Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 11
Chapter 11
Uploaded by
api-3044860520 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views2 pagesThe document defines the knee joint as permitting movement in one plane. It then lists and describes the roles of various structures in the elbow joint, including cartilage, synovial fluid, synovial membrane, capsular ligament, motor neurons, bones, tendons, antagonistic muscles like the biceps and triceps, and their attachments. It also mentions drawing a labelled diagram of a sarcomere and explaining the roles of calcium ions, motor neurons, and the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction.
Original Description:
Original Title
chapter 11
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document defines the knee joint as permitting movement in one plane. It then lists and describes the roles of various structures in the elbow joint, including cartilage, synovial fluid, synovial membrane, capsular ligament, motor neurons, bones, tendons, antagonistic muscles like the biceps and triceps, and their attachments. It also mentions drawing a labelled diagram of a sarcomere and explaining the roles of calcium ions, motor neurons, and the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views2 pagesChapter 11
Chapter 11
Uploaded by
api-304486052The document defines the knee joint as permitting movement in one plane. It then lists and describes the roles of various structures in the elbow joint, including cartilage, synovial fluid, synovial membrane, capsular ligament, motor neurons, bones, tendons, antagonistic muscles like the biceps and triceps, and their attachments. It also mentions drawing a labelled diagram of a sarcomere and explaining the roles of calcium ions, motor neurons, and the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Term Definition
Knee joint Function: Permits movement in one plane
Draw and describe the roles of structures at the elbow joint
- Cartilage reduces friction
- Synovial fluid lubricates the joint
- Synovial membrane secretes synovial fluid
- Capsular ligament seals the joint
- Ligament prevents dislocation
- Motor neurons stimulate muscles to contract
- Bones provide a firm anchorage for muscles
- Bones act as levers
- Tendons attach muscles to bone
- Biceps and triceps are antagonistic
- Biceps is the flexor and triceps is the extensor
- Biceps is attached to the radius and triceps is attached to the ulna
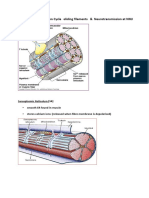
Draw a labelled diagram to show the structure of a sarcomere
Explain the role of calcium ions in muscle contraction
- Action potential causes release of calcium
- Calcium released from sarcoplasmic reticulum
- Calcium causes binding sites on actin to be exposed
- Tropomyosin moves away from and uncovers binding sites
- Allows myosin head to bind to actin for contraction
- Sarcomere shortens
Explain how a nerve impulse is transmitted from a motor neuron to a muscle
- Impulse reaches the motor end plates
- Synaptic vesicles contain neurotransmitters(acetylcholine)
- Calcium enters through the presynaptic membrane
- Calcium causes the vesicles to move to and fuse with the membrane (exocytosis)
- Neurotransmitter released into the synaptic cleft
- Diffuses across the synaptic cleft to the postsynaptic membrane
- Binds to receptor sites
- Causes depolarisation of the postsynaptic membrane
- By opening sodium gates
- Threshold of stimulation most be reached
- Enzyme breaks down the neurotransmitter
- Depolarisation causes sarcoplasmic reticulum to release calcium ions
- Calcium ions cause muscle contraction
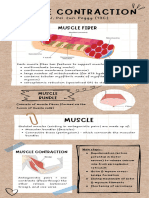
Explain how skeletal muscle contracts
- Actin and myosin slide past each other
- Action potential arrives at motor end plate
- Neurotransmitter released causing action potential
- Sarcoplasmic reticulum releases calcium ions
- Calcium ions cause binding sites on actin to be exposed
- Myosin heads bind to sites on actin/form cross bridges
- Myosin heads moves actin filament using energy from ATP
- Actin moved toward the centre of sarcomere
- Sarcomere shortened
- ATP causes release of myosin head from actin
- Conversion of ATP to ADP and Pi causes myosin heads to change angle
- Cycle of events repeated during muscle contraction
You might also like
- Skeletal MuscleDocument72 pagesSkeletal Musclekiedd_0475% (4)
- Honeywell CM707 Installation GuideDocument2 pagesHoneywell CM707 Installation GuideMatei Plesu0% (1)
- CWZD-600C+CS Manual BookDocument73 pagesCWZD-600C+CS Manual BookSharon ChNo ratings yet
- HL IB BiologyDocument3 pagesHL IB Biologycoolcat132100% (2)
- Excitation & Contraction of Skeletal & Smooth MuscleDocument44 pagesExcitation & Contraction of Skeletal & Smooth MuscleTahir AhmadNo ratings yet
- Biophysics of Muscle ContractionDocument53 pagesBiophysics of Muscle ContractionMaitree UpadhayayNo ratings yet
- IB Bio HL 11.2 Muscles NotesDocument6 pagesIB Bio HL 11.2 Muscles NotesLynnNo ratings yet
- 10.3 Muscle Fiber Excitation, Contraction, and Relaxation - Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument1 page10.3 Muscle Fiber Excitation, Contraction, and Relaxation - Anatomy & Physiologyjszkutak24No ratings yet
- 11.2 Muscles and MovementDocument1 page11.2 Muscles and MovementweliveandbreathewordsNo ratings yet
- ch9 NotesDocument31 pagesch9 NotesChris Baden HadawayNo ratings yet
- Events at The Neuromuscular JunctionDocument9 pagesEvents at The Neuromuscular JunctionVioletteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Structure and FunctionDocument15 pagesChapter 1 - Structure and Functiontjewert23No ratings yet
- Muscle and NMJ-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesMuscle and NMJ-WPS OfficeMangushoNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System: B. Pimentel, M.D. University of Makati - College of NursingDocument71 pagesThe Muscular System: B. Pimentel, M.D. University of Makati - College of Nursingapi-19824701No ratings yet
- A P Muscular Chap 7Document41 pagesA P Muscular Chap 7api-285078865No ratings yet
- Muscle: Myofilaments: Actin & MyosinDocument23 pagesMuscle: Myofilaments: Actin & MyosinDarla FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue Week 15 HGAPDocument4 pagesMuscle Tissue Week 15 HGAPboultonbaileyNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Muscle Contraction 2010Document69 pagesKuliah Muscle Contraction 2010bagir_dm10No ratings yet
- Physiology of Muscle ContractionDocument3 pagesPhysiology of Muscle ContractionAJ AbraganNo ratings yet
- Cross Bridge CycleDocument14 pagesCross Bridge CycleIdenyi Daniel Ewa EdeNo ratings yet
- Muscle PhysiologyDocument49 pagesMuscle PhysiologyNauval Zilal FananyNo ratings yet
- BBT221 Lecture 7Document29 pagesBBT221 Lecture 7Al Sabri Bhuiyan 1812098042No ratings yet
- Sliding Filament Theory Sem 5 AssignmentDocument2 pagesSliding Filament Theory Sem 5 Assignmentparth choudharyNo ratings yet
- Short Answer Essay Dec15Document4 pagesShort Answer Essay Dec159pjh6pzxmsNo ratings yet
- Chap 6Document82 pagesChap 6eratilNo ratings yet
- 6 Contraction of Skeletal MuscleDocument109 pages6 Contraction of Skeletal MuscleHaslinNo ratings yet
- The Muscular SystemDocument22 pagesThe Muscular SystemFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- Initiation of Muscle Contraction MuscleDocument3 pagesInitiation of Muscle Contraction MuscleManu JamesNo ratings yet
- 15 Control and CoordinationDocument6 pages15 Control and CoordinationKevin XingNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Mechanisms of Skeletal Muscle ContractionDocument14 pagesInvestigation of Mechanisms of Skeletal Muscle Contractiongeddy D.No ratings yet
- Sarcolemma - Cell MembraneDocument66 pagesSarcolemma - Cell MembraneAman SyedNo ratings yet
- Chap11muscular TissueDocument64 pagesChap11muscular TissueCalvo AdrianNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology - For Nursing and Healthcare StudentsDocument6 pagesFundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology - For Nursing and Healthcare StudentsAbu BakrNo ratings yet
- Week 8 Anph111 MidtermDocument17 pagesWeek 8 Anph111 MidtermCASTRO, ANDREI KARL Z.No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - An Introduction To Muscle TissueDocument7 pagesChapter 10 - An Introduction To Muscle Tissuetomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesMuscular SystemKaren JulaoNo ratings yet
- Cells Capable of Shortening & Converting The Chemical Energy of ATP Into Mechanical Energy - Types of Muscle - Physiology of Skeletal MuscleDocument64 pagesCells Capable of Shortening & Converting The Chemical Energy of ATP Into Mechanical Energy - Types of Muscle - Physiology of Skeletal MusclevanderphysNo ratings yet
- LECTURE OUTLINE - UNIT 7 Muscles and Muscle TissueDocument12 pagesLECTURE OUTLINE - UNIT 7 Muscles and Muscle TissueFlowers LuNo ratings yet
- Unctional Uman Hysiology: E S S M PDocument88 pagesUnctional Uman Hysiology: E S S M Pandre andreNo ratings yet
- Joints and Muscle Movement FinalDocument10 pagesJoints and Muscle Movement FinalNevandi ThenuwaraNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument22 pagesMuscular SystemGarri AtaydeNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular JunctionDocument11 pagesNeuromuscular JunctionIdenyi Daniel Ewa EdeNo ratings yet
- 10 Muscular ContractionDocument29 pages10 Muscular ContractionMark Piedad MillanoNo ratings yet
- By Dr.H.Gusbakti, MD, MSC, PKK, AIFM Professor of Physiology University Islamic of North SumateraDocument83 pagesBy Dr.H.Gusbakti, MD, MSC, PKK, AIFM Professor of Physiology University Islamic of North SumateraJennifer WootenNo ratings yet
- Mean While,: ("Center" or "Circle") - So, Concentric Things Have A Center in Common. (Document4 pagesMean While,: ("Center" or "Circle") - So, Concentric Things Have A Center in Common. (Karylle SequinaNo ratings yet
- Excitation Contraction CouplingDocument34 pagesExcitation Contraction CouplingRUdraNo ratings yet
- BBT221 L-14,15 Musculo-Skeletal 2Document33 pagesBBT221 L-14,15 Musculo-Skeletal 2iamraiyan123No ratings yet
- L3. Muscle Contraction Cycle - Sliding Filaments & Neurotransmission at NMJDocument9 pagesL3. Muscle Contraction Cycle - Sliding Filaments & Neurotransmission at NMJYolande ClothierNo ratings yet
- Muscle Contraction and Anaerobic RespDocument2 pagesMuscle Contraction and Anaerobic Respapi-247243068No ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument44 pagesMuscular SystemVidya SagarNo ratings yet
- 07 Human Physiology The Muscular SystemDocument68 pages07 Human Physiology The Muscular SystemsuNo ratings yet
- Muscoskeletal SystemDocument5 pagesMuscoskeletal SystemJeevikaGoyalNo ratings yet
- 16 Skeletal Muscle 3 - Electrical Phenomena in Contracting Skeletal Muscle PDFDocument1 page16 Skeletal Muscle 3 - Electrical Phenomena in Contracting Skeletal Muscle PDFVikiNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Muscle Contraction NotesDocument2 pagesIB Biology Muscle Contraction Notespeggyyu12345No ratings yet
- Muscular 2Document7 pagesMuscular 2Elyka Alivan Valdez PolonioNo ratings yet
- Module 10 Kin 267 Muscle TissueDocument4 pagesModule 10 Kin 267 Muscle TissueJ aNo ratings yet
- Muscles 1Document25 pagesMuscles 1sairash.khan23No ratings yet
- The Horse in Motion: The Anatomy and Physiology of Equine LocomotionFrom EverandThe Horse in Motion: The Anatomy and Physiology of Equine LocomotionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- EKG/ECG Interpretation Made Easy: A Practical Approach to Passing the ECG/EKG Portion of NCLEXFrom EverandEKG/ECG Interpretation Made Easy: A Practical Approach to Passing the ECG/EKG Portion of NCLEXRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document1 pageChapter 2api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document1 pageChapter 2api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document1 pageChapter 2api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document2 pagesChapter 4api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document2 pagesChapter 5api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document1 pageChapter 4api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document3 pagesChapter 4api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document2 pagesChapter 6api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document1 pageChapter 9api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document3 pagesChapter 6api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document1 pageChapter 7api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document2 pagesChapter 6api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document2 pagesChapter 9api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document1 pageChapter 7api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document1 pageChapter 7api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document1 pageChapter 10api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document1 pageChapter 9api-304486052No ratings yet
- Horner Wadsworth Emmons ReactionDocument17 pagesHorner Wadsworth Emmons Reactiond1s7euu+rqc23kNo ratings yet
- Rana Pratap Sagar Power Plant Rawatbhata: A Practical Training Report OnDocument11 pagesRana Pratap Sagar Power Plant Rawatbhata: A Practical Training Report Onyogesh dhakerNo ratings yet
- Modvat and CenvatDocument3 pagesModvat and CenvatpravinsankalpNo ratings yet
- Stress Isometric Cal 1834 104Document20 pagesStress Isometric Cal 1834 104Kailash SangareNo ratings yet
- Distribution System Grounding FundamentalsDocument17 pagesDistribution System Grounding FundamentalsJose Alberto RodriguezNo ratings yet
- RENR8341-04-00-T&A Hydraulic FanDocument32 pagesRENR8341-04-00-T&A Hydraulic FanJesus Antonio Salazar WaldronNo ratings yet
- Methods For The Reduction of Line LossesDocument5 pagesMethods For The Reduction of Line Lossesapi-232121477No ratings yet
- Specifications POMPADocument4 pagesSpecifications POMPAArataNo ratings yet
- Electronic EyeDocument14 pagesElectronic EyeHajarath Prasad Abburu100% (1)
- Effect of EGR On Diesel EngineDocument17 pagesEffect of EGR On Diesel EngineVikas PoddarNo ratings yet
- Basic Troubleshooting Repair ProceduresDocument65 pagesBasic Troubleshooting Repair ProceduresOtai EzraNo ratings yet
- TAD1343GE: Volvo Penta Genset EngineDocument2 pagesTAD1343GE: Volvo Penta Genset EngineAndres SorinNo ratings yet
- Alfa Laval CB10 / CBH10: Brazed Plate Heat ExchangerDocument2 pagesAlfa Laval CB10 / CBH10: Brazed Plate Heat ExchangerAfonso LopesNo ratings yet
- AluminiumDocument20 pagesAluminiumregita cahyani butar butarNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Homologous SeriesDocument5 pagesAlcohol Homologous SeriesChia Sann Roo CynthiaNo ratings yet
- Power Quality DisturbancesDocument24 pagesPower Quality DisturbancesSunil SinghNo ratings yet
- Diris A60Document60 pagesDiris A60Valentin Andrei100% (1)
- LS Cable: Offshore & MarineDocument4 pagesLS Cable: Offshore & MarinetranminhtrunglsvinaNo ratings yet
- Animation Video of The Working of A Rotary (Vane) PumpDocument6 pagesAnimation Video of The Working of A Rotary (Vane) PumpBubai111No ratings yet
- 9.5 Giant Metallic StructuresDocument2 pages9.5 Giant Metallic StructureshadenluiNo ratings yet
- Early dimmers were directly controlled through the manual manipulation of large dimmer panels. This required all power to come through the lighting control location, which could be inconvenient, inefficient and potentially dangerous for large or high-powered systems, such as those used for stage lighting. In 1896, Granville Woods patented his "Safety Dimmer", which greatly reduced wasted energy by reducing the amount of energy generated to match desired demand rather than burning off unwanted energy.[1] In 1959, Joel S. Spira, who would found the Lutron Electronics Company in 1961, invented a dimmer based on a diode and a tapped autotransformer, saving energy and allowing the dimmer to be installed in a standard electrical wallbox.[2][3]Document2 pagesEarly dimmers were directly controlled through the manual manipulation of large dimmer panels. This required all power to come through the lighting control location, which could be inconvenient, inefficient and potentially dangerous for large or high-powered systems, such as those used for stage lighting. In 1896, Granville Woods patented his "Safety Dimmer", which greatly reduced wasted energy by reducing the amount of energy generated to match desired demand rather than burning off unwanted energy.[1] In 1959, Joel S. Spira, who would found the Lutron Electronics Company in 1961, invented a dimmer based on a diode and a tapped autotransformer, saving energy and allowing the dimmer to be installed in a standard electrical wallbox.[2][3]abhywaNo ratings yet
- ICS Series 12ICS100: Intensive Cycle ServiceDocument2 pagesICS Series 12ICS100: Intensive Cycle ServiceFandhuNo ratings yet
- Blohm + Voss Power Unit 9pu-7200Document37 pagesBlohm + Voss Power Unit 9pu-7200juan moreno100% (1)
- Graco Autolube Mode 12Document2 pagesGraco Autolube Mode 12Riyan AditiaNo ratings yet
- Geophysics and Medical PhysicsDocument5 pagesGeophysics and Medical PhysicsjanetpriscillaNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of Motorized LiftDocument62 pagesFabrication of Motorized LiftANAND KRISHNANNo ratings yet
- Vibrant International Academy, Masma, SuratDocument14 pagesVibrant International Academy, Masma, SuratJatin PahujaNo ratings yet
- Content Handbook of Energy and Economic Statistics of Indonesia 2020Document111 pagesContent Handbook of Energy and Economic Statistics of Indonesia 2020Fabiola Marella PardedeNo ratings yet




































































































![Early dimmers were directly controlled through the manual manipulation of large dimmer panels. This required all power to come through the lighting control location, which could be inconvenient, inefficient and potentially dangerous for large or high-powered systems, such as those used for stage lighting. In 1896, Granville Woods patented his "Safety Dimmer", which greatly reduced wasted energy by reducing the amount of energy generated to match desired demand rather than burning off unwanted energy.[1] In 1959, Joel S. Spira, who would found the Lutron Electronics Company in 1961, invented a dimmer based on a diode and a tapped autotransformer, saving energy and allowing the dimmer to be installed in a standard electrical wallbox.[2][3]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/318437784/149x198/2f1fbec41e/1468638713?v=1)






