Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bacteria: Tuesday, January 23, 2018 2:04 PM
Bacteria: Tuesday, January 23, 2018 2:04 PM
Uploaded by
chip_darrisCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Cefazolin Ancef Drug CardDocument2 pagesCefazolin Ancef Drug CardLisaNo ratings yet
- Bacterial ID FlowchartDocument6 pagesBacterial ID FlowchartTom Tsou50% (2)
- PassiveDocument2 pagesPassiveTop Secret0% (1)
- HEMATOLOGY NOTESDocument31 pagesHEMATOLOGY NOTESALIZA BAKILNo ratings yet
- Protozoans - Amebae: Medically Important ParasitesDocument10 pagesProtozoans - Amebae: Medically Important ParasitesBrylle LumberioNo ratings yet
- 2A-Sarigumba - 10 MEDICALLY IMPORTANT BACTERIA PDFDocument18 pages2A-Sarigumba - 10 MEDICALLY IMPORTANT BACTERIA PDFSean SarigumbaNo ratings yet
- Western Blot Troubleshooting Smeared Bands Sino BiologicalDocument1 pageWestern Blot Troubleshooting Smeared Bands Sino Biologicalอิษฎาภร ภูมิชัยชนะNo ratings yet
- Exam Review05 Part2Document6 pagesExam Review05 Part2api-26602387No ratings yet
- BioPIN Sternheimer-Malbin-Concentrate - Bioanalytic (En)Document2 pagesBioPIN Sternheimer-Malbin-Concentrate - Bioanalytic (En)Yan PetrovNo ratings yet
- Enterobacteriaceae 2Document11 pagesEnterobacteriaceae 2odhiambo samwelNo ratings yet
- Acute Thyroid Thyroiditis Sub-Acute / Granulomatous / de Quevains's Thyroiditis Chronic / Hashimoto's Thyroiditis Fibrosing / Reidel's ThyroiditisDocument2 pagesAcute Thyroid Thyroiditis Sub-Acute / Granulomatous / de Quevains's Thyroiditis Chronic / Hashimoto's Thyroiditis Fibrosing / Reidel's ThyroiditisZuhra JabeenNo ratings yet
- BIO204 - Chapter 2Document1 pageBIO204 - Chapter 2Holin DolanNo ratings yet
- CT CellsDocument1 pageCT CellsTarlan SharifiNo ratings yet
- TB MeningitisDocument46 pagesTB MeningitishenniwtNo ratings yet
- DDX of Hematological DisordersDocument1 pageDDX of Hematological DisordersOlivia LimNo ratings yet
- PARASITOLOGY P1 Table SummaryDocument4 pagesPARASITOLOGY P1 Table Summaryiananicole.b30No ratings yet
- Final Notebook BioDocument16 pagesFinal Notebook Biolorina p del rosarioNo ratings yet
- (MT 57) PARA - Pathogenic ProtozoaDocument5 pages(MT 57) PARA - Pathogenic ProtozoaLiana JeonNo ratings yet
- Differential CountDocument2 pagesDifferential CountMARY KAYE YVONNE OTILLANo ratings yet
- Special StainsDocument27 pagesSpecial Stainsambadepravin100% (1)
- CYTOGEN: Chapter 3 Meiosis, Development, and AgingDocument6 pagesCYTOGEN: Chapter 3 Meiosis, Development, and AgingpangetkoNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasmic InheritanceDocument5 pagesCytoplasmic InheritancesumanparajuliNo ratings yet
- Lange Smart Charts: Pharmacology, 2e Oncologic DrugsDocument3 pagesLange Smart Charts: Pharmacology, 2e Oncologic DrugsFlorence MarzanNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom Digital NotesDocument20 pagesAnimal Kingdom Digital NotesKshreeNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Immersion BasicsDocument18 pagesLaboratory Immersion BasicsAprian AcunaNo ratings yet
- Igcse Biology: Topic 1: Characteristics of Living OrganismsDocument63 pagesIgcse Biology: Topic 1: Characteristics of Living OrganismsIndia IB 2020No ratings yet
- MicrosDocument6 pagesMicrosJheshari VinaNo ratings yet
- AmoebaDocument5 pagesAmoebaMhizzy ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Cell Biology and OrganisationDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Cell Biology and OrganisationRAYMOND CHIENG CHING BING Moe100% (1)
- G1 Checkpoint - Monitors Cell Size and Integrity G2 Checkpoint - DNA Damage CheckpointDocument3 pagesG1 Checkpoint - Monitors Cell Size and Integrity G2 Checkpoint - DNA Damage CheckpointErica GarciaNo ratings yet
- Diversity AnimalsDocument20 pagesDiversity AnimalsnithinjothimuruganNo ratings yet
- C24 CellsDocument13 pagesC24 Cellsjunaidfatimah765haNo ratings yet
- Case Studies On Major Concepts: MetabolismDocument37 pagesCase Studies On Major Concepts: MetabolismJek Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-01-19 at 5.10.09 PMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2024-01-19 at 5.10.09 PMdhruvrana1133No ratings yet
- ANAPHY LEC CVS BloodDocument6 pagesANAPHY LEC CVS BloodMarjorie ViescaNo ratings yet
- Arasitology: Intestinal AmoebaeDocument5 pagesArasitology: Intestinal AmoebaeMa. Mil Adrianne PamaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Diagnostic Parasitology and Specimen CollectionDocument3 pagesOverview of Diagnostic Parasitology and Specimen CollectionBrylle LumberioNo ratings yet
- History Taking in HematologyDocument1 pageHistory Taking in HematologyNarmin Abubaker AliNo ratings yet
- 13 - ELGAR - Activity Sheet 2Document1 page13 - ELGAR - Activity Sheet 2Eul MojoNo ratings yet
- Ch. 21: Vascular Plants Without Seeds: ConceptsDocument4 pagesCh. 21: Vascular Plants Without Seeds: ConceptsNexNo ratings yet
- Cytological TechniquesDocument4 pagesCytological TechniquesJamie100% (2)
- Hematopoietic SystemDocument47 pagesHematopoietic SystemAbbi Yanto ArtNo ratings yet
- Cell Morphologies: Summary of Cell Structures Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Bacteria ArchaeaDocument1 pageCell Morphologies: Summary of Cell Structures Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Bacteria ArchaeaAna GrimaldoNo ratings yet
- B3 Human ReproductionDocument1 pageB3 Human ReproductionSatyam AnandNo ratings yet
- Aspergillus Species PPT 2Document1 pageAspergillus Species PPT 2ajisozymeNo ratings yet
- 6.1 MicrobiologyDocument32 pages6.1 MicrobiologyYsabelle BautistaNo ratings yet
- Parasites CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesParasites CharacteristicsNiezel EncalladoNo ratings yet
- PARA LAB - 2 Intestinal Amoeba111Document24 pagesPARA LAB - 2 Intestinal Amoeba111Brigit DueñasNo ratings yet
- Urine AnalysisDocument1 pageUrine Analysisعبدالرحمن ابراهيمNo ratings yet
- Aubf Lab MidtermDocument8 pagesAubf Lab MidtermNiezel EncalladoNo ratings yet
- AntiprotozoalDocument2 pagesAntiprotozoalxelo_27No ratings yet
- Haematoxylin and Eosin (H+E) - Aldehyde-Fuchsin - Van Geison's Picro Fuchsin Technique - Masson's Trichrome - Nuclei - Blue/backDocument9 pagesHaematoxylin and Eosin (H+E) - Aldehyde-Fuchsin - Van Geison's Picro Fuchsin Technique - Masson's Trichrome - Nuclei - Blue/backsilentscreamsofloveNo ratings yet
- Components of BloodDocument1 pageComponents of BloodEmson ChipfumbuNo ratings yet
- Parasitology (Lect #6) TransDocument3 pagesParasitology (Lect #6) TransAndrea Galang CruzNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - 23-07-2021 BBDocument7 pagesLecture 2 - 23-07-2021 BBpaulinemahlangu88No ratings yet
- Kista Bartholine NewDocument12 pagesKista Bartholine NewZulfy AzharyNo ratings yet
- PATHOLOGY MAIN HANDOUT - ExtractDocument15 pagesPATHOLOGY MAIN HANDOUT - ExtractAshley Chloé UyNo ratings yet
- Blood Components Where Do They Come From?: Introduction To HaematologyDocument11 pagesBlood Components Where Do They Come From?: Introduction To Haematologydorsa koraeiNo ratings yet
- Microbio 1Document3 pagesMicrobio 1JaellaNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus Updated Nov. 2010Document13 pagesCourse Syllabus Updated Nov. 2010chip_darrisNo ratings yet
- 2011 年秋季班 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Part I: Translate Phrases / 翻譯詞Document1 page2011 年秋季班 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Part I: Translate Phrases / 翻譯詞chip_darrisNo ratings yet
- LABM 429 Foundations of Medical Laboratory Science Lab Math AssignmentDocument5 pagesLABM 429 Foundations of Medical Laboratory Science Lab Math Assignmentchip_darrisNo ratings yet
- 2011 年秋季班 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Part I: Translate Phrases / 翻譯詞Document1 page2011 年秋季班 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Part I: Translate Phrases / 翻譯詞chip_darrisNo ratings yet
- 2011 年秋季班 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Part I: Translate Phrases / 翻譯詞Document1 page2011 年秋季班 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Part I: Translate Phrases / 翻譯詞chip_darrisNo ratings yet
- Chquiz 03 F2011Document1 pageChquiz 03 F2011chip_darrisNo ratings yet
- 31 Greene Liver LM 428 2017Document59 pages31 Greene Liver LM 428 2017chip_darrisNo ratings yet
- Chquiz 01 F2011Document1 pageChquiz 01 F2011chip_darrisNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2.5.18 RBC Destruction CH23-26 JHDocument84 pagesLecture 2.5.18 RBC Destruction CH23-26 JHchip_darrisNo ratings yet
- Financing Campaigns: NameDocument3 pagesFinancing Campaigns: Namechip_darrisNo ratings yet
- Thursday, January 5, 2017 3:35 PM: For Export Page 1Document5 pagesThursday, January 5, 2017 3:35 PM: For Export Page 1chip_darrisNo ratings yet
- ALEKS Objective #5 Is Due Sunday - Pre-Lab #3 Is Due Today. - Midterm #1 Has Being Graded (Mostly)Document23 pagesALEKS Objective #5 Is Due Sunday - Pre-Lab #3 Is Due Today. - Midterm #1 Has Being Graded (Mostly)chip_darrisNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiotechnologyDocument39 pagesIntroduction To BiotechnologyKate Lyle ParfanNo ratings yet
- Immunization Schedule in India 2017 (Latest !!)Document13 pagesImmunization Schedule in India 2017 (Latest !!)rajNo ratings yet
- Disaster Management and Nurses RoleDocument27 pagesDisaster Management and Nurses RolesweetpeaNo ratings yet
- FOGSI Current Updates Vol 2Document1 pageFOGSI Current Updates Vol 2Banu NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Equine Eyelid Disease Sarcoid TraatmentDocument11 pagesEquine Eyelid Disease Sarcoid TraatmentLuis MartinNo ratings yet
- Microbes NotesDocument22 pagesMicrobes Notesapi-218511741100% (1)
- Leuren Moret Population ControlDocument10 pagesLeuren Moret Population ControlMike D.100% (2)
- Activity Based Costing in Health Care Center PDFDocument6 pagesActivity Based Costing in Health Care Center PDFFreddy VargasNo ratings yet
- White Papeer On Covid 19Document10 pagesWhite Papeer On Covid 19SAI HARI HARAN NARAYANANNo ratings yet
- Microchem ASTM E2315 Study Report NG6838 05MAR2016Document9 pagesMicrochem ASTM E2315 Study Report NG6838 05MAR2016Vilva ManikandanNo ratings yet
- Hypersensitivity ReactionsDocument12 pagesHypersensitivity Reactionsella Sy100% (1)
- Immunization Schedule 27-07-2016Document2 pagesImmunization Schedule 27-07-2016SandraniNo ratings yet
- Second Sempre Finals PHC EXAM K2Document4 pagesSecond Sempre Finals PHC EXAM K2yabaeveNo ratings yet
- Science Magazine 5695 2004-10-15Document117 pagesScience Magazine 5695 2004-10-15WillimSmith100% (1)
- Avian Encephalomyelitis (AE)Document22 pagesAvian Encephalomyelitis (AE)Dr.Kedar Karki ,M.V.Sc.Preventive Vet.Medicine CLSU Philippines100% (1)
- Dairy Goat Production HandbookDocument27 pagesDairy Goat Production HandbookGrowel Agrovet Private Limited.No ratings yet
- Operations For The Executive Suite MediumDocument196 pagesOperations For The Executive Suite MediumsilversurfersNo ratings yet
- mRNA Drug ListDocument48 pagesmRNA Drug ListCarrieNo ratings yet
- Travel To England From Another Country During Coronavirus (COVID-19) - GOV - UkDocument4 pagesTravel To England From Another Country During Coronavirus (COVID-19) - GOV - UkVickfor LucaniNo ratings yet
- UNIT V ED FDocument46 pagesUNIT V ED FJahnavi VaswaniNo ratings yet
- Aedes Aegypti Dengan Teknik Imunositokimia MenggunakanDocument10 pagesAedes Aegypti Dengan Teknik Imunositokimia MenggunakanNiken CahyaningrumNo ratings yet
- The Lesser Writings of Von Boenninghausen 1000055197Document361 pagesThe Lesser Writings of Von Boenninghausen 1000055197Frank NavaNo ratings yet
- PNLE II Nursing PracticeDocument16 pagesPNLE II Nursing PracticeIk-ik MiralNo ratings yet
- I/M Injection Sites Acording To AgeDocument2 pagesI/M Injection Sites Acording To Ageman0billiNo ratings yet
- An 17500Document20 pagesAn 17500nivratNo ratings yet
- 170.315 b1 Toc Amb Sample1 v13Document10 pages170.315 b1 Toc Amb Sample1 v13Muhammad SaqibNo ratings yet
- Pneumococcus ExpertRules V3.2 20190613Document3 pagesPneumococcus ExpertRules V3.2 20190613Julyadharma Wangsa DharmaNo ratings yet
- Vaccination Warranty FormDocument4 pagesVaccination Warranty FormBrett AmbroseNo ratings yet
Bacteria: Tuesday, January 23, 2018 2:04 PM
Bacteria: Tuesday, January 23, 2018 2:04 PM
Uploaded by
chip_darrisOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bacteria: Tuesday, January 23, 2018 2:04 PM
Bacteria: Tuesday, January 23, 2018 2:04 PM
Uploaded by
chip_darrisCopyright:
Available Formats
Bacteria
Tuesday, January 23, 2018 2:04 PM
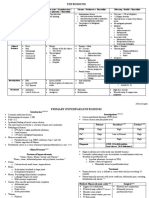
Bacteria Aerobic Growth in medium Appearance under Environment Gram Stain Nutrition Tests Pathogen Other characteristics
Name /Anaerobic the microscope
Corynebacte • Facultative • Non-motile • Rods • Widely • Gram positive • Catalase positive
rium anaerobes • Club-shaped distributed • Gram stain • Non-motile
• V-formations • Mucous irregularly
• Bacteria often at membranes/ski
weird angles to n of humans
each otehr and other
• Non-spore animals
forming
• May contain
metachromatic
granules
Corynebacte • Blood agar • Polyphosphate • May be hemolytic • Causes diptheria • Definite diagnosis
rium • Small granules under • Reduces tellurite to • Colonizes upper requires testing for
diptheriae • Opaque white methylene blue tellurium (appears black) respiratory toxigenity by guinea pig
• Selective/differentia (particularly • Non-motile tract/throat injection or by Elek test
l medium often from Loeffler's) • Positive for nitrate • Virulence is due
contains tellurite reduction to an exotoxin
• Appears black on • Negative for urease that is then
tellurite medium • Acidic sugar fermentation, carried
• Loeffler's slant gas production throughout the
body through
blood
• Toxin mostly
affects heart and
peripheral nerves
• Inhibits
eukaryotic
protein synthesis
(kills cells)
• Causes death of
cells in the upper
respiratory tract
• Pseudomembrane
• Phage encoded
(lysogenic
conversion)
• Vaccine = toxoid
(formalin-
inactivated toxin)
Enterococcu • Aerotolerant • Blood agar • Tends to form • Common • Gram positive • Hardy • Catalase negative • Opportunist
s anaerobes • Grow in 6.5% NaCl short chains normal fecal • Not nutritionally • Bile-esculin positive • Urinary tract
• Obligate • Small Cocci microbiota fastidious • Sometimes slightly infections
fermenters • Smaller than hemolytic • Bacteremia
Streptococcus • Pyrase positive
pneumoniae
• Gray
Microm 443 Page 1
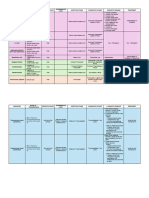
Listeria • Facultative • Blood agar • Rods • Very common • Gram positive • Catalase positive • Rare cause of
anaerobes • Small • Non-spore environmental • Umbrella motility sepsis and
• Translucent forming organism • Nitrate reduction negative meningitis
• Narrow zone of • Soil and • Urease negative • Foodborn
hemolysis decaying • Lab must always
vegetables R/O Listeria when
• Intestinal tract GPR seen in CSF
• Food products or blood
• Pregnant
women/neonates
/elderly/immunoc
ompromised are
at highest risk
Moraxell • Obligate • Chocolate agar • Diplocci or rods • Grows on • Gram • Fastidious to varying • Catalase positive • Can cause disease
respirers • Blood agar • Typically occurs mucous negative degrees • Oxidase positive in ears, sinus,
a • Some are • Nutrient agar in pairs (i.e. membranes • Somewhat • Fragile to varying degrees • No acid detected from lungs
capnophiles • TSY kidney • Upper resistant to digestion of glucose and
• Medium large beans/coffee respiratory decolarization maltose
• Whitish gray to beans) tract of
pinkish brown humans
• "hockey puck"
consistency
• Opaque gray to
white colonies
Moraxell • Doesn't required • Grows well on CA, • Rods • Normal oral • Gram • Least fastidious out of N. • Cannot ferment
increased CO2 BA, and NA bacteria negative meningitidis and N. glucose/maltose/sucrose/l
a gonorrheae actose
catarrhal
is
Neisseria • Obligate • Adjacent sides of • Diplocci or rods • Grows on • Gram • Fastidious to varying • Catalase positive • Species identification
respirers the pairs are • Typically occurs mucous negative degrees • Oxidase positive mostly based on
• Under clinical flattened in pairs (i.e. membranes of • Somewhat • Fragile to varying degrees degradation of sugars
cultivation they • Opaque gray to kidney warm blooded resistant to
are strict white colonies beans/coffee animals decolarization
aerobes • Grows only a little beans)
• Some are on CTA slants
capnophiles
Neisseria • Needs • Chocolate agar • Cocci • Fragile • Acid production from • Causes gonorrhea • Also known as
incubation in • High humidity • Fastidious pathogen glucose only • Transmitted gonococcus or GC
gonorrho increased CO2 • VCN medium-> • Blood and • NOT fermentation through genital
eae • Plain candle antibiotics chocolate agar • Was penicillin sensitive, tract,
vancomycin (acts on don't have but most strains are now mouth/throat,
gram positives), enough nutrients penicillin resistant as well rectum, eyes
colistin (acts on to support their as resistant to other drugs • Always
gram negatives), growth considered a
nystatin (yeasts) • Inoculate at collection pathogen
• VCN may inhibit • Incubate immediately or • Can progress to
some strains of use non-nutritive pelvic
gonococci-> also transport medium inflammatory
plate on BA disease in women
• Small to medium (Infertility)
• Grayish white • Urethral
Microm 443 Page 2
• Grayish white • Urethral
• Convex (raised) discharge in
• Colony type varies males
even in a single • 50% asymptoma
strain, due to in women
antigenic variation • GNDC inside
• CTA agar with sugar PMNs diagnostic
+ pH indicator for males
• GNDC inside
PMNs not
diagnostic for
females-> confirm
with culture
Neisseria • Blood agar • Cocci • Found in upper • Gram • Fragile • Acid from glucose and • Causes • Subdivided into
• High humidity respiratory negative • Less fastidious than maltose meningoccemia serological groups
menigiti • Increased CO2 tract of 3-15% gonococcus and meningitis based on presence of
dis • Medium of people • Will grow well on blood that can go from capsular or cell wall
• Gray agar blood -> brain antigens
• Smooth • Vaccine
• Glistening • Intra and
• Convex extracellular
• Won't grow on GNDC in PMNs
nutrient agar
Staphylococ • Facultative • Clusters, single, • Common skin • Gram Positive • Generally hardy • Catalase positive
cus anaerobes pairs, short microbiota of • Not nutritionally
chains mammals fastidious
• Cocci • Found on
mucous
membranes
Staphylococ "" • Medium to large • Carried in the • Coagulase positive • Opportunistic
cus Aureus • Use blood agar nose and on • Beta hemolytic pathogen
• Large the skin of • Novobiocin susceptible • Healthcare-
• Creamy to golden 0people associated
color infection
• Typically hemolytic, • Surgical wounds
may show double (a nosocomial
zone (particularly infection)
after refrigeration) • Abscesses (boils)
• Pneumonia
• Septicemia
• Most likely Staph.
To be pathogenic
Staphylococ • Use blood agar • Urinary tract • Coagulase negative • Species
cus • Medium size infections • Novobiocin resistant identification not
saprophytic colonies usually done
us • Looks very similar to except in urinary
Staph. epidermis tract infections
Staphylococ • Blood agar • Common • Coagulase negative • Occasional
cus • Generally porcelain normal skin • Novobiocin sensitive opportunist
epidermidis white microbiota • Non-hemolytic • Hospitalized
• white • Novobiocin sensitive patients,
• Non-hemolytic especially those
• Slightly smaller than with indwelling
Staphylococcus catheters, most
Microm 443 Page 3
Staphylococcus catheters, most
Aureus susceptible
Streptococc • Aerotolerant • Tends to form • Common oral • Gram positive • Nutritionally fastidious
us anaerobe chains microbiota
• Obligate • Cocci
fermenter
• Some are
capnophiles
(CO2)
Streptococc • Can grow in the • Blood agar • Beta hemolytic • Upper respiratory • Group A strep
us presence of • Small • 100% in anaerobic infections
pyrogenes oxygen • White conditions (O, • Pharyngitis (strep
• Anaerobic • Colonies remain oxygen labile) throat)
incubation is intact when pushed • 85% in aerobic • Wound infections
used in order to with a loop conditions (S, • Pneumonia
reliably observe oxygen stable) • Bacteremia/sepsis
B-hemolysis • Sensitive to Bacitracin • Scarlet fever
• Positive for Pyrase • Septicemia
• Latex agglutination using • Streptococcal
Ab to Group A toxic shock
carbohydrate antigen • For throat
• Fluorescent Ab test cultures "R/O
GrpA"
Streptococc • Anaerobic • Use blood agar • Beta hemolytic • Pathogen • Group B strep
us agalactiae hemolysis in • Small • Less obvious • Neonatal
order to more • Creamy aerobically meningitis
reliably observe • May be orange • Bacitracin resistant • Neonatal sepsis
B-hemolysis • Sodium hippurate positive • Post-partum
• Latex agglutination using infections
Ab to group B antigen • Bacteremia
Streptococc • Blood agar • Commonly • Alpha hemolytic • Opportunist
us • Small carried in the • Optochin sensitive • Pneumonia
pneumoniae • Larger than throat • Bile soluble (will lyse) • Meningitis
enterococcus • The colonies will
• Often mucoid on disappear but not
primary isolation the surrounding
due to hemolysis
encapsulation
• Flatten over time
• Produces an
autolysin
Viridans • Blood agar • Normal in the • Alpha-hemolytic • Occasional • Must be distinguished
streptococci • Very Tiny throat • Optochin resistant opportunists from pneumococcus in
• Bile insoluble • Can cause tooth a sputum specimen
decayd
Microm 443 Page 4
You might also like
- Cefazolin Ancef Drug CardDocument2 pagesCefazolin Ancef Drug CardLisaNo ratings yet
- Bacterial ID FlowchartDocument6 pagesBacterial ID FlowchartTom Tsou50% (2)
- PassiveDocument2 pagesPassiveTop Secret0% (1)
- HEMATOLOGY NOTESDocument31 pagesHEMATOLOGY NOTESALIZA BAKILNo ratings yet
- Protozoans - Amebae: Medically Important ParasitesDocument10 pagesProtozoans - Amebae: Medically Important ParasitesBrylle LumberioNo ratings yet
- 2A-Sarigumba - 10 MEDICALLY IMPORTANT BACTERIA PDFDocument18 pages2A-Sarigumba - 10 MEDICALLY IMPORTANT BACTERIA PDFSean SarigumbaNo ratings yet
- Western Blot Troubleshooting Smeared Bands Sino BiologicalDocument1 pageWestern Blot Troubleshooting Smeared Bands Sino Biologicalอิษฎาภร ภูมิชัยชนะNo ratings yet
- Exam Review05 Part2Document6 pagesExam Review05 Part2api-26602387No ratings yet
- BioPIN Sternheimer-Malbin-Concentrate - Bioanalytic (En)Document2 pagesBioPIN Sternheimer-Malbin-Concentrate - Bioanalytic (En)Yan PetrovNo ratings yet
- Enterobacteriaceae 2Document11 pagesEnterobacteriaceae 2odhiambo samwelNo ratings yet
- Acute Thyroid Thyroiditis Sub-Acute / Granulomatous / de Quevains's Thyroiditis Chronic / Hashimoto's Thyroiditis Fibrosing / Reidel's ThyroiditisDocument2 pagesAcute Thyroid Thyroiditis Sub-Acute / Granulomatous / de Quevains's Thyroiditis Chronic / Hashimoto's Thyroiditis Fibrosing / Reidel's ThyroiditisZuhra JabeenNo ratings yet
- BIO204 - Chapter 2Document1 pageBIO204 - Chapter 2Holin DolanNo ratings yet
- CT CellsDocument1 pageCT CellsTarlan SharifiNo ratings yet
- TB MeningitisDocument46 pagesTB MeningitishenniwtNo ratings yet
- DDX of Hematological DisordersDocument1 pageDDX of Hematological DisordersOlivia LimNo ratings yet
- PARASITOLOGY P1 Table SummaryDocument4 pagesPARASITOLOGY P1 Table Summaryiananicole.b30No ratings yet
- Final Notebook BioDocument16 pagesFinal Notebook Biolorina p del rosarioNo ratings yet
- (MT 57) PARA - Pathogenic ProtozoaDocument5 pages(MT 57) PARA - Pathogenic ProtozoaLiana JeonNo ratings yet
- Differential CountDocument2 pagesDifferential CountMARY KAYE YVONNE OTILLANo ratings yet
- Special StainsDocument27 pagesSpecial Stainsambadepravin100% (1)
- CYTOGEN: Chapter 3 Meiosis, Development, and AgingDocument6 pagesCYTOGEN: Chapter 3 Meiosis, Development, and AgingpangetkoNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasmic InheritanceDocument5 pagesCytoplasmic InheritancesumanparajuliNo ratings yet
- Lange Smart Charts: Pharmacology, 2e Oncologic DrugsDocument3 pagesLange Smart Charts: Pharmacology, 2e Oncologic DrugsFlorence MarzanNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom Digital NotesDocument20 pagesAnimal Kingdom Digital NotesKshreeNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Immersion BasicsDocument18 pagesLaboratory Immersion BasicsAprian AcunaNo ratings yet
- Igcse Biology: Topic 1: Characteristics of Living OrganismsDocument63 pagesIgcse Biology: Topic 1: Characteristics of Living OrganismsIndia IB 2020No ratings yet
- MicrosDocument6 pagesMicrosJheshari VinaNo ratings yet
- AmoebaDocument5 pagesAmoebaMhizzy ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Cell Biology and OrganisationDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Cell Biology and OrganisationRAYMOND CHIENG CHING BING Moe100% (1)
- G1 Checkpoint - Monitors Cell Size and Integrity G2 Checkpoint - DNA Damage CheckpointDocument3 pagesG1 Checkpoint - Monitors Cell Size and Integrity G2 Checkpoint - DNA Damage CheckpointErica GarciaNo ratings yet
- Diversity AnimalsDocument20 pagesDiversity AnimalsnithinjothimuruganNo ratings yet
- C24 CellsDocument13 pagesC24 Cellsjunaidfatimah765haNo ratings yet
- Case Studies On Major Concepts: MetabolismDocument37 pagesCase Studies On Major Concepts: MetabolismJek Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-01-19 at 5.10.09 PMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2024-01-19 at 5.10.09 PMdhruvrana1133No ratings yet
- ANAPHY LEC CVS BloodDocument6 pagesANAPHY LEC CVS BloodMarjorie ViescaNo ratings yet
- Arasitology: Intestinal AmoebaeDocument5 pagesArasitology: Intestinal AmoebaeMa. Mil Adrianne PamaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Diagnostic Parasitology and Specimen CollectionDocument3 pagesOverview of Diagnostic Parasitology and Specimen CollectionBrylle LumberioNo ratings yet
- History Taking in HematologyDocument1 pageHistory Taking in HematologyNarmin Abubaker AliNo ratings yet
- 13 - ELGAR - Activity Sheet 2Document1 page13 - ELGAR - Activity Sheet 2Eul MojoNo ratings yet
- Ch. 21: Vascular Plants Without Seeds: ConceptsDocument4 pagesCh. 21: Vascular Plants Without Seeds: ConceptsNexNo ratings yet
- Cytological TechniquesDocument4 pagesCytological TechniquesJamie100% (2)
- Hematopoietic SystemDocument47 pagesHematopoietic SystemAbbi Yanto ArtNo ratings yet
- Cell Morphologies: Summary of Cell Structures Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Bacteria ArchaeaDocument1 pageCell Morphologies: Summary of Cell Structures Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Bacteria ArchaeaAna GrimaldoNo ratings yet
- B3 Human ReproductionDocument1 pageB3 Human ReproductionSatyam AnandNo ratings yet
- Aspergillus Species PPT 2Document1 pageAspergillus Species PPT 2ajisozymeNo ratings yet
- 6.1 MicrobiologyDocument32 pages6.1 MicrobiologyYsabelle BautistaNo ratings yet
- Parasites CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesParasites CharacteristicsNiezel EncalladoNo ratings yet
- PARA LAB - 2 Intestinal Amoeba111Document24 pagesPARA LAB - 2 Intestinal Amoeba111Brigit DueñasNo ratings yet
- Urine AnalysisDocument1 pageUrine Analysisعبدالرحمن ابراهيمNo ratings yet
- Aubf Lab MidtermDocument8 pagesAubf Lab MidtermNiezel EncalladoNo ratings yet
- AntiprotozoalDocument2 pagesAntiprotozoalxelo_27No ratings yet
- Haematoxylin and Eosin (H+E) - Aldehyde-Fuchsin - Van Geison's Picro Fuchsin Technique - Masson's Trichrome - Nuclei - Blue/backDocument9 pagesHaematoxylin and Eosin (H+E) - Aldehyde-Fuchsin - Van Geison's Picro Fuchsin Technique - Masson's Trichrome - Nuclei - Blue/backsilentscreamsofloveNo ratings yet
- Components of BloodDocument1 pageComponents of BloodEmson ChipfumbuNo ratings yet
- Parasitology (Lect #6) TransDocument3 pagesParasitology (Lect #6) TransAndrea Galang CruzNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - 23-07-2021 BBDocument7 pagesLecture 2 - 23-07-2021 BBpaulinemahlangu88No ratings yet
- Kista Bartholine NewDocument12 pagesKista Bartholine NewZulfy AzharyNo ratings yet
- PATHOLOGY MAIN HANDOUT - ExtractDocument15 pagesPATHOLOGY MAIN HANDOUT - ExtractAshley Chloé UyNo ratings yet
- Blood Components Where Do They Come From?: Introduction To HaematologyDocument11 pagesBlood Components Where Do They Come From?: Introduction To Haematologydorsa koraeiNo ratings yet
- Microbio 1Document3 pagesMicrobio 1JaellaNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus Updated Nov. 2010Document13 pagesCourse Syllabus Updated Nov. 2010chip_darrisNo ratings yet
- 2011 年秋季班 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Part I: Translate Phrases / 翻譯詞Document1 page2011 年秋季班 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Part I: Translate Phrases / 翻譯詞chip_darrisNo ratings yet
- LABM 429 Foundations of Medical Laboratory Science Lab Math AssignmentDocument5 pagesLABM 429 Foundations of Medical Laboratory Science Lab Math Assignmentchip_darrisNo ratings yet
- 2011 年秋季班 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Part I: Translate Phrases / 翻譯詞Document1 page2011 年秋季班 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Part I: Translate Phrases / 翻譯詞chip_darrisNo ratings yet
- 2011 年秋季班 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Part I: Translate Phrases / 翻譯詞Document1 page2011 年秋季班 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Part I: Translate Phrases / 翻譯詞chip_darrisNo ratings yet
- Chquiz 03 F2011Document1 pageChquiz 03 F2011chip_darrisNo ratings yet
- 31 Greene Liver LM 428 2017Document59 pages31 Greene Liver LM 428 2017chip_darrisNo ratings yet
- Chquiz 01 F2011Document1 pageChquiz 01 F2011chip_darrisNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2.5.18 RBC Destruction CH23-26 JHDocument84 pagesLecture 2.5.18 RBC Destruction CH23-26 JHchip_darrisNo ratings yet
- Financing Campaigns: NameDocument3 pagesFinancing Campaigns: Namechip_darrisNo ratings yet
- Thursday, January 5, 2017 3:35 PM: For Export Page 1Document5 pagesThursday, January 5, 2017 3:35 PM: For Export Page 1chip_darrisNo ratings yet
- ALEKS Objective #5 Is Due Sunday - Pre-Lab #3 Is Due Today. - Midterm #1 Has Being Graded (Mostly)Document23 pagesALEKS Objective #5 Is Due Sunday - Pre-Lab #3 Is Due Today. - Midterm #1 Has Being Graded (Mostly)chip_darrisNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiotechnologyDocument39 pagesIntroduction To BiotechnologyKate Lyle ParfanNo ratings yet
- Immunization Schedule in India 2017 (Latest !!)Document13 pagesImmunization Schedule in India 2017 (Latest !!)rajNo ratings yet
- Disaster Management and Nurses RoleDocument27 pagesDisaster Management and Nurses RolesweetpeaNo ratings yet
- FOGSI Current Updates Vol 2Document1 pageFOGSI Current Updates Vol 2Banu NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Equine Eyelid Disease Sarcoid TraatmentDocument11 pagesEquine Eyelid Disease Sarcoid TraatmentLuis MartinNo ratings yet
- Microbes NotesDocument22 pagesMicrobes Notesapi-218511741100% (1)
- Leuren Moret Population ControlDocument10 pagesLeuren Moret Population ControlMike D.100% (2)
- Activity Based Costing in Health Care Center PDFDocument6 pagesActivity Based Costing in Health Care Center PDFFreddy VargasNo ratings yet
- White Papeer On Covid 19Document10 pagesWhite Papeer On Covid 19SAI HARI HARAN NARAYANANNo ratings yet
- Microchem ASTM E2315 Study Report NG6838 05MAR2016Document9 pagesMicrochem ASTM E2315 Study Report NG6838 05MAR2016Vilva ManikandanNo ratings yet
- Hypersensitivity ReactionsDocument12 pagesHypersensitivity Reactionsella Sy100% (1)
- Immunization Schedule 27-07-2016Document2 pagesImmunization Schedule 27-07-2016SandraniNo ratings yet
- Second Sempre Finals PHC EXAM K2Document4 pagesSecond Sempre Finals PHC EXAM K2yabaeveNo ratings yet
- Science Magazine 5695 2004-10-15Document117 pagesScience Magazine 5695 2004-10-15WillimSmith100% (1)
- Avian Encephalomyelitis (AE)Document22 pagesAvian Encephalomyelitis (AE)Dr.Kedar Karki ,M.V.Sc.Preventive Vet.Medicine CLSU Philippines100% (1)
- Dairy Goat Production HandbookDocument27 pagesDairy Goat Production HandbookGrowel Agrovet Private Limited.No ratings yet
- Operations For The Executive Suite MediumDocument196 pagesOperations For The Executive Suite MediumsilversurfersNo ratings yet
- mRNA Drug ListDocument48 pagesmRNA Drug ListCarrieNo ratings yet
- Travel To England From Another Country During Coronavirus (COVID-19) - GOV - UkDocument4 pagesTravel To England From Another Country During Coronavirus (COVID-19) - GOV - UkVickfor LucaniNo ratings yet
- UNIT V ED FDocument46 pagesUNIT V ED FJahnavi VaswaniNo ratings yet
- Aedes Aegypti Dengan Teknik Imunositokimia MenggunakanDocument10 pagesAedes Aegypti Dengan Teknik Imunositokimia MenggunakanNiken CahyaningrumNo ratings yet
- The Lesser Writings of Von Boenninghausen 1000055197Document361 pagesThe Lesser Writings of Von Boenninghausen 1000055197Frank NavaNo ratings yet
- PNLE II Nursing PracticeDocument16 pagesPNLE II Nursing PracticeIk-ik MiralNo ratings yet
- I/M Injection Sites Acording To AgeDocument2 pagesI/M Injection Sites Acording To Ageman0billiNo ratings yet
- An 17500Document20 pagesAn 17500nivratNo ratings yet
- 170.315 b1 Toc Amb Sample1 v13Document10 pages170.315 b1 Toc Amb Sample1 v13Muhammad SaqibNo ratings yet
- Pneumococcus ExpertRules V3.2 20190613Document3 pagesPneumococcus ExpertRules V3.2 20190613Julyadharma Wangsa DharmaNo ratings yet
- Vaccination Warranty FormDocument4 pagesVaccination Warranty FormBrett AmbroseNo ratings yet