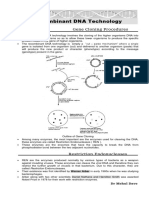
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 7
Chapter 7
Uploaded by
api-3044860520 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pageThe document distinguishes between unique sequences and highly repetitive sequences in nuclear DNA. Unique sequences occur once in the genome, contain long base sequences that code for genes, and can vary slightly between individuals. Highly repetitive sequences occur many times, contain short sequences that do not code for genes, and can vary greatly. Unique sequences make up a smaller proportion of the genome and include exons, while highly repetitive sequences make up a higher proportion and include introns.
Original Description:
Original Title
chapter 7
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document distinguishes between unique sequences and highly repetitive sequences in nuclear DNA. Unique sequences occur once in the genome, contain long base sequences that code for genes, and can vary slightly between individuals. Highly repetitive sequences occur many times, contain short sequences that do not code for genes, and can vary greatly. Unique sequences make up a smaller proportion of the genome and include exons, while highly repetitive sequences make up a higher proportion and include introns.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pageChapter 7
Chapter 7
Uploaded by
api-304486052The document distinguishes between unique sequences and highly repetitive sequences in nuclear DNA. Unique sequences occur once in the genome, contain long base sequences that code for genes, and can vary slightly between individuals. Highly repetitive sequences occur many times, contain short sequences that do not code for genes, and can vary greatly. Unique sequences make up a smaller proportion of the genome and include exons, while highly repetitive sequences make up a higher proportion and include introns.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
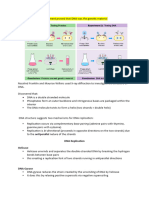
Distinguish between unique and highly repetitive sequences in nuclear
DNA
Unique single copy sequence Highly repetitive sequence
Occur once in genome Occur many times
Long base sequences Short sequences
Genes Not Genes
Translated Not translated
Small differences between individuals Can vary greatly
Exons Introns
Smaller proportion of genome Higher proportion of genome
Outline transcription in prokaryotes
- Transcription is the copying of a strand of DNA into RNA
- RNA polymerase binds to promoter region of DNA
- Anti-sense strand as template
- RNA polymerase unwinds DNA
- RNA nucleotides pair with complementary bases on DNA
- Adenine to Uracil, Guanine with Cytosine
- Strand grows 5’ to 3’
- RNA nucleotides joined with covalent bonds
- ENA polymerase separates from DNA when reaches terminator
- No introns, no post-transcriptional modification
You might also like
- Genome OrganizationDocument19 pagesGenome OrganizationChristin Natalia KalembangNo ratings yet
- Discussion On NucleotidesDocument2 pagesDiscussion On NucleotidesEyob TeferaNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument19 pagesDNA ReplicationLouis HilarioNo ratings yet
- DNAReplication 103108Document22 pagesDNAReplication 103108Wellian Gell AlarconNo ratings yet
- ASS 7 (bbt193003) MGDocument7 pagesASS 7 (bbt193003) MGAbuzar KhanNo ratings yet
- Biological BackgroundDocument15 pagesBiological Backgroundrustyryan77No ratings yet
- Central DogmaDocument4 pagesCentral DogmaRodriguez MiaNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument20 pagesCentral Dogma of Molecular BiologyCharles Darren QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- 2 - Dna ReplicationDocument25 pages2 - Dna Replicationwonderwolfblood17No ratings yet
- Lect 3 - 4 DOGMA CENTRAL-1Document76 pagesLect 3 - 4 DOGMA CENTRAL-1Asfi AniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document4 pagesLecture 3skarthikumar@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Mira Molecular Biology Part1Document63 pagesMira Molecular Biology Part1Ranim MiraNo ratings yet
- Summary OCPEG and Cancer 2018Document18 pagesSummary OCPEG and Cancer 2018Jonathan Wee Cheng YangNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of BiologyDocument6 pagesCentral Dogma of BiologyJhun Lerry TayanNo ratings yet
- Chromosome, DNA, RNADocument5 pagesChromosome, DNA, RNAShahrat Farsim ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- MBB425 - Lecture 2-3 GENOME STRUCTUREDocument35 pagesMBB425 - Lecture 2-3 GENOME STRUCTUREEMMANUEL ABEL IMAHNo ratings yet
- Gene Silencing: Presented byDocument23 pagesGene Silencing: Presented byRouf Ahmad100% (1)
- Quiz Microbial Genetics TortoraDocument17 pagesQuiz Microbial Genetics TortorapascabioNo ratings yet
- PCR With Variations III GNADocument18 pagesPCR With Variations III GNAmaxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- Lecture-2 - Molecular and Cellular BiologyDocument20 pagesLecture-2 - Molecular and Cellular Biologymdeaqub hasanNo ratings yet
- Part 3Document18 pagesPart 3Ultima PhaseNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Molecular Biology IDocument12 pagesLecture 5 - Molecular Biology IbesillysillyNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument31 pagesTranscriptionParth ShahNo ratings yet
- Dna Viruses: DNA Viruses Most Often Encountered in Humans IncludeDocument5 pagesDna Viruses: DNA Viruses Most Often Encountered in Humans IncludeAhmad Alfiansyah SaidNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Steps: Dna ReplicationDocument2 pagesPreliminary Steps: Dna Replicationbunso padillaNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument62 pagesDNA Structure and ReplicationREYNANTE SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry SemiDocument5 pagesBiochemistry SemiTsukishima RinNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument15 pagesTranscriptioncamila hartmannNo ratings yet
- VNTR Human DNA Typing Using PCRDocument13 pagesVNTR Human DNA Typing Using PCRNada OsmanNo ratings yet
- Slide 3Document36 pagesSlide 3OdaiNo ratings yet
- M.I.T LessonsDocument12 pagesM.I.T LessonsChassy KammyNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Replication of DNADocument62 pagesTopic 2 - Replication of DNAKirrthanaGaneshNo ratings yet
- 3rdgrad NOTES GeneticsDocument3 pages3rdgrad NOTES GeneticsKarl SiaganNo ratings yet
- Mollecular and Cellular Biology: Lecture - 2Document31 pagesMollecular and Cellular Biology: Lecture - 2sk3 khanNo ratings yet
- Central DogmaDocument28 pagesCentral DogmaBryant Villarin BaldivicioNo ratings yet
- Inheritance and Regulation ReviewerDocument7 pagesInheritance and Regulation ReviewerAngelo LopezNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience Reviewerkarljosefdelacruz1017No ratings yet
- Maja Dad Na Replication and Protein SynthesisDocument45 pagesMaja Dad Na Replication and Protein SynthesisParsottambhai RathaviNo ratings yet
- Dna Repl Molecular GeneticsDocument8 pagesDna Repl Molecular GeneticsAmna NawazNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Dr. Muhammad Tahir Assistant Professor COMSATS University Islamabad, Attock CampusDocument16 pagesDNA Replication: Dr. Muhammad Tahir Assistant Professor COMSATS University Islamabad, Attock CampusSaqlain Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Principles of Molecular BiologyDocument39 pagesPrinciples of Molecular BiologyNando NanginNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of GeneticsDocument4 pagesCentral Dogma of Geneticsmiguel gaquitNo ratings yet
- Sequence-Dependent Special Structures Can Form in DNA and RNADocument48 pagesSequence-Dependent Special Structures Can Form in DNA and RNANoor-E-Khadiza ShamaNo ratings yet
- General Biology - DNA ReplicationDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology - DNA ReplicationChristine Marylou PalomoNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNADocument1 pageDNA and RNADaly DaliaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-11 Nucleic AcidDocument31 pagesChapter-11 Nucleic AcidMD Limon IslamNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument25 pagesDNA ReplicationPhilani KheswaNo ratings yet
- Genetics 2Document52 pagesGenetics 2Le Phuong LyNo ratings yet
- 11 - DNA ReplicationDocument32 pages11 - DNA ReplicationR yNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument5 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentAnonymous Ne3gPmoINo ratings yet
- Replikasi, Transkripsi, Dan TranslasiDocument160 pagesReplikasi, Transkripsi, Dan TranslasiRenaldy PamungkasNo ratings yet
- Information Flow From DNA To Protein - Lecture SlidesDocument66 pagesInformation Flow From DNA To Protein - Lecture Slidesjudssssk46No ratings yet
- Class 12-UNITS 3-4 NotesDocument4 pagesClass 12-UNITS 3-4 NotesDimas HernadyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24Document13 pagesChapter 24Venus LandichoNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument12 pagesNucleic AcidsKelly ZhuNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument48 pagesDNA ReplicationAamir MumtazNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument54 pagesTopic 1 - DNA Structure and ReplicationWaikeat SamNo ratings yet
- Module 11Document97 pagesModule 11theaNo ratings yet
- R DNA TechnologyDocument17 pagesR DNA TechnologyDRMEHUL DAVENo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document1 pageChapter 2api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document1 pageChapter 2api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document1 pageChapter 2api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document2 pagesChapter 4api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document2 pagesChapter 5api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document1 pageChapter 4api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document3 pagesChapter 4api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document2 pagesChapter 6api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document1 pageChapter 9api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document3 pagesChapter 6api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document1 pageChapter 7api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document2 pagesChapter 6api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document1 pageChapter 9api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document1 pageChapter 7api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document2 pagesChapter 9api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document1 pageChapter 10api-304486052No ratings yet