Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Induction Log Borehole Correction
Induction Log Borehole Correction
Uploaded by
bagus adhityaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Induction Log Borehole Correction
Induction Log Borehole Correction
Uploaded by
bagus adhityaCopyright:
Available Formats
Resistivity
Schlumberger
Induction Log Borehole Correction
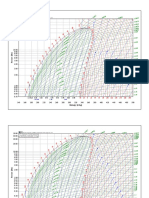
Rcor-4a
Hole diameter (mm)
100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500
0.01 –10
6FF40, ID For very low mud resistivities,
IM divide Rm scale by 10 and
6FF28 0.009 –5
multiply hole signal scale by 10.
0
0.008 0
5
2
0
0.007 5
1.0
Borehole geometrical factor
0.006 10
0.5
0
Hole signal (mS/m)
0.3 )
m
0.005 15
m-
Standoff (in.)
0.2 (oh
m
1.5
R
38 2.5 1.5 0.004 20
2.0 64 38
51
0.5 0.003 25
12
0.1
2.0
51
0.002 30
5
1.0
0 .0
25 2.5
64 0.001 35
Rcor
0 40
Hole signal = hole GF/Rm
–0.001 45
4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
Hole diameter (in. )
© Schlumberger
The hole-conductivity signal is to be subtracted, where neces- Rcor-4 gives corrections for 6FF40 or ID, IM and 6FF28 for
sary, from the induction log conductivity reading before other various wall standoffs. Dashed lines illustrate the use of the chart
corrections are made.† This correction applies to all zones for a 6FF40 sonde with a 1.5-in. standoff in a 14.6-in. borehole,
(including shoulder beds) having the same hole size and mud and R m = 0.35 ohm-m. The hole signal is found to be 5.5 mS/m.
resistivity. If the log reads R I = 20 ohm-m, C I (conductivity) = 50 mS/m.
The corrected C I is then (50 – 5.5) = 44.5 mS/m. R I = 1000/44.5
† Some induction logs, especially in salty muds, are adjusted so that the hole
signal for the nominal hole size is already subtracted out of the recorded curve. = 22.4 ohm-m.
Refer to the log heading.
6-10
You might also like
- Stargate SG1 AddressesDocument18 pagesStargate SG1 AddressesTeguh Nguyen100% (2)
- Đồ Thị Kỹ Thuật NhiệtDocument5 pagesĐồ Thị Kỹ Thuật NhiệtTrang VũNo ratings yet
- Diagrama de Moolier R717 (Amônia)Document1 pageDiagrama de Moolier R717 (Amônia)Jeferson Nobre0% (1)
- Zodiac DiceDocument1 pageZodiac DiceBlanca PazNo ratings yet
- Refrigerante R125 - NuevoDocument1 pageRefrigerante R125 - NuevoSergio TorresNo ratings yet
- ĐỒ THỊ logP hđồ thị môi chất lạnh đóDocument7 pagesĐỒ THỊ logP hđồ thị môi chất lạnh đóTrung Bùi QuốcNo ratings yet
- Dtu, Department of Energy Engineering S in (KJ/ (KG K) ) - V in (M 3/Kg) - T in (ºc) M.J. Skovrup & H.J.H Knudsen. 19-09-04 Ref:Dupont Suva Mp39Document1 pageDtu, Department of Energy Engineering S in (KJ/ (KG K) ) - V in (M 3/Kg) - T in (ºc) M.J. Skovrup & H.J.H Knudsen. 19-09-04 Ref:Dupont Suva Mp39luutruvideo2000No ratings yet
- R 407cDocument1 pageR 407cAhmadd Soultounii Arex TptuNo ratings yet
- Tevaporación Aumentada - UntitledDocument1 pageTevaporación Aumentada - UntitledJesusDavidDeantonioPelaezNo ratings yet
- S in (KJ/ (KG K) ) - V in (M 3/kg) - T in (ºC)Document1 pageS in (KJ/ (KG K) ) - V in (M 3/kg) - T in (ºC)Mahmoud AlFarajNo ratings yet
- ANEXO 2 - Diagrama Mollier - R717Document1 pageANEXO 2 - Diagrama Mollier - R717Túlio André PaivaNo ratings yet
- BADAN - Sheet1Document1 pageBADAN - Sheet1TRASA VIDEONo ratings yet
- Gráfica Refrigerantes P-HDocument6 pagesGráfica Refrigerantes P-HCINTIA GOMEZ AUCEBIASNo ratings yet
- E E E E: Chamfer 0.3 X 45° Any Dimond Knurling Knurling Dia 7.2 Section E-EDocument1 pageE E E E: Chamfer 0.3 X 45° Any Dimond Knurling Knurling Dia 7.2 Section E-EAyush NarangNo ratings yet
- Septic Vault Plan: National Housing AuthorityDocument1 pageSeptic Vault Plan: National Housing AuthorityDJNo ratings yet
- Tech Schlumberger Charts 08 CPSWK 4 34-4-40.p5Document1 pageTech Schlumberger Charts 08 CPSWK 4 34-4-40.p5AshrafNo ratings yet
- Tech-Schlumberger Charts-08 - CPSWK - 4-34 - 4-40.p5Document1 pageTech-Schlumberger Charts-08 - CPSWK - 4-34 - 4-40.p5AshrafNo ratings yet
- DTU, Department of Energy Engineering S in (KJ/ (KG K) ) - V in (M 3/kg) - T in (ºC) M.J. Skovrup & H.J.H Knudsen. 17-04-10 Ref:R.Döring. Klima+Kälte Ingenieur Ki-Extra 5, 1978Document1 pageDTU, Department of Energy Engineering S in (KJ/ (KG K) ) - V in (M 3/kg) - T in (ºC) M.J. Skovrup & H.J.H Knudsen. 17-04-10 Ref:R.Döring. Klima+Kälte Ingenieur Ki-Extra 5, 1978cbdk71No ratings yet
- Termodinamica R-407CDocument1 pageTermodinamica R-407CAndré LealNo ratings yet
- Yks400 5Document1 pageYks400 5Paing Phyo AungNo ratings yet
- Ciclo 5545 V 5 S 5 Dvs 5 VDocument1 pageCiclo 5545 V 5 S 5 Dvs 5 VRibeiro Elias ConcursosNo ratings yet
- BTC Mep DM KH 01 001Document1 pageBTC Mep DM KH 01 001suleiman004No ratings yet
- Efb505010 515937Document2 pagesEfb505010 515937Fabian MirandaNo ratings yet
- DTU, Department of Energy Engineering S in (KJ/ (KG K) ) - V in (M 3/kg) - T in (ºC) M.J. Skovrup & H.J.H Knudsen. 19-09-04 Ref:R.Döring. Klima+Kälte Ingenieur Ki-Extra 5, 1978Document1 pageDTU, Department of Energy Engineering S in (KJ/ (KG K) ) - V in (M 3/kg) - T in (ºC) M.J. Skovrup & H.J.H Knudsen. 19-09-04 Ref:R.Döring. Klima+Kälte Ingenieur Ki-Extra 5, 1978Trần ViệtNo ratings yet
- R717Document1 pageR717Thu Hoài Nguyễn ThịNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration ChartsDocument6 pagesRefrigeration Chartsahmed el-sayedNo ratings yet
- Cricket Pitch - Outdoor DATED 12-05-2023-ModelDocument1 pageCricket Pitch - Outdoor DATED 12-05-2023-ModelShlok JoshiNo ratings yet
- CARTA PSICO Sea - Level - IPDocument1 pageCARTA PSICO Sea - Level - IPSeñor PolloNo ratings yet
- 96 Voting ResultDocument10 pages96 Voting ResultforexpeindiaNo ratings yet
- GBJ Kris Agst 2022Document1 pageGBJ Kris Agst 2022Bidang MedikNo ratings yet
- EQ Acoustics Class 0 Foam DatasheetDocument2 pagesEQ Acoustics Class 0 Foam DatasheetwilldoyeahNo ratings yet
- PH AmoniacoDocument1 pagePH AmoniacoLeonardo AndresNo ratings yet
- TECHNICAL Lowara EHM-td-En 50 HZ Part49Document1 pageTECHNICAL Lowara EHM-td-En 50 HZ Part49Alberto GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Đồ thị bảng tra R410A-R134a-R717-R22Document18 pagesĐồ thị bảng tra R410A-R134a-R717-R22Hưng Thịnh TrịnhNo ratings yet
- R 170 Diagrama de Refrigerante P HDocument1 pageR 170 Diagrama de Refrigerante P HJuan QuispeNo ratings yet
- Bronjong Standar 2020Document20 pagesBronjong Standar 2020Topik SobirinNo ratings yet
- DTU, Department of Energy Engineering S in (KJ/ (KG K) ) - V in (M 3/kg) - T in (ºC) M.J. Skovrup & H.J.H Knudsen. 10-11-07 Ref:R.Döring. Klima+Kälte Ingenieur Ki-Extra 5, 1978Document1 pageDTU, Department of Energy Engineering S in (KJ/ (KG K) ) - V in (M 3/kg) - T in (ºC) M.J. Skovrup & H.J.H Knudsen. 10-11-07 Ref:R.Döring. Klima+Kälte Ingenieur Ki-Extra 5, 1978Willian SouzaNo ratings yet
- Taras PHD Full2011Document329 pagesTaras PHD Full2011Seymur AkbarovNo ratings yet
- Retrofitting of Column-Beam JointDocument1 pageRetrofitting of Column-Beam Jointshams sultaniNo ratings yet
- R 740Document1 pageR 740Jose LuisNo ratings yet
- Anexo 7Document1 pageAnexo 7christianNo ratings yet
- Dtu, Department of Energy Engineering S in (KJ/ (KG K) ) - V in (M 3/Kg) - T in (ºc) M.J. Skovrup & H.J.H Knudsen. 19-11-29 Ref:Dupont Suva Hp62Document1 pageDtu, Department of Energy Engineering S in (KJ/ (KG K) ) - V in (M 3/Kg) - T in (ºc) M.J. Skovrup & H.J.H Knudsen. 19-11-29 Ref:Dupont Suva Hp62Diego RamirezNo ratings yet
- Schema R717Document1 pageSchema R717KenosaNo ratings yet
- PsychrometricChart IPDocument1 pagePsychrometricChart IPmalikimranaliNo ratings yet
- Dtu, Department of Energy Engineering S in (KJ/ (KG K) ) - V in (M 3/Kg) - T in (ºc) M.J. Skovrup & H.J.H Knudsen. 19-01-21 Ref:Dupont Suva Mp39Document1 pageDtu, Department of Energy Engineering S in (KJ/ (KG K) ) - V in (M 3/Kg) - T in (ºc) M.J. Skovrup & H.J.H Knudsen. 19-01-21 Ref:Dupont Suva Mp39sebastianNo ratings yet
- Dtu, Department of Energy Engineering S in (KJ/ (KG K) ) - V in (M 3/Kg) - T in (ºc) M.J. Skovrup & H.J.H Knudsen. 19-01-21 Ref:Dupont Suva Mp39Document1 pageDtu, Department of Energy Engineering S in (KJ/ (KG K) ) - V in (M 3/Kg) - T in (ºc) M.J. Skovrup & H.J.H Knudsen. 19-01-21 Ref:Dupont Suva Mp39Diego RamirezNo ratings yet
- Dtu, Department of Energy Engineering S in (KJ/ (KG K) ) - V in (M 3/Kg) - T in (ºc) M.J. Skovrup & H.J.H Knudsen. 19-01-21 Ref:Dupont Suva Mp39Document1 pageDtu, Department of Energy Engineering S in (KJ/ (KG K) ) - V in (M 3/Kg) - T in (ºc) M.J. Skovrup & H.J.H Knudsen. 19-01-21 Ref:Dupont Suva Mp39Fernando Cordova PardoNo ratings yet
- DTU, Department of Energy Engineering S in (KJ/ (KG K) ) - V in (M 3/kg) - T in (ºC) M.J. Skovrup & H.J.H Knudsen. 19-09-04 Ref:W.C.Reynolds: Thermodynamic Properties in SIDocument1 pageDTU, Department of Energy Engineering S in (KJ/ (KG K) ) - V in (M 3/kg) - T in (ºC) M.J. Skovrup & H.J.H Knudsen. 19-09-04 Ref:W.C.Reynolds: Thermodynamic Properties in SITrần ViệtNo ratings yet
- TYPICAL ROAD SECTION-ModelDocument1 pageTYPICAL ROAD SECTION-ModelEmmanuel Simangon AgudaNo ratings yet
- Diagramme LogP-H - T-S À ImprimerDocument2 pagesDiagramme LogP-H - T-S À ImprimerRiad OualiNo ratings yet
- پارتیکل سایزDocument1 pageپارتیکل سایزsaeid.mehregan.shNo ratings yet
- CPT Interpretation and Seismic Analysis SummaryDocument1 pageCPT Interpretation and Seismic Analysis SummaryTran Vu QuocNo ratings yet
- R404ADocument1 pageR404AElizabeth CorreaNo ratings yet
- Entalpia R410ADocument1 pageEntalpia R410Acarlitos_barbosaNo ratings yet
- R 507Document1 pageR 507Fernando Cordova PardoNo ratings yet
- Sieve BH#1 & BH#2 3881Document7 pagesSieve BH#1 & BH#2 3881wafikmh4No ratings yet
- Mollier r410 PDFDocument1 pageMollier r410 PDFbenja zeta peNo ratings yet
- Dtu, Department of Energy Engineering S in (KJ/ (KG K) ) - V in (M 3/Kg) - T in (ºc) M.J. Skovrup & H.J.H Knudsen. 19-11-29 Ref:Peng-Robinson-Stryjek-Vera Equation and Dupont Suva Ac9000Document1 pageDtu, Department of Energy Engineering S in (KJ/ (KG K) ) - V in (M 3/Kg) - T in (ºc) M.J. Skovrup & H.J.H Knudsen. 19-11-29 Ref:Peng-Robinson-Stryjek-Vera Equation and Dupont Suva Ac9000raul correaNo ratings yet
- Smallest Physical Size: Under 50 MicronsDocument1 pageSmallest Physical Size: Under 50 MicronsDaniel RestrepoNo ratings yet
- Final Model PANNADocument1 pageFinal Model PANNAANKESH SHRIVASTAVANo ratings yet
- AQ F215 Feeder Protection Device Instruction Manual v2.10 EnglishDocument546 pagesAQ F215 Feeder Protection Device Instruction Manual v2.10 EnglishRicardo LyraNo ratings yet
- Long Quiz About HeatDocument2 pagesLong Quiz About HeatLynne Tuiza EndonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Psychology NotesDocument57 pagesIntroduction To Psychology NotesRic DNo ratings yet
- NAME: DATE: CLASS: Review Unit 3,4,5Document4 pagesNAME: DATE: CLASS: Review Unit 3,4,5Hạnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Bakti MW Linkbudget 20230705Document2,033 pagesBakti MW Linkbudget 20230705muhammad alibNo ratings yet
- Animal Slide Preparation TechniqueDocument10 pagesAnimal Slide Preparation Techniqueraja nur aimiNo ratings yet
- Workbook Sampling Distributions PracticeDocument3 pagesWorkbook Sampling Distributions PracticeOhio1432No ratings yet
- The Diagnosis and Management of Atypical Types of Diabetes: Kathryn Evans Kreider, DNP, FNP-BCDocument7 pagesThe Diagnosis and Management of Atypical Types of Diabetes: Kathryn Evans Kreider, DNP, FNP-BCromyNo ratings yet
- 3Document22 pages3amanNo ratings yet
- 2018 Root Cause CategoriesDocument3 pages2018 Root Cause CategoriesRidwan AriefNo ratings yet
- Health Requirements For Hotels & Furnished ApartmentsDocument4 pagesHealth Requirements For Hotels & Furnished ApartmentsPatel KalingaNo ratings yet
- Find User Manual For Your Device in The CDDocument1 pageFind User Manual For Your Device in The CDMilciv FaithNo ratings yet
- Baker Street Journal - Os v1n2 - April 1946Document136 pagesBaker Street Journal - Os v1n2 - April 1946Наталья СекачеваNo ratings yet
- AWS A1.1 2001 Metric Practice GuideDocument41 pagesAWS A1.1 2001 Metric Practice GuideAlexander Jose Chacin NavarroNo ratings yet
- Exhibit 1Document6 pagesExhibit 1jamesosborne77-1No ratings yet
- Twist of FaithonesheetDocument1 pageTwist of FaithonesheetpepperbashamNo ratings yet
- Test Certificate of Boilo 18.00 MM - 20211228 - 0001Document2 pagesTest Certificate of Boilo 18.00 MM - 20211228 - 0001Dtl DiagNo ratings yet
- Brown Bag Introduction SpeechDocument3 pagesBrown Bag Introduction Speechcathy johnsonNo ratings yet
- Marine 2017 Small PDFDocument166 pagesMarine 2017 Small PDFpcatruongNo ratings yet
- CMC Kuhnke Can Seam Analysis A Non Destructive Look at The Effects of Thermal Processing PDFDocument22 pagesCMC Kuhnke Can Seam Analysis A Non Destructive Look at The Effects of Thermal Processing PDFfranzdiaz7314No ratings yet
- Soda-Lime and Zoelite MethodDocument4 pagesSoda-Lime and Zoelite MethodcIBIM29No ratings yet
- Atheist Science3Document179 pagesAtheist Science3Howard HillNo ratings yet
- Laporan Kimia Organik - Asam FumaratDocument40 pagesLaporan Kimia Organik - Asam FumaratTuttaTutiWidyaNo ratings yet
- Loctite Ablestik 8290: Technical Data SheetDocument2 pagesLoctite Ablestik 8290: Technical Data SheetAl Haba Ahmad Zaki Abdul HamidNo ratings yet
- Virtual Inertia ControlDocument13 pagesVirtual Inertia ControlSM FerdousNo ratings yet
- Emerging HorizonsDocument28 pagesEmerging Horizonsmanishkanojia_0% (1)
- 0594-0598 (1058) Analytical Instrument QualificationDocument5 pages0594-0598 (1058) Analytical Instrument QualificationRaf RafNo ratings yet
- Logarithm sht2Document3 pagesLogarithm sht2Ainee100% (1)