Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 viewsBtech - Semi - Erotx - 6 To 8 PDF
Btech - Semi - Erotx - 6 To 8 PDF
Uploaded by
Raj VishwakarmaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- New Format Kiosk BankingDocument2 pagesNew Format Kiosk BankingRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Working Capital Template: Strictly ConfidentialDocument2 pagesWorking Capital Template: Strictly ConfidentialRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 4 AIM: To Study RE Cascaded Transistor Amplifier ApparatusDocument6 pagesExperiment No. 4 AIM: To Study RE Cascaded Transistor Amplifier ApparatusRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Family MembersDocument1 pageFamily MembersRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Declaration by The Applicant For Engagement As CSP (To Be Obtained by CSP Code Generating Office)Document1 pageDeclaration by The Applicant For Engagement As CSP (To Be Obtained by CSP Code Generating Office)Raj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Declaration by The Applicant For Engagement As CSP (To Be Obtained by Link Branch)Document1 pageDeclaration by The Applicant For Engagement As CSP (To Be Obtained by Link Branch)Raj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Human Rights in IndiaDocument13 pagesHuman Rights in IndiaRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
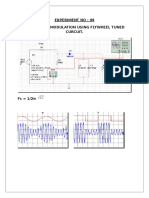
- Experiment No: 09 Am and Ask Modulation Using Flywheel Tuned CurcuitDocument1 pageExperiment No: 09 Am and Ask Modulation Using Flywheel Tuned CurcuitRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Veermata Jijabbai Technological Institute Green RevolutionDocument8 pagesVeermata Jijabbai Technological Institute Green RevolutionRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- PLD NotesDocument10 pagesPLD NotesRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 09 Am and Ask Modulation Using Flywheel Tuned CurcuitDocument1 pageExperiment No: 09 Am and Ask Modulation Using Flywheel Tuned CurcuitRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Btech Semi Erotx 3 To 5Document98 pagesBtech Semi Erotx 3 To 5Raj Vishwakarma0% (1)
Btech - Semi - Erotx - 6 To 8 PDF
Btech - Semi - Erotx - 6 To 8 PDF
Uploaded by
Raj Vishwakarma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views144 pagesOriginal Title
BTECH_SEMI_EROTX_6 TO 8.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views144 pagesBtech - Semi - Erotx - 6 To 8 PDF
Btech - Semi - Erotx - 6 To 8 PDF
Uploaded by
Raj VishwakarmaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
You are on page 1of 144
VEERMATA JIJABAI TECHNOLOGICAL INSTITUTE
[Central Technological Institute, Maharashtea State]
Matunga, Mumbai-400 019
SEMESTER EXAMINATION S6- Api) 291° DATE OF BXAM 5)sheis
SEMESTER & PROGRAM = VI/T.¥.B. Tech TIME 9°30 ~ 2:30
(Eléctronies)
TIME ALLOWED 3 HRS. MARKS 100
COURSE (CourseCode) Image Processing
Instructions 4, All questions carry equal marks.
2. Figures to the right indicate full marks.
Q.1 a. State & prove separability property of DFT
b. Explain structure of human eye. Hence explain image formation in the
human eye
What is segmentation? Explain any one method of segmentation
a2 Perform noise smoothening using mean / average filter for the following 3x3
image
12 2
fo #4
11 2
b. Consider following 4x4 grey scale image with 3-bit quanti
below
wourn
Perform the following operations:
|. Digital negative
il. LSB & MSB bit plan slicing
Ul. Plot histogram
'V.Thresholding with T=4
Q3 a. What do you mean by Unitary transform? Show that 4x4 DFT
transformation matrix represents unitary transform
b. Obtain 2-D DFT of the following image using DIT-FFT algorithm-
Q.4 a. Explain discrete cosine transform. Hence obtain discrete cosine transform
of the following 4x4 image
fae
bite
b, Explain Hotelling transform
Qs Solve any two
Explain Karhunen-Loeve (KL) transform
Explain JPEG compression scheme
Explain sampling and quantization for obtaining digital image
Explain Point, line and edge detection
05
05
10
10
08
20
VEERMATA JIJABA! TECHNOLOGICAL INSTITUTE
[Central Technological institute, Maharashtra State]
Matunga, Mumbai - 400019
End Semester Examination: May-2012 Date of Exam: 18/05/12
‘Semester & Programme: VI Sem, B.Tech. Electronics ‘Max. Marks: 100
Course: Image Processing (Elective) Duration: 3 Hours {0930Hrs to 1230Hrs]
All Questions are Compulsory. Figures to the right indicate full marks.
Q1 Answer the following. 20
a In photo studio, umbrella style frontal reflector is used, how is it related to
basic image formation process mathematically?
b Propose an algorithm based on binary morphology to make a 2D image
appear as 3D image. Clearly state the morphological operations involved
and details of structuring element. (Output image is allowed to contain
grey levels other than 0 & 1)
¢ Discuss the utility of hysteresis thresholding and non-maxima suppression
in Canny detector.
d Discuss the issues to be noted about accumulator cell array during line
fitting using Hough transform
Q2 a What is histogram equalization? Derive the necessary mathematical 10
equation for histogram equalization, Hence perform histogram
equalization on given histogram and plot the same.
ofi1[2]314 75 |6]7
aa | 17 [2st [63 | 335 [2992 |
b Apply KL transform on following vector set X and find the transformed set 10
Y. Obtain the original set using 2 different A values by inverse KL
x=( 3.41" (4,3), 14,41", (4,8]")
In what sense KL transform Is optimal?
Q3 a The basic approach used to approximate a discrete derivative involves 10
taking differences of the form f(x+1,y) —-f(xy). Obtain the filter transfer
function H(u,v) for performing the equivalent process in frequency
domain. Prove that H(u,v) is a highpass filter
b Compare box filter, weighted average filter, Sobel & Laplacian masks for 10
different applications,
Q4 a Find 2D Fourier transform of image A, find Fourier magnitude and phase 10
of image B using properties not otherwise. Comment of results
fr) 20
Tals) ® 513
b Ifa vector x=[xy x2 xe] is given by the linear combination of the orthogonal 5
basis vectors p.u+a.v4r.w, where U=[us Uz Us", V=[vi V2 Vs)! and
w=[W1 Wa Wo)". Write the equations for p, q and r in terms of x, u, v & w.
c Discuss the principle of quadtree based region segmentation. 5
PTO
Q5 a For the given image,
i) Find negative of the image
il) Find histogram,
il) Find threshold for segmentation,
iv) Segment the image with calculated threshold in (ii), redraw the image
after segmentation.
2]2[7
14) 3/2)
8|7 [7
e[5it
3[717
b Discuss valley analysis for unimodal histogram in segmentation. What is
the disadvantage of this method?
¢ Find Fourier transform of signum function x(t)
x(Q) =-1 for tt Uisd=tma
rovims Z a @
Rove
|p} 2500hm
1, Explain the working of FET Voltmeter. 4)
2. Explain working of Duat Slope type DVM. (6)
4. Explain Universal counter frequency mater. (4)
2. Explain principle and working of Successive Aproximation type DVM. (6)
1. Describe the principle and working of Amplifier Rectifier type Frequency (5)
meter,
2. Explain Digital readout oscilloscope. (8)
With neat block diagram explain working of CRO, (40)
4. Explain the working of Sampling Oscilloscope. (5)
2. Explain balanced modulator type phase meter. ©)
Describe how Spot Wheel method is used for frequency and phase (10)
measurement,
1, Explain working of Wein-Bridge Oscillator. (5)
2. Find the value of self capacitance of a coll when the following (5)
measurements are made. At frequency f1= 1MHz, the tuning capacitor
is set at 500pF, When frequency is increased to 2MHz, the tuning
capacitor is tuned at 410pF. Also calculate the value of inductance(l.).
4, Explain the measurement of Characteristic impedance(Zo) of a (5)
transmission line using Q-meter
2. Describe the working of Function generator. Co}
VEERMATA JIJABAI TECHNOLOGICAL INSTITUTE
{Central Technological Institute, Maharashtra State]
Matunga, Mumbai-400 019
SEMESTER EXAMINATION End Semester Test pareor exam 29/04] 2018
SEMESTER & PROGRAM — VI T.¥.B.Tech. (EQ) TIME 8!Z0~12180 pry
TIME ALLOWED SHR MARKS 100
COURSE (CourseCode) = Electronic Measuring Inst ments(EC0310)
Insicsions 1. All questions carry equal mari.
2. Figures tothe night incest fli marks
at ‘Write notes on: (20)
4, Three and half digit digital voltmeter.
2. R2R Ladder type DAC.
3. Digital phase meter.
4. Large impedance measurement using Q-meter.
5. FET Voltmeter.
Q2 a). 4. Two different voltmeters are used to measure the voltage across (8)
resistor Ry in the circuit. Find which voltmeter will read the accurate
values of voltage across Re. Both the meters are used on the 10 V
range. The full scale deflection current of Meter A and Meter B are imA
and 0.05mA respectively.
40Vv Rb=4K
2. Explain AC Voltmeter using rectifiers. (6)
b}. 4. Explain working of Successive ‘Approximation type DVM (8)
2. Describe the principle and working of digital Frequency meter using (5)
flip-flop.
3 a). 1. Explain Universal counter frequency meter. 6)
2. Explain balanced modulator type phase meter 6)
b). With neat block diagram explain the working of Cathode Ray Oscilloscope. (10)
Q4 a). 1. Explain the working of Analog storage oscilloscope. 6)
2. Explain Digital readout oscilloscope. (5)
b). Describe how Lissajous pattom is used for frequency and phase (10)
measurement.
5 a). 4. Measure Characteristic impedance ‘of a transmission line using Q- (5)
meter
2, Compute the value of self capacitance of a coil when the following (5)
measurements are made, Al frequency {1= 2MHz, the tuning capacitor
ig sot at 450pF. When frequency is increased to 5MHz, the tuning
capacitor is tuned at 60 pF. Find inductance(L) also. 7
b). 4. Explain working of Weln-Bridge Oscillator, (8)
2. Explain block diagram of Function generator (6)
VEERMATA JIJABAI TECHNOLOGICAL INSTITUTE
[Central Tochnological Institute, Maharashtra State]
Matunga, Mumbai-400 019
SEMESTER EXAMINATION End Semester Examinations DATE OF EXAM: 07/08/2012
MAY 2012
SEMESTER & PROGRAM SEM-V1, TIME: 9:30AM to 12:30PM
T. YB. Tech (Electronics)
‘TIME ALLOWED 03 Hrs. MARKS: 100
COURSE (Course Code) Electronics Measuring Instruments (EC0310)
{Instructions
41, Figures to the right indicate full marks.
2, Assume suitable data wherever necessary.
3. Support your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary.
Qa Attempt following: [20]
A. State the effect if signal to be observed is applied to ¥ as well as X-section of CRO, [10]
afier selecting XY mode, along with suitable waveforms. Is it possible to view two
waveforms simultaneously on single CRT seréen using only one electron gun? Justify
your opinion.
B. Explain Ratio meter type DVM. [10)
Q. Attempt any two: [20]
Give a significance of Delay Line, Trigger Circuit and Sweep circuit in CRO, [10}
B. How Phase difference is measured using addition method along with FET? [10)
C. Draw and Explain frequency synthesized signal generator. {10}
Qs. Attempt any Two: [20]
A. Explain phase measurement with Flip Flop method state its advantages. (10)
B. Explain True RMS Voltmeter. (10)
C, Compare R-2R ladder and binary weighted DAC. What will be output of 4-bit R-2R [10]
DAC if input is 100 and Vref = -10V
or Attempt any Two: (20)
‘A. Draw and explain Dual slope type DVM. {10}
B. Draw and explain practical FET voltmeter. _ [10)
C. How actual Q value is affected with stray capacitance? Explain it with suitable circuit. {10}
How to calculate %Error in Q value?
Qs. Attempt any Two: P20)
‘A. Explain effect of Ry on actual value of Q, Derive its formula, Comment what should [10]
be the value of Rar and why? Give appropriate circuitry,
B, Write Short Notes on ‘significance of Q-Meter’. cf ty)
C. Give significance of stray capacitance and give 4 mechanism to identify and to (10)
‘measure unknown impedance using parallel conneetion type Q-meter
i Kr
VEERMATA JIJABA! TECHNOLOGICAL INSTITUTE
[Central Technological Institute, Maharashtra State)
Matunga, Mumbai-400 019
SEMESTER & (Sem:-V) & DATE OF EXAM: 28 /\02015
EXAMINIATION
PROGRAM T.Y.B.tech (Electronics) TIME: 4:30 4220pm,
COURSE (Course Code) Electromagnetic Wave Propagation MARKS 100
(EC0301)
Instructions All questions are compulsory & answers should be written in group.
Marks for each question are given on the RHS.
Only important points will be consider
Solve numerical problems upto three decimal points
Q.1 (a) Determine the frequency of radiation, if electric flux detached from dipole (2)
antenna at 15cm also mentions type of transmission line used to feed
antenna.
{b) The finite sheet 0 OY -4 6)S~
MARKS 100
All questions are compulsory.
Marks for each question are given on the RHS.
Assume suitable data where necessary
Derive algorithm of DIF-FFT and hence find DFT of x(n)=f 1,2,1,2,0,2,1,2] 40
Find DFT of x(n) =[1,2,3,4,5,6] using DIT 40
A third order FIR filter has magnitude zero at w=n/3 and unity at w=0. Find the 8
poles and zeros, Obtain transfer function,
A digital filter has frequency specifications as: pass band frequency w,=0.2mand 12
stop band frequency we=0.3n. What are corresponding specifications for passband
and stopband frequencies in analog domain if,
(@ Impulse invariance technique and
(ii) Bilinear transformation technique is used for designing.
Design a linear phase FIR high-pass filter using symmetry condition, for 20
w.=0.2arad/sample and N=7. Use rectangular function, Verify its result by plotting
frequency response for at least 8-points
Design a Butterworth digital IIR HP filter using bilinear transformation by taking 20
1s to satisfy the following specifications:
He") O.7ns wen
HE") |[<0.1; 0s w<0.35x
Draw Direct form-I and II structure of filter, Verify design by sketching frequency
Response considering at least 8-points,
Specifications: passband ripple < 4.436db, Stopband attenuation> 20db
Passband edge frequeney=0.7x rad/sample
Stopband edge frequency=0.35n rad/sample
Gait in passband, Ay=0.6
Gain in stopband, A=0.1
A filter is to be designed with the following desired frequency range: 10
Hae™)=0 -n/4sw sald
=e) 4s |w| Explain different line tracing mechanism in TV scanning.
seenemtt All the Bestt*tetens
[Central Technological institute, Maharashtra Stato]
VEERMATA JIJABAI TECHNOLOGICAL INSTITUTE
Matunga, Mumbai-400 019
SEMESTER EXAMINATION. APRIL.2015 DATE OF EXAM 2-04-2015
SEMESTER & PROGRAM ‘LY. Electonics VISem. TIME 9:30am to I
‘TIME ALLOWED HRS. MARKS 100
COURSE (CowseCode): Communication Systems (ECD312)
insueons 3. Al. questons cy onus marke
2, Pigies tothe righ nical fl marks.
1. (@)_ Explain the log-periodic antenna and its radiation pattern. ©
() An antenna has the uniform flekd pattern given by: U(6) = 4 for 0<@< 7/3, (5)
‘and L(G) = 0 for W/3 <6 <7r, where U(B) is independent of ®. What will be
the directivity of the antenna”?
(©) Define & explain the following terms with respect to antennas: a0
(), Beam Angle.
(i) Effective Aperture.
(Gi) Radiation Pattern
(iv)Radiation Resistance,
(W) Directive Gain of an antenna.
2.2 (2). Differentiate between MTI Radar and Pulse Doppler Radar.
(b) What Is meant by blind speed in MTI Radar? An MT! Radars operating at (6)
40 GHz with a pulse repatition frequency of 1000 pps. Calculate the lowest
three blind speeds.
(Ifa RADAR is designed for operation at 10 GHz with an antenna diameter (8)
‘of 2m, calculate the peak pulse power required to have a maximum range
‘of 1000km with target crass section area 20m. Assume aperture efficiency
as 0.7 and receiver minimum detectable signal to be 10"°W.
(@)_ With suitable block diagram explain FM CW Rader. o
3 (@)_ Explain the following with respect to Satelite System: «10
() Types of Satellte Services.
(i) LEQ and MEO Satelite.
(b) What ate equatorial, polar and inclined orbits. What is Geostationary orbit? (10)
‘Why are such satellites used for worldwide communication?
4 (e) What do you understand by resolution or Kellfactor? How does itaffect the (8)
vertical resolution of a television picture? Show that the vertical resolution
increases with increase in number of scanning lines,
(b) What is meant by interlaced scanning? Why is it done? “
(0) Justify the need for pre and post equalizing pulses. Why itis necessary 10 (5)
Keep their duration equal to the hal-line period?
(a) What is the composite video signals for 2 monochrome TV? Draw aneat (5)
sketch of composite video signal
5. (a) The maximum electric field strength radiated by an antenna is GmVim (8)
measured at 40 km from the antenna. if the antenna radiates a total power
bf 1OOKW, what will be the directivity of the antenna? Ifthe efficiency of the
radiation is 95% then what will be the maximum power gain?
(©) Explain the principle of pattern muttiplication. ®
{o)_ State and explain Keplar’s Laws. ©
(@) A2cm iong Hertzian Dipole antenna radiates 2W of power ata frequency (4)
of 0.6 GHz. Calculate the rms current inthe antenna
@
VEERMATA JIJABAI TECHNOLOGICAL INSTITUTE
{Central Technological Institute, Maharashtra State]
Matunga, Mumbai-400 049
SEMESTER & PROGRAM —_TY. Electronics VI Sem. TIME
TIME ALLOWED. SHR:
Re Exaun | Mayr is aofosfic
SEMESTER EXAMINATION APRIL 2015 DATE OF EXAM 0-201
im
MARKS
COURSE (Course Code) ‘Communication Systems (C0312)
Instructions:
4. All questions cary equal marks.
2. Figutes tothe right indicate ful marks
0.4 (a) What is meant by End Fire Antenna Array? Explain the case for the array (7)
a2
a3
(b)
©
(a)
fa)
)
(c)
(d)
(a)
of point sources having same amplitude and opposite phase.
A Hertzian dipole of length 4/100 is located at the origin and fed with a (5)
current of i(t}= 2 sin10%t A. A point P is located at a distance + from the
dipole as shown in figure. What will be the magnetic field at P?
x
Explain in brief how the directivity and effective aperture of an antenna are (5)
related to each other.
Define the radiation resistance of an antenna. 8
‘An antenna has a radiation resistance of 72 ohms, a loss resistance of 8
‘ohms and a power gain of 12 dB, Determine the antenna efficiency ang its
directivity
What is the Doppler Effect? What are its radar applications? @
What is the peak power of a radar whose average power is 200 W, pulse (7)
width of ‘is and pulse repetition frequency of 1000 Hz? What is the duty
cycle of this radar?
What is the range (in nm) of this ground based air-surveillance radar, if it
has to detect a target with radar cross section of 2 square meters when it
operates at a frequency of 2.9 GHz (S-Band), with rectangular shaped
antenna that is 5 m wide and 2.7 m high, antenna aperture efficiency of
0.6 and minimum detectable signal of 10° W?
‘An MTI Radar is operating at 5 GHz with a pulse repetition frequency of (3)
44000 pps. Calculate the lowest three blind speeds.
Draw the block diagram of a pulsed MT! Radar System and explain its (7)
operation.
Explain the compatibility in TV systems. 6
a4
Qs
(b)
(c)
(a)
(b)
(a)
()
‘What is meant by interlaced scanning? Why is it done?
Draw and explain the composite video signal, giving all the necessary
details in it
With a neat sketch explain the working of a Telemetry, Tracking and
Command system of Satellite. Expiain the role and function of transponders
in Satellite T-V.
Explain the following terms
(i) Antenna Look Angles
(i) Fixed Satellite Services.
{ili) Geostationary Satellites.
(iv) Satellite Multiple Access.
‘A Radar operates at a frequency in the middle of X Band, What magnitude
of Doppler frequency will occur for a target with speed of 290m/s?
Justify the choice of rectangular frame with width to height ratio = 4/3 for
television transmission and reception.
Sketch the geometry of a parabolic antenna with a cassegrain feed and
explain the working.
‘2m long Hertzian dipole antenna radiates 2WV of power at a frequency
‘of 0.6GHz, What will be the rms current in the antenna?
©
(10)
(10)
(0)
4)
©
@
6)
VEERMATA JIJABAI TECHNOLOGICAL INSTITUTE
{Central Technological institute, Maharashtra State]
Matunga, Mumbai ~ 400019
End Semester Examination: May-2012 Date of Exam: 18/05/12
‘Semester & Programme: Vi Sem, B.Tech. Electronics Max. Marks: 100
Course: Computer Organization (Elective) Duration: 3 Hours [0930HFs to 1230Hrs)
All Questions are Compulsory. Figures to the right Indicate full marks.
Q1 Answer the following. (Any Four) 20
a Explain Context Switching in brief
b Discuss utilities of polling and vectored interrupts.
© Paging is useful in implementing Virtual memory.-Justify or contradict
d Compare RISC and CISC systems.
€ Explain different levels of RAID.
Q2 a Explain the general organization of CPU. State the function of following 10
registers.
1) Memory Address Register
2) Memory Data Register
3) Instruction Register
4) Program Counter
5) Stack Pointer
'b What is the role of Hypervisor in Virtual Machines? 5
¢ What is memory interleaving? Discuss various memory interleaving 5
techniques.
Q3 a What is the principle of locality? Explain different types of jocalities. 10
Explain performance characteristics of two level memory with respect to
cost, access time and performance.
b Explain different mapping techniques of cache memory, 10
Suppose physical addresses are 22 bits wide, a cache containing 258K
words of data (not including tag bits), and each cache block contains 4
words. For each of the following cache configurations,
a. Direct mapped
b. 2-way set associative
©. 4-way set associative '
d. Fully associative
Specify how the 32-bit address would be partitioned
Q4 a Define the term “softwired” and “hardwired”. Explain with a diagram and 10
‘example showing separate decoding, encoding function of the hardwired
control
b Explain Bus Arbitration schemes with diagram, : 5
© What is pipelining? Show that K stage pipelined processor has K times 5
speed up compared to non pipelined systems.
Q5 aA CPU which addresses the data through its 6 registers in one of 12 10
different modes is to be designed to support 10 arithmetic, 15 logic, 24
data transfer, 6 branch and & control type instructions. Of these
instructions respectively 20%, 60%, 50%, 50% and 60% are either single
operand or no-operand instruction and the remaining are of double —
operand type, What is the minimum size of the CPU's instruction word?
b Explain Non-Restoring Division Algorithm. Hence perform 13/3, 10
seeses+t" All the Bost***eremene
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- New Format Kiosk BankingDocument2 pagesNew Format Kiosk BankingRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Working Capital Template: Strictly ConfidentialDocument2 pagesWorking Capital Template: Strictly ConfidentialRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 4 AIM: To Study RE Cascaded Transistor Amplifier ApparatusDocument6 pagesExperiment No. 4 AIM: To Study RE Cascaded Transistor Amplifier ApparatusRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Family MembersDocument1 pageFamily MembersRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Declaration by The Applicant For Engagement As CSP (To Be Obtained by CSP Code Generating Office)Document1 pageDeclaration by The Applicant For Engagement As CSP (To Be Obtained by CSP Code Generating Office)Raj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Declaration by The Applicant For Engagement As CSP (To Be Obtained by Link Branch)Document1 pageDeclaration by The Applicant For Engagement As CSP (To Be Obtained by Link Branch)Raj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Human Rights in IndiaDocument13 pagesHuman Rights in IndiaRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 09 Am and Ask Modulation Using Flywheel Tuned CurcuitDocument1 pageExperiment No: 09 Am and Ask Modulation Using Flywheel Tuned CurcuitRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Veermata Jijabbai Technological Institute Green RevolutionDocument8 pagesVeermata Jijabbai Technological Institute Green RevolutionRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- PLD NotesDocument10 pagesPLD NotesRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 09 Am and Ask Modulation Using Flywheel Tuned CurcuitDocument1 pageExperiment No: 09 Am and Ask Modulation Using Flywheel Tuned CurcuitRaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Btech Semi Erotx 3 To 5Document98 pagesBtech Semi Erotx 3 To 5Raj Vishwakarma0% (1)