Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Uploaded by
Farina Acosta0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views2 pagesVitamin B12 deficiency can cause megaloblastic anemia and neurological symptoms. It is most commonly caused by malabsorption due to conditions like pernicious anemia or intestinal diseases. Testing for vitamin B12 deficiency includes measuring serum B12 levels, methylmalonic acid, homocysteine, and the deoxyuridine suppression test. Holotranscobalamin may be a more sensitive indicator of deficiency compared to total serum B12.
Original Description:
vitamin b12
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentVitamin B12 deficiency can cause megaloblastic anemia and neurological symptoms. It is most commonly caused by malabsorption due to conditions like pernicious anemia or intestinal diseases. Testing for vitamin B12 deficiency includes measuring serum B12 levels, methylmalonic acid, homocysteine, and the deoxyuridine suppression test. Holotranscobalamin may be a more sensitive indicator of deficiency compared to total serum B12.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views2 pagesVitamin B12 Deficiency
Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Uploaded by
Farina AcostaVitamin B12 deficiency can cause megaloblastic anemia and neurological symptoms. It is most commonly caused by malabsorption due to conditions like pernicious anemia or intestinal diseases. Testing for vitamin B12 deficiency includes measuring serum B12 levels, methylmalonic acid, homocysteine, and the deoxyuridine suppression test. Holotranscobalamin may be a more sensitive indicator of deficiency compared to total serum B12.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Vitamin B12 Deficiency vitamin B12 will be absorbed, the proportion falling
markedly with higher doses.
Definition of terms 5. The enterocytes have a refractory period of about 6
h before they can absorb any more vitamin B 12.
1. Megaloblastic anaemia - give rise to characteristic
6. Within the enterocyte, the vitamin B12 is liberated
morphological appearances: the red cells are
and, after binding to the β-globulin carrier
macrocytic and hypersegmented neutrophils are transcobalamin II (TCII), is released into the blood.
present. Ineffective erythropoiesis is apparent 7. The TCII–vitamin B12 complex is termed
‘holotranscobalamin’.
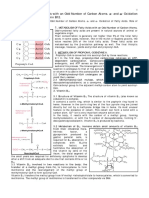
Structure of Vit B12
8. Transcobalamin II readily releases the vitamin B12 to
1. The vitamin B12 (cobalamin) molecule is centred on the bone marrow and other tissues, and, for this
an atom of cobalt; this is the only known function of reason, holotranscobalamin is also described as
cobalt in humans. ‘active B12’.
9. Other transcobalamins also exist; transcobalamin I
2. Vitamin B12 is mainly contained within the
and III derive mainly from specific granules found
mitochondria in the 5′-deoxyadenosyl form, where
in neutrophils and bind vitaminB12 tightly, in
it plays a role in the conversion of l-methylmalonyl- contrast to TCII, and do not release it into the
CoA to succinyl-CoA. tissues.
3. The other main form, methylcobalamin, is found 10. Congenital TCII deficiency can occur, the affected
within the cytoplasm and plasma where it is a infant presenting with megaloblastic anaemia a few
cofactor for the conversion of homocysteine to weeks after birth.
methionine, a vital part of the pathway that creates a
universal methyl donor Causes of vitamin B12 deficiency
1. Nutritional: this is rare and is only seen in very strict
Source of vitamin B12. vegans.
1. Vitamin B12 is synthesized only by microorganisms 2. Malabsorption: the commonest cause of vitamin
and the only source for humans is food of animal B12 malabsorption is the autoimmune condition,
origin. pernicious anaemia, where gastric atrophy develops
2. Liver is the richest source of vitamin B12, but it is secondary to an inflammatory infiltrate.
present in almost all animal products, including Autoantibodies to gastric parietal cells are seen in
milk. 90% of individuals with the condition and 50%
3. No vegetable food source contains significant develop IF autoantibodies, which either prevent
amounts of vitamin B12 unless contaminated by vitamin B12–IF complex formation (binding
bacteria antibodies) or the subsequent attachment of the
vitamin B12 to the enterocyte mucosa (blocking
Vitamin B12 requirements. antibodies).
1. An adult human requires only 1 μg of vitamin B12 3. Gastric causes: such as total or partial gastrectomy.
per 24 h and has stores of 2–3 mg. 4. Intestinal causes: ileal resection and diseases of the
2. Thus, it can take 3–4 years for vitamin B12 terminal ileum such as Crohn disease or tropical
deficiency to develop sprue prevent vitamin B12 absorption. Deficiency is
also associated with intestinal blind loop syndrome
Absorption of vitamin B12. (because of metabolism of the vitamin B12 by the
1. Dietary vitamin B12 is bound to food proteins and overgrowth of intestinal bacteria) and fish tapeworm
must be freed by gastric acid. Acid pH and pepsin (Diphyllobothrium latum), which binds cobalamin,
release cobalamin. preventing its absorption.
2. The parietal cells of the stomach secrete the 5. Acquired: prolonged nitrous oxide exposure
glycoprotein intrinsic factor (IF), which combines oxidizes methylcobalamin to an inactive state and
with vitamin B12 to form a complex, which resists results in functional vitamin B12 deficiency. This
proteolytic digestion. has been seen in dentists and anaesthetists.
3. The vitamin B12–IF complex passes through the Metformin may be associated with low serum
small intestine until it binds to cubilin, a surface vitamin B12 concentrations. The exact mechanism
receptor on the enterocytes of the terminal ileum, for this is unknown but it has been postulated to be
where it is internalized. caused by metformin interfering with the calcium
4. The enterocytes of the ileum have a limited capacity dependent channels responsible for the ileal
to absorb vitamin B12 because of a limited number of absorption of the vitamin.
receptor sites; about half of a dose of 1 μg of
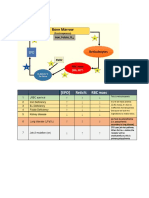
Features of vitamin B12 deficiency normal pregnancy. Measurement
Vitamin B12 is a coenzyme in the interconversion of the holotranscobalamin (TCII - bound vitamin B12, or
different forms of folate so its deficiency results in a ‘active B12’) may be a more sensitive and specific
megaloblastic anaemia identical to that seen in folate indicator of physiologically relevant vitamin B12
deficiency. deficiency.
Deficiency may also result in neurological symptoms (e.g. 2. Serum methylmalonate and homocysteine.
peripheral neuropathy, dysfunction of the posterior columns Vitamin B12 deficiency results in the elevation of
of the spinal cord and sometimes psychotic illnesses and methylmalonate and homocysteine concentrations
dementia). (see Fig. 27.6). However, concentrations of both
The precise mechanism for this has not been elucidated but compounds fluctuate and may be raised in renal
may be linked with impaired conversion of homocysteine to impairment, smoking and (on single occasions) in
methionine, resulting in either reduced availability of S- up to 30% of normal volunteers, making definition
adenosylmethionine impairing sphingomyelin synthesis or in of a specific cut-off level difficult.
the toxic accumulation of the homocysteine metabolite S- 3. Deoxyuridine suppression test. The conversion of
adenosylhomocysteine. deoxyuridine monophosphate (dUMP) to
deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP) during
DNA synthesis is by methyl group transfer,
facilitated by both vitamin B12 and folate. The other
source of dTMP is via phosphorylation of
deoxythymidine, catalysed by thymidine kinase,
which is subject to feedback inhibition by its
product, dTMP. Normal marrow, pre-incubated
with dUMP, successfully converts this to dTMP,
and incorporates less subsequently added tritiated
thymidine into DNA. If the marrow is deficient in
either vitamin B12 or folate, methyl group transfer
is reduced, so the cells have greater capacity to
incorporate tritiated thymidine into DNA following
pre-incubation with dUMP.
4. Antibody tests. Tests for the presence of antibodies
to gastric parietal cells are positive in 90% of
patients with pernicious anaemia; however, this test
is not specific as it is also positive in around 15% of
healthy elderly people. The presence of IF
antibodies is more specific but is found in only 50%
of patients with pernicious anaemia.
5.
Laboratory determination of vitamin B12 status
1. Serum vitamin B12. This is usually measured by
automated immunoassay. Normal concentrations
are 160–1000 ng/L. A low concentration is not
specific for vitamin B12 deficiency and may be found
in one-third of patients with folate deficiency and in
You might also like
- NCC-SickleCellAnemiaManagement ConceptMap InteractivePDFDocument2 pagesNCC-SickleCellAnemiaManagement ConceptMap InteractivePDFLoggerz Arck100% (1)
- Approach To Diagnosis of Haemolytic AnaemiasDocument2 pagesApproach To Diagnosis of Haemolytic AnaemiasGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Agents Used in Anemias 2Document25 pagesAgents Used in Anemias 2Raboha TawilNo ratings yet
- Macrocytic AnemiasDocument7 pagesMacrocytic AnemiasMohona Rahman KhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lec.2 (Vitamins 2)Document6 pagesChemistry Lec.2 (Vitamins 2)Muhammed AbdulsamadNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12Document19 pagesVitamin B12Hari PrasathNo ratings yet
- Chap139 PDFDocument3 pagesChap139 PDFvivianNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12:: A Water Soluble Hematopoietic VitaminDocument25 pagesVitamin B12:: A Water Soluble Hematopoietic Vitamindr. SheryarOrakzaiNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12: Harsha Vardhini.SDocument17 pagesVitamin B12: Harsha Vardhini.SScindiaaNo ratings yet
- Lec. B12Document94 pagesLec. B12Arshad Mehmood MinhasNo ratings yet
- Megaloblastic Anaemia Lecture 1Document6 pagesMegaloblastic Anaemia Lecture 1Nauzaina IjazNo ratings yet
- Nutrients: Vitamin B in Health and DiseaseDocument18 pagesNutrients: Vitamin B in Health and DiseaseSrinivas RajanalaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B: Chapter OutlineDocument18 pagesVitamin B: Chapter OutlineCỏPhongSươngNo ratings yet
- Vit B12Document6 pagesVit B12shereefadoma96No ratings yet
- Vitamin b12Document18 pagesVitamin b12api-3770131100% (1)
- Macrocytic Anemia - Megaloblastic AnemiaDocument42 pagesMacrocytic Anemia - Megaloblastic AnemiaDarien LiewNo ratings yet
- Megaloblastic AnemiasDocument37 pagesMegaloblastic AnemiasL3mi DNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5. Vitamin B12Document8 pagesChapter 5. Vitamin B12Ryn ShadowNo ratings yet
- Vitamin b12 Production - ParulDocument20 pagesVitamin b12 Production - Parulanon-90455980% (5)
- Elgar, 2022Document17 pagesElgar, 2022Caoimhe O'BrienNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12Document17 pagesVitamin B12madhujayarajNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12 and FolateDocument12 pagesVitamin B12 and FolateAllessandria DimaggioNo ratings yet
- Deficiencia de B12 PerspectivasDocument9 pagesDeficiencia de B12 PerspectivasMartínez Ramírez Brenda KarinaNo ratings yet
- Hema Chapter 21Document6 pagesHema Chapter 21EMETERIO TUTOR IIINo ratings yet
- 6.megaloblastic AnaemiasDocument34 pages6.megaloblastic AnaemiasWissam AlwazaniNo ratings yet
- Animal Nutrition and FeedingDocument16 pagesAnimal Nutrition and Feedingmarianette balucasNo ratings yet
- Nutrition For Anemia - ImunologiDocument75 pagesNutrition For Anemia - ImunologiZerry Reza SyahrulNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Macrocytic Anemia 2017Document40 pagesKuliah Macrocytic Anemia 2017igus696No ratings yet
- Vitamin B12, Demyelination, Remyelination and Repair in Multiple SclerosisDocument5 pagesVitamin B12, Demyelination, Remyelination and Repair in Multiple SclerosisMonica ViverosNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Anemia: Dr. Marlina Dewiastuti MkesDocument37 pagesNutrition in Anemia: Dr. Marlina Dewiastuti MkesPrimarini RiatiNo ratings yet
- Makalah MateriDocument17 pagesMakalah MateriRuwindaNo ratings yet
- Nutrients: Vitamin B in Health and DiseaseDocument18 pagesNutrients: Vitamin B in Health and DiseaseMuhammad FaqihNo ratings yet
- 3 - Metabolisme Vitamin B12 B9 CDocument49 pages3 - Metabolisme Vitamin B12 B9 CPaulinNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12: Properties and MetabolismDocument7 pagesVitamin B12: Properties and Metabolismkalaiarasi ravichandranNo ratings yet
- VitaminDocument32 pagesVitaminmohammed aliNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12Document16 pagesVitamin B12sadaq84No ratings yet
- Davao Medical School Foundation, Inc. ONE MED: EIKOSI 1A, 1B, 1C NMD 2020Document4 pagesDavao Medical School Foundation, Inc. ONE MED: EIKOSI 1A, 1B, 1C NMD 2020t4gjzhpfjcNo ratings yet
- Vitamin b12, Folic Acid, and TheDocument4 pagesVitamin b12, Folic Acid, and TheFAZRI MONo ratings yet
- VitaminDocument32 pagesVitaminmohammed aliNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12 ReviewDocument12 pagesVitamin B12 ReviewMunyaradzi Nhambure100% (1)
- Md. Riazuddin (MS - 210931) DocsDocument10 pagesMd. Riazuddin (MS - 210931) DocsMohona Rahman KhanNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12 in Vegetarian DietsDocument4 pagesVitamin B12 in Vegetarian DietsJesica DiazNo ratings yet
- b12 DefDocument7 pagesb12 DefSakina FatimaNo ratings yet
- Watanabe02 PDFDocument9 pagesWatanabe02 PDFsmartjohnsmith10No ratings yet
- Cobalamin: A Critical Vitamin in The ElderlyDocument11 pagesCobalamin: A Critical Vitamin in The ElderlyLuis ÓnidasNo ratings yet
- Workineh Case Studyy 1Document17 pagesWorkineh Case Studyy 1HABTAMU MOLLANo ratings yet
- Megaloblastic AnemiaDocument26 pagesMegaloblastic AnemiaAbdifatah Abdiwali mohamedNo ratings yet
- Materi V - Vitamin B12Document35 pagesMateri V - Vitamin B12Salwa Kamilia100% (1)
- Pharmacy Practice and Res - 2023 - Mouchaileh - Vitamin B12 Deficiency in Older People A Practical Approach To RecognitionDocument9 pagesPharmacy Practice and Res - 2023 - Mouchaileh - Vitamin B12 Deficiency in Older People A Practical Approach To RecognitionBiblioteca Medica HEPNo ratings yet
- Est - B12Document32 pagesEst - B12klinsman campuzanoNo ratings yet
- Megaloblastic AnaemiaDocument5 pagesMegaloblastic AnaemiaBhavya agarwalNo ratings yet
- .Vnendownloadssnibe-Maglumi-Vitamin-B12-Clia - PDF 2Document4 pages.Vnendownloadssnibe-Maglumi-Vitamin-B12-Clia - PDF 28f4rvb2ssgNo ratings yet
- Megaloblastic AnaemiaDocument11 pagesMegaloblastic AnaemiaJesmin_36No ratings yet
- Englec 29 Fa Odd 2021Document3 pagesEnglec 29 Fa Odd 2021Yannick fokaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12Document10 pagesVitamin B12api-388948078No ratings yet
- Macrocytic AnemiasDocument28 pagesMacrocytic AnemiasDeepankar SrigyanNo ratings yet
- Megaloblastic Anemia: Hematology - Chapter 21Document14 pagesMegaloblastic Anemia: Hematology - Chapter 21Matt McAndrew GarciaNo ratings yet
- Hoffbrand's Essential Haematology, 8e 2Document3 pagesHoffbrand's Essential Haematology, 8e 2Yasimini RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 - Anemia 4Document27 pagesTopic 9 - Anemia 4Vince Martin ManaigNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12 PDFDocument22 pagesVitamin B12 PDFjcoppala4476No ratings yet
- Megbl, Pernicious ADocument23 pagesMegbl, Pernicious Aacs.pathNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12 Deficiency, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandVitamin B12 Deficiency, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Complete Blood Count: at A GlanceDocument6 pagesComplete Blood Count: at A Glancecsy123No ratings yet
- Algoritma Diagnosis AnemiaDocument2 pagesAlgoritma Diagnosis AnemiaathrahrNo ratings yet
- Mini - Atlas Gastrointestinal SurgeryDocument427 pagesMini - Atlas Gastrointestinal Surgeryمحمد حسنNo ratings yet
- Iron Deficiency AnemiaDocument12 pagesIron Deficiency AnemiaMargarita TorresNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing Mukhtar AbobakerDocument4 pagesPediatric Nursing Mukhtar AbobakerAbo AmgadNo ratings yet
- 04 Hemoglobin HemoglobinopathiesDocument32 pages04 Hemoglobin HemoglobinopathiesBianca OcampoNo ratings yet
- 100q Post-Test May2005Document15 pages100q Post-Test May2005Asmaa Naser100% (1)
- Laboratory Rules and Regulation: Brief History of SiwesDocument12 pagesLaboratory Rules and Regulation: Brief History of Siwesgolden abidemNo ratings yet
- Cold AgglutinationDocument4 pagesCold AgglutinationSajjad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Abdon MelodyDocument4 pagesAbdon MelodyChirs Nicole CaguitlaNo ratings yet
- Red Blood Cell Reviewer MCQDocument10 pagesRed Blood Cell Reviewer MCQSitty CamamaNo ratings yet
- PE10 q1 Mod1 Strengthtraining Ver2-1Document34 pagesPE10 q1 Mod1 Strengthtraining Ver2-1Tresha BaretoNo ratings yet
- The Diagnosis of PregnancyDocument76 pagesThe Diagnosis of PregnancyCnette S. LumboNo ratings yet
- Practice Question Week 1Document9 pagesPractice Question Week 1Gps PandetteNo ratings yet
- Pre Gestational GestationalDocument19 pagesPre Gestational GestationalRoger Jr PumarenNo ratings yet
- Regulation of ErythropoiesisDocument3 pagesRegulation of ErythropoiesisFlowerNo ratings yet
- Hematology Romania-1Document88 pagesHematology Romania-1Ştefania MafteiNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Laboratory TestsDocument6 pagesDiagnostic Laboratory TestsKiana Mae Wong Diwag100% (1)
- CBC2Document14 pagesCBC2Khayar KhanNo ratings yet
- Xenotransfusion of Canine Blood To A CatDocument3 pagesXenotransfusion of Canine Blood To A CatFelipe GonzalezNo ratings yet
- экзамен здоровье взрослыхDocument93 pagesэкзамен здоровье взрослыхdrsunil278No ratings yet
- Medical Diseases in PregnancyDocument37 pagesMedical Diseases in PregnancyAsteway MesfinNo ratings yet
- MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY PRAKTIKUM.2020docxDocument17 pagesMEDICAL TERMINOLOGY PRAKTIKUM.2020docxEvangeline EngieNo ratings yet
- Effect of Tectona Grandis On Phenylhydrazine-Induced Anaemia in RatsDocument5 pagesEffect of Tectona Grandis On Phenylhydrazine-Induced Anaemia in RatsYohanaNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Iron-Enriched Baker's Yeast and Its Efficiency in Recovery of Rats From Dietary Iron DeficiencyDocument11 pagesPreparation of Iron-Enriched Baker's Yeast and Its Efficiency in Recovery of Rats From Dietary Iron DeficiencyAsdfNo ratings yet
- Pathology Exam AnswersDocument14 pagesPathology Exam AnswersRana ElNo ratings yet
- Pure Red Cell Aplasia PRCADocument14 pagesPure Red Cell Aplasia PRCANikkiRoxasNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1Document20 pagesNursing Care Plan 1Mary Beth Smyrl Stalnaker100% (1)