Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tugas 1 MS2230 Sem II 17-18 Total
Tugas 1 MS2230 Sem II 17-18 Total
Uploaded by
Admin AspirasiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- PS Compilation For 2019Document10 pagesPS Compilation For 2019Nicole RamirezNo ratings yet
- Final Exam AT 2018 AnsDocument8 pagesFinal Exam AT 2018 AnsHassan AzouzNo ratings yet
- Termodinamik I Ornek Sorular 2 (Ilk 4 Unite)Document33 pagesTermodinamik I Ornek Sorular 2 (Ilk 4 Unite)llHA ZYllNo ratings yet
- Physics I ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9Document4 pagesTutorial 9Jyoti Krishna PandaNo ratings yet
- Tarea No 7 ExergiaDocument3 pagesTarea No 7 ExergiaAndres RomeroNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Cengel ProblemsDocument3 pagesThermodynamics Cengel ProblemsHaardikGargNo ratings yet
- Assignment AETDDocument2 pagesAssignment AETDPratham M JariwalaNo ratings yet
- BT Quiz - 2Document8 pagesBT Quiz - 2Navdha KapoorNo ratings yet
- Tut 6,7,8 - 2013Document3 pagesTut 6,7,8 - 2013SourabhNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Thermo I PDF 1Document13 pagesWorksheet Thermo I PDF 1roba angasuNo ratings yet
- MEE 302 - Tutorial 1Document2 pagesMEE 302 - Tutorial 1acemumbiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2Angelina PutriNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument3 pagesThermopranavNo ratings yet
- Thapar University, Patiala Thermofluids (Ues011) Tutorial Sheet No.5 Faculty: GCH, HPB, RKG, SMB, NS, PMS 1)Document2 pagesThapar University, Patiala Thermofluids (Ues011) Tutorial Sheet No.5 Faculty: GCH, HPB, RKG, SMB, NS, PMS 1)s barmanNo ratings yet
- Maae 3400: Applied Thermodynamics Problem Set 1Document4 pagesMaae 3400: Applied Thermodynamics Problem Set 1minyoun0% (1)
- Vtu Previous Year Question PapersDocument26 pagesVtu Previous Year Question Papersprashanth prabhuNo ratings yet
- TASKDocument1 pageTASKDaniiarNo ratings yet
- ESO201 IIT AssignmentDocument4 pagesESO201 IIT AssignmentSunitNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - QuestionsDocument5 pagesTutorial 1 - Questions2200851No ratings yet
- Thermo Qbank2Document8 pagesThermo Qbank2atmiyabhalodiNo ratings yet
- ETD - Question BankDocument6 pagesETD - Question BankGopinath VNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document3 pagesAssignment 3Akatew Haile MebrahtuNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 1Document2 pagesAssignment No 1Fikrie MuhdNo ratings yet
- TD Thermo GTIERDocument14 pagesTD Thermo GTIERAHMED AL MERSNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1, Autumn 2023Document2 pagesAssignment 1, Autumn 2023cocodarshi2022No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document1 pageChapter 5Train DiskenthNo ratings yet
- 062 - ME8391 ME6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Question BankDocument12 pages062 - ME8391 ME6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Question BankAjay KaviNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 2021 FinalDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 2021 FinalRichard GrahamNo ratings yet
- CHMT3040 2022 Semester Test 21 April 2022Document3 pagesCHMT3040 2022 Semester Test 21 April 2022Buyisile NyongwanaNo ratings yet
- Assignment-4 ModDocument2 pagesAssignment-4 ModSai naveenNo ratings yet
- Me6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - May June 2016Document4 pagesMe6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - May June 2016BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 2: Dr. Gamal NadaDocument3 pagesThermodynamics 2: Dr. Gamal NadaEmptySilenceNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction DesignDocument3 pagesChemical Reaction DesignZohaib AliNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet 3 Heat, Work and The First Law of Thermodynamics PDFDocument4 pagesProblem Sheet 3 Heat, Work and The First Law of Thermodynamics PDFS DNo ratings yet
- II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Dec - 2015 ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesII B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Dec - 2015 ThermodynamicsAshok DaraNo ratings yet
- 16TF603 Entropy AssignmentDocument2 pages16TF603 Entropy AssignmentMd Sharique AkhtarNo ratings yet
- 05-1-Collection of Problems PDFDocument15 pages05-1-Collection of Problems PDFFistia MaulinaNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument3 pagesThermoAmrinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment#3Document2 pagesAssignment#3Ashish ManwarNo ratings yet
- ME214 BTD Tutorial QuestionsDocument2 pagesME214 BTD Tutorial QuestionsKONDALRAONo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument3 pagesQuestionsVinoth BillaNo ratings yet
- QUESTION BANK ThermodynamicsDocument9 pagesQUESTION BANK Thermodynamicsvikas_1989No ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering Department of Mechanical and Marine Engineering Thermodynamics (TDN620S)Document4 pagesFaculty of Engineering Department of Mechanical and Marine Engineering Thermodynamics (TDN620S)Wilbard IitulaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 5Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 5Syed YousufuddinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document1 pageTutorial 3B V V HANUMA GAYATHRINo ratings yet
- ME6301-Engineering Thermodynamics 2013 RegulationDocument12 pagesME6301-Engineering Thermodynamics 2013 RegulationLogesh LoganNo ratings yet
- Examples On Chapter Four (Thermodynamics) : Answers: (A) 2.08, (B) 1110 Kj/minDocument2 pagesExamples On Chapter Four (Thermodynamics) : Answers: (A) 2.08, (B) 1110 Kj/minGODNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment 5 PDFkiruba karanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document2 pagesAssignment 5kiruba karanNo ratings yet
- Modul 3Document3 pagesModul 3Anonymous OecsqTANo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics ReviewDocument5 pagesChemical Engineering Thermodynamics ReviewGeorge Isaac McQuiles100% (2)
- Assignment For G2E 2 1Document2 pagesAssignment For G2E 2 1achok williamNo ratings yet
- AssyDocument2 pagesAssyNithishkumar BaskerNo ratings yet
- B.Tech II Year II Semester (R19) Supplementary Examinations March 2022Document2 pagesB.Tech II Year II Semester (R19) Supplementary Examinations March 2022MECH HODNo ratings yet
- 16.050 Thermal Energy: Page 1 of 2Document2 pages16.050 Thermal Energy: Page 1 of 2ZeroRecoNo ratings yet
- At Least TWO Questions From Each Part. Data Hand Book and Steam Tables Is PermittedDocument2 pagesAt Least TWO Questions From Each Part. Data Hand Book and Steam Tables Is PermittedPruthvi HareeshNo ratings yet
- HW 4 (2) Thermo UEM Aerospace 2021Document2 pagesHW 4 (2) Thermo UEM Aerospace 2021Marina Gil JimenezNo ratings yet
- Tutorial ExergyDocument3 pagesTutorial Exergyمحمد خالدNo ratings yet
Tugas 1 MS2230 Sem II 17-18 Total
Tugas 1 MS2230 Sem II 17-18 Total
Uploaded by
Admin AspirasiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tugas 1 MS2230 Sem II 17-18 Total
Tugas 1 MS2230 Sem II 17-18 Total
Uploaded by
Admin AspirasiCopyright:
Available Formats
MS2230 ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS II
Assignment 1, should be done individually
Must be submitted on Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2018, before 80:00 a.m. at Thermodynamics
Lab.
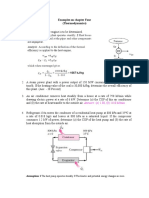
1. A 12-ft3 rigid tank contains refrigerant-134a at 40 psia and 60 percent quality. Heat is
transferred now to the refrigerant from a source at 120°F until the pressure rises to 60
psia. Assuming the surroundings to be at 75°F, determine (a) the amount of heat transfer
between the source and the refrigerant and (b) the exergy destroyed during this process.
2. The electric power needs of a community in a beach are to be met by wind turbines with
10-m-diameter rotors. The wind turbines are to be located where the wind is blowing
steadily at an average velocity of 8 m/s. Determine power exergy of each wind turbine
and the minimum number of the wind turbines that need to be installed if the required
power output is 500 kW. Take properties of the air at a standard condition 1 atm and 25oC.
3. One kmol of carbon dioxide gas is contained in a 4 m 3 rigid, insulated vessel initially at 4
bar. An electric resistor with negligible mass transfer energy to the gas at constant rate of
12 kW for 1 minute. Employing the ideal gas model and ignoring the effects of motion
and gravity, determine: (a) the change of exergy of the gas, (b) the electrical work, (c) the
exergy destruction. Let T0 = 20oC, and p0 = 1 bar.
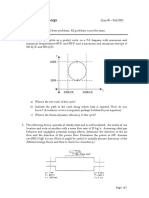
4. The right figure shows a turbine operating at
steady state and fluid properties at the entrance
and exits of the turbine. Stray heat transfer and the
effects of motion and gravity are negligible. Let T0
= 25oC, and p0 = 1 bar. Determine the power
developed and rate of exergy destruction of the
turbine. Evaluate an exergetic efficiency of the
turbine.
Good Luck
You might also like
- PS Compilation For 2019Document10 pagesPS Compilation For 2019Nicole RamirezNo ratings yet
- Final Exam AT 2018 AnsDocument8 pagesFinal Exam AT 2018 AnsHassan AzouzNo ratings yet
- Termodinamik I Ornek Sorular 2 (Ilk 4 Unite)Document33 pagesTermodinamik I Ornek Sorular 2 (Ilk 4 Unite)llHA ZYllNo ratings yet
- Physics I ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9Document4 pagesTutorial 9Jyoti Krishna PandaNo ratings yet
- Tarea No 7 ExergiaDocument3 pagesTarea No 7 ExergiaAndres RomeroNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Cengel ProblemsDocument3 pagesThermodynamics Cengel ProblemsHaardikGargNo ratings yet
- Assignment AETDDocument2 pagesAssignment AETDPratham M JariwalaNo ratings yet
- BT Quiz - 2Document8 pagesBT Quiz - 2Navdha KapoorNo ratings yet
- Tut 6,7,8 - 2013Document3 pagesTut 6,7,8 - 2013SourabhNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Thermo I PDF 1Document13 pagesWorksheet Thermo I PDF 1roba angasuNo ratings yet
- MEE 302 - Tutorial 1Document2 pagesMEE 302 - Tutorial 1acemumbiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2Angelina PutriNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument3 pagesThermopranavNo ratings yet
- Thapar University, Patiala Thermofluids (Ues011) Tutorial Sheet No.5 Faculty: GCH, HPB, RKG, SMB, NS, PMS 1)Document2 pagesThapar University, Patiala Thermofluids (Ues011) Tutorial Sheet No.5 Faculty: GCH, HPB, RKG, SMB, NS, PMS 1)s barmanNo ratings yet
- Maae 3400: Applied Thermodynamics Problem Set 1Document4 pagesMaae 3400: Applied Thermodynamics Problem Set 1minyoun0% (1)
- Vtu Previous Year Question PapersDocument26 pagesVtu Previous Year Question Papersprashanth prabhuNo ratings yet
- TASKDocument1 pageTASKDaniiarNo ratings yet
- ESO201 IIT AssignmentDocument4 pagesESO201 IIT AssignmentSunitNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - QuestionsDocument5 pagesTutorial 1 - Questions2200851No ratings yet
- Thermo Qbank2Document8 pagesThermo Qbank2atmiyabhalodiNo ratings yet
- ETD - Question BankDocument6 pagesETD - Question BankGopinath VNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document3 pagesAssignment 3Akatew Haile MebrahtuNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 1Document2 pagesAssignment No 1Fikrie MuhdNo ratings yet
- TD Thermo GTIERDocument14 pagesTD Thermo GTIERAHMED AL MERSNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1, Autumn 2023Document2 pagesAssignment 1, Autumn 2023cocodarshi2022No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document1 pageChapter 5Train DiskenthNo ratings yet
- 062 - ME8391 ME6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Question BankDocument12 pages062 - ME8391 ME6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Question BankAjay KaviNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 2021 FinalDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 2021 FinalRichard GrahamNo ratings yet
- CHMT3040 2022 Semester Test 21 April 2022Document3 pagesCHMT3040 2022 Semester Test 21 April 2022Buyisile NyongwanaNo ratings yet
- Assignment-4 ModDocument2 pagesAssignment-4 ModSai naveenNo ratings yet
- Me6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - May June 2016Document4 pagesMe6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - May June 2016BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 2: Dr. Gamal NadaDocument3 pagesThermodynamics 2: Dr. Gamal NadaEmptySilenceNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction DesignDocument3 pagesChemical Reaction DesignZohaib AliNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet 3 Heat, Work and The First Law of Thermodynamics PDFDocument4 pagesProblem Sheet 3 Heat, Work and The First Law of Thermodynamics PDFS DNo ratings yet
- II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Dec - 2015 ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesII B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Dec - 2015 ThermodynamicsAshok DaraNo ratings yet
- 16TF603 Entropy AssignmentDocument2 pages16TF603 Entropy AssignmentMd Sharique AkhtarNo ratings yet
- 05-1-Collection of Problems PDFDocument15 pages05-1-Collection of Problems PDFFistia MaulinaNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument3 pagesThermoAmrinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment#3Document2 pagesAssignment#3Ashish ManwarNo ratings yet
- ME214 BTD Tutorial QuestionsDocument2 pagesME214 BTD Tutorial QuestionsKONDALRAONo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument3 pagesQuestionsVinoth BillaNo ratings yet
- QUESTION BANK ThermodynamicsDocument9 pagesQUESTION BANK Thermodynamicsvikas_1989No ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering Department of Mechanical and Marine Engineering Thermodynamics (TDN620S)Document4 pagesFaculty of Engineering Department of Mechanical and Marine Engineering Thermodynamics (TDN620S)Wilbard IitulaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 5Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 5Syed YousufuddinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document1 pageTutorial 3B V V HANUMA GAYATHRINo ratings yet
- ME6301-Engineering Thermodynamics 2013 RegulationDocument12 pagesME6301-Engineering Thermodynamics 2013 RegulationLogesh LoganNo ratings yet
- Examples On Chapter Four (Thermodynamics) : Answers: (A) 2.08, (B) 1110 Kj/minDocument2 pagesExamples On Chapter Four (Thermodynamics) : Answers: (A) 2.08, (B) 1110 Kj/minGODNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment 5 PDFkiruba karanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document2 pagesAssignment 5kiruba karanNo ratings yet
- Modul 3Document3 pagesModul 3Anonymous OecsqTANo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics ReviewDocument5 pagesChemical Engineering Thermodynamics ReviewGeorge Isaac McQuiles100% (2)
- Assignment For G2E 2 1Document2 pagesAssignment For G2E 2 1achok williamNo ratings yet
- AssyDocument2 pagesAssyNithishkumar BaskerNo ratings yet
- B.Tech II Year II Semester (R19) Supplementary Examinations March 2022Document2 pagesB.Tech II Year II Semester (R19) Supplementary Examinations March 2022MECH HODNo ratings yet
- 16.050 Thermal Energy: Page 1 of 2Document2 pages16.050 Thermal Energy: Page 1 of 2ZeroRecoNo ratings yet
- At Least TWO Questions From Each Part. Data Hand Book and Steam Tables Is PermittedDocument2 pagesAt Least TWO Questions From Each Part. Data Hand Book and Steam Tables Is PermittedPruthvi HareeshNo ratings yet
- HW 4 (2) Thermo UEM Aerospace 2021Document2 pagesHW 4 (2) Thermo UEM Aerospace 2021Marina Gil JimenezNo ratings yet
- Tutorial ExergyDocument3 pagesTutorial Exergyمحمد خالدNo ratings yet