Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1579 3884 1 PB
1579 3884 1 PB
Uploaded by
Alexandru SrgCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Colorectal CancerDocument39 pagesColorectal CancerMuvenn Kannan100% (2)
- Syndromic Gastric PolypsDocument15 pagesSyndromic Gastric PolypsTheDrakairNo ratings yet
- Familial Adenomatous PolyposisDocument40 pagesFamilial Adenomatous Polyposisapi-19641337100% (1)
- Prostho Rehabilitation - HypodontiaDocument24 pagesProstho Rehabilitation - HypodontiaAmniAzmiNo ratings yet
- Midline Diastema Treatment OptionsDocument6 pagesMidline Diastema Treatment OptionsnandaNo ratings yet
- Multidisciplin Ary Approach IN Prosthodonti CS: Veena PG III YearDocument111 pagesMultidisciplin Ary Approach IN Prosthodonti CS: Veena PG III Yearbharathi krishnaNo ratings yet
- 3C's - Resham PDFDocument5 pages3C's - Resham PDFGirish M SNo ratings yet
- Regional Odontodysplasia - A Rare Case ReportDocument3 pagesRegional Odontodysplasia - A Rare Case ReportIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Overlay DentureDocument5 pagesOverlay DentureAmar BhochhibhoyaNo ratings yet
- Prosthetic Rehabilitation of Severe Hypodontia: A Clinical ReportDocument12 pagesProsthetic Rehabilitation of Severe Hypodontia: A Clinical ReportAmniAzmiNo ratings yet
- Ambarkova Meskova, Karakamcev, Igor PDFDocument7 pagesAmbarkova Meskova, Karakamcev, Igor PDFVesna AmbarkovaNo ratings yet
- 6-Year-Follo Up. 3 Steps Techniques. Francesca Valati-1 PDFDocument25 pages6-Year-Follo Up. 3 Steps Techniques. Francesca Valati-1 PDFAdriana CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Articol Protetica-1Document6 pagesArticol Protetica-1LauraNo ratings yet
- FMR of Worn Out DentititonDocument6 pagesFMR of Worn Out Dentititonrayavarapu sunilNo ratings yet
- Case Report KonservasiDocument7 pagesCase Report KonservasiBintang AyuNo ratings yet
- Supernumerary Lateral IncisorDocument2 pagesSupernumerary Lateral IncisorNatasa StojkovicNo ratings yet
- Dracula ToothDocument3 pagesDracula ToothLjubomirErdoglijaNo ratings yet
- Partial PulpotomyDocument5 pagesPartial PulpotomyLeena Losheene VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Improving Aesthetics in Patients With Complete DenturesDocument4 pagesImproving Aesthetics in Patients With Complete DenturesMohsin HabibNo ratings yet
- Articulo PDFDocument4 pagesArticulo PDFMile MolinaNo ratings yet
- Aldrigui 2011Document5 pagesAldrigui 2011Javier Farias VeraNo ratings yet
- ContempClinDent32219 6162101 - 170701 2Document4 pagesContempClinDent32219 6162101 - 170701 2Andres CoboNo ratings yet
- 322 1403 1 PB PDFDocument2 pages322 1403 1 PB PDFAdityaNo ratings yet
- Caldo Teixeira2004Document4 pagesCaldo Teixeira2004hugogrupononnaNo ratings yet
- Asds 02 0215Document3 pagesAsds 02 02156mf9jf6h99No ratings yet
- International Journal of Current Advanced Research International Journal of Current Advanced ResearchDocument3 pagesInternational Journal of Current Advanced Research International Journal of Current Advanced ResearchgilangNo ratings yet
- Fusion/Double Teeth: Sandhya Shrivastava, Manisha Tijare, Shweta SinghDocument3 pagesFusion/Double Teeth: Sandhya Shrivastava, Manisha Tijare, Shweta SinghNurwahit IksanNo ratings yet
- An Integrated Treatment Approach: A Case Report For Dentinogenesis Imperfecta Type IIDocument4 pagesAn Integrated Treatment Approach: A Case Report For Dentinogenesis Imperfecta Type IIpritasyaNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Correction of Tongue Thrust Habit AloDocument7 pagesSingle Phase Correction of Tongue Thrust Habit AloAkhil SinghNo ratings yet
- Oligodontia: A Case Report: Fatma Ünalan / Is in Ulukapi / Juliana BakirgilDocument4 pagesOligodontia: A Case Report: Fatma Ünalan / Is in Ulukapi / Juliana BakirgilfatimahNo ratings yet
- Treatment of A Patient With Oligodontia A Case ReportDocument5 pagesTreatment of A Patient With Oligodontia A Case ReportWindaNo ratings yet
- AmelogenesisimperfectaDocument4 pagesAmelogenesisimperfectaalyssaNo ratings yet
- Dentinogenesis Imperfecta A Case ReportDocument3 pagesDentinogenesis Imperfecta A Case ReporthadriaanaNo ratings yet
- Endodontic Considerations in The Elderly: ReviewarticleDocument10 pagesEndodontic Considerations in The Elderly: ReviewarticleYasmine SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Supernumerary Teeth Associated With An Impacted Maxillary Central Incisor: Surgical and Orthodontic ManagementDocument4 pagesMultiple Supernumerary Teeth Associated With An Impacted Maxillary Central Incisor: Surgical and Orthodontic ManagementCalin CristianNo ratings yet
- An Unusual Case of Gemination in Mandibular Second Premolar A Case ReportDocument4 pagesAn Unusual Case of Gemination in Mandibular Second Premolar A Case ReportDanish NasirNo ratings yet
- Jurnal CRSS Prothesa 4 (Sixna Agitha Claresta 20204020100)Document7 pagesJurnal CRSS Prothesa 4 (Sixna Agitha Claresta 20204020100)sixnaagithaNo ratings yet
- Artìculo CareDocument6 pagesArtìculo CareARLET KRISTEL PAMELA REMUZGO ALVARADONo ratings yet
- Literature Review of Amelogenesis Imperfecta With Case ReportDocument6 pagesLiterature Review of Amelogenesis Imperfecta With Case Reportc5t9rejgNo ratings yet
- An Alternative Solution For A Complex Prosthodontic Problem: A Modified Andrews Fixed Dental ProsthesisDocument5 pagesAn Alternative Solution For A Complex Prosthodontic Problem: A Modified Andrews Fixed Dental ProsthesisDragos CiongaruNo ratings yet
- CRID2015 579169 PDFDocument7 pagesCRID2015 579169 PDFNawaf RuwailiNo ratings yet
- OverdentureDocument47 pagesOverdenturemohid sheikhNo ratings yet
- 8 Tooth Ankylosis Andits Orthodontic ImplicationDocument6 pages8 Tooth Ankylosis Andits Orthodontic ImplicationPretty HiaNo ratings yet
- Amelogenesisvaka NYSDJDocument6 pagesAmelogenesisvaka NYSDJRuxandra FitaNo ratings yet
- Dental Twinning in Primary Dentition A Case ReportDocument4 pagesDental Twinning in Primary Dentition A Case ReporthaidirNo ratings yet
- 2015 DU - Consv Managment of MacrodontiaDocument4 pages2015 DU - Consv Managment of MacrodontiaGeorge JoseNo ratings yet
- Indirect Veneer Treatment of Anterior Maxillary Teeth With Enamel HypoplasiaDocument5 pagesIndirect Veneer Treatment of Anterior Maxillary Teeth With Enamel Hypoplasiaamalia rieska mauliddyaNo ratings yet
- Periodontal Changes in Ortho Treatment / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument81 pagesPeriodontal Changes in Ortho Treatment / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNo ratings yet
- Prosthodontic Management of Severely ResorbedDocument2 pagesProsthodontic Management of Severely ResorbedAamir BugtiNo ratings yet
- Dental Anomalies in Orthodontic Patients in Cali, Colombia: ArtículosDocument10 pagesDental Anomalies in Orthodontic Patients in Cali, Colombia: ArtículosJeison ramosNo ratings yet
- Regional Early Development and Eruption of Permanent Teeth Case ReportDocument5 pagesRegional Early Development and Eruption of Permanent Teeth Case ReportAngelia PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Article - 1596794701 2Document8 pagesArticle - 1596794701 2drakashverma7No ratings yet
- Dental Implant Therapy in A Patient With Acromegaly: A Clinical ReportDocument6 pagesDental Implant Therapy in A Patient With Acromegaly: A Clinical ReportAkanksha MahajanNo ratings yet
- Orthodontics and Periodontal Therapy (Vandarshall)Document18 pagesOrthodontics and Periodontal Therapy (Vandarshall)Priya SJNo ratings yet
- Oktawati 2020Document3 pagesOktawati 2020Mariatun ZahronasutionNo ratings yet
- CU-Sil Dentures - A Novel Approach To ConserveDocument27 pagesCU-Sil Dentures - A Novel Approach To Conservereshma shaikNo ratings yet
- Erupted Odontoma: A Case Report: Abst TDocument2 pagesErupted Odontoma: A Case Report: Abst TGonzalo Millán ZardainNo ratings yet
- Gigi Tiruan GasketDocument5 pagesGigi Tiruan GasketGus BasyaNo ratings yet
- Article - 1653239529 2Document5 pagesArticle - 1653239529 2Mega AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Primary Double Tooth With Partial Anodontia of Permanent Dentition - A Case ReportDocument3 pagesPrimary Double Tooth With Partial Anodontia of Permanent Dentition - A Case ReportadriiianaiiioanaNo ratings yet
- Complete Denture Fabrication For Old Denture Wearer in One DayDocument3 pagesComplete Denture Fabrication For Old Denture Wearer in One DayAsma Akram - ProsthodonticsNo ratings yet
- Case Report Gigi Tiruan LengkapDocument3 pagesCase Report Gigi Tiruan LengkapGus BasyaNo ratings yet
- Oral Medicine & Pathology from A-ZFrom EverandOral Medicine & Pathology from A-ZRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- Molecular Characteristics of Young Onset Colorectal Cancer in Vietnamese PatientsDocument8 pagesMolecular Characteristics of Young Onset Colorectal Cancer in Vietnamese PatientsHuỳnh Công BằngNo ratings yet
- Ca Caput Pankreas PDFDocument42 pagesCa Caput Pankreas PDFOvamelia JulioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 39: Nursing Assessment: Gastrointestinal System Test BankDocument6 pagesChapter 39: Nursing Assessment: Gastrointestinal System Test BankNurse UtopiaNo ratings yet
- Colorectal CancerDocument19 pagesColorectal CancerAyra Batore LaguitaoNo ratings yet
- Definition, Risk Factors and Epidemiology of Colorectal CancerDocument3 pagesDefinition, Risk Factors and Epidemiology of Colorectal Cancerdeer muNo ratings yet
- Diz 2Document6 pagesDiz 2Dulce TulaNo ratings yet
- SOFIE FAP Webinar 2023Document42 pagesSOFIE FAP Webinar 2023Shibin JayakrishnanNo ratings yet
- The Pathology of Gastric and Duodenal Polyps: Current ConceptsDocument19 pagesThe Pathology of Gastric and Duodenal Polyps: Current Conceptsaccess pathologicNo ratings yet
- Stomach Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and PreventionDocument15 pagesStomach Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and PreventionJibba kamaraNo ratings yet
- Per Rectal Bleeding CompiledDocument33 pagesPer Rectal Bleeding CompiledRajhmuniran Kandasamy100% (1)
- All CANCERDocument40 pagesAll CANCERKaren Joyce Costales MagtanongNo ratings yet
- GastroenterologyDocument35 pagesGastroenterologyGuilherme Mariante NetoNo ratings yet
- Desmoid Tumor in A Scar From Inguinal Hernia Repair: A Case ReportDocument3 pagesDesmoid Tumor in A Scar From Inguinal Hernia Repair: A Case ReportInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- Gastric CancerDocument31 pagesGastric CancerHarleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Oral Revalida Round 2Document63 pagesOral Revalida Round 2Mercy Anne EcatNo ratings yet
- Colorectal: Understanding The Cancer ProcessDocument14 pagesColorectal: Understanding The Cancer ProcessSeli adalah SayaNo ratings yet
- Gardners SyndromeDocument4 pagesGardners SyndromeTesis ShaioNo ratings yet
- Periampullary TumorsDocument30 pagesPeriampullary TumorsAsif.N.IqbalNo ratings yet
- Gastroentrology LastDocument48 pagesGastroentrology LastAbdallah K. RamadanNo ratings yet
- (Medicine) Surgical Removal of A Portion of The Colon.: Hemicolectomy-P1. AnastomosesDocument5 pages(Medicine) Surgical Removal of A Portion of The Colon.: Hemicolectomy-P1. AnastomosesMuhammad MalikNo ratings yet
- 2020 Molecular Biochemistry Handout PDFDocument12 pages2020 Molecular Biochemistry Handout PDFFlowerNo ratings yet
- Genetoc Aspect of CancerDocument33 pagesGenetoc Aspect of CancermichaelcylNo ratings yet
- Colon CancerDocument25 pagesColon Cancerchori2008No ratings yet
- Colorectal Cancer Prevention and Early DetectionDocument33 pagesColorectal Cancer Prevention and Early DetectionNesyah AyuNo ratings yet
- Colorectal Cancer - Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Protective FactorsDocument31 pagesColorectal Cancer - Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Protective FactorsLuz ClaritaNo ratings yet
- ColonDocument14 pagesColonpaola andrea cabrera erazoNo ratings yet
- Rectal Cancer,: Clinical Practice Guidelines in OncologyDocument28 pagesRectal Cancer,: Clinical Practice Guidelines in OncologyRaíla SoaresNo ratings yet
1579 3884 1 PB
1579 3884 1 PB
Uploaded by
Alexandru SrgOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1579 3884 1 PB
1579 3884 1 PB
Uploaded by
Alexandru SrgCopyright:
Available Formats
Dental Research Journal
Case Report
Prosthodontic management of a patient with Gardner’s syndrome:
A clinical case report
Kunwarjeet Singh1, Abhishek Singh2, Prince Kumar3, Nidhi Gupta4
1
Department of Prosthodontics and 4Pedodontics, Institute of Dental Studies and Technologies, Modinagar, Ghaziabad, 2Department of
Prosthodontics, Sarjug Dental College and Hospital, Darbhanga, Bihar, 3Department of Prosthodontics, Shree Bankey Bihari Dental College and
Research Centre, Masuri, Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh, India
Received: August 2012 ABSTRACT
Accepted: May 2013
Gardner’s syndrome is a genetic condition demonstrating an autosomal dominant trait and characterized
Address for correspondence:
Dr. Prince Kumar,
by the multiple colonic polyps (familial adenomatous polyposis coli) with sebaceous cysts and jaw
Department of osteomas.Various dental abnormalities present in patient’s suffering with this syndrome includes multiple
Prosthodontics, Shree impacted or unerupted teeth, supernumerary teeth, hypodontia, compound odontomes and dentigerous
Bankey Bihari Dental College cyst. In this case report, a patient with Gardner’s syndrome who suffered from functional and psychological
and Research Centre,
Masuri, Ghaziabad,
problems owing to multiple impacted, unerupted teeth and hypodontia was presented. Patient was treated
Uttar Pradesh, India. with a maxillary conventional overdenture opposing mandibular custom bar supported overdentures.
E-mail: princekumar
@its.edu.in Key Words: Dentigerous cyst, Gardner syndrome, osteoma
INTRODUCTION the colon and rectum, but they may develop throughout
the gastro intestinal tract, including stomach,
Gardner syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized duodenum and the terminal ileum.[3] The polyps start
by hereditary intestinal polyposis, osteomas, tumors appearing in puberty, but they develop extensively
of soft-tissues, cutenous and subcutaneous cystic during the second and third decade of life.[4] Most of
lesions and multiple impacted teeth.[1] This syndrome the polyps undergo malignant transformation.[5] The
is named by Eldon J. Gardner who first described the incidence of malignant transformation is about 5%
characteristics of syndrome in 1951. It is caused by at puberty, which increases to 100% for the patients
mutation of adenomatous polyposis coli gene located at more than 50 years of age.[6]
chromosome 5q 21, which is the same gene mutant in
familial adenomatous polyposis. It has a high dominant The dental abnormalities are present in about 30%
penetrance and variable expressivity with incidence of patients with Gardner syndrome and may include
between 1:8,000 and 1:1,4000 live births.[1] The majority multiple impacted or unerupted teeth, hypodontia,
of patients have a family history of this syndrome, but supernumerary teeth, odontomes and dentigerous
25% can present with a new dominant mutation and be cyst. The most of erupted teeth have calcified canals.
the first member of the family.[2] Periodontal space around the teeth is mostly absent.
Owing to extremely dense nature of the alveolar bone
Intestinal polyps are the most important characteristic and the almost complete absence of the periodontal
feature of this syndrome, which are mostly located in space caused by hypercementosis, tooth extraction in
these patients is very difficult.[7]
Access this article online
Most of the young patients with this syndrome
suffer from severe mental distress and psychological
Website: http//:drj.mui.ac.ir
problems due to multiple missing teeth resulting in
poor esthetics.[8] Some of the patients disassociate
themselves from attending social engagements. Due
to hypodontia, masticatory efficiency is decreased;
276 Dental Research Journal / March 2014 / Vol 11 / Issue 2
Singh, et al.: Prosthodontic management of a patient with Gardner’s syndrome
patients are not able to chew food properly resulting 1.5 cm in diameter, which were associated with a high
in digestive problems. risk of malignant transformation. Colonoscopy and
the following histological examination confirmed the
Osteomas of jaw bones, presence of dentigerous cyst,
presence of colonic adenomatous polyps for which he
multiple impacted and unerupted teeth, hypodontia,
was advised for colectomy. Moreover, as the cystic
multiple missing teeth in both jaws, offers limited
lesion at the left corner of the angle of the mandible
prosthodontic options for successful esthetic and
was completely asymptomatic, he refused its resective
functional rehabilitation of these patients.[7] Prosthetic
surgical treatment.
rehabilitation with implant-supported and fixed dental
prosthesis, most of the times is contraindicated Due to the presence of multiple impacted teeth,
when multiple impacted teeth and cysts are present the placement of the implants and fabrication of an
in the jaw bones.[3] Saving the few erupted teeth implant- supported overdenture was not considered.
and fabrication of overdenture is a good option for The fabrication of fixed partial denture and removable
long-term functional restoration of these patients. cast partial denture was also not considered due to few
The presented case report describes prosthodontic remaining teeth, unfavorable crown root ratio and large
management of Gardener syndrome in a young male spacing between the remaining teeth. The treatment
with mandibular custom bar supported overdenture option presented to the patient was overdentures. On
opposing conventional maxillary overdenture. careful clinical assessment of the vertical space (inter
arch distance), it was concluded that sufficient vertical
CASE REPORT space for placement of metal bar, copings, denture
base and teeth arrangement was available; so keeping
A 25- year- old male reported to the dental office for in mind the biomechanical principles of conventional
prosthetic evaluation. Patient had received a maxillary complete dentures, fabrication of a maxillary over
and mandibular acrylic resin removable partial denture denture and mandibular custom bar supported over
and he had major complaint of difficulty in chewing dentures was decided.
and wearing the prostheses due to their loose fit and
The root canals and pulp chambers of erupted teeth
unsatisfactory esthetics. He also had given the history
were calcified, so no intentional root canal treatment of
of psychological trauma due to multiple missing teeth
remaining teeth was done. Abutments were prepared
and associated poor esthetics. Intraoral examination
with chamfer finish line at paragingival level with a
of patient revealed, multiple missing teeth and broad,
15° convergence and 1.25 mm incisal and 0.75 mm
well- defined maxillary and mandibular residual ridge.
axial reduction, using diamond points (ISO#223/016
Only remaining teeth were maxillary right first molar,
and 223/018, Shofu Dental Corporation, San Marcos,
second premolar and left first molar and mandibular
CA). After preparation, suitable size stock trays
central and lateral incisors and right second premolar
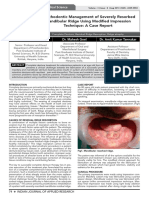
were selected and impressions were made with putty
[Figure 1]. The past dental history of the patient
(Aquasil soft putty/regular set, Dentsply, Mannheim,
revealed no extraction of any missing tooth.
Germany) and light body (Aquasil LV, Dentsply) of
The dental panoramic tomogram (DPT) revealed poly vinylsiloxane elastomeric impression material
multiple unerupted and impacted teeth [Figure 2], by double step putty wash technique. The impression
well-defined cystic lesion at the left corner of the angle was poured in the type IV dental stone (Ultra rock,
of the mandible, generalized increased density of the Kala bhai Karson Pvt. Ltd., Mumbai, India) to obtain
mandible, almost complete absence of periodontal cast on which pattern of copings and the bar was
space caused by hypercementosis, incomplete root fabricated with inlay wax (Blue inlay wax, Kemdent,
formation of many teeth and radiopaque lesion in Swindon, United Kingdom). The pattern of copings
left mandibular premolar and molar region. He also was dome shaped and that of the bar was rectangular.
gave the history of two painless soft-tissues swellings The pattern was then sprued, invested (Bellasum,
in the scalp and neck. With a provisional diagnosis Bego, Bremen, Germany), burnout and casted in
of Gardner syndrome in mind, when he was asked base metal alloy (BEGOW irocast S, Bego). After
directly about his bowel habits, he gave a 2 year retrieving casting from the investment, it was finished
history of diarrhea with occasional bleeding. Computed and its fit was evaluated on the cast [Figure 3] and
tomography colonoscopy of the patient was performed, in the patient mouth. The copings and bar assembly
which revealed three polyps in the colon measuring were cemented on the abutments with glass ionomer
Dental Research Journal / March 2014 / Vol 11 / Issue 2 277
Singh, et al.: Prosthodontic management of a patient with Gardner’s syndrome
cement (Hy-bond Glass ionomer CX, Shofu Inc., Corporation, Fort Collins, Colorado, United States).
Kyoto, Japan). Complete denture impressions were Artificial teeth were selected and arranged on the
made after cementation. record base for a trial denture arrangement and
Custom acrylic resin tray were fabricated with auto- evaluated intraorally for phonetics, esthetics, occlusal
poly merized acrylic resin (Meliodent, Heraus Kulzer, vertical dimension and centric relation. After waxup,
Newbury, UK) after adapting 1 mm base plate wax the denture was processed in heat polymerized acrylic
spacer on maxillary cast except posterior palatal seal resin (Lucitone 199, Dentsply), finished, polished
and on mandibular cast except buccal shelf area and and inserted. Figures 4 and 5 shows intaglio surfaces
retromolar pad. After adjusting custom trays, single of the maxillary and mandibular overdentures while
step border molding was carried out with medium Figure 6 represents intraoral view of overdentures in
body poly vinylsiloxane (Reprosil, Dentsply) and occlusion. Patient was scheduled for follow-up visits
secondary impression was made with light body every 3 months and reported no complaints during
(Aquasil LV, Dentsply). Master cast was obtained by 1 year of follow-up.
pouring the secondary impression in type IV dental
stone (Ultrarock, Kalabhai Karson Pvt. Ltd.). DISCUSSION
The trial denture bases were fabricated with auto-
Most of the patients suffering from Gardner’s
polymerized acrylic resin (Meliodent, Heraus Kulzer)
syndrome have digestive problems with diarrhea and
after applying the separating media over the master
bleeding.[2] The condition gets further complicated due
cast. Occlusion rims were fabricated over trial denture
bases and horizontal and vertical maxillomandibular to difficulty in chewing and digestion of the food, due
records were obtained and transferred to a semi- to multiple missing teeth, which directly affect their
adjustable articulator using a facebow (Whip Mix
Figure 2: Dental panoramic tomogram showing various well
defined dental abnormalities in both jaws
Figure 1: Intraoral view showing remaining mandibular and
maxillary teeth with well-defined ridges
Figure 3: Mandibular custom bar splinting the remaining teeth
together Figure 4: Intaglio surface of mandibular overdenture
278 Dental Research Journal / March 2014 / Vol 11 / Issue 2
Singh, et al.: Prosthodontic management of a patient with Gardner’s syndrome
Figure 6: Intraoral view of overdentures in centric occlusion
Figure 5: Intaglio surface of maxillary overdenture basic principles of complete denture fabrication must
take precedence over mechanical considerations of
health and well-being.[4] The functional rehabilitation custom bar.[7] The main objective must be to gain
by proper prosthodontic management is one of the support from the maximum possible area and reduce to
very important aspect, which allow these patients to a minimum any displacing loads falling on the denture.
continue to live there normal life. Hence, the proper Custom bar significantly improve the level of satisfaction
diagnosis and treatment planning for prosthetic of denture wearing patients by enhancing the retention,
rehabilitation is very important.[5,6] support and stability of the prosthesis thereby improving
In this case, the fabrication of implant-supported the chewing efficiency and comfort of the patient by
prosthesis was not considered because of multiple reducing the forward sliding of the mandibular denture,
impacted teeth, which preclude the placement of the maintaining the occlusion and minimizing the trauma of
implants. Keeping in mind, the economic condition the underlying supporting tissues.[7,8]
of the patient, the crown root ratio and the space
between erupted remaining mandibular teeth, a CONCLUSION
custom bar retained mandibular over denture and
Successful functional and esthetic rehabilitation of
maxillary over denture were considered. The bar
a young patient with multiple missing teeth, with
splints the remaining teeth; minimize the mobility
an oral prosthesis have a great effect on the mental
and helps in broad distribution of the forces between
attitude of the patient. A general dental practitioner
the abutments.[6] It also improves the retention and
may be the first health- care professional to review
stability of the denture. The bar should be positioned the DPT of a patient with Gardner syndrome. His
directly above the crest of the ridge. This position or her knowledge on the clinical and radiological
makes it easy to clean the bar and fabricate the stigmas of this syndrome may lead to appropriate
prosthesis above the bar.[7] If the bar is positioned further investigation and treatment, which might be
lingual to the crest of the ridge, it will interfere with life saving not only for the patient, but also for their
tongue space and its function and the patient’s speech. family members. By saving the remaining teeth and
The vertical relationship of the bar to the alveolar fabricating an overdenture significantly improve their
ridge is very important. When sufficient vertical space functional ability by enhancing the retention, support
is available, providing 2-4 mm or more space between and stability of the prosthesis thereby improving the
the bar and mucosa will allow easy passage of saliva chewing efficiency.
and food particles as well as oral hygiene aids. Hygiene
maintenance in this situation is very easy. Unfortunately, REFERENCES
there is seldom adequate space for this arrangement
1. Amla B, Banu GK, Cigdem O. Oral and maxillofacial
unless across a cleft palate or an area of gross resorption. manifestions of Gargner’s syndrome: case report. Acta Stomatal
Hence, in the majority of patients, the bar needs to be Croat 2009;43:60-5.
placed in even/passive contact with the mucosa. During 2. Patel H, Rees RT. Unicystic ameloblastoma presentingin
the fabrication of custom bar retained prosthesis, the Gardner’s syndrome: A case report. Br Dent J 2005;198:747-8.
Dental Research Journal / March 2014 / Vol 11 / Issue 2 279
Singh, et al.: Prosthodontic management of a patient with Gardner’s syndrome
3. Bussey HJ, Veale AM, Morson BC. Genetics of gastrointestinal 7. Madani M, Madani F. Gardner’s syndrome presenting with dental
polyposis. Gastroenterol1978;74:1325-30. complaints. Arch Iran Med 2007;10:535-9.
4. Oner AY, Pocan S. Gardner’s syndrome: A case report. Br Dent 8. Cristofaro MG, Giudice A, Amantea M, Riccelli U, Giudice M.
J 2006;200:666-7. Gardner’s syndrome: A clinical and genetic study of a family.
5. Gu GL, Wang SL, Wei XM, Bai L. Diagnosis and treatment of Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 2013;115:e1-6.
Gardner syndrome with gastric polyposis: A case report and
review of the literature. World J Gastroenterol 2008;14:2121-3. How to cite this article: Singh K, Singh A, Kumar P, Gupta N.
6. Silva CA, MoraesPde C, Furuse C, Junqueira JL, Thomaz LA, Prosthodontic management of a patient with Gardner’s syndrome: A
clinical case report. Dent Res J 2014;11:276-80.
deAraújo VC. Gardner syndrome with no clinical family history.
Source of Support: Nil. Conflict of Interest: None declared.
J Craniofac Surg2009;20:1186-9.
280 Dental Research Journal / March 2014 / Vol 11 / Issue 2
You might also like
- Colorectal CancerDocument39 pagesColorectal CancerMuvenn Kannan100% (2)
- Syndromic Gastric PolypsDocument15 pagesSyndromic Gastric PolypsTheDrakairNo ratings yet
- Familial Adenomatous PolyposisDocument40 pagesFamilial Adenomatous Polyposisapi-19641337100% (1)
- Prostho Rehabilitation - HypodontiaDocument24 pagesProstho Rehabilitation - HypodontiaAmniAzmiNo ratings yet
- Midline Diastema Treatment OptionsDocument6 pagesMidline Diastema Treatment OptionsnandaNo ratings yet
- Multidisciplin Ary Approach IN Prosthodonti CS: Veena PG III YearDocument111 pagesMultidisciplin Ary Approach IN Prosthodonti CS: Veena PG III Yearbharathi krishnaNo ratings yet
- 3C's - Resham PDFDocument5 pages3C's - Resham PDFGirish M SNo ratings yet
- Regional Odontodysplasia - A Rare Case ReportDocument3 pagesRegional Odontodysplasia - A Rare Case ReportIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Overlay DentureDocument5 pagesOverlay DentureAmar BhochhibhoyaNo ratings yet
- Prosthetic Rehabilitation of Severe Hypodontia: A Clinical ReportDocument12 pagesProsthetic Rehabilitation of Severe Hypodontia: A Clinical ReportAmniAzmiNo ratings yet
- Ambarkova Meskova, Karakamcev, Igor PDFDocument7 pagesAmbarkova Meskova, Karakamcev, Igor PDFVesna AmbarkovaNo ratings yet
- 6-Year-Follo Up. 3 Steps Techniques. Francesca Valati-1 PDFDocument25 pages6-Year-Follo Up. 3 Steps Techniques. Francesca Valati-1 PDFAdriana CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Articol Protetica-1Document6 pagesArticol Protetica-1LauraNo ratings yet
- FMR of Worn Out DentititonDocument6 pagesFMR of Worn Out Dentititonrayavarapu sunilNo ratings yet
- Case Report KonservasiDocument7 pagesCase Report KonservasiBintang AyuNo ratings yet
- Supernumerary Lateral IncisorDocument2 pagesSupernumerary Lateral IncisorNatasa StojkovicNo ratings yet
- Dracula ToothDocument3 pagesDracula ToothLjubomirErdoglijaNo ratings yet
- Partial PulpotomyDocument5 pagesPartial PulpotomyLeena Losheene VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Improving Aesthetics in Patients With Complete DenturesDocument4 pagesImproving Aesthetics in Patients With Complete DenturesMohsin HabibNo ratings yet
- Articulo PDFDocument4 pagesArticulo PDFMile MolinaNo ratings yet
- Aldrigui 2011Document5 pagesAldrigui 2011Javier Farias VeraNo ratings yet
- ContempClinDent32219 6162101 - 170701 2Document4 pagesContempClinDent32219 6162101 - 170701 2Andres CoboNo ratings yet
- 322 1403 1 PB PDFDocument2 pages322 1403 1 PB PDFAdityaNo ratings yet
- Caldo Teixeira2004Document4 pagesCaldo Teixeira2004hugogrupononnaNo ratings yet
- Asds 02 0215Document3 pagesAsds 02 02156mf9jf6h99No ratings yet
- International Journal of Current Advanced Research International Journal of Current Advanced ResearchDocument3 pagesInternational Journal of Current Advanced Research International Journal of Current Advanced ResearchgilangNo ratings yet
- Fusion/Double Teeth: Sandhya Shrivastava, Manisha Tijare, Shweta SinghDocument3 pagesFusion/Double Teeth: Sandhya Shrivastava, Manisha Tijare, Shweta SinghNurwahit IksanNo ratings yet
- An Integrated Treatment Approach: A Case Report For Dentinogenesis Imperfecta Type IIDocument4 pagesAn Integrated Treatment Approach: A Case Report For Dentinogenesis Imperfecta Type IIpritasyaNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Correction of Tongue Thrust Habit AloDocument7 pagesSingle Phase Correction of Tongue Thrust Habit AloAkhil SinghNo ratings yet
- Oligodontia: A Case Report: Fatma Ünalan / Is in Ulukapi / Juliana BakirgilDocument4 pagesOligodontia: A Case Report: Fatma Ünalan / Is in Ulukapi / Juliana BakirgilfatimahNo ratings yet
- Treatment of A Patient With Oligodontia A Case ReportDocument5 pagesTreatment of A Patient With Oligodontia A Case ReportWindaNo ratings yet
- AmelogenesisimperfectaDocument4 pagesAmelogenesisimperfectaalyssaNo ratings yet
- Dentinogenesis Imperfecta A Case ReportDocument3 pagesDentinogenesis Imperfecta A Case ReporthadriaanaNo ratings yet
- Endodontic Considerations in The Elderly: ReviewarticleDocument10 pagesEndodontic Considerations in The Elderly: ReviewarticleYasmine SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Supernumerary Teeth Associated With An Impacted Maxillary Central Incisor: Surgical and Orthodontic ManagementDocument4 pagesMultiple Supernumerary Teeth Associated With An Impacted Maxillary Central Incisor: Surgical and Orthodontic ManagementCalin CristianNo ratings yet
- An Unusual Case of Gemination in Mandibular Second Premolar A Case ReportDocument4 pagesAn Unusual Case of Gemination in Mandibular Second Premolar A Case ReportDanish NasirNo ratings yet
- Jurnal CRSS Prothesa 4 (Sixna Agitha Claresta 20204020100)Document7 pagesJurnal CRSS Prothesa 4 (Sixna Agitha Claresta 20204020100)sixnaagithaNo ratings yet
- Artìculo CareDocument6 pagesArtìculo CareARLET KRISTEL PAMELA REMUZGO ALVARADONo ratings yet
- Literature Review of Amelogenesis Imperfecta With Case ReportDocument6 pagesLiterature Review of Amelogenesis Imperfecta With Case Reportc5t9rejgNo ratings yet
- An Alternative Solution For A Complex Prosthodontic Problem: A Modified Andrews Fixed Dental ProsthesisDocument5 pagesAn Alternative Solution For A Complex Prosthodontic Problem: A Modified Andrews Fixed Dental ProsthesisDragos CiongaruNo ratings yet
- CRID2015 579169 PDFDocument7 pagesCRID2015 579169 PDFNawaf RuwailiNo ratings yet
- OverdentureDocument47 pagesOverdenturemohid sheikhNo ratings yet
- 8 Tooth Ankylosis Andits Orthodontic ImplicationDocument6 pages8 Tooth Ankylosis Andits Orthodontic ImplicationPretty HiaNo ratings yet
- Amelogenesisvaka NYSDJDocument6 pagesAmelogenesisvaka NYSDJRuxandra FitaNo ratings yet
- Dental Twinning in Primary Dentition A Case ReportDocument4 pagesDental Twinning in Primary Dentition A Case ReporthaidirNo ratings yet
- 2015 DU - Consv Managment of MacrodontiaDocument4 pages2015 DU - Consv Managment of MacrodontiaGeorge JoseNo ratings yet
- Indirect Veneer Treatment of Anterior Maxillary Teeth With Enamel HypoplasiaDocument5 pagesIndirect Veneer Treatment of Anterior Maxillary Teeth With Enamel Hypoplasiaamalia rieska mauliddyaNo ratings yet
- Periodontal Changes in Ortho Treatment / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument81 pagesPeriodontal Changes in Ortho Treatment / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNo ratings yet
- Prosthodontic Management of Severely ResorbedDocument2 pagesProsthodontic Management of Severely ResorbedAamir BugtiNo ratings yet
- Dental Anomalies in Orthodontic Patients in Cali, Colombia: ArtículosDocument10 pagesDental Anomalies in Orthodontic Patients in Cali, Colombia: ArtículosJeison ramosNo ratings yet
- Regional Early Development and Eruption of Permanent Teeth Case ReportDocument5 pagesRegional Early Development and Eruption of Permanent Teeth Case ReportAngelia PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Article - 1596794701 2Document8 pagesArticle - 1596794701 2drakashverma7No ratings yet
- Dental Implant Therapy in A Patient With Acromegaly: A Clinical ReportDocument6 pagesDental Implant Therapy in A Patient With Acromegaly: A Clinical ReportAkanksha MahajanNo ratings yet
- Orthodontics and Periodontal Therapy (Vandarshall)Document18 pagesOrthodontics and Periodontal Therapy (Vandarshall)Priya SJNo ratings yet
- Oktawati 2020Document3 pagesOktawati 2020Mariatun ZahronasutionNo ratings yet
- CU-Sil Dentures - A Novel Approach To ConserveDocument27 pagesCU-Sil Dentures - A Novel Approach To Conservereshma shaikNo ratings yet
- Erupted Odontoma: A Case Report: Abst TDocument2 pagesErupted Odontoma: A Case Report: Abst TGonzalo Millán ZardainNo ratings yet
- Gigi Tiruan GasketDocument5 pagesGigi Tiruan GasketGus BasyaNo ratings yet
- Article - 1653239529 2Document5 pagesArticle - 1653239529 2Mega AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Primary Double Tooth With Partial Anodontia of Permanent Dentition - A Case ReportDocument3 pagesPrimary Double Tooth With Partial Anodontia of Permanent Dentition - A Case ReportadriiianaiiioanaNo ratings yet
- Complete Denture Fabrication For Old Denture Wearer in One DayDocument3 pagesComplete Denture Fabrication For Old Denture Wearer in One DayAsma Akram - ProsthodonticsNo ratings yet
- Case Report Gigi Tiruan LengkapDocument3 pagesCase Report Gigi Tiruan LengkapGus BasyaNo ratings yet
- Oral Medicine & Pathology from A-ZFrom EverandOral Medicine & Pathology from A-ZRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- Molecular Characteristics of Young Onset Colorectal Cancer in Vietnamese PatientsDocument8 pagesMolecular Characteristics of Young Onset Colorectal Cancer in Vietnamese PatientsHuỳnh Công BằngNo ratings yet
- Ca Caput Pankreas PDFDocument42 pagesCa Caput Pankreas PDFOvamelia JulioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 39: Nursing Assessment: Gastrointestinal System Test BankDocument6 pagesChapter 39: Nursing Assessment: Gastrointestinal System Test BankNurse UtopiaNo ratings yet
- Colorectal CancerDocument19 pagesColorectal CancerAyra Batore LaguitaoNo ratings yet
- Definition, Risk Factors and Epidemiology of Colorectal CancerDocument3 pagesDefinition, Risk Factors and Epidemiology of Colorectal Cancerdeer muNo ratings yet
- Diz 2Document6 pagesDiz 2Dulce TulaNo ratings yet
- SOFIE FAP Webinar 2023Document42 pagesSOFIE FAP Webinar 2023Shibin JayakrishnanNo ratings yet
- The Pathology of Gastric and Duodenal Polyps: Current ConceptsDocument19 pagesThe Pathology of Gastric and Duodenal Polyps: Current Conceptsaccess pathologicNo ratings yet
- Stomach Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and PreventionDocument15 pagesStomach Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and PreventionJibba kamaraNo ratings yet
- Per Rectal Bleeding CompiledDocument33 pagesPer Rectal Bleeding CompiledRajhmuniran Kandasamy100% (1)
- All CANCERDocument40 pagesAll CANCERKaren Joyce Costales MagtanongNo ratings yet
- GastroenterologyDocument35 pagesGastroenterologyGuilherme Mariante NetoNo ratings yet
- Desmoid Tumor in A Scar From Inguinal Hernia Repair: A Case ReportDocument3 pagesDesmoid Tumor in A Scar From Inguinal Hernia Repair: A Case ReportInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- Gastric CancerDocument31 pagesGastric CancerHarleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Oral Revalida Round 2Document63 pagesOral Revalida Round 2Mercy Anne EcatNo ratings yet
- Colorectal: Understanding The Cancer ProcessDocument14 pagesColorectal: Understanding The Cancer ProcessSeli adalah SayaNo ratings yet
- Gardners SyndromeDocument4 pagesGardners SyndromeTesis ShaioNo ratings yet
- Periampullary TumorsDocument30 pagesPeriampullary TumorsAsif.N.IqbalNo ratings yet
- Gastroentrology LastDocument48 pagesGastroentrology LastAbdallah K. RamadanNo ratings yet
- (Medicine) Surgical Removal of A Portion of The Colon.: Hemicolectomy-P1. AnastomosesDocument5 pages(Medicine) Surgical Removal of A Portion of The Colon.: Hemicolectomy-P1. AnastomosesMuhammad MalikNo ratings yet
- 2020 Molecular Biochemistry Handout PDFDocument12 pages2020 Molecular Biochemistry Handout PDFFlowerNo ratings yet
- Genetoc Aspect of CancerDocument33 pagesGenetoc Aspect of CancermichaelcylNo ratings yet
- Colon CancerDocument25 pagesColon Cancerchori2008No ratings yet
- Colorectal Cancer Prevention and Early DetectionDocument33 pagesColorectal Cancer Prevention and Early DetectionNesyah AyuNo ratings yet
- Colorectal Cancer - Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Protective FactorsDocument31 pagesColorectal Cancer - Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Protective FactorsLuz ClaritaNo ratings yet
- ColonDocument14 pagesColonpaola andrea cabrera erazoNo ratings yet
- Rectal Cancer,: Clinical Practice Guidelines in OncologyDocument28 pagesRectal Cancer,: Clinical Practice Guidelines in OncologyRaíla SoaresNo ratings yet