Season) - Ghana - Feb W7, 2020JonathanNo ratings yet
- SF2 - 2021 - Grade 4 - KINDNESSDocument6 pagesSF2 - 2021 - Grade 4 - KINDNESSAlberto SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Tingkat Stres Dan Kualitas Tidur Mahasiswa: Keywords: Level of Stress, Stress Management, Sleep QualityDocument6 pagesTingkat Stres Dan Kualitas Tidur Mahasiswa: Keywords: Level of Stress, Stress Management, Sleep QualityJemmy KherisnaNo ratings yet
- Lutysha: Regina Irma Pangastuti, S.Tr. KebDocument3 pagesLutysha: Regina Irma Pangastuti, S.Tr. KeblexaNo ratings yet
- How Is Low Health Literacy IdentifiedDocument2 pagesHow Is Low Health Literacy IdentifiedlefanNo ratings yet
- Pocket Guide On First AidDocument17 pagesPocket Guide On First AidSrividya Kondagunta87% (15)
- Pediatrics Ratio PresentationDocument112 pagesPediatrics Ratio PresentationRobert John SaronaNo ratings yet
- Ashrae Standard 170 CalculatorDocument38 pagesAshrae Standard 170 Calculatormehedi hasan rajanNo ratings yet
- Kielene Copy: Nararapat Na Maging Bukas Ang Aborsyon para Sa Lahat NG Kababaihan (Panig NG Di Sang-Ayon)Document11 pagesKielene Copy: Nararapat Na Maging Bukas Ang Aborsyon para Sa Lahat NG Kababaihan (Panig NG Di Sang-Ayon)Kielene PalosNo ratings yet
- (FINAL) PRC DR Actual Assist Form 2324Document5 pages(FINAL) PRC DR Actual Assist Form 2324Sheherrazzeid BulagasNo ratings yet
- Case Study For Environmental ChemistryDocument8 pagesCase Study For Environmental ChemistryELai Guaza100% (1)
- Neurological HistoryDocument9 pagesNeurological HistorysamiNo ratings yet
- Apiterapia em PortugalDocument88 pagesApiterapia em PortugalMarcelo OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Tooth Numbering System: Whydoweneed?Document3 pagesTooth Numbering System: Whydoweneed?najwan domaNo ratings yet
- Child - ImmunizationsDocument1 pageChild - ImmunizationsJOHN100% (1)
- Therapeutic TouchDocument2 pagesTherapeutic TouchNurhefi SikumbangNo ratings yet
- NCP Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements DIARRHEADocument2 pagesNCP Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements DIARRHEAMa. Elaine Carla TatingNo ratings yet
- Health Aging and The Top 10 Things To Ask - Dr.-William-DalzielDocument54 pagesHealth Aging and The Top 10 Things To Ask - Dr.-William-DalzielJason WongNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics: "In Data We Trust"Document18 pagesNursing Informatics: "In Data We Trust"Melissa Marie Custodio100% (1)
- NCM 112 LEC Topic 14 Communicable DiseasesDocument6 pagesNCM 112 LEC Topic 14 Communicable DiseasesViviene Faye FombuenaNo ratings yet
- Prostho VI - Lec 7 - Template Denture & Acrylic RPDDocument11 pagesProstho VI - Lec 7 - Template Denture & Acrylic RPDبراءة أحمد السلاماتNo ratings yet
- M2C Grant Application GuidanceDocument3 pagesM2C Grant Application GuidanceWalid SasiNo ratings yet
- Previous Board Exam Questions With Key AnswerDocument58 pagesPrevious Board Exam Questions With Key Answergian carlo pagdanganan100% (1)
- Tracheostomy: S.No: Time Specific Objective Content Teachin G Activity Learning Activity Av Aids EvaluationDocument13 pagesTracheostomy: S.No: Time Specific Objective Content Teachin G Activity Learning Activity Av Aids EvaluationaparnaNo ratings yet
- Ledermix DR 1314011841211Document5 pagesLedermix DR 1314011841211Hadil AltilbaniNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading FixDocument20 pagesJournal Reading FixElsa MayoraNo ratings yet
- Productflyer - 978 1 58829 211 7Document1 pageProductflyer - 978 1 58829 211 7Nadya Rahmawati PutriNo ratings yet
- CMC No. 05 2021 DTD Feb 15 2021Document13 pagesCMC No. 05 2021 DTD Feb 15 2021PSSg Junie Grebialde BotabaraNo ratings yet