Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Loop Diuretic Heart Failure Furosemide Hoffmann-La Roche Bioavailability
Loop Diuretic Heart Failure Furosemide Hoffmann-La Roche Bioavailability
Uploaded by
Nagababu AndrajuCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- S.S. Sastry-Introductory Methods of Numerical Analysis-PHI Learning PVT LTD (2012)Document463 pagesS.S. Sastry-Introductory Methods of Numerical Analysis-PHI Learning PVT LTD (2012)Nagababu Andraju64% (11)
- Sedation of Patients in ICUDocument9 pagesSedation of Patients in ICUAlfrin AntonyNo ratings yet
- Drug CardsDocument10 pagesDrug CardsMaria Robustelli100% (3)
- Barbiturate ToxicityDocument12 pagesBarbiturate ToxicityDayagNo ratings yet
- Butisol Sodium: (Butabarbital Sodium Tablets, USP and Butabarbital Sodium Oral Solution, USP) Tablets & Oral SolutionDocument5 pagesButisol Sodium: (Butabarbital Sodium Tablets, USP and Butabarbital Sodium Oral Solution, USP) Tablets & Oral SolutionBrian HarrisNo ratings yet
- Fu Rose MideDocument4 pagesFu Rose MidelintangpurwatiNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol PKPD Drugs PDFDocument10 pagesParacetamol PKPD Drugs PDFFahmi M FaturahmanNo ratings yet
- FurosemideDocument5 pagesFurosemideRaja Mashood ElahiNo ratings yet
- Seconal Sodium PI 9 08Document2 pagesSeconal Sodium PI 9 08Brian HarrisNo ratings yet
- Chlorpromazine: Pharmacology Indications Contraindications Precautions Adverse Effects Overdose Dosage ResearchDocument36 pagesChlorpromazine: Pharmacology Indications Contraindications Precautions Adverse Effects Overdose Dosage Researchnwaon4realNo ratings yet
- BARBITURATESDocument21 pagesBARBITURATESHamza DossaNo ratings yet
- FurosemDocument10 pagesFurosemMir ElaNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptics PD 501Document27 pagesAntiepileptics PD 501SidraNo ratings yet
- Ulcer Gastrointestinal TractDocument6 pagesUlcer Gastrointestinal TractHossam ArafaNo ratings yet
- PPIDocument2 pagesPPISohail RiazNo ratings yet
- Bupropion 4Document17 pagesBupropion 4Robert MovileanuNo ratings yet
- Obat Antihypertensi: DR Med DR - Widharto PH, SPFK Farmakologi Dan Terapi Fak - Kedokteran UgmDocument38 pagesObat Antihypertensi: DR Med DR - Widharto PH, SPFK Farmakologi Dan Terapi Fak - Kedokteran UgmNi Made Dwiki AndriyaniNo ratings yet
- Non Clinical Overview of BumetanideDocument15 pagesNon Clinical Overview of BumetanideKrishna MahidaNo ratings yet
- Febo G Tab Leaflet Export GADocument2 pagesFebo G Tab Leaflet Export GAAung Myat SweNo ratings yet
- Non-Bz SedativesDocument22 pagesNon-Bz SedativesHamza DossaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The CNS - 2Document41 pagesDrugs Acting On The CNS - 2Daniel OkakaNo ratings yet
- Domperidone ReviewDocument6 pagesDomperidone ReviewKen Cheung100% (1)
- HW3 PharmacologyDocument8 pagesHW3 PharmacologyMICHAEL GABRIEL JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- Panadol Sinus Relief Original Formula Tablets Product InformationDocument8 pagesPanadol Sinus Relief Original Formula Tablets Product Informationredof markzNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Epilepsy: Maha M. Saber, MD, MRCP (UK) Assistant Professor of Pharmacology, UOSDocument40 pagesTreatment of Epilepsy: Maha M. Saber, MD, MRCP (UK) Assistant Professor of Pharmacology, UOSSofiane TighiltNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument116 pagesPharmacologyvargheseNo ratings yet
- Sebuah Model Farmakokinetik Sederhana Berdasarkan Berarti Hotel Times Untuk Memprediksi Paparan Furosemide Setelah Dosis OralDocument16 pagesSebuah Model Farmakokinetik Sederhana Berdasarkan Berarti Hotel Times Untuk Memprediksi Paparan Furosemide Setelah Dosis OralnurulNo ratings yet
- Barbiturate PoisoningDocument17 pagesBarbiturate PoisoningRaymond ManjengwaNo ratings yet
- 2004 4050B1 14 Fosinopril Label PedsDocument23 pages2004 4050B1 14 Fosinopril Label PedsМаргарет ВејдNo ratings yet
- Dosages of DiureticsDocument4 pagesDosages of DiureticsShuhada HamidNo ratings yet
- AnesthesiaDocument12 pagesAnesthesiaعلي الاسديNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Healing Drugs 140420Document50 pagesPeptic Ulcer Healing Drugs 140420Tehreem NadeemNo ratings yet
- Ziac (Bisoprolol+HCT)Document21 pagesZiac (Bisoprolol+HCT)San-Clin-Eq LaboratoryNo ratings yet
- VentolinDocument4 pagesVentolinArlan AbraganNo ratings yet
- Sedatives and Hypnotics-2Document10 pagesSedatives and Hypnotics-2FRANCA JAMGBADINo ratings yet
- Fluoxetine HCLDocument2 pagesFluoxetine HCLDianie VillapaniaNo ratings yet
- Buprenorphine Management: DR Brenda Mogaka Ngara MAT Pharmacy LeadDocument25 pagesBuprenorphine Management: DR Brenda Mogaka Ngara MAT Pharmacy LeadJared KeburiNo ratings yet
- Uspi LomotilDocument8 pagesUspi LomotilhaiduvnNo ratings yet
- Desirable Properties of PSA Pharmacologic AgentsDocument42 pagesDesirable Properties of PSA Pharmacologic AgentsMarjan HusniNo ratings yet
- AmbroxolDocument4 pagesAmbroxoldiannuryandaNo ratings yet
- Anxiolytic & Hypnotics Part 2Document24 pagesAnxiolytic & Hypnotics Part 2Sarah ArkanNo ratings yet
- Furosemide Summary Report Committee Veterinary Medicinal Products enDocument9 pagesFurosemide Summary Report Committee Veterinary Medicinal Products enLucijaRomićNo ratings yet
- Dias2009 Article PantoprazoleDocument10 pagesDias2009 Article PantoprazoleTan JayNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System DepressantsDocument11 pagesCentral Nervous System Depressantsاسامه عمر عثمانNo ratings yet
- BromazepamDocument6 pagesBromazepamMariusNeicuNo ratings yet
- Drug - Drug Int2Document35 pagesDrug - Drug Int2alishba100% (2)
- Week 3 (Ncma216)Document3 pagesWeek 3 (Ncma216)Rhaiza RebustilloNo ratings yet
- Furosemide in Infant and XhildrenDocument5 pagesFurosemide in Infant and XhildrenAbdi KebedeNo ratings yet
- Dilemmas in The Dosing of Heart Failure Drugs Titrating DiureticsDocument5 pagesDilemmas in The Dosing of Heart Failure Drugs Titrating DiureticsRuslan RidcodubskiiNo ratings yet
- Barbiturate PoisoningDocument9 pagesBarbiturate PoisoningSourabh ManhareNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyWayne Ivan DugayNo ratings yet
- DR - Husam Git 2023Document19 pagesDR - Husam Git 2023ManWol JangNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On GITDocument20 pagesDrugs Acting On GITDaniel AtiehNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic AntagonistsDocument23 pagesAdrenergic AntagonistsMirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- Mata Drug Study FurosemideDocument14 pagesMata Drug Study FurosemideNicole Keesha MataNo ratings yet
- Drugs Coronary Ward IIDocument7 pagesDrugs Coronary Ward IITimothy Joy VercelesNo ratings yet
- Proses F.kinetik-F.dinamik Ppds 2017Document33 pagesProses F.kinetik-F.dinamik Ppds 2017intan purnamaNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- How to Treat Your MTHFR Gene Mutations the Right Way - the Genetic Advantage: The genetic advantage, #1From EverandHow to Treat Your MTHFR Gene Mutations the Right Way - the Genetic Advantage: The genetic advantage, #1No ratings yet
- Explain Different Types of Shear Failures and Flexural in Prestressed Concrete Beams? 6.a)Document1 pageExplain Different Types of Shear Failures and Flexural in Prestressed Concrete Beams? 6.a)Nagababu AndrajuNo ratings yet
- Explain Different Types of Shear Failures and Flexural in Prestressed Concrete Beams? 6.a)Document1 pageExplain Different Types of Shear Failures and Flexural in Prestressed Concrete Beams? 6.a)Nagababu AndrajuNo ratings yet
- Gracilaria: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument3 pagesGracilaria: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchNagababu AndrajuNo ratings yet
- Explain Different Types of Shear Failures and Flexural in Prestressed Concrete Beams? 6.a)Document1 pageExplain Different Types of Shear Failures and Flexural in Prestressed Concrete Beams? 6.a)Nagababu AndrajuNo ratings yet
- Explain Different Types of Shear Failures and Flexural in Prestressed Concrete Beams? 6.a)Document1 pageExplain Different Types of Shear Failures and Flexural in Prestressed Concrete Beams? 6.a)Nagababu AndrajuNo ratings yet
- 5a) Write Short Notes On Layered Soils. 5b) Write Short Notes On Classical Theories of Earth PressuressDocument1 page5a) Write Short Notes On Layered Soils. 5b) Write Short Notes On Classical Theories of Earth PressuressNagababu AndrajuNo ratings yet
- 5 .Using Separation of VariablesDocument1 page5 .Using Separation of VariablesNagababu AndrajuNo ratings yet
- Sub: Earth Retaining Structures M-Tech Ii Sem Unit-1Document1 pageSub: Earth Retaining Structures M-Tech Ii Sem Unit-1Nagababu AndrajuNo ratings yet
- Advanced Control TheoryDocument1 pageAdvanced Control TheoryNagababu AndrajuNo ratings yet
- by The Method of Least Squares Fit A Third Degree Polynomial For The Following DataDocument1 pageby The Method of Least Squares Fit A Third Degree Polynomial For The Following DataNagababu AndrajuNo ratings yet
- by The Method of Least Squares Fit A Third Degree Polynomial For The Following DataDocument1 pageby The Method of Least Squares Fit A Third Degree Polynomial For The Following DataNagababu AndrajuNo ratings yet
- TESTDocument1 pageTESTNagababu AndrajuNo ratings yet
Loop Diuretic Heart Failure Furosemide Hoffmann-La Roche Bioavailability
Loop Diuretic Heart Failure Furosemide Hoffmann-La Roche Bioavailability
Uploaded by
Nagababu AndrajuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Loop Diuretic Heart Failure Furosemide Hoffmann-La Roche Bioavailability
Loop Diuretic Heart Failure Furosemide Hoffmann-La Roche Bioavailability
Uploaded by
Nagababu AndrajuCopyright:
Available Formats
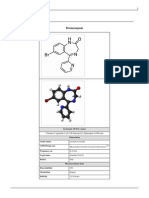
Bumetanide (trade names Bumex or Burinex) is a loop diuretic of the sulfamyl category, most
often used to treat heart failure. It is often used in people in whom high doses of furosemide or
other diuretics are ineffective. It is marketed by Hoffmann-La Roche. The main difference
between bumetanide and furosemide is in their bioavailability and potency. About 60% of
furosemide is absorbed in the intestine, and there are substantial inter- and intraindividual
differences in bioavailability (range 10-90%). About 80% of bumetanide is absorbed, and its
absorption does not change when it is taken with food. It is said to be a more predictable diuretic,
meaning that the predictable absorption is reflected in a more predictable effect.[1]
Bumetanide is 40 times more potent than furosemide for patients with normal renal function.[1]
In the brain, bumetanide blocks the NKCC1 cation-chloride co-transporter, and thus decreases
internal chloride concentration in neurons. In turn, this concentration change makes the action
of GABA more hyperpolarizing, which may be useful for treatment of neonatal seizures, which
quite often are not responsive to traditional GABA-targeted treatment, such as barbiturates.
Bumetanide is therefore currently[when?] under evaluation as a prospective antiepileptic drug.[2]
You might also like
- S.S. Sastry-Introductory Methods of Numerical Analysis-PHI Learning PVT LTD (2012)Document463 pagesS.S. Sastry-Introductory Methods of Numerical Analysis-PHI Learning PVT LTD (2012)Nagababu Andraju64% (11)
- Sedation of Patients in ICUDocument9 pagesSedation of Patients in ICUAlfrin AntonyNo ratings yet
- Drug CardsDocument10 pagesDrug CardsMaria Robustelli100% (3)
- Barbiturate ToxicityDocument12 pagesBarbiturate ToxicityDayagNo ratings yet
- Butisol Sodium: (Butabarbital Sodium Tablets, USP and Butabarbital Sodium Oral Solution, USP) Tablets & Oral SolutionDocument5 pagesButisol Sodium: (Butabarbital Sodium Tablets, USP and Butabarbital Sodium Oral Solution, USP) Tablets & Oral SolutionBrian HarrisNo ratings yet
- Fu Rose MideDocument4 pagesFu Rose MidelintangpurwatiNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol PKPD Drugs PDFDocument10 pagesParacetamol PKPD Drugs PDFFahmi M FaturahmanNo ratings yet
- FurosemideDocument5 pagesFurosemideRaja Mashood ElahiNo ratings yet
- Seconal Sodium PI 9 08Document2 pagesSeconal Sodium PI 9 08Brian HarrisNo ratings yet
- Chlorpromazine: Pharmacology Indications Contraindications Precautions Adverse Effects Overdose Dosage ResearchDocument36 pagesChlorpromazine: Pharmacology Indications Contraindications Precautions Adverse Effects Overdose Dosage Researchnwaon4realNo ratings yet
- BARBITURATESDocument21 pagesBARBITURATESHamza DossaNo ratings yet
- FurosemDocument10 pagesFurosemMir ElaNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptics PD 501Document27 pagesAntiepileptics PD 501SidraNo ratings yet
- Ulcer Gastrointestinal TractDocument6 pagesUlcer Gastrointestinal TractHossam ArafaNo ratings yet
- PPIDocument2 pagesPPISohail RiazNo ratings yet
- Bupropion 4Document17 pagesBupropion 4Robert MovileanuNo ratings yet
- Obat Antihypertensi: DR Med DR - Widharto PH, SPFK Farmakologi Dan Terapi Fak - Kedokteran UgmDocument38 pagesObat Antihypertensi: DR Med DR - Widharto PH, SPFK Farmakologi Dan Terapi Fak - Kedokteran UgmNi Made Dwiki AndriyaniNo ratings yet
- Non Clinical Overview of BumetanideDocument15 pagesNon Clinical Overview of BumetanideKrishna MahidaNo ratings yet
- Febo G Tab Leaflet Export GADocument2 pagesFebo G Tab Leaflet Export GAAung Myat SweNo ratings yet
- Non-Bz SedativesDocument22 pagesNon-Bz SedativesHamza DossaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The CNS - 2Document41 pagesDrugs Acting On The CNS - 2Daniel OkakaNo ratings yet
- Domperidone ReviewDocument6 pagesDomperidone ReviewKen Cheung100% (1)
- HW3 PharmacologyDocument8 pagesHW3 PharmacologyMICHAEL GABRIEL JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- Panadol Sinus Relief Original Formula Tablets Product InformationDocument8 pagesPanadol Sinus Relief Original Formula Tablets Product Informationredof markzNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Epilepsy: Maha M. Saber, MD, MRCP (UK) Assistant Professor of Pharmacology, UOSDocument40 pagesTreatment of Epilepsy: Maha M. Saber, MD, MRCP (UK) Assistant Professor of Pharmacology, UOSSofiane TighiltNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument116 pagesPharmacologyvargheseNo ratings yet
- Sebuah Model Farmakokinetik Sederhana Berdasarkan Berarti Hotel Times Untuk Memprediksi Paparan Furosemide Setelah Dosis OralDocument16 pagesSebuah Model Farmakokinetik Sederhana Berdasarkan Berarti Hotel Times Untuk Memprediksi Paparan Furosemide Setelah Dosis OralnurulNo ratings yet
- Barbiturate PoisoningDocument17 pagesBarbiturate PoisoningRaymond ManjengwaNo ratings yet
- 2004 4050B1 14 Fosinopril Label PedsDocument23 pages2004 4050B1 14 Fosinopril Label PedsМаргарет ВејдNo ratings yet
- Dosages of DiureticsDocument4 pagesDosages of DiureticsShuhada HamidNo ratings yet
- AnesthesiaDocument12 pagesAnesthesiaعلي الاسديNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Healing Drugs 140420Document50 pagesPeptic Ulcer Healing Drugs 140420Tehreem NadeemNo ratings yet
- Ziac (Bisoprolol+HCT)Document21 pagesZiac (Bisoprolol+HCT)San-Clin-Eq LaboratoryNo ratings yet
- VentolinDocument4 pagesVentolinArlan AbraganNo ratings yet
- Sedatives and Hypnotics-2Document10 pagesSedatives and Hypnotics-2FRANCA JAMGBADINo ratings yet
- Fluoxetine HCLDocument2 pagesFluoxetine HCLDianie VillapaniaNo ratings yet
- Buprenorphine Management: DR Brenda Mogaka Ngara MAT Pharmacy LeadDocument25 pagesBuprenorphine Management: DR Brenda Mogaka Ngara MAT Pharmacy LeadJared KeburiNo ratings yet
- Uspi LomotilDocument8 pagesUspi LomotilhaiduvnNo ratings yet
- Desirable Properties of PSA Pharmacologic AgentsDocument42 pagesDesirable Properties of PSA Pharmacologic AgentsMarjan HusniNo ratings yet
- AmbroxolDocument4 pagesAmbroxoldiannuryandaNo ratings yet
- Anxiolytic & Hypnotics Part 2Document24 pagesAnxiolytic & Hypnotics Part 2Sarah ArkanNo ratings yet
- Furosemide Summary Report Committee Veterinary Medicinal Products enDocument9 pagesFurosemide Summary Report Committee Veterinary Medicinal Products enLucijaRomićNo ratings yet
- Dias2009 Article PantoprazoleDocument10 pagesDias2009 Article PantoprazoleTan JayNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System DepressantsDocument11 pagesCentral Nervous System Depressantsاسامه عمر عثمانNo ratings yet
- BromazepamDocument6 pagesBromazepamMariusNeicuNo ratings yet
- Drug - Drug Int2Document35 pagesDrug - Drug Int2alishba100% (2)
- Week 3 (Ncma216)Document3 pagesWeek 3 (Ncma216)Rhaiza RebustilloNo ratings yet
- Furosemide in Infant and XhildrenDocument5 pagesFurosemide in Infant and XhildrenAbdi KebedeNo ratings yet
- Dilemmas in The Dosing of Heart Failure Drugs Titrating DiureticsDocument5 pagesDilemmas in The Dosing of Heart Failure Drugs Titrating DiureticsRuslan RidcodubskiiNo ratings yet
- Barbiturate PoisoningDocument9 pagesBarbiturate PoisoningSourabh ManhareNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyWayne Ivan DugayNo ratings yet
- DR - Husam Git 2023Document19 pagesDR - Husam Git 2023ManWol JangNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On GITDocument20 pagesDrugs Acting On GITDaniel AtiehNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic AntagonistsDocument23 pagesAdrenergic AntagonistsMirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- Mata Drug Study FurosemideDocument14 pagesMata Drug Study FurosemideNicole Keesha MataNo ratings yet
- Drugs Coronary Ward IIDocument7 pagesDrugs Coronary Ward IITimothy Joy VercelesNo ratings yet
- Proses F.kinetik-F.dinamik Ppds 2017Document33 pagesProses F.kinetik-F.dinamik Ppds 2017intan purnamaNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- How to Treat Your MTHFR Gene Mutations the Right Way - the Genetic Advantage: The genetic advantage, #1From EverandHow to Treat Your MTHFR Gene Mutations the Right Way - the Genetic Advantage: The genetic advantage, #1No ratings yet
- Explain Different Types of Shear Failures and Flexural in Prestressed Concrete Beams? 6.a)Document1 pageExplain Different Types of Shear Failures and Flexural in Prestressed Concrete Beams? 6.a)Nagababu AndrajuNo ratings yet
- Explain Different Types of Shear Failures and Flexural in Prestressed Concrete Beams? 6.a)Document1 pageExplain Different Types of Shear Failures and Flexural in Prestressed Concrete Beams? 6.a)Nagababu AndrajuNo ratings yet
- Gracilaria: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument3 pagesGracilaria: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchNagababu AndrajuNo ratings yet
- Explain Different Types of Shear Failures and Flexural in Prestressed Concrete Beams? 6.a)Document1 pageExplain Different Types of Shear Failures and Flexural in Prestressed Concrete Beams? 6.a)Nagababu AndrajuNo ratings yet
- Explain Different Types of Shear Failures and Flexural in Prestressed Concrete Beams? 6.a)Document1 pageExplain Different Types of Shear Failures and Flexural in Prestressed Concrete Beams? 6.a)Nagababu AndrajuNo ratings yet
- 5a) Write Short Notes On Layered Soils. 5b) Write Short Notes On Classical Theories of Earth PressuressDocument1 page5a) Write Short Notes On Layered Soils. 5b) Write Short Notes On Classical Theories of Earth PressuressNagababu AndrajuNo ratings yet
- 5 .Using Separation of VariablesDocument1 page5 .Using Separation of VariablesNagababu AndrajuNo ratings yet
- Sub: Earth Retaining Structures M-Tech Ii Sem Unit-1Document1 pageSub: Earth Retaining Structures M-Tech Ii Sem Unit-1Nagababu AndrajuNo ratings yet
- Advanced Control TheoryDocument1 pageAdvanced Control TheoryNagababu AndrajuNo ratings yet
- by The Method of Least Squares Fit A Third Degree Polynomial For The Following DataDocument1 pageby The Method of Least Squares Fit A Third Degree Polynomial For The Following DataNagababu AndrajuNo ratings yet
- by The Method of Least Squares Fit A Third Degree Polynomial For The Following DataDocument1 pageby The Method of Least Squares Fit A Third Degree Polynomial For The Following DataNagababu AndrajuNo ratings yet
- TESTDocument1 pageTESTNagababu AndrajuNo ratings yet