Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BGP RIB Failure and BGP Synchronization
BGP RIB Failure and BGP Synchronization
Uploaded by
Angel VikonteCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BGP RIB Failure and BGP Synchronization
BGP RIB Failure and BGP Synchronization
Uploaded by
Angel VikonteCopyright:
Available Formats
BGP RIB Failures and BGP Synchronization
BGP RIB-Failures are common when BGP synchronization is enabled. In general BGP RIB-
Failures are BAD, but in the case of BGP Synchronization, they are GOOD. When you check the
reason for the RIB-Failure using the "sh ip bgp rib-failure" command you should see the comment
"Higher admin distance". Then if you check the output of the "sh ip bgp <route prefix/prefix-
length>" you should see the route as "synchronized". This is a GOOD RIB-Failure, because the
route is advertised to the eBGP speakers. See the example outputs below.
R3_AS65100#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 48, local router ID is 3.3.3.3
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* i10.0.0.0 10.10.45.5 0 100 0i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 20.0.0.0/12 192.168.13.1 0 0 65200 i
*> 20.0.0.0 192.168.13.1 0 0 65200 i
*> 20.16.0.0/12 192.168.13.1 0 0 65200 i
*> 20.32.0.0/12 192.168.13.1 0 0 65200 i
*> 20.48.0.0/12 192.168.13.1 0 0 65200 i
*> 30.0.0.0/12 192.168.23.2 0 0 65300 i
*> 30.0.0.0 192.168.23.2 0 0 65300 i
*> 30.16.0.0/12 192.168.23.2 0 0 65300 i
*> 30.32.0.0/12 192.168.23.2 0 0 65300 i
*> 30.48.0.0/12 192.168.23.2 0 0 65300 i
* i40.0.0.0/12 10.10.45.5 0 100 0 65400 i
r>i40.0.0.0 10.10.45.5 0 100 0 65400 i
* i40.16.0.0/12 10.10.45.5 0 100 0 65400 i
* i40.32.0.0/12 10.10.45.5 0 100 0 65400 i
* i40.48.0.0/12 10.10.45.5 0 100 0 65400 i
R3_AS65100#sh ip bgp rib-failure
Network Next Hop RIB-failure RIB-NH Matches
40.0.0.0 10.10.45.5 Higher admin distance n/a
R3_AS65100#sh ip bgp 40.0.0.0/8
BGP routing table entry for 40.0.0.0/8, version 38
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table, RIB-failure(17))
Advertised to update-groups:
2
© BTS Communications, LLC 1 01/02/12
BGP RIB Failures and BGP Synchronization
65400, (received & used)
10.10.45.5 (metric 128) from 10.10.45.5 (5.5.5.5)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, synchronized, best
R3_AS65100#sh ip bgp nei 192.168.13.1 advertised-routes
BGP table version is 48, local router ID is 3.3.3.3
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 20.0.0.0/12 192.168.13.1 0 0 65200 i
*> 20.0.0.0 192.168.13.1 0 0 65200 i
*> 20.16.0.0/12 192.168.13.1 0 0 65200 i
*> 20.32.0.0/12 192.168.13.1 0 0 65200 i
*> 20.48.0.0/12 192.168.13.1 0 0 65200 i
*> 30.0.0.0/12 192.168.23.2 0 0 65300 i
*> 30.0.0.0 192.168.23.2 0 0 65300 i
*> 30.16.0.0/12 192.168.23.2 0 0 65300 i
*> 30.32.0.0/12 192.168.23.2 0 0 65300 i
*> 30.48.0.0/12 192.168.23.2 0 0 65300 i
r>i40.0.0.0 10.10.45.5 0 100 0 65400 i <--- route is still advertised
Total number of prefixes 12
R3_AS65100#
On R5 we have two routes that show up as RIB-Failures. Again, when we look at the outputs of the
"sh ip bgp rib-failure" and "sh ip bgp <prefix/prefix-length> commands we want to look for the
those keywords "Higher admin distance" and "synchronized". See the outputs below.
R5_AS65100#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 86, local router ID is 5.5.5.5
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*i 10.10.34.3 0 100 0i
* i20.0.0.0/12 10.10.34.3 0 100 0 65200 i
r>i20.0.0.0 10.10.34.3 0 100 0 65200 i
© BTS Communications, LLC 2 01/02/12
BGP RIB Failures and BGP Synchronization
* i20.16.0.0/12 10.10.34.3 0 100 0 65200 i
* i20.32.0.0/12 10.10.34.3 0 100 0 65200 i
* i20.48.0.0/12 10.10.34.3 0 100 0 65200 i
* i30.0.0.0/12 10.10.34.3 0 100 0 65300 i
r>i30.0.0.0 10.10.34.3 0 100 0 65300 i
* i30.16.0.0/12 10.10.34.3 0 100 0 65300 i
* i30.32.0.0/12 10.10.34.3 0 100 0 65300 i
* i30.48.0.0/12 10.10.34.3 0 100 0 65300 i
*> 40.0.0.0/12 192.168.56.6 0 0 65400 i
*> 40.0.0.0 192.168.56.6 0 0 65400 i
*> 40.16.0.0/12 192.168.56.6 0 0 65400 i
*> 40.32.0.0/12 192.168.56.6 0 0 65400 i
*> 40.48.0.0/12 192.168.56.6 0 0 65400 i
R5_AS65100#sh ip bgp rib-failure
Network Next Hop RIB-failure RIB-NH Matches
20.0.0.0 10.10.34.3 Higher admin distance n/a
30.0.0.0 10.10.34.3 Higher admin distance n/a
R5_AS65100#sh ip bgp 20.0.0.0/8
BGP routing table entry for 20.0.0.0/8, version 72
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table, RIB-failure(17))
Advertised to update-groups:
2
65200, (received & used)
10.10.34.3 (metric 128) from 10.10.34.3 (3.3.3.3)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, synchronized, best
R5_AS65100#sh ip bgp 30.0.0.0/8
BGP routing table entry for 30.0.0.0/8, version 73
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table, RIB-failure(17))
Advertised to update-groups:
2
65300, (received & used)
10.10.34.3 (metric 128) from 10.10.34.3 (3.3.3.3)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, synchronized, best
R5_AS65100#
But what about the /12 subnet routes we have in the BGP table? Why do these show no RIB-
Failure, yet they are not advertised to our external BGP speaker R6? Because they are "not
synchronized". Remember the BGP Synchronization rule. See the output below.
© BTS Communications, LLC 3 01/02/12
BGP RIB Failures and BGP Synchronization
R5_AS65100#sh ip bgp 20.0.0.0/12
BGP routing table entry for 20.0.0.0/12, version 0
Paths: (1 available, no best path)
Not advertised to any peer
65200, (received & used)
10.10.34.3 (metric 128) from 10.10.34.3 (3.3.3.3)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, not synchronized
R5_AS65100#sh ip bgp 20.16.0.0 /12
BGP routing table entry for 20.16.0.0/12, version 0
Paths: (1 available, no best path)
Not advertised to any peer
65200, (received & used)
10.10.34.3 (metric 128) from 10.10.34.3 (3.3.3.3)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, not synchronized
R5_AS65100#sh ip bgp 20.32.0.0 /12
BGP routing table entry for 20.32.0.0/12, version 0
Paths: (1 available, no best path)
Not advertised to any peer
65200, (received & used)
10.10.34.3 (metric 128) from 10.10.34.3 (3.3.3.3)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, not synchronized
R5_AS65100#sh ip bgp 20.48.0.0 /12
BGP routing table entry for 20.48.0.0/12, version 0
Paths: (1 available, no best path)
Not advertised to any peer
65200, (received & used)
10.10.34.3 (metric 128) from 10.10.34.3 (3.3.3.3)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, not synchronized
R5_AS65100#
Notice in R6s routing table there are no entries for the 20.0.0.0/12, 20.16.0.0/12, 20.32.0.0/12 and
20.48.0.0/12 subnets.
R6_AS65400#sh ip rou
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
© BTS Communications, LLC 4 01/02/12
BGP RIB Failures and BGP Synchronization
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
B 20.0.0.0/8 [20/0] via 192.168.56.5, 00:28:33
C 192.168.56.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/0
40.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 2 masks
C 40.32.0.0/12 is directly connected, Loopback32
C 40.48.0.0/12 is directly connected, Loopback48
C 40.0.0.0/12 is directly connected, Loopback0
S 40.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, Null0
C 40.16.0.0/12 is directly connected, Loopback16
B 10.0.0.0/8 [20/0] via 192.168.56.5, 00:12:12
B 30.0.0.0/8 [20/0] via 192.168.56.5, 00:28:33
R6_AS65400#
So how do we get these to be advertised? We have to "synchronize" our iBGP and IGP. Then we
will see these routes on R6. We need to include the "subnets" keyword on our redistribution
command back on R3. Now the routes show as “synchronized” in the BGP table.
R5_AS65100#sh ip bgp 20.0.0.0/12
BGP routing table entry for 20.0.0.0/12, version 90
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table, RIB-failure(17))
Advertised to update-groups:
2
65200, (received & used)
10.10.34.3 (metric 128) from 10.10.34.3 (3.3.3.3)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, synchronized, best
R5_AS65100#sh ip bgp 20.16.0.0/12
BGP routing table entry for 20.16.0.0/12, version 88
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table, RIB-failure(17))
Advertised to update-groups:
2
65200, (received & used)
10.10.34.3 (metric 128) from 10.10.34.3 (3.3.3.3)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, synchronized, best
© BTS Communications, LLC 5 01/02/12
BGP RIB Failures and BGP Synchronization
R5_AS65100#sh ip bgp 20.32.0.0/12
BGP routing table entry for 20.32.0.0/12, version 97
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table, RIB-failure(17))
Advertised to update-groups:
2
65200, (received & used)
10.10.34.3 (metric 128) from 10.10.34.3 (3.3.3.3)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, synchronized, best
R5_AS65100#sh ip bgp 20.48.0.0/12
BGP routing table entry for 20.48.0.0/12, version 98
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table, RIB-failure(17))
Advertised to update-groups:
2
65200, (received & used)
10.10.34.3 (metric 128) from 10.10.34.3 (3.3.3.3)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, synchronized, best
R5_AS65100#
Now we see the routes in R6s routing table as well.
R6_AS65400#sh ip rou
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
20.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 2 masks
B 20.16.0.0/12 [20/0] via 192.168.56.5, 00:11:23
B 20.0.0.0/12 [20/0] via 192.168.56.5, 00:11:23
B 20.0.0.0/8 [20/0] via 192.168.56.5, 01:08:48
B 20.48.0.0/12 [20/0] via 192.168.56.5, 00:11:23
B 20.32.0.0/12 [20/0] via 192.168.56.5, 00:11:23
C 192.168.56.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/0
40.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 2 masks
C 40.32.0.0/12 is directly connected, Loopback32
C 40.48.0.0/12 is directly connected, Loopback48
© BTS Communications, LLC 6 01/02/12
BGP RIB Failures and BGP Synchronization
C 40.0.0.0/12 is directly connected, Loopback0
S 40.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, Null0
C 40.16.0.0/12 is directly connected, Loopback16
B 10.0.0.0/8 [20/0] via 192.168.56.5, 00:52:28
30.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 2 masks
B 30.16.0.0/12 [20/0] via 192.168.56.5, 00:11:24
B 30.0.0.0/12 [20/0] via 192.168.56.5, 00:11:24
B 30.0.0.0/8 [20/0] via 192.168.56.5, 01:08:48
B 30.48.0.0/12 [20/0] via 192.168.56.5, 00:11:24
B 30.32.0.0/12 [20/0] via 192.168.56.5, 00:11:24
R6_AS65400#
Notice we also get the /12 subnet routes for 30.0.0.0/8 network. In addition, you might have noticed
in the lab we have the same problem on R5 with the 40.0.0.0/8 network. I will let you try your hand
at fixing the 40.0.0.0/12, 40.16.0.0/12, 40.32.0.0/12 and 40.48.0.0/12 subnets received on R5 from
R6. Do you see these routes on R3? How about R1? R2? Go ahead give it try!
© BTS Communications, LLC 7 01/02/12
You might also like
- CL650 Shared Cockpit Quick Start GuideDocument15 pagesCL650 Shared Cockpit Quick Start GuideJoão MazzaropiNo ratings yet
- Dumps CCNP ENARSI 300-410: AnswerDocument22 pagesDumps CCNP ENARSI 300-410: AnsweryabrebenyNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting BGPDocument144 pagesTroubleshooting BGPinnovativekalu100% (3)
- 4.4.3.5 Lab - Configure and Verify EBGPDocument5 pages4.4.3.5 Lab - Configure and Verify EBGPIvan GeiryNo ratings yet
- 4.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Configure IP ACLs To Mitigate Attacks - InstructorDocument20 pages4.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Configure IP ACLs To Mitigate Attacks - InstructorMario SuarezNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkingDocument21 pagesComputer NetworkingShankar Lingam0% (1)
- FEX CheatSheet V1.00Document1 pageFEX CheatSheet V1.00kamarajk22No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Lab 4-1 - Configuring BGP With Default RoutingDocument20 pagesChapter 4 - Lab 4-1 - Configuring BGP With Default RoutingMpho MalumedzhaNo ratings yet
- BGP LabDocument6 pagesBGP LabzizozoroNo ratings yet
- How BGP Routers Use The Multi Exit Discriminator For Best Path SelectionDocument8 pagesHow BGP Routers Use The Multi Exit Discriminator For Best Path SelectionHamid HoteitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, Configuring BGP With Default Routing: TopologyDocument13 pagesChapter 6 Lab 6-1, Configuring BGP With Default Routing: TopologyMeliko ianNo ratings yet
- Ccnpv7 Route Lab7-2 BGP As Path InstructorDocument11 pagesCcnpv7 Route Lab7-2 BGP As Path InstructorAnonymous ua647t0% (2)
- Configuring Advanced BGP: BSCI Module 6Document34 pagesConfiguring Advanced BGP: BSCI Module 6Kenet LascàNo ratings yet
- R4 Part4Document3 pagesR4 Part4Ahmed KamhawyNo ratings yet
- Allowas in BGP Config ExampleDocument5 pagesAllowas in BGP Config ExampleHernán Velarde GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring BGP With Default Routing: TopologyDocument15 pagesChapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring BGP With Default Routing: TopologyGuruparan PrakashNo ratings yet
- MTCINEDocument25 pagesMTCINEoffice engitechNo ratings yet
- BGP Rib FailureDocument4 pagesBGP Rib FailureAbbas KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Lab 7-2, Using The AS - PATH Attribute: Ccnpv7 RouteDocument16 pagesChapter 7 Lab 7-2, Using The AS - PATH Attribute: Ccnpv7 RoutekevinNo ratings yet
- 23-CCNP-Route Using The AS - PATH AttributeDocument8 pages23-CCNP-Route Using The AS - PATH Attributetouaiti2009No ratings yet
- Centro de Soporte de HPE: HP 5800/5830 Switch/6600 Router Series - BGP Configuration: BGP Configuration ExamplesDocument14 pagesCentro de Soporte de HPE: HP 5800/5830 Switch/6600 Router Series - BGP Configuration: BGP Configuration ExamplesJavierLozaLlucoNo ratings yet
- Lab - Configure and Verify EBGPDocument7 pagesLab - Configure and Verify EBGPratacleNo ratings yet
- BGP An IntroDocument47 pagesBGP An Introrvs_rv11No ratings yet
- 25-CCNP-Route BGP Route Reflectors and Route FiltersDocument10 pages25-CCNP-Route BGP Route Reflectors and Route Filterstouaiti2009No ratings yet
- BGP NeighborDocument5 pagesBGP NeighborRamprasanth RajaNo ratings yet
- BGP Route Reflectors and Route FiltersDocument12 pagesBGP Route Reflectors and Route Filtersgarp5791No ratings yet
- How BGP Routers Use The Multi Exit Discriminator For Best Path Selection............................................. 1Document10 pagesHow BGP Routers Use The Multi Exit Discriminator For Best Path Selection............................................. 1Yensid AraveugNo ratings yet
- SOP For Cisco Router TroubleshootDocument13 pagesSOP For Cisco Router TroubleshootHeera Singh100% (1)
- iBGP Lab FinalDocument84 pagesiBGP Lab Finalrashmi mNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using The AS - PATH Attribute: TopologyDocument8 pagesChapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using The AS - PATH Attribute: TopologyMeliko ianNo ratings yet
- Lecture 49 BGPDocument10 pagesLecture 49 BGPkamilbaba2241No ratings yet
- BGP Route Reflectors and Route Filters PDFDocument12 pagesBGP Route Reflectors and Route Filters PDFjaoc121786No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Controlling Routing Updates Topology: Ccnpv7 RouteDocument20 pagesChapter 4 Lab 4-2, Controlling Routing Updates Topology: Ccnpv7 RouteErid RocaNo ratings yet
- BGP TutorialDocument100 pagesBGP Tutorialvnt151085No ratings yet
- HP-MSR Router Troubleshooting: ContentsDocument7 pagesHP-MSR Router Troubleshooting: ContentsHeera SinghNo ratings yet
- Cis185 BSCI Lecture8 BGP Part3Document27 pagesCis185 BSCI Lecture8 BGP Part3Mauro NuñezNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 11 1Document7 pagesLab 9 11 1silindeanNo ratings yet
- Configure EIGRP and Verify Path Control Using Policy Based Routing PBRDocument8 pagesConfigure EIGRP and Verify Path Control Using Policy Based Routing PBRcciersmanNo ratings yet
- BGP - Part 5 (Packet Tracer BGP Configuration Example)Document11 pagesBGP - Part 5 (Packet Tracer BGP Configuration Example)Gerardo - SolorzanoNo ratings yet
- IOS XR Routing Policy LanguageDocument17 pagesIOS XR Routing Policy LanguageSurath KumarNo ratings yet
- Ip RoutingDocument34 pagesIp RoutingericmscNo ratings yet
- Mutual Redistribution Between EIGRP and BGP Configuration ExampleDocument5 pagesMutual Redistribution Between EIGRP and BGP Configuration ExampleiNet MHNNo ratings yet
- 3.5.3.5 Lab - Configure and Verify eBGPDocument5 pages3.5.3.5 Lab - Configure and Verify eBGPDwiki WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Failover Between Two WAN Links - PacketLifeDocument10 pagesDynamic Failover Between Two WAN Links - PacketLifefqtsysNo ratings yet
- CCNA 2 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 2 Exam Answers 2019 - 100% FullDocument21 pagesCCNA 2 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 2 Exam Answers 2019 - 100% FullLuis Blanco BelverNo ratings yet
- Lab 5: DMVPN - BGPDocument9 pagesLab 5: DMVPN - BGPDevdutt VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 11 3Document4 pagesLab 9 11 3silindeanNo ratings yet
- Cisco Press - Ccie - Cisco Bgp-4 Command and Configuration HandbookDocument382 pagesCisco Press - Ccie - Cisco Bgp-4 Command and Configuration Handbookrashokkumar82100% (1)
- BGP Aggregate PDFDocument2 pagesBGP Aggregate PDFFaizan JavedNo ratings yet
- Redistribute BGP To EIGRPDocument5 pagesRedistribute BGP To EIGRPJorge Joaquin Gomez MarrugoNo ratings yet
- 11.1.2 Lab - Implement eBGP For IPv4Document20 pages11.1.2 Lab - Implement eBGP For IPv4Lilifilm OfficialNo ratings yet
- CCNPv7 ROUTE Lab7-1 BGP Config InstructorDocument15 pagesCCNPv7 ROUTE Lab7-1 BGP Config InstructorAnonymous GK9mHwnrNo ratings yet
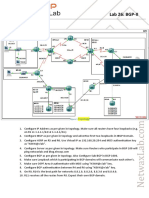
- Lab 26: BGP-II: TopologyDocument13 pagesLab 26: BGP-II: TopologysugapriyaNo ratings yet
- BRKRST-3320 BGP TshootDocument108 pagesBRKRST-3320 BGP TshootKevin KimNo ratings yet
- BGP RACE CONDITION - Networks Baseline - Cisco Engineers LiveDocument10 pagesBGP RACE CONDITION - Networks Baseline - Cisco Engineers LiveMatt CarterNo ratings yet
- Lab - Configure and Verify eBGP: TopologyDocument4 pagesLab - Configure and Verify eBGP: TopologyjohnathanNo ratings yet
- 7.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 Instructions IGDocument5 pages7.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 Instructions IGkarenNo ratings yet
- BGP As Path ManipulationDocument16 pagesBGP As Path ManipulationMilan JovanovicNo ratings yet
- 1 bgp1Document161 pages1 bgp1Nandan BishtNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting BGP by Brad Edgeworth CCIE# 31574Document103 pagesTroubleshooting BGP by Brad Edgeworth CCIE# 31574CK HamNo ratings yet
- 12.1.2 Lab - Implement BGP Path Manipulation - ITExamAnswersDocument22 pages12.1.2 Lab - Implement BGP Path Manipulation - ITExamAnswersiqmalkuaciNo ratings yet
- HP A-Series (H3C) BGP Configuration Basic ExamplesDocument10 pagesHP A-Series (H3C) BGP Configuration Basic ExamplesHugues ADDIHNo ratings yet
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkFrom EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo ratings yet
- Exploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxFrom EverandExploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Intro To SDH and PDHDocument48 pagesIntro To SDH and PDHAshwin RajaratnamNo ratings yet
- Maple Model(s) PLC or ControllerDocument4 pagesMaple Model(s) PLC or ControllerFelipeNo ratings yet
- PL04Document2 pagesPL04Ivanildo CostaNo ratings yet
- My Ccde Cheat SheetsDocument45 pagesMy Ccde Cheat SheetsBalan WvNo ratings yet
- Automatic OMCH Establishment (SRAN9.0 - 01) PDFDocument131 pagesAutomatic OMCH Establishment (SRAN9.0 - 01) PDFriamaNo ratings yet
- VRF On HP SwitchDocument17 pagesVRF On HP SwitchAkhil GuptaNo ratings yet
- 4.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Configure IP ACLs To Mitigate Attacks - InstructorDocument14 pages4.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Configure IP ACLs To Mitigate Attacks - InstructorMiguel JiménezNo ratings yet
- Cisco Router ConfigDocument32 pagesCisco Router ConfigNixbie (Pemula yg serba Kepo)No ratings yet
- ModbusDocument35 pagesModbusyoussef mimmis100% (1)
- Exam JN0-664 Topic 1 Question 29 Discussion - ExamTopicsDocument2 pagesExam JN0-664 Topic 1 Question 29 Discussion - ExamTopicslivia.pandaruNo ratings yet
- X05-Konfigurasi Sistem CCTV LPGDocument4 pagesX05-Konfigurasi Sistem CCTV LPGVeterly DandyNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2022-23 STS3204 SS CH2022235002579 Reference Material I 01-03-2023 L39 NetworkingDocument20 pagesWINSEM2022-23 STS3204 SS CH2022235002579 Reference Material I 01-03-2023 L39 NetworkingRATNESHWAR 20BAI1192No ratings yet
- Configuring The Avaya B179 SIP Conference Phone With Avaya Aura® Communication Manager and Avaya Aura® Session ManagerDocument12 pagesConfiguring The Avaya B179 SIP Conference Phone With Avaya Aura® Communication Manager and Avaya Aura® Session ManagerMohsin HabibNo ratings yet
- GPON TechnologyDocument33 pagesGPON TechnologyRendiPutraFirmansyahNo ratings yet
- CCNAS Final Exam Answer 2Document54 pagesCCNAS Final Exam Answer 2ayion100% (1)
- Route Leaking in MPLS/VPN Networks: Document ID: 47807Document5 pagesRoute Leaking in MPLS/VPN Networks: Document ID: 47807a3172741No ratings yet
- Zenworks 2017 Update 1: User Source and Authentication ReferenceDocument54 pagesZenworks 2017 Update 1: User Source and Authentication ReferenceshockspikesNo ratings yet
- SMS Push Protocol v1.9.6Document9 pagesSMS Push Protocol v1.9.6ZahirKemang100% (1)
- ISCOM2608G Product DescriptionDocument52 pagesISCOM2608G Product DescriptionAdrian OneteNo ratings yet
- PP PDFDocument57 pagesPP PDFDheeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Improved Shortest Path First Algorithm For Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP)Document12 pagesImproved Shortest Path First Algorithm For Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP)eero nahirNo ratings yet
- Ceragon FibeAir IP-20S ETSI Datasheet 7.7.5 Rev A.03Document6 pagesCeragon FibeAir IP-20S ETSI Datasheet 7.7.5 Rev A.03ReinaNeudysNo ratings yet
- CDM 625Document690 pagesCDM 625Pablo BarbozaNo ratings yet
- Dovetail Dumps Latest Phase2Document47 pagesDovetail Dumps Latest Phase2Arun Tez Marata50% (2)
- IP Addressing ExamDocument21 pagesIP Addressing Examrania stellNo ratings yet
- Optimux-108L: Fiber Multiplexer For 4E1 and EthernetDocument4 pagesOptimux-108L: Fiber Multiplexer For 4E1 and EthernetАннаNo ratings yet