Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Key Terms
Chapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Key Terms
Uploaded by
JAGDEV PANESARCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- EKG Exam Study Guide PDFDocument31 pagesEKG Exam Study Guide PDFmeb100% (1)
- Chapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Key TermsDocument1 pageChapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Key TermsJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Key TermsDocument1 pageChapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Key TermsJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Key TermsDocument1 pageChapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Key TermsJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels: Key TermsDocument1 pageChapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels: Key TermsJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels: Key TermsDocument1 pageChapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels: Key TermsJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels: Key TermsDocument1 pageChapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels: Key TermsJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels: Key TermsDocument1 pageChapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels: Key TermsJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument40 pagesCardiovascular SystemDouglas Jacques100% (1)
- Heart 2018 - Part IDocument57 pagesHeart 2018 - Part Iwww.hudevaa6No ratings yet
- Chapter 011Document10 pagesChapter 011api-281340024No ratings yet
- Week 9 CVS WorkbookDocument24 pagesWeek 9 CVS Workbooksupriyakunwar2019No ratings yet
- Heart ChambersDocument14 pagesHeart Chambersberniebernie20No ratings yet
- Cardiology Test#2 PrepDocument3 pagesCardiology Test#2 PrepEmily YangNo ratings yet
- Vascular & Lymphatic System - F2023 - DR D CostaDocument47 pagesVascular & Lymphatic System - F2023 - DR D CostaJose PerezNo ratings yet
- Physiology Important QUESTIONDocument30 pagesPhysiology Important QUESTIONcoolguygoodpersonNo ratings yet
- Ch15 AADocument6 pagesCh15 AASammy DeeNo ratings yet
- EXS 208 - Anatomy and Physiology II Cardiovascular System Study Guide General AbilitiesDocument3 pagesEXS 208 - Anatomy and Physiology II Cardiovascular System Study Guide General AbilitiesAnonymous CHVzVzf3uRNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2405844023000944 MainDocument25 pages1 s2.0 S2405844023000944 MainUli Urio-LegoNo ratings yet
- Curriculum CVS BLOCK 3Document25 pagesCurriculum CVS BLOCK 3usman aliNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Study GuideDocument1 pageCardiovascular Study Guideapi-306342919No ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT NO. 17 Middle MediastinumDocument8 pagesASSIGNMENT NO. 17 Middle MediastinumShreyasi DongreNo ratings yet
- DTC1Document10 pagesDTC1camilaaedovNo ratings yet
- PDF JTN 2135 PDFDocument8 pagesPDF JTN 2135 PDFandreiNo ratings yet
- CH 21: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - : GoalsDocument21 pagesCH 21: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - : GoalsgopscharanNo ratings yet
- Simple Rhythm Strip InterpretationDocument41 pagesSimple Rhythm Strip InterpretationChong TengNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document71 pagesLesson 3Angel joyce ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Revision Questions For CVSDocument3 pagesRevision Questions For CVSmichellenkwaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Conduction System - WikipediaDocument32 pagesCardiac Conduction System - Wikipediakirubel demelashNo ratings yet
- Bondgraph Published CardioVascular 1Document4 pagesBondgraph Published CardioVascular 1AhmedNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology-1 PDFDocument39 pagesFundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology-1 PDFNovely MerlynNo ratings yet
- CVSassignement 1 AnatomyDocument12 pagesCVSassignement 1 AnatomyRista SimamNo ratings yet
- L6 7 CVS (2022) PDFDocument51 pagesL6 7 CVS (2022) PDFFung Shan CheungNo ratings yet
- Struktur Dan Fungsi Jantung Dasar: Ken Young Lin Elazer R. Edelman Gary Strichartz Leonard S. LillyDocument8 pagesStruktur Dan Fungsi Jantung Dasar: Ken Young Lin Elazer R. Edelman Gary Strichartz Leonard S. LillyThieFeezaeNo ratings yet
- EcgDocument52 pagesEcgعبد الله الحربيNo ratings yet
- Important Seqs of Physiology by Dr. Mudassar Ali Roomi: ST NDDocument2 pagesImportant Seqs of Physiology by Dr. Mudassar Ali Roomi: ST NDsujit patraNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument72 pagesHeartfyzanfroshie100% (1)
- Study Guide # 4 Human Anatomy: Exam IV On Chapters 21 Through 23Document2 pagesStudy Guide # 4 Human Anatomy: Exam IV On Chapters 21 Through 23dr amjadNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument53 pagesThe Circulatory SystemVera June RañesesNo ratings yet
- 101 709e1714ef6cd74 HeartPracticeQuizDocument2 pages101 709e1714ef6cd74 HeartPracticeQuizbtheresakNo ratings yet
- Anato IMAO BrainDocument220 pagesAnato IMAO BrainVilasecaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 35 Cardiac DisordersDocument93 pagesCHAPTER 35 Cardiac DisordersIfy OhansonNo ratings yet
- Bio Medical ModerateDocument5 pagesBio Medical ModerateRohit BhamuNo ratings yet
- ISL PJM Anatomi Fisiologi Minggu 11 - JantungDocument4 pagesISL PJM Anatomi Fisiologi Minggu 11 - Jantungcuksam27No ratings yet
- CH 21: Cardiovascular System - The HeartDocument21 pagesCH 21: Cardiovascular System - The HeartMadhuri DandamudiNo ratings yet
- Name: No:: Ligamentum ArteriosumDocument4 pagesName: No:: Ligamentum ArteriosumSaid Taysir AbdlJawadNo ratings yet
- 3 Jautajumi CVS ColloquiumDocument1 page3 Jautajumi CVS Colloquiummigas1996No ratings yet
- ANAPHY Lec Session #15 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Document11 pagesANAPHY Lec Session #15 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaNo ratings yet
- BEPAA-Organ Systems A and P - CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM (H.S. 10-12)Document27 pagesBEPAA-Organ Systems A and P - CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM (H.S. 10-12)Marc Imhotep Cray, M.D.No ratings yet
- 1st Term PhysiologyDocument3 pages1st Term PhysiologyAbdul QuaiyumNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Anatomy, Physiology, and Cardiac Cycle: Ayu Puspita SariDocument42 pagesCardiac Anatomy, Physiology, and Cardiac Cycle: Ayu Puspita SariAyu PuspitaNo ratings yet
- Ni Hms 589535Document26 pagesNi Hms 589535Sara TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- ArticleDocument2 pagesArticlejuliana sachicaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Heart Marie BDocument29 pagesChapter 19 Heart Marie BomarNo ratings yet
- CARDIOVASCULARDocument41 pagesCARDIOVASCULARNor Jeannah PolaoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3: Biomechanics - Mech9017Document17 pagesAssignment 3: Biomechanics - Mech9017lucas washingtonNo ratings yet
- Activity 7 The Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesActivity 7 The Cardiovascular SystemEllen Mynelle MabulacNo ratings yet
- Ijireeice 12Document5 pagesIjireeice 12Vinoth NatarajanNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument11 pagesThe Cardiovascular SystemBlack QueenNo ratings yet
- 134708Document1 page134708JAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- 134654Document1 page134654JAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Determ Health Part III Fall 2017Document3 pagesModule 7 Determ Health Part III Fall 2017JAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Grading Rubric Becoming A NurseDocument1 pageGrading Rubric Becoming A NurseJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels: Key TermsDocument1 pageChapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels: Key TermsJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Assessing Health AssignmentDocument2 pagesAssessing Health AssignmentJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Bearing Failures 13Document1 pageBearing Failures 13JAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Becoming A Nurse Assignment W2018Document1 pageBecoming A Nurse Assignment W2018JAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Key TermsDocument1 pageChapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Key TermsJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels: Key TermsDocument1 pageChapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels: Key TermsJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Key TermsDocument1 pageChapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Key TermsJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
Chapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Key Terms
Chapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Key Terms
Uploaded by
JAGDEV PANESAROriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Key Terms
Chapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Key Terms
Uploaded by
JAGDEV PANESARCopyright:
Available Formats
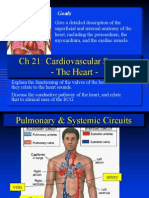
Chapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart
The student should be able to:
1. Describe the external and internal anatomy of the heart.
2. Construct a labelled diagram showing the flow of blood through the heart.
3. Compare and contrast the microscopic structure, metabolism, and contraction of
skeletal and cardiac muscle. (See summary in Tables 9.3 and 18.1)
4. Draw and label an action potential for cardiac pacemaker cells (Figure 18.12) and for
contractile cardiac muscle cells (Figure 18.15). Compare the changes in membrane
potential and membrane permeability that occur during each action potential.
5. Name and locate the components of the intrinsic cardiac conduction system. Describe
the initiation and spread of an impulse from the SA node to the ventricular contractile
cells.
6. Draw and label a normal ECG and explain the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave.
7. Describe the sequence and timing of events (related to cardiac contractions, blood
flow, and valve function) that occur during a normal cardiac cycle.
8. Define cardiac output and identify the intrinsic and extrinsic factors that regulate
stroke volume and heart rate. Contrast the effects of preload, contractility, and
afterload; compare and contrast the effects of the sympathetic and parasympathetic
neurotransmitters; state the role of baroreceptors and the effects of ion imbalances
and thyroxine.
9. Do the following Review Questions at the end of Chapter 18: 1 – 13(a), 14 – 19.
Key Terms:
base, apex, pericardium, fibrous pericardium, serous pericardium, parietal layer,
pericardial cavity, visceral layer (epicardium), myocardium, cardiac skeleton, endocardium,
atrium (pl. atria), ventricles, interatrial septum, interventricular septum, coronary sulcus,
auricles, fossa ovalis, superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, coronary sinus, pulmonary
veins, papillary muscles, pulmonary trunk, right and left pulmonary arteries, aorta,
pulmonary circuit, systemic circuit, coronary circulation, left and right coronary arteries,
cardiac veins, atrioventricular (AV) valves (tricuspid and mitral valves), chordae tendineae,
aortic and pulmonary semilunar (SL) valves
intercalated discs, functional syncytium, automaticity (autorhythmicity),
Page 5 of 25
You might also like
- EKG Exam Study Guide PDFDocument31 pagesEKG Exam Study Guide PDFmeb100% (1)
- Chapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Key TermsDocument1 pageChapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Key TermsJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Key TermsDocument1 pageChapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Key TermsJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Key TermsDocument1 pageChapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Key TermsJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels: Key TermsDocument1 pageChapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels: Key TermsJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels: Key TermsDocument1 pageChapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels: Key TermsJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels: Key TermsDocument1 pageChapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels: Key TermsJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels: Key TermsDocument1 pageChapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels: Key TermsJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument40 pagesCardiovascular SystemDouglas Jacques100% (1)
- Heart 2018 - Part IDocument57 pagesHeart 2018 - Part Iwww.hudevaa6No ratings yet
- Chapter 011Document10 pagesChapter 011api-281340024No ratings yet
- Week 9 CVS WorkbookDocument24 pagesWeek 9 CVS Workbooksupriyakunwar2019No ratings yet
- Heart ChambersDocument14 pagesHeart Chambersberniebernie20No ratings yet
- Cardiology Test#2 PrepDocument3 pagesCardiology Test#2 PrepEmily YangNo ratings yet
- Vascular & Lymphatic System - F2023 - DR D CostaDocument47 pagesVascular & Lymphatic System - F2023 - DR D CostaJose PerezNo ratings yet
- Physiology Important QUESTIONDocument30 pagesPhysiology Important QUESTIONcoolguygoodpersonNo ratings yet
- Ch15 AADocument6 pagesCh15 AASammy DeeNo ratings yet
- EXS 208 - Anatomy and Physiology II Cardiovascular System Study Guide General AbilitiesDocument3 pagesEXS 208 - Anatomy and Physiology II Cardiovascular System Study Guide General AbilitiesAnonymous CHVzVzf3uRNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2405844023000944 MainDocument25 pages1 s2.0 S2405844023000944 MainUli Urio-LegoNo ratings yet
- Curriculum CVS BLOCK 3Document25 pagesCurriculum CVS BLOCK 3usman aliNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Study GuideDocument1 pageCardiovascular Study Guideapi-306342919No ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT NO. 17 Middle MediastinumDocument8 pagesASSIGNMENT NO. 17 Middle MediastinumShreyasi DongreNo ratings yet
- DTC1Document10 pagesDTC1camilaaedovNo ratings yet
- PDF JTN 2135 PDFDocument8 pagesPDF JTN 2135 PDFandreiNo ratings yet
- CH 21: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - : GoalsDocument21 pagesCH 21: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - : GoalsgopscharanNo ratings yet
- Simple Rhythm Strip InterpretationDocument41 pagesSimple Rhythm Strip InterpretationChong TengNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document71 pagesLesson 3Angel joyce ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Revision Questions For CVSDocument3 pagesRevision Questions For CVSmichellenkwaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Conduction System - WikipediaDocument32 pagesCardiac Conduction System - Wikipediakirubel demelashNo ratings yet
- Bondgraph Published CardioVascular 1Document4 pagesBondgraph Published CardioVascular 1AhmedNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology-1 PDFDocument39 pagesFundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology-1 PDFNovely MerlynNo ratings yet
- CVSassignement 1 AnatomyDocument12 pagesCVSassignement 1 AnatomyRista SimamNo ratings yet
- L6 7 CVS (2022) PDFDocument51 pagesL6 7 CVS (2022) PDFFung Shan CheungNo ratings yet
- Struktur Dan Fungsi Jantung Dasar: Ken Young Lin Elazer R. Edelman Gary Strichartz Leonard S. LillyDocument8 pagesStruktur Dan Fungsi Jantung Dasar: Ken Young Lin Elazer R. Edelman Gary Strichartz Leonard S. LillyThieFeezaeNo ratings yet
- EcgDocument52 pagesEcgعبد الله الحربيNo ratings yet
- Important Seqs of Physiology by Dr. Mudassar Ali Roomi: ST NDDocument2 pagesImportant Seqs of Physiology by Dr. Mudassar Ali Roomi: ST NDsujit patraNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument72 pagesHeartfyzanfroshie100% (1)
- Study Guide # 4 Human Anatomy: Exam IV On Chapters 21 Through 23Document2 pagesStudy Guide # 4 Human Anatomy: Exam IV On Chapters 21 Through 23dr amjadNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument53 pagesThe Circulatory SystemVera June RañesesNo ratings yet
- 101 709e1714ef6cd74 HeartPracticeQuizDocument2 pages101 709e1714ef6cd74 HeartPracticeQuizbtheresakNo ratings yet
- Anato IMAO BrainDocument220 pagesAnato IMAO BrainVilasecaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 35 Cardiac DisordersDocument93 pagesCHAPTER 35 Cardiac DisordersIfy OhansonNo ratings yet
- Bio Medical ModerateDocument5 pagesBio Medical ModerateRohit BhamuNo ratings yet
- ISL PJM Anatomi Fisiologi Minggu 11 - JantungDocument4 pagesISL PJM Anatomi Fisiologi Minggu 11 - Jantungcuksam27No ratings yet
- CH 21: Cardiovascular System - The HeartDocument21 pagesCH 21: Cardiovascular System - The HeartMadhuri DandamudiNo ratings yet
- Name: No:: Ligamentum ArteriosumDocument4 pagesName: No:: Ligamentum ArteriosumSaid Taysir AbdlJawadNo ratings yet
- 3 Jautajumi CVS ColloquiumDocument1 page3 Jautajumi CVS Colloquiummigas1996No ratings yet
- ANAPHY Lec Session #15 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Document11 pagesANAPHY Lec Session #15 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaNo ratings yet
- BEPAA-Organ Systems A and P - CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM (H.S. 10-12)Document27 pagesBEPAA-Organ Systems A and P - CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM (H.S. 10-12)Marc Imhotep Cray, M.D.No ratings yet
- 1st Term PhysiologyDocument3 pages1st Term PhysiologyAbdul QuaiyumNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Anatomy, Physiology, and Cardiac Cycle: Ayu Puspita SariDocument42 pagesCardiac Anatomy, Physiology, and Cardiac Cycle: Ayu Puspita SariAyu PuspitaNo ratings yet
- Ni Hms 589535Document26 pagesNi Hms 589535Sara TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- ArticleDocument2 pagesArticlejuliana sachicaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Heart Marie BDocument29 pagesChapter 19 Heart Marie BomarNo ratings yet
- CARDIOVASCULARDocument41 pagesCARDIOVASCULARNor Jeannah PolaoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3: Biomechanics - Mech9017Document17 pagesAssignment 3: Biomechanics - Mech9017lucas washingtonNo ratings yet
- Activity 7 The Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesActivity 7 The Cardiovascular SystemEllen Mynelle MabulacNo ratings yet
- Ijireeice 12Document5 pagesIjireeice 12Vinoth NatarajanNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument11 pagesThe Cardiovascular SystemBlack QueenNo ratings yet
- 134708Document1 page134708JAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- 134654Document1 page134654JAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Determ Health Part III Fall 2017Document3 pagesModule 7 Determ Health Part III Fall 2017JAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Grading Rubric Becoming A NurseDocument1 pageGrading Rubric Becoming A NurseJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels: Key TermsDocument1 pageChapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels: Key TermsJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Assessing Health AssignmentDocument2 pagesAssessing Health AssignmentJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Bearing Failures 13Document1 pageBearing Failures 13JAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Becoming A Nurse Assignment W2018Document1 pageBecoming A Nurse Assignment W2018JAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Key TermsDocument1 pageChapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Key TermsJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels: Key TermsDocument1 pageChapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels: Key TermsJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Key TermsDocument1 pageChapter 18: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Key TermsJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet