Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
156 viewsOLFU College of Medicine Class 2015: Parasitology
OLFU College of Medicine Class 2015: Parasitology
Uploaded by
rochelle_gThis document provides an introduction to parasitology, including key terms and concepts. It discusses:
1) The definition of parasitology as the study of organisms that live in or on other living organisms.
2) Different types of hosts and their roles in parasite life cycles, mechanisms of pathogenesis, and modes of transmission.
3) The main divisions of medical parasitology including protozoology, helminthology, and medical entomology.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Coventry 06.2012Document14 pagesCoventry 06.2012karan270No ratings yet
- Hesi Psych Study GuideDocument16 pagesHesi Psych Study GuideR100% (17)
- MCQ Trop-Med All - KARUNDocument23 pagesMCQ Trop-Med All - KARUNDapot SianiparNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics Midterms Rationale 2nd Sem 2018 2019Document21 pagesObstetrics Midterms Rationale 2nd Sem 2018 2019Gene Paulo UyNo ratings yet
- 1.entamoeba Histolytica - Is The Major Pathogen in This GroupDocument14 pages1.entamoeba Histolytica - Is The Major Pathogen in This GroupJoseph De JoyaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Lab Midterms Transes PDFDocument3 pagesParasitology Lab Midterms Transes PDFLouisse Anne Monique CayloNo ratings yet
- Parasitology 2019 Lecture Notes: Prepared By: Ariane T. Laranang, RMT, MT (Ascpi), MSMTDocument39 pagesParasitology 2019 Lecture Notes: Prepared By: Ariane T. Laranang, RMT, MT (Ascpi), MSMTShane Ann RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 3.5 PHARMA ANTI MYCOBACTERIAL AGENTSpdfDocument18 pages3.5 PHARMA ANTI MYCOBACTERIAL AGENTSpdfJanet SantosNo ratings yet
- ParasitologyDocument3 pagesParasitologyKCSotelo_xxviiNo ratings yet
- Merged PDF 2021 11 16T12 - 01 - 01Document15 pagesMerged PDF 2021 11 16T12 - 01 - 01Ericsson CarabbacanNo ratings yet
- Par201 S1lab4 Midterm Phamids Aphasmids PDFDocument27 pagesPar201 S1lab4 Midterm Phamids Aphasmids PDFHanna Alyssa Grace DimarananNo ratings yet
- Bates Chapter 8 Lung and ThoraxDocument15 pagesBates Chapter 8 Lung and ThoraxAdrian CaballesNo ratings yet
- Preventive MedicineDocument106 pagesPreventive Medicinemain.genevive.diligNo ratings yet
- RMTnotes PARASITOLOGYDocument68 pagesRMTnotes PARASITOLOGYArvin O-CaféNo ratings yet
- PARA 1.03 Nematodes I - Dra. Chiong-RiveraDocument14 pagesPARA 1.03 Nematodes I - Dra. Chiong-RiveraTMC PGI GENER MICKONo ratings yet
- Microbial Diseases of The Nervous System: DR Sonnie P. Talavera 08162009 OlfuDocument162 pagesMicrobial Diseases of The Nervous System: DR Sonnie P. Talavera 08162009 Olfuone_nd_onlyu0% (1)
- Oral Revalida ReviewerDocument10 pagesOral Revalida RevieweranneNo ratings yet
- Nematodes: 2B - MicrobiomanDocument41 pagesNematodes: 2B - Microbioman2013SecBNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Urine and Other Body Fluids - , RMT Sputum & Bronchoalveolar Lavage (Bal)Document11 pagesAnalysis of Urine and Other Body Fluids - , RMT Sputum & Bronchoalveolar Lavage (Bal)jeffreyNo ratings yet
- Medical Parasitology in The Philippines (Belizario, de Leon) - Pages-307-340Document34 pagesMedical Parasitology in The Philippines (Belizario, de Leon) - Pages-307-340Mae Rose Charlene MendozaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Laboratory Questionnaires 2TDocument21 pagesParasitology Laboratory Questionnaires 2TJen CANo ratings yet
- Biochemistry (1-20)Document30 pagesBiochemistry (1-20)Stetho LoveNo ratings yet
- Parasitic AmoebaDocument23 pagesParasitic AmoebaJethrö MallariNo ratings yet
- Nematode Common Name Associated Disease Mode of Transmission Habitat Definitive Host Intermediate HostDocument5 pagesNematode Common Name Associated Disease Mode of Transmission Habitat Definitive Host Intermediate HostAnjelo PerenNo ratings yet
- ReviewersDocument1 pageReviewersRalph Renon CasamayorNo ratings yet
- Giardiasis PDFDocument14 pagesGiardiasis PDFSaad Motawéa0% (1)
- CELL OVERVIEW PREVENTION Notes 2015Document7 pagesCELL OVERVIEW PREVENTION Notes 2015Alexander LukashenkoNo ratings yet
- Activity Tabulation ParasitologyDocument18 pagesActivity Tabulation ParasitologyStephen YorNo ratings yet
- Rash Fever DDXDocument7 pagesRash Fever DDXirsaNo ratings yet
- CestodesDocument7 pagesCestodesRubenson CantigaNo ratings yet
- Leukocytes, Granulocytes, The Monocyte-Macrophage System, and InflammationDocument10 pagesLeukocytes, Granulocytes, The Monocyte-Macrophage System, and InflammationShi no MeNo ratings yet
- Parasitic Infection in GI TractDocument123 pagesParasitic Infection in GI TractUtami HandayaniNo ratings yet
- Nematodes: Specie Infecti VE Stage Diagnos TIC Stage Morphology Pathogen Esis Diagnosi S Treatme NT Life CycleDocument4 pagesNematodes: Specie Infecti VE Stage Diagnos TIC Stage Morphology Pathogen Esis Diagnosi S Treatme NT Life CycleMarinelle TumanguilNo ratings yet
- Parasitology NotesDocument5 pagesParasitology NotesAyaAlforque100% (1)
- Trematodes: Blood FlukesDocument3 pagesTrematodes: Blood FlukesFrance Louie JutizNo ratings yet
- Parasite Trematodes PDFDocument2 pagesParasite Trematodes PDFGougle MuteNo ratings yet
- MED1 Samplex Rationale 9 - Breast ExaminationDocument4 pagesMED1 Samplex Rationale 9 - Breast ExaminationMartina GarciaNo ratings yet
- Plasmodium Vivax Plasmodium Ovale Plasmodium Malariae Plasmodium FalciparumDocument2 pagesPlasmodium Vivax Plasmodium Ovale Plasmodium Malariae Plasmodium FalciparumJulia SinajonNo ratings yet
- Legal Medicine and Medical Jurisprudence Comprehensive Exam ReviewerDocument17 pagesLegal Medicine and Medical Jurisprudence Comprehensive Exam ReviewerYeshua Tura100% (1)
- 2 Parasitology Parasitic AmoebasDocument8 pages2 Parasitology Parasitic AmoebasknkjnNo ratings yet
- Trematodes Outline L. MDocument1 pageTrematodes Outline L. MleoNo ratings yet
- Summary Table - TrematodesDocument4 pagesSummary Table - TrematodesNeil Joshua SuyatNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - General Properties and Classification of FungiDocument4 pagesLecture 1 - General Properties and Classification of FungiRemelou Garchitorena AlfelorNo ratings yet
- Day 1 BacteriaDocument251 pagesDay 1 BacteriaLisa NetherlandNo ratings yet
- Nematodes-Reviewer (Revised)Document4 pagesNematodes-Reviewer (Revised)Primo GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Trematodes Schistosoma Spp. General CharacteristicsDocument3 pagesTrematodes Schistosoma Spp. General CharacteristicsGlenn PerezNo ratings yet
- Parasitology TableDocument9 pagesParasitology TablehumanupgradeNo ratings yet
- pm2 TREMATODESDocument39 pagespm2 TREMATODESshastaNo ratings yet
- Summary TrematodesDocument3 pagesSummary TrematodesJ Pao Bayro - LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- Tissue and Blood NematodesDocument53 pagesTissue and Blood NematodesVincent ManganaanNo ratings yet
- The Ameba ReportingDocument49 pagesThe Ameba ReportingALLISON PAMITTANNo ratings yet
- Topnotch Waiver Oath and Checklist April 2015 PDFDocument2 pagesTopnotch Waiver Oath and Checklist April 2015 PDFRalph JuicoNo ratings yet
- Wuchereria Bancrofti Brugia Malayi Loa Loa Onchocerca Volvulus Mansonella Perstans Mansonella Ozzardi Dracunculus MedinensisDocument4 pagesWuchereria Bancrofti Brugia Malayi Loa Loa Onchocerca Volvulus Mansonella Perstans Mansonella Ozzardi Dracunculus MedinensisJoshua TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Microbiology - : University of Santo Tomas - Medical TechnologyDocument6 pagesDiagnostic Microbiology - : University of Santo Tomas - Medical TechnologyWynlor AbarcaNo ratings yet
- Preventive MedDocument74 pagesPreventive MedSherlock HolmesNo ratings yet
- MBR 2019 - CNS Pathology HandoutDocument6 pagesMBR 2019 - CNS Pathology HandoutNica Lopez FernandezNo ratings yet
- ParasitologyLec 3 Nematodes 2 PDFDocument6 pagesParasitologyLec 3 Nematodes 2 PDFDJ RelojNo ratings yet
- (Parasitology) Prelim-Final Reviewer 2015Document13 pages(Parasitology) Prelim-Final Reviewer 2015Andrassy Twinkle Alinea100% (1)
- 1-2. - Introduction-PARA-LecDocument6 pages1-2. - Introduction-PARA-LecLian MallareNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - TransDocument8 pagesModule 1 - TransJohanna Kate DiestroNo ratings yet
- Parasitology. ProtozoaDocument23 pagesParasitology. ProtozoaGelo mirandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Intro To Med. ParasitologyDocument7 pagesChapter 1 Intro To Med. ParasitologyFrances Riane SimoyNo ratings yet
- F Occlusal Therapy in Prosthodontics FinalDocument17 pagesF Occlusal Therapy in Prosthodontics FinalJyoti TripathiNo ratings yet
- Dyslipidemia 2023Document39 pagesDyslipidemia 2023medt80No ratings yet
- Jurnal Carpal Tunnel SyndromeDocument11 pagesJurnal Carpal Tunnel SyndromeArjuna MarzaNo ratings yet
- Gingival InflammationDocument19 pagesGingival InflammationmirfanulhaqNo ratings yet
- I Can'T Breathe If Breathing Is Without: Bronchial AsthmaDocument33 pagesI Can'T Breathe If Breathing Is Without: Bronchial AsthmaklamorenaNo ratings yet
- Case Record Form For ChildrenDocument32 pagesCase Record Form For ChildrenPrasad javvajiNo ratings yet
- ANTH QUIZZES & EXAM 1 Midterm Question PoolDocument41 pagesANTH QUIZZES & EXAM 1 Midterm Question PoolSaumier Stables67% (3)
- Planet Karak Short List by OPVDocument76 pagesPlanet Karak Short List by OPVKumar100% (1)
- PCOL TRivias 2Document3 pagesPCOL TRivias 2Maria Izabelle QuemiNo ratings yet
- Digital Revolution in Healthcare - EPSA AA '17 - Daniel Vertessy - 2Document34 pagesDigital Revolution in Healthcare - EPSA AA '17 - Daniel Vertessy - 2Karlo ŽiliNo ratings yet
- Data Quality - Facilitators Manual FINAL - July242018Document78 pagesData Quality - Facilitators Manual FINAL - July242018Ambaasaaddara Kiristoosiin Addunyaarratti MuudameNo ratings yet
- Sistrunk Operation ArticleDocument4 pagesSistrunk Operation Articleআবু আব্দুল্লাহ শাদীদNo ratings yet
- Y. Hirschfeld, The Crisis of The Sixth Century. Climatic Change, Natural Disasters and The PlagueDocument8 pagesY. Hirschfeld, The Crisis of The Sixth Century. Climatic Change, Natural Disasters and The PlagueedinjuveNo ratings yet
- Biogenic Amines by HPLCDocument7 pagesBiogenic Amines by HPLCNeidys SanchezNo ratings yet
- Vital Sign #1: Body TemperatureDocument5 pagesVital Sign #1: Body TemperaturePrimelift Safety Resources LimitedNo ratings yet
- JSA Excavation For Lighting Pole FoundationDocument18 pagesJSA Excavation For Lighting Pole FoundationMohammad Al Masa'deh100% (1)
- Idsr Implementation PDFDocument4 pagesIdsr Implementation PDFamaha alemayehuNo ratings yet
- Lapsal Juni 2016 Arief BrownDocument427 pagesLapsal Juni 2016 Arief BrownZainalArifinNo ratings yet
- Coex + MatriciDocument5 pagesCoex + MatricivalentinnNo ratings yet
- Lab HistoryDocument8 pagesLab HistoryAlbin StigoNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Mouth Breathing and Maxillary Anterior ProclinationDocument4 pagesTreatment of Mouth Breathing and Maxillary Anterior ProclinationVaniaNo ratings yet
- Tplasty AishwaryaDocument2 pagesTplasty Aishwaryaankitkawale111No ratings yet
- 1114-Article Text-2259-1-10-20210503Document10 pages1114-Article Text-2259-1-10-20210503Guna SoundariNo ratings yet
- Applications of MicrobiologyDocument5 pagesApplications of MicrobiologyLloyd LozanoNo ratings yet
- First Year B.Sc. Nursing Question Paper 2009Document15 pagesFirst Year B.Sc. Nursing Question Paper 2009Biju Antony100% (7)
- Ecology Action Research Project FinalDocument13 pagesEcology Action Research Project Finalapi-357358935No ratings yet
- yudaturana,+Manajer+Jurnal,+dr +nelson+rev+2+ (162-172)Document12 pagesyudaturana,+Manajer+Jurnal,+dr +nelson+rev+2+ (162-172)Fath TiaraNo ratings yet
- Jeong Et Al-2001-Nature PDFDocument2 pagesJeong Et Al-2001-Nature PDFThibextraNo ratings yet
OLFU College of Medicine Class 2015: Parasitology
OLFU College of Medicine Class 2015: Parasitology
Uploaded by
rochelle_g0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
156 views2 pagesThis document provides an introduction to parasitology, including key terms and concepts. It discusses:
1) The definition of parasitology as the study of organisms that live in or on other living organisms.
2) Different types of hosts and their roles in parasite life cycles, mechanisms of pathogenesis, and modes of transmission.
3) The main divisions of medical parasitology including protozoology, helminthology, and medical entomology.
Original Description:
Intro to Parasitology
Original Title
Intro to PARA
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an introduction to parasitology, including key terms and concepts. It discusses:
1) The definition of parasitology as the study of organisms that live in or on other living organisms.
2) Different types of hosts and their roles in parasite life cycles, mechanisms of pathogenesis, and modes of transmission.
3) The main divisions of medical parasitology including protozoology, helminthology, and medical entomology.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
156 views2 pagesOLFU College of Medicine Class 2015: Parasitology
OLFU College of Medicine Class 2015: Parasitology
Uploaded by
rochelle_gThis document provides an introduction to parasitology, including key terms and concepts. It discusses:
1) The definition of parasitology as the study of organisms that live in or on other living organisms.
2) Different types of hosts and their roles in parasite life cycles, mechanisms of pathogenesis, and modes of transmission.
3) The main divisions of medical parasitology including protozoology, helminthology, and medical entomology.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
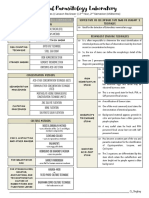
OLFU College of Medicine Class 2015
Parasitology Lecture 1: Introduction to Parasitology
Dr. Mateo June 22, 2012
Parasitology Type of Host in Relation to Various Stages of the Life
Area of biology with the phenomenon of Cycle of Parasites
dependence of one living organism on another 1. Definitive Host
Science in which deals most with living animals o in which the sexual life cycle takes place
living at the expense of other living beings and 2. Intermediate Host
able to develop and reproduce in them o in which asexual life cycle takes place
Science that deals with organism that take up before it is deposited in the definitive
their abode temporarily or permanently host
Way by Which Egg & Larvae Leave the Body of the
Medical Parasitology Host
Concerned primarily with the animal parasites of 1. Liberated with feces, urine, sputum
humans and their medical significance as well as 2. Larvae maybe sucked from circulation by
their importance in human communities liberating agent such as flies and mosquitoes
3. Larvae may leave out with products of
Tropical Medicine suppuration coming out from ulcers
Branch of medicine which deals with tropical 4. Larvae may be ingested with flesh of the
diseases and other medical problems of tropical intermediate host by the ultimate host
regions
Mechanisms of Pathogenesis
Epidemiology A. General Life Cycle
Body of knowledge concerning disease in human Parasite host migrate to location for
population or community maturation reproduce parasite
Host B. Factors that determine intensity of Parasite
Organism which provides food and shelter for Infection
parasites 1. Topography of locality – low-fat areas with warm
moist soil
Habitat 2. Faulty sanitary and hygienic measures
Natural abode of parasites 3. Poor social condition
4. Young age
Opportunistic parasites 5. Presence of intermediate host
Parasites which are not normally pathogens but 6. Custom of people
become so due to impairment of the host
resistance C. How Parasites Damage the Host
1. Toxic or Lytic
Vectors o Produce lysis of mucosa
responsible for transmitting the parasite from o Production of lytic enzyme – ulcer of
one host to another stomach
insect that carries the infective stage of an o Ex. Entamoeba histolytica
2. Traumatic
organism to another person
o Actual destruction by biting or eating up
o Destruction brought about by
Divisions of Medical Parasitology
mechanical or lytic or toxic substances
I. Protozoology
3. Mechanical destruction
II. Helminthology
o Ball of Ascaris
A. Roundworms (Nematodes)
4. Migration to delicate organs
B. Flatworms (Trematodes & Cestodes)
o Ascaris from intestine to bile duct to the
III. Medical Entomology (Arthropods)
liver
5. Complicating Factor
Type of Parasite according to the Position in the Host
o Perforation of Ulceration
1. Ectoparasite
6. Obstruction of Food
o organism which lives and develops
o Ex. Taenia solium
outside the body of the host
7. Irritative or Inflammatory
2. Endoparasite
o Trichuris trichuria
o organism which lives and develops
8. Excessive reproduction
inside the body of the host
9. Specific pathogenicity
Ut In Omnibus Glorificetur Deus Page 1 of 2
OLFU College of Medicine Class 2015
Parasitology Lecture 1: Introduction to Parasitology
Dr. Mateo June 22, 2012
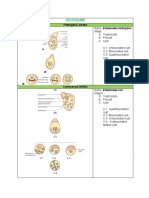
Sources of Exposure B. Portal of Exit
1. Contaminated soil 1. Feces
o A. lumbricoides o mostly all kinds of parasite
o T. trichuria 2. Urine
o Stronglyoides stercoralis o Trichomonas vaginalis
o Hookworms o Strongyloides stercoralis
2. Contaminated water o Schistosoma hematobium
o Amoeba 3. Sputum
o Flagellates o Paragonimus westermani
o blood flukes o Ascaris lumbricoides
o Taenia solium 4. Discharges
3. Food containing the immature infective stage o from cervix Trichomonas vaginalis
of the parasite o Drancunculus medinensis
o Fish, crab snail tapeworms, Capillaria
o Beef, pork Taenia, Trichinella Mode of Living of Parasites
4. Blood-sucking insect 1. Facultative
o Malaria o Organisms which may live either as a
o Leishmania parasitic or free-living existence under
o Trypanosoma favorable or appropriate circumstances
5. Domestic or wild animal harboring the 2. Temporary
parasite o Lives on the host only for a short period
o Dogs Dipylidum caninum of time
o Cats Toxocara cati 3. Permanent
o Herbivorous animals Trichostrongylus o Remains on or in the body of the host
6. Another person, his clothing, bedding or for its entire life
immediate environment that he has 4. Periodic
contaminated o When parasite is in its larval stage, it
o Entamoeba histolytica develops in a host that is different that
o Enterobius vermicularis of an adult
o scabies 5. Obligatory
7. Oneself/Auto-infection o Need a host at some stage of their life
o Enterobius vermicularis cycle to complete their development and
o Strongyloides stercoralis to propagate their species
6. Transitory
Mode of Transmission o When parasite passes
7. Incidental
A. Portal of Entry o A parasite which establishes itself in a
1. Mouth host where it does not ordinarily live
2. Skin penetration from the soil, fresh water 8. Pathogenic
o Necator o Parasite during its association with the
o Ancyclostoma host may cause certain local or general
3. percutaneously by blood-sucking insects body changes
o Plasmodium
4. Inhalation of airborne eggs
o E. vermicularis
5. Transplacental
o A. lumbricoides
o T. gondii
o Plasmodium
6. Transmammary
o Strongyloides
o Ancyclostoma
o Plasmodium
7. Sexual intercourse
o Trichomonas vaginalis
Jamie Sebastian
Ut In Omnibus Glorificetur Deus Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- Coventry 06.2012Document14 pagesCoventry 06.2012karan270No ratings yet
- Hesi Psych Study GuideDocument16 pagesHesi Psych Study GuideR100% (17)
- MCQ Trop-Med All - KARUNDocument23 pagesMCQ Trop-Med All - KARUNDapot SianiparNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics Midterms Rationale 2nd Sem 2018 2019Document21 pagesObstetrics Midterms Rationale 2nd Sem 2018 2019Gene Paulo UyNo ratings yet
- 1.entamoeba Histolytica - Is The Major Pathogen in This GroupDocument14 pages1.entamoeba Histolytica - Is The Major Pathogen in This GroupJoseph De JoyaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Lab Midterms Transes PDFDocument3 pagesParasitology Lab Midterms Transes PDFLouisse Anne Monique CayloNo ratings yet
- Parasitology 2019 Lecture Notes: Prepared By: Ariane T. Laranang, RMT, MT (Ascpi), MSMTDocument39 pagesParasitology 2019 Lecture Notes: Prepared By: Ariane T. Laranang, RMT, MT (Ascpi), MSMTShane Ann RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 3.5 PHARMA ANTI MYCOBACTERIAL AGENTSpdfDocument18 pages3.5 PHARMA ANTI MYCOBACTERIAL AGENTSpdfJanet SantosNo ratings yet
- ParasitologyDocument3 pagesParasitologyKCSotelo_xxviiNo ratings yet
- Merged PDF 2021 11 16T12 - 01 - 01Document15 pagesMerged PDF 2021 11 16T12 - 01 - 01Ericsson CarabbacanNo ratings yet
- Par201 S1lab4 Midterm Phamids Aphasmids PDFDocument27 pagesPar201 S1lab4 Midterm Phamids Aphasmids PDFHanna Alyssa Grace DimarananNo ratings yet
- Bates Chapter 8 Lung and ThoraxDocument15 pagesBates Chapter 8 Lung and ThoraxAdrian CaballesNo ratings yet
- Preventive MedicineDocument106 pagesPreventive Medicinemain.genevive.diligNo ratings yet
- RMTnotes PARASITOLOGYDocument68 pagesRMTnotes PARASITOLOGYArvin O-CaféNo ratings yet
- PARA 1.03 Nematodes I - Dra. Chiong-RiveraDocument14 pagesPARA 1.03 Nematodes I - Dra. Chiong-RiveraTMC PGI GENER MICKONo ratings yet
- Microbial Diseases of The Nervous System: DR Sonnie P. Talavera 08162009 OlfuDocument162 pagesMicrobial Diseases of The Nervous System: DR Sonnie P. Talavera 08162009 Olfuone_nd_onlyu0% (1)
- Oral Revalida ReviewerDocument10 pagesOral Revalida RevieweranneNo ratings yet
- Nematodes: 2B - MicrobiomanDocument41 pagesNematodes: 2B - Microbioman2013SecBNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Urine and Other Body Fluids - , RMT Sputum & Bronchoalveolar Lavage (Bal)Document11 pagesAnalysis of Urine and Other Body Fluids - , RMT Sputum & Bronchoalveolar Lavage (Bal)jeffreyNo ratings yet
- Medical Parasitology in The Philippines (Belizario, de Leon) - Pages-307-340Document34 pagesMedical Parasitology in The Philippines (Belizario, de Leon) - Pages-307-340Mae Rose Charlene MendozaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Laboratory Questionnaires 2TDocument21 pagesParasitology Laboratory Questionnaires 2TJen CANo ratings yet
- Biochemistry (1-20)Document30 pagesBiochemistry (1-20)Stetho LoveNo ratings yet
- Parasitic AmoebaDocument23 pagesParasitic AmoebaJethrö MallariNo ratings yet
- Nematode Common Name Associated Disease Mode of Transmission Habitat Definitive Host Intermediate HostDocument5 pagesNematode Common Name Associated Disease Mode of Transmission Habitat Definitive Host Intermediate HostAnjelo PerenNo ratings yet
- ReviewersDocument1 pageReviewersRalph Renon CasamayorNo ratings yet
- Giardiasis PDFDocument14 pagesGiardiasis PDFSaad Motawéa0% (1)
- CELL OVERVIEW PREVENTION Notes 2015Document7 pagesCELL OVERVIEW PREVENTION Notes 2015Alexander LukashenkoNo ratings yet
- Activity Tabulation ParasitologyDocument18 pagesActivity Tabulation ParasitologyStephen YorNo ratings yet
- Rash Fever DDXDocument7 pagesRash Fever DDXirsaNo ratings yet
- CestodesDocument7 pagesCestodesRubenson CantigaNo ratings yet
- Leukocytes, Granulocytes, The Monocyte-Macrophage System, and InflammationDocument10 pagesLeukocytes, Granulocytes, The Monocyte-Macrophage System, and InflammationShi no MeNo ratings yet
- Parasitic Infection in GI TractDocument123 pagesParasitic Infection in GI TractUtami HandayaniNo ratings yet
- Nematodes: Specie Infecti VE Stage Diagnos TIC Stage Morphology Pathogen Esis Diagnosi S Treatme NT Life CycleDocument4 pagesNematodes: Specie Infecti VE Stage Diagnos TIC Stage Morphology Pathogen Esis Diagnosi S Treatme NT Life CycleMarinelle TumanguilNo ratings yet
- Parasitology NotesDocument5 pagesParasitology NotesAyaAlforque100% (1)
- Trematodes: Blood FlukesDocument3 pagesTrematodes: Blood FlukesFrance Louie JutizNo ratings yet
- Parasite Trematodes PDFDocument2 pagesParasite Trematodes PDFGougle MuteNo ratings yet
- MED1 Samplex Rationale 9 - Breast ExaminationDocument4 pagesMED1 Samplex Rationale 9 - Breast ExaminationMartina GarciaNo ratings yet
- Plasmodium Vivax Plasmodium Ovale Plasmodium Malariae Plasmodium FalciparumDocument2 pagesPlasmodium Vivax Plasmodium Ovale Plasmodium Malariae Plasmodium FalciparumJulia SinajonNo ratings yet
- Legal Medicine and Medical Jurisprudence Comprehensive Exam ReviewerDocument17 pagesLegal Medicine and Medical Jurisprudence Comprehensive Exam ReviewerYeshua Tura100% (1)
- 2 Parasitology Parasitic AmoebasDocument8 pages2 Parasitology Parasitic AmoebasknkjnNo ratings yet
- Trematodes Outline L. MDocument1 pageTrematodes Outline L. MleoNo ratings yet
- Summary Table - TrematodesDocument4 pagesSummary Table - TrematodesNeil Joshua SuyatNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - General Properties and Classification of FungiDocument4 pagesLecture 1 - General Properties and Classification of FungiRemelou Garchitorena AlfelorNo ratings yet
- Day 1 BacteriaDocument251 pagesDay 1 BacteriaLisa NetherlandNo ratings yet
- Nematodes-Reviewer (Revised)Document4 pagesNematodes-Reviewer (Revised)Primo GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Trematodes Schistosoma Spp. General CharacteristicsDocument3 pagesTrematodes Schistosoma Spp. General CharacteristicsGlenn PerezNo ratings yet
- Parasitology TableDocument9 pagesParasitology TablehumanupgradeNo ratings yet
- pm2 TREMATODESDocument39 pagespm2 TREMATODESshastaNo ratings yet
- Summary TrematodesDocument3 pagesSummary TrematodesJ Pao Bayro - LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- Tissue and Blood NematodesDocument53 pagesTissue and Blood NematodesVincent ManganaanNo ratings yet
- The Ameba ReportingDocument49 pagesThe Ameba ReportingALLISON PAMITTANNo ratings yet
- Topnotch Waiver Oath and Checklist April 2015 PDFDocument2 pagesTopnotch Waiver Oath and Checklist April 2015 PDFRalph JuicoNo ratings yet
- Wuchereria Bancrofti Brugia Malayi Loa Loa Onchocerca Volvulus Mansonella Perstans Mansonella Ozzardi Dracunculus MedinensisDocument4 pagesWuchereria Bancrofti Brugia Malayi Loa Loa Onchocerca Volvulus Mansonella Perstans Mansonella Ozzardi Dracunculus MedinensisJoshua TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Microbiology - : University of Santo Tomas - Medical TechnologyDocument6 pagesDiagnostic Microbiology - : University of Santo Tomas - Medical TechnologyWynlor AbarcaNo ratings yet
- Preventive MedDocument74 pagesPreventive MedSherlock HolmesNo ratings yet
- MBR 2019 - CNS Pathology HandoutDocument6 pagesMBR 2019 - CNS Pathology HandoutNica Lopez FernandezNo ratings yet
- ParasitologyLec 3 Nematodes 2 PDFDocument6 pagesParasitologyLec 3 Nematodes 2 PDFDJ RelojNo ratings yet
- (Parasitology) Prelim-Final Reviewer 2015Document13 pages(Parasitology) Prelim-Final Reviewer 2015Andrassy Twinkle Alinea100% (1)
- 1-2. - Introduction-PARA-LecDocument6 pages1-2. - Introduction-PARA-LecLian MallareNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - TransDocument8 pagesModule 1 - TransJohanna Kate DiestroNo ratings yet
- Parasitology. ProtozoaDocument23 pagesParasitology. ProtozoaGelo mirandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Intro To Med. ParasitologyDocument7 pagesChapter 1 Intro To Med. ParasitologyFrances Riane SimoyNo ratings yet
- F Occlusal Therapy in Prosthodontics FinalDocument17 pagesF Occlusal Therapy in Prosthodontics FinalJyoti TripathiNo ratings yet
- Dyslipidemia 2023Document39 pagesDyslipidemia 2023medt80No ratings yet
- Jurnal Carpal Tunnel SyndromeDocument11 pagesJurnal Carpal Tunnel SyndromeArjuna MarzaNo ratings yet
- Gingival InflammationDocument19 pagesGingival InflammationmirfanulhaqNo ratings yet
- I Can'T Breathe If Breathing Is Without: Bronchial AsthmaDocument33 pagesI Can'T Breathe If Breathing Is Without: Bronchial AsthmaklamorenaNo ratings yet
- Case Record Form For ChildrenDocument32 pagesCase Record Form For ChildrenPrasad javvajiNo ratings yet
- ANTH QUIZZES & EXAM 1 Midterm Question PoolDocument41 pagesANTH QUIZZES & EXAM 1 Midterm Question PoolSaumier Stables67% (3)
- Planet Karak Short List by OPVDocument76 pagesPlanet Karak Short List by OPVKumar100% (1)
- PCOL TRivias 2Document3 pagesPCOL TRivias 2Maria Izabelle QuemiNo ratings yet
- Digital Revolution in Healthcare - EPSA AA '17 - Daniel Vertessy - 2Document34 pagesDigital Revolution in Healthcare - EPSA AA '17 - Daniel Vertessy - 2Karlo ŽiliNo ratings yet
- Data Quality - Facilitators Manual FINAL - July242018Document78 pagesData Quality - Facilitators Manual FINAL - July242018Ambaasaaddara Kiristoosiin Addunyaarratti MuudameNo ratings yet
- Sistrunk Operation ArticleDocument4 pagesSistrunk Operation Articleআবু আব্দুল্লাহ শাদীদNo ratings yet
- Y. Hirschfeld, The Crisis of The Sixth Century. Climatic Change, Natural Disasters and The PlagueDocument8 pagesY. Hirschfeld, The Crisis of The Sixth Century. Climatic Change, Natural Disasters and The PlagueedinjuveNo ratings yet
- Biogenic Amines by HPLCDocument7 pagesBiogenic Amines by HPLCNeidys SanchezNo ratings yet
- Vital Sign #1: Body TemperatureDocument5 pagesVital Sign #1: Body TemperaturePrimelift Safety Resources LimitedNo ratings yet
- JSA Excavation For Lighting Pole FoundationDocument18 pagesJSA Excavation For Lighting Pole FoundationMohammad Al Masa'deh100% (1)
- Idsr Implementation PDFDocument4 pagesIdsr Implementation PDFamaha alemayehuNo ratings yet
- Lapsal Juni 2016 Arief BrownDocument427 pagesLapsal Juni 2016 Arief BrownZainalArifinNo ratings yet
- Coex + MatriciDocument5 pagesCoex + MatricivalentinnNo ratings yet
- Lab HistoryDocument8 pagesLab HistoryAlbin StigoNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Mouth Breathing and Maxillary Anterior ProclinationDocument4 pagesTreatment of Mouth Breathing and Maxillary Anterior ProclinationVaniaNo ratings yet
- Tplasty AishwaryaDocument2 pagesTplasty Aishwaryaankitkawale111No ratings yet
- 1114-Article Text-2259-1-10-20210503Document10 pages1114-Article Text-2259-1-10-20210503Guna SoundariNo ratings yet
- Applications of MicrobiologyDocument5 pagesApplications of MicrobiologyLloyd LozanoNo ratings yet
- First Year B.Sc. Nursing Question Paper 2009Document15 pagesFirst Year B.Sc. Nursing Question Paper 2009Biju Antony100% (7)
- Ecology Action Research Project FinalDocument13 pagesEcology Action Research Project Finalapi-357358935No ratings yet
- yudaturana,+Manajer+Jurnal,+dr +nelson+rev+2+ (162-172)Document12 pagesyudaturana,+Manajer+Jurnal,+dr +nelson+rev+2+ (162-172)Fath TiaraNo ratings yet
- Jeong Et Al-2001-Nature PDFDocument2 pagesJeong Et Al-2001-Nature PDFThibextraNo ratings yet