Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Indian Polity PDF
Indian Polity PDF
Uploaded by
rajaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Indian Polity PDF
Indian Polity PDF
Uploaded by
rajaCopyright:
Available Formats
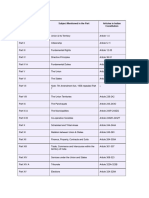
Parts of the Constitution
Part Articles Areas
I 1-4 The Union & its Territories
II 5-11 Citizenship
III 12-35 Fundamental Rights
IV 36-51 Directive Principles of State Policy
IV A 51A Fundamental Duties (42nd Amendment)
V 52-151 The Union Government
VI 152-237 The State Government
VII 238 Dealt with states in Part B of the First Schedule. Repealed in 1956 by the
Seventh Amendment.
VIII 239-241 Union Territories. Article 242 repealed.
IX 243 A-O The Panchayats
IX-A 243 P-ZG The Muncipalities
X 244-244 A The Scheduled & Tribal Areas
XI 245-263 Relations between the Union & the States
XII 264-300A Finance, Property, Contracts & Suits
XIII 301-307 Trade, Commerce & Intercouse within the territory of India
XIV 308-323 Services under the Union & the States
XIV A 323A-323B Administrative Tribunals (42nd Amendment 1976)
XV 324-329 Elections
XVI 330-342 Special Provisions (Reservations of SC, ST, Anglo Indian etc)
XVII 343-351 Official Language
XVIII 352-360 Emergency Provisions
XIX 361-367 Miscellaneous Provisions (Immunity of President, Legislature etc)
XX 368 Amendment of the Constitution
XXI 369-392 Temporary, Transitional & Special Provision
XXII 393-395 Short Title, Commencement, Authoritative
Schedules of the Constitution
Schedule I Deals with territories of the 28 states & 7 union territories
Schedule II Salaries allowances of president, V.P, Speaker, Judges, CAG etc.
Schedule III Various forms of Oaths & affirmation which various incumbents have to take.
Schedule IV Seats allotted to various states & UTs in the Rajya Sabha (Council of States)
Schedule V Administration & Control of scheduled areas.
Schedule VI Administration of tribal areas in Assam, Meghalaya & Mizoram
Schedule VII Subjects in the three lists – Union, State & Concurrent
Schedule VIII List of 22 regional languages
Schedule IX Certain acts & regulations dealing with land reforms & zamidari system abolition.
((Added by first constitutional amendment).
Schedule X Disqualifications on grounds of defection. (52nd Amendment)
Schedule XI 29 subjects on which panchayats can legislate. (73rd Amendment)
Schedule XII 18 subjects on which municipalities have control. (74th Amendment)
Ghanshyam Thori 1 Indian Polity
Indian Constitution Borrowed Features
1. British Constitution Parliamentary form of Government, Rule of Law, Law making
procedure, Single Citizenship; Institution of Speaker, doctrine of
pleasure tenure of civil servants.
2. American Constitution Judicial System, Fundamental Rights
3. Canadian Constitution Federal System with a strong central authority; Residual powers,
Centre State Relation.
4. Irish Constitution Directive Principles, Election of the President of India
5. Australian Constitution Concurrent list; Freedom of Trade & Service within country
6. Weimar Constitution Emergency Provision
7. Soviet Constitution Five Year Plans; Fundamental duties
8. Govt of India Act 1935 Office of the governor, powers of the federal jury.
9. South African Amendment of Constitution.
Important Cases of the Constitution
1. Berubari Case Preamble not a part of the constitution
2. Golaknath Case Supreme court held that the Parliament had no power to amend any of the
1967 provisions of Part III (Fundamental rights) The Indira Gandhi government
in 1971 carried out the 24th Amendment with a view to assert the right of
the parliament to amend any part of the constitution.
3. Keshvanada Bharti Preamble was a part of the constitution & can be amended by Parliament
Case under Article 368. Parliament can also amend the fundamental rights
(Against Golaknath case) but ruled that the parliament cannot destroy the
basic structure of the constitution.
4. Minerval Mills Case The 42nd.amendment carried out in 1976 gave asserted that parliament had
1980 unlimited powers to amend the constitution & tried to accord precedence to
Directive principles over fundamental rights. But in the Minerva Mills
Case the Supreme court struck down those provisions
5. Maneka Gandhi Vs Right to live is not merely confined to physical existence but includes
Union of India within its ambit the right to live with human dignity
Preamble
We, the people of India, having solemnly resolved to constitute India into a Sovereign socialist secular
democratic republic and to secure to all its citizens :
Justice, social, economic and political;
Liberty of thought, expression, belief, faith and worship;
Equality of status and of opportunity;
and to promote among them all
Fraternity assuring the dignity of the individual and the unity and integrity of the Nation.
In our constituent assembly this twenty-sixth day of November, 1949, do hereby adopt, enact and give to
ourselves this constitution.
* Italicized word added by 42nd amendment
Ghanshyam Thori 2 Indian Polity
Reorganization of States
1. 1956 Act 14 States & 6 Union territories formed.
States - Andhra Pradesh, Assam, Bihar, Bombay, J&K, Kerala, M.P., Madras,
Mysore, Orissa, Punjab, Rajasthan, U.P & West Bengal.
UTs – Andaman & Nicobar, Delhi, Himachal Pradesh, Laccadive, Minicoy &
Amindivi Islands, Manipur & Tripura
2. 1960 The states of Maharashtra & Gujarat created by bifurcating the state of Bombay.
3. 1963 Nagaland formed
4. 1966 Punjab & Haryana formed out of Punjab & hill areas merged with H.P (UT then).
5. 1969 Meghalaya created out of Assam.
6. 1971 Himachal Pradesh, Tripura & Manipur raised to the status of a state
7. 1975 Sikkim admitted as a state.
8. 1986 Mizormam & Arunachal Pradesh (UTs till then) given status of state
9. 1987 Goa created by separating it from the UT of Daman & Diu.
10. 2000 Chattisgarh, Jharkhand & Uttaranchal
Various Political/Non Political Offices of India
President Name proposed by 50 electors & security deposit of Rs 15000. Disputes in
connection with the election of President are decided by Supreme Court. Oath by
Chief justice of India. MLAs & members of both house of the parliament vote in the
election. The president submits his resignation to the Vice President. Impeachment
can be initiated by either house of parliament (2/3 majority). Nominated members can
also participate but they do not participate in the election of president. MLAs do not
participate in impeachment. In case the office becomes vacant fresh elections within
6 months. The president enjoys suspensive veto powers & it applies only to the non
money bills. With regards to constitutional amendments president has no veto
powers. President can promulgate ordinances when the parliament is in recess only
on matters in the union & concurrent list. The ordinances must be approved by
parliament within 6 weeks. All money bills originate on the recommendation of the
President. Appoints finance commission. If there is no party with clear cut majority
the president can use his discretion. He cannot declare any emergency on his own.
Can summon both houses separately.
Vice President Name seconded by at least 25 members & security deposit of 15,000. More than 35
years of age. Elected by the members of Lok Sabha & Rajya Sabha at a joint meeting.
Oath before the president or some other person appointed by him. Can act as
president for a maximum 6 months period. Not a member of Rajya sabha only an ex-
officio chairman.
Prime Minister Gets the same salary & allowances as MPs but additional sumptuary allowance of
3000 per month. If the prime minister is taken from Rajya Sabha he cannot part in
voting when a vote of no confidence is under consideration. In the event of his death
the council of ministers stand automatically dissolved.
Deputy PM Position not known to the constitution although 7 persons have occupies this post.
Vallabhbhai Patel, Morarji Desai, Charan Singh, Jagjivan Ram, Y.B Chavan, Devi
Lal & L. K. Advani have served the office.
Council of Should be a member of either house or do so within 6 months. Vote of no confidence
Ministers against any minister leads to resignation of entire council. The cabinet, state & deputy
ministers get sumptuary allowance of 2000, 1000 & 600 respectively. Present the
budget before the parliament. Collectively responsible to parliament but individual
Ghanshyam Thori 3 Indian Polity
ministers responsible to President.
Lok Sabha Strength of Lok Sabha fixed at 543 plus 2 nominated members of Anglo-Indian
community in 1976. Minimum 25 years of age. The security deposit has been
increased from Rs 500 to Rs 10,000. In case of SC/ST it has been increased from Rs
250 to Rs 5000. 10 electors should propose. No candidate can contest elections from
more than 2 constituencies. Oath before president or some person appointed by him.
Can vacant seat by writing to speaker. Seat vacant if absents from meetings for 60
days without intimation. The speaker continues in the house even after the dissolution
of the Lok Sabha till a newly elected Lok Sabha meets. MPs are entitled to a monthly
salary of Rs 12000 & pension of 3000 which increases according to the number of
years served. The joint session is called if a bill passed is rejected by other house or
no action is taken. Speaker presides over joint sessions.
Rajya Sabha 238 elected & 12 nominated. Minimum 30 years of age. Elected by members of state
legislative assemblies on the basis of proportional representation through a single
transferable vote. It is not subjected to dissolution. In the event of dissolution of Lok
Sabha, any bill pendin in the Rajya Sabha but not passed by Lok Sabha does not
lapse.
Supreme Court 5 years as high court judge or 10 years as advocate. Hold office till the age of 65.
Judge Address their resignation to president. The salaries of chief justice & other judges are
33000 & 30,000 respectively. Impeachment requires 2/3rd majority in the two houses
of the parliament. Original Jurisdiction (Centre-state & fundamental rights),
Appellate jurisdiction (Only if high court certifies or the high court has awarded
death sentence after reversing judgement or after withdrawing case from lower court
& Advisory jurisdiction.
Governor Oath before chief justice of high court of that state. 35 years of age. Draws
36000.Adresses first session of state legislature after elections. Appoint one sixth
members of legislative council. Nominates one member of Anglo Indian community
to the legislative assembly. Makes laws through ordinances. Can grant pardon but not
in case of death sentence. Reserve a bill for president’s consideration. He is permitted
to act without the advice of the council of ministers unlike president. Ordinance
issued by him remains in force for a maximum 6 months. The constitution does not
contain any provision for his impeachment.
Advocate Person who is qualified to be a judge of the high court. Remunerations as the
General governor may determine.
Legislative 60 to 500 members according to population but Sikkim has only 32 members. 25
Assembly years of age. Goa, Mizoram, Pondicherry have only 30 members.
Legislative Its members are elected by legislative assembly (1/3rd) local bodies (1/3rd), teachers
Council (1/12th), university graduates (1/12th) & nominated by governor (1/6th). The
maximum membership can be 1/3rd that of Legislative Assembly but in no case less
than 40 members. 30 years of age. The legislative council can delay an ordinary bill
for 3 months & a money bill for 14 days. There is no provision for joint sitting here.
High Court To become a judge – advocate for 10 years or held judicial office in Indian Territory
for a period of at least 10 years. 62 years of age. Chief justice gets 30,000 & other
judges 26000. The pension of the high court judges is charged to the Consolidated
fund of India.
Administrative Incorporated by 42nd amendment through addition of articles 323A & 323B. CAT is
Tribunals located at Delhi. The retirement of chairman & VC at 65 & others at 62. The decision
of CAT can be challenged in a high court.
Ghanshyam Thori 4 Indian Polity
Inter State Created on the recommendations of the Sarkaria commission although constitution
Council provided for it. Appointed by president. Advises on disputes between various states.
Comprises of PM & CMs of all states & UTs. PM can nominate 6 ministers of
cabinet rank. Meets atleast 3 times a year.
Zonal Council Set up under state reorganization act 1956. 5 before & 6th added in 1972 called NE
council. Consists of Union minister nominated by president, CM of each state in the
zone, two ministers from each state nominated by governor & one member per UT.
The CM of the state where the zonal council meets is the ex-officio chairman.
UPSC Chairman & 8 members. Members appointed for a 6 year term or till they attain 65
years of age. President can issue orders for the removal of the members of the UPSC
only after supreme court makes such recommendation on the basis of an enquiry.
Members not eligible for employment by the government after retirement. The state
can restrict the fundamental rights of civil servants.
Comptroller & 6 years or till the age of 65 years. The president can remove CAG only after
Auditor recommendation of the two houses of parliament. Salary of 30,000. He only conducts
General audit. Submits report to President who in turn places it before parliament.
Attorney Qualification same as judge of supreme court. Appears before supreme court &
General various high courts involving the Government of India.
Election Two commissioners with equivalent power. Period of 5 years. Job also includes
Commission delimitation of constituency to ensure same number of people in each. The election
commission of India appoints the ‘Returning officers’ for the state assembly elections
to help conduct fair elections. Election of local bodies comes under state election
commission. The state election commission is a single member commission
comprising SEC.
Finance Qualified to be appointed as judges of the high court or special knowledge of finance
Commission & accounts of government. Comprises chairman & four other members. Functions:-
recommend distribution of taxes between centre & states, grant-in-aid to states,
advice president on any matter.
Planning Non-statutory body which formulates 5 year plans. The Commission works through
Commission its various divisions, of which there are three kind: General Planning Divisions,
Special Planning Divisions, Programme Administration Divisions
NDC Extra constitutional & extra legal body. Its recommendations are binding in nature as
per convention.
Minorities Seven members. The states of M.P, Orissa & Bihar are obliged to appoint a separate
commission minister the welfare of SC/ST/OBC.
NHRC Statutory body.
Panchayat Panchayat is responsible to gram sabha, the general body of villagers comprising all
adults. Members usually range from 5 to 31. Members have same requirements as
MLAs except lower age of 21. Can legislate on 29 subjects which are listed in XI
schedule
Panchayat Genearlly comprises of the sarpanches of village panchayats under the block. Its
Samiti chairman called ‘Pradhan’ is elected from among its members. Responsible to gram
panchayat as well as gram sabhas. Gets a share of cess of land revenue from the gram
panchayat & Zilla Parishad
Zila Parishad Consists of representatives of panchayat samiti, local members of state legislature,
members of parliament, members representing SC/ST/Women/cooperative bodies.
Zilla parishad elects its chairman called ‘Pradhan’ form amongst its members.
Depends entirely on state government for grants.
Ghanshyam Thori 5 Indian Polity
Constitution of India (Upto Part IV)
Part I The Union and its Territory
Article 1 Name and territory of the Union
Article 2 Admission or establishment of new States
Article 2a [Repealed] Sikkim to be associated with the Union
Article 3 Formation of new States and alteration of areas, boundaries or names of existing States
Article 4 Laws made under articles 2 and 3 to provide for the amendment of the First and the
Fourth Schedule and supplemental, incidental and consequential matters
Part II Citizenship
Article 5 Citizenship at the commencement of the Constitution
Article 6 Rights of citizenship of certain persons who have migrated to India from Pakistan
Article 7 Rights of citizenship of certain migrants to Pakistan
Article 8 Rights of citizenship of certain persons of Indian origin residing outside India
Article 9 Persons voluntarily acquiring citizenship of a foreign State not to be citizens
Article 10 Continuance of the rights of citizenship
Article 11 Parliament to regulate the right of citizenship by law
Part III Fundamental Rights
Article 12 Definition
Article 13 Laws inconsistent with or in derogation of the fundamental rights
Article 14 Equality before law meaning ‘equality of treatment within a class’
Article 15 Prohibition of discrimination on grounds of religion, race, caste, sex or place of birth
Article 16 Equality of opportunity in matters of public employment
Article 17 Abolition of Untouchability
Article 18 Abolition of titles
Article 19 Protection of certain rights regarding freedom of speech, etc.
Article 20 Protection in respect of conviction for offenses
Article 21 Protection of life and personal liberty
Article 21A Right to education.
Article 22 Protection against arrest and detention in certain cases
Article 23 Prohibition of traffic in human beings and forced labour
Article 24 Prohibition of employment of children in factories, etc.
Article 25 Freedom of conscience and free profession, practice and propagation of religion
Article 26 Freedom to manage religious affairs
Article 27 Freedom as to payment of taxes for promotion of any particular religion
Article 28 Freedom as to attendance at religious instruction or religious worship in certain
educational institutions
Article 29 Protection of interests of minorities
Article 30 Right of minorities to establish and administer educational institutions
Article 31 [Repealed] Compulsory acquisition of property
Article 31A Saving of laws providing for acquisition of estates, etc.
Article 31B Validation of certain Acts and Regulations
Article 31C Saving of laws giving effect to certain directive principles
Article 31D [Repealed] Saving of laws in respect of anti-national activities
Article 32 Remedies for enforcement of rights conferred by this Part
Article 32A [Repealed]
Article 33 Power of Parliament to modify the rights conferred by this Part in their application to
Forces, etc.
Ghanshyam Thori 6 Indian Polity
Article 34 Restriction on rights conferred by this Part while marital law is in force in any area
Article 35 Legislation to give effect to the provisions of this Part
Part IV Directive Principles of State Policy
Article 36 Definition
Article 37 Application of the principles contained in this Part
Article 38 State to secure a social order for the promotion of welfare of the people
Article 39 Certain principles of policy to be followed by the State
Article 39A A Equal justice and free legal aid
Article 40 Organisation of village panchayats
Article 41 Right to work, to education and to public assistance in certain cases
Article 42 Provision for just and humane conditions of work and maternity relief
Article 43 Living wage, etc., for workers
Article 43A Participation of workers in management of industries
Article 44 Uniform civil code for the citizen
Article 45 Provision for free and compulsory education for children
Article 46 Promotion of educational and economic interests of Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes
and other weaker sections
Article 47 Duty of the State to raise the level of nutrition and the standard of living and to improve
public health
Article 48 Organisation of agriculture and animal husbandry
Article 48A Protection and improvement of environment and safeguarding of forests and wild life
Article 49 Protection of monuments and places and objects of national importance
Article 50 Separation of judiciary from executive
Article 51 Promotion of international peace and security
Article 51A Fundamental Duties
Parliamentary Committees
1. Business Advisory Committee 15 members. Speaker is chairman
2. Committee on Private Members Bills & 15 members. Deputy Chairman is chairman.
Resolutions Classifies bills according to importance.
3. Select Committees Constituted for considering different bills.
4. Committee on Petitions 15 members.
5. Rules Committee 15 members. Speaker is head. Rules of House
6. Committee on Privileges 15 members. Violation of Privileges of M.P
7. Committee on Subordinate Legislations
8. Committee on Welfare of Scheduled Castes 30 Members. 20 M.Ps & 10 R.S.
& Scheduled Tribes
9. Committee on Government Assurances 15 members. How far assurances given by the
ministers have been implemented
10. Committee on Absence of Members Examines leave applications of members
11. Estimates Committee 30 members. Examines Annual Estimates &
suggests alternative policies
12. Public Accounts Committee 22 members. 15 M.Ps & 7 R.S. Assisted by
Comptroller & Auditor general. It acts as a watch
dog of expenditure.
13. Committee on Public Undertakings 15 members. 10 M.Ps & 5 R.S. Examines working
of public undertakings
Ghanshyam Thori 7 Indian Polity
14. Joint Committee on Salaries & Allowances 15 members. 10 nominated by speaker & 5 by the
chairman of Rajya Sabha.
15. Joint Committee on Offices of Profit 15 members. 10 L.S & 5 R.S.
16. Parliamentary Subject Committees 17 parliamentary committees were constituted. 11
by Speaker & 6 by chairman of Rajya Sabha
Parliamentary Terms
1. Question Hour First hour of every sitting in the two houses of the parliament is devoted to
asking & answering questions known as Question hour. The questions
consist of starred (oral), unstarred (written) & short notice question.
2. Zero Hour The hour after the question hour. There is no mention of zero hour in the
rules of the parliamentary procedure & the term was coined by press in the
early 1960’s. Members raise matters which cannot brook any delay.
3. Adjournment Motion Moved to draw the attention to a recent matter of urgent public importance.
Only if 50 members support it & speaker grants permission.
4. Calling Attention A member with prior attention of the speaker may call the attention of a
Notice minister to a matter of urgent public importance.
5. Short Duration Private members can also bring matters of urgent public importance to the
Discussions notice of the House. The notice must be signed by at least 3 members
6. Cut Motion Motions to reduce the amount of demand for grants. They are of 3 types:
Disapproval of policy cut, Economy cut, Token Cut.
7. Guillotine When the discussion cannot be completed within stipulated time, the
speaker can put the matter to vote even without concluding discussion.
8. Censure Motion At least 50 members support it & speaker should admit it. If the motion is
passed in the Lok Sabha, the council of ministers have to resign.
9. By Elections To fill up the seat rendered vacant due to death.
Lists
Union List (99) Defence, Foreign affaris, currency, banking, communication, inter-state
trade, commerce, atomic energy, railways, highways, aerodromes.
[Originally 97 items – one deleted, 3 added]
State List (61) Health, sanitation, public order, agriculture, prisons, local government,
liquor, transportation, relief of disabled, sales tax & octroi, taxes on
entertainment & wealth. [Originally 66 items out of which 5 transferred to
concurrent list].
Concurrent list (52) Criminal law, electricity, factories, forests, education, marriage & divorce,
drugs, newspapers, books & printing press, social insurance, trade unions,
preventive detention, stamp duties. [Originally 47 but 5 items transferred to
this list from state list]
Commissions/committees & their Purpose
1. S.K Dhar committee Reorganization of states on linguistic basis
2. JVP committee Jawahar, Vallabh, Pattabhi Sitaramayya (same as above)
3. Shah Commission Punjab Reorganization Act
4. Tarkunde Committee Electoral Reforms. Voting age to be reduced to 18 years (61st
amendment). Voter councils to be formed.
5. Dinesh Goswami Electoral Reforms. To save the security candidates should secure
Committe at least 1/4th of valid votes.
Ghanshyam Thori 8 Indian Polity
6. Balwant Rai Mehta Recommendations approved by NDC. Rajasthan first adopted 3
tier structure, followed by Andhra Pradesh & Bihar.
7. Ashok Mehta Committee Working of panchayati raj institutions.
8. Rajamannar Commission Recommended abolition of IAS & the IPS
Select Political Doctrines & Principles
The Doctrine Of Idea that when the legislature wants to do something that it cannot do
Colourability, within the constraints of the constitution, it colours the law with a
substitute purpose which will still allow it to accomplish its original goal.
Pith And Substance Interpretation used to determine under which head of power a given piece
of legislation falls. The doctrine is primarily used when a law is
challenged on the basis that one level of government (be it provincial or
federal) has encroached upon the exclusive jurisdiction of another level of
government.
Doctrine of Severability Associated with declaration of law as unconstitutional & void by the
courts.
Principle of Harmonious Concerned with the relationship between the fundamental rights & the
Construction directive principles.
Miscellaneous Facts
1. The idea of a constituent assembly to frame a constitution for India was first mooted by the Swaraja
Party in 1928. Dr. Sachhidanand Sinha was the Provincial president of the assembly that drafted the
Indian constitution later Rajendra Prasad took over. The constituent assembly set up 13 committees for
framing the constitution. On the basis of the reports, a draft of the constitution was prepared by a
seven member drafting committee under the chairmanship of Dr. B. R. Ambedkar. B.N. Rau acted as
the constitutional advisor to the constituent assembly. The preamble was proposed before the drafting
committee by J.L. Nehru.
2. While dealing with the reorganization of princely states, the constitution provided a four-fold
distribution of states, viz. A, B, C & D. Part A states comprised of nine erstwhile states under the
government of British India. Part B comprised of five princely states with legislatures. Part C of five
centrally administered areas & Part D comprised of Andamans & Nicobar.
3. The citizenship act of 1955 was first amended in 1986 & later in 2003. In 2003 a new law was passed
which permits PIO residing in 16 countries to have dual citizenship status. This will enable them to
participate in economic activities & real estate. However they cannot participate in elections.
4. The right to property (Article 31) eliminated from the list of fundamental rights by 44th amendment in
1978. Now it is a constitutional right.
5. The writ of Prohibition is available during the period when the proceedings are pending & the final
order is not made. Certiorari (meaning ‘to be informed’) can be issued only after the final order has
been made.
Ghanshyam Thori 9 Indian Polity
6. Right to education is granted by the 86th amendment carried out in 2002. Under this the government
shall provide free & compulsory education to all children from the age of 6 to 14. The right to
information has been granted to the citizens under the information act 2002.
7. In 1976 the delimitation of constituencies was freezed on the basis of the 1971 census upto 2001. In
2002 the 84th amendment extended the freeze up to 2026.
8. The Parliament can also legislate on subjects in the state list if (a) the Rajya Sabha passes a resolution
by 2/3rd majority (b.) if the legislatures of two or more states recommend to parliament (c) For the
implementation of treaty with foreign powers (d) during emergency.
9. The stages of bill introduction are first reading, publishing in gazette, second reading, referred to
committee, committee submits its report with recommendations (amendments can be introduced here)
& third reading involving formal voting to accept or reject the bill (No amendments possible here).
10. The final decision whether a bill is a money bill or not rests with the speaker. Rajya Sabha can delay
money bill only by 14 days.
11. Vote of Account is a provision to meet the expenses due the gap between the presentation & passage
of the budget. Normally vote of account is taken as two months for a sum equivalent to one-sixth of
the estimated expenditure of the whole financial year.
12. The government is collectively responsible only to the Lok Sabha.
13. In the appointment of the judges of the Supreme Court & the high courts, the president is bound t act
in accordance with the opinion of the Chief Justice of India who would tender his opinion after
consulting his colleagues.
14. The court appoints its officer & servants in consultation with the UPSC.
15. Bihar, J&K, Karnataka, Maharashtra & U.P are the only states with bicameral legislature.
16. Family Courts, Lok Adalats (under State Legal Aid & Advice Boards) & Nyaya Panchayat are other
judicial bodies.
17. The administrators are known as lieutenant governors (Daman & Pondicherry), Chief commissioners
(Andamans & Chandigarh) & as administrators (Lakshadweep)
18. In UTs with legislative assembly the right to legislate on subjects enumerated in the state list &
concurrent list vests with the assembly but for other UTs parliament enacts the laws.
19. The constitution has made special provision for the administration of scheduled areas in a state other
than Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura & Mizoram. The right to declare any area as scheduled area rests
with the President & is subject to legislation by the parliament.
20. Comptroller & auditor general looks after the accounts of both the centre & the state.
Ghanshyam Thori 10 Indian Polity
21. In case the law is passed by the state legislature & received the approval of the President before the
enactment of law on the same subject by the Parliament, the former prevails.
22. Sarkaria commissions recommendations included inter-governmental council formation, sparing use
of article 356, governor post/All India services/NDC to continue.
23. National Emergency: The proclamation of emergency should be approved by both houses within one
month of the date of issue & passed by 2/3rd majority otherwise ceases to operate in one month. Once
it has been approved it remains in force for a period of 6 months. The life of Lok Sabha can be
extended upto one year at a time & up to the period not exceeding beyond six months after the
proclamation ceases to operate. Fundamental rights except guaranteed in article 20 & 21 cannot be
suspended. Emergency was form 1962-68 & 1971-78. However according to 44th amendment, national
emergency cannot be declared on grounds of internal disturbances.
24. Emergency due to constitutional failure in state: Ceases to be in operation after the expiry of two
months unless approved by each house. After approval valid for 6 months. It can be extended by
parliament for a further period of 6 months. To extend further election commission should certify &
still maximum period is 3 years. Declared more than 100 times, first time in Punjab. The court can
strike down emergency if found unconstitutional & revive the dissolved state assembly.
25. Financial Emergency: Remains in force for a period of 2 months unless approved. After approval 6
months. The maximum period is 3 years. President can reduce salary of judges of all courts & ask all
money bills passed by state legislature to be reserved.
26. Initially the constitution recognized 14 regional languages which were Hindi, Sanskrit, Urdu, Telugu,
Tamil, Malayalam, Kannada, Marathi, Gujarati, Oriya, Bengali, Assamese, Punjabi, Kashmiri. Sindhi
was added through 21st amendment. In 1992 three additional languages – Konkani, Manipuri & Nepali
were added by 71st amendment. In 2003 four more languages – Bodo, Maithili, Santhali & Dogri were
added to the eighth schedule raising the number to 22.
27. Special Provisions for J&K: Directive priniciples & fundamental duties do not apply. High court of
J&K enjoys very limited powers & cannot declare any law unconstitutional or issue writs except for
enforcement of fundamental rights. Residuary powers rest with the state government. The V & VI
schedule of constitution regarding scheduled areas & scheduled tribes not applicable. Assembly
consists of 100 members & legislative council 36 members. Urdu is official language. The constitution
was adopted on November 17, 1957. No emergency except that due to war/external aggression can be
automatically extended to the state.
Ghanshyam Thori 11 Indian Polity
28. Money comes to consolidated fund of India from revenues, fresh loans, repayment of loans. Money
can be spent out of this fund only after approval of parliament. Expenses charged on this fund include
debt charges of GOI, sums payable due to court award & salaries of CAG, Auditor general, judges etc.
29. Contingency fund is at the disposal of President & was constituted in 1950 by parliament. Expenses
should be subsequently authorized by parliament. State govt contingency fund is with governor.
30. The security deposit for general elections is Rs 10,000 & for reserved seats 5,000.
31. The 52nd amendment added tenth schedule to the constitution which dealt with anti-defection. The
final decision rested with speaker regarding defection, though it can be challenged in court.
32. 6 all India party & over 40 regional parties. National party if it secures more 6 per cent of the votes
polled in any four or more states. In addition it must win at least four seats in the House of the People
or should have at least 2 percent of the Lok Sabha seats from at least three different states (ie 11 MPs).
Regional party only six percent in a single state or at least 3 seats in the Assembly.
33. 73rd amendment gave constitutional status to panchayati raj. If panchayat is dissolved before 5 years,
fresh elections should be held within 6 months.
34. Amendment normally needs at least two-thirds of the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha to pass it. When
Rajya Sabha disagrees with the proposals, the amenment bill is lost.
35. Proportional representation with single transferable vote is followed in the elections of President, Vice
President & Members of Rajya Sabha.
36. The government of India instituted Bharat Ratna & Padma Shri under Article 18 of the constitution.
37. The procedure of election of the President can be modified through an amendment passed by two-
thirds majority by both the houses & be ratified by legislatures of at least half of the states.
38. V.P Singh resigned after loosing vote of no confidence in the Lok Sabha.
39. Finance bill & appropriation bill are presented along with the budget. The recommendation of creation
of new all India services is the exclusive power of Rajya Sabha. A member of the panel of chairman
announced by the speaker presides over lok sabha if neither the speaker nor the depty speaker present.
40. 30 seats are reserved for STs in the Lok Sabha.
41. The concept of PIL originated in U.K. The number of judges of high court is determined by the
President.
42. The salary & emoluments of the president are exempt from income tax. This is not the case with chief
justice of India & election commissioner.
Ghanshyam Thori 12 Indian Polity
43. Disputes regarding the age of the judge of a highcourt shall be decided by the president in consultation
with the Chief Justice of India. A bench consisting of five or more judges is called a full bench of the
supreme court.
44. National commission for SC & the State Election Commission are not statutory body. Keeping the
units of Indian union under control & serving as the agents of the central government is not the
purpose of All India services.
45. Only war & external aggression can lead to suspension of fundamental rights under article 19. Armed
rebellion does not cause the suspension.
46. Provisions regarding citizenship & provisional parliament were given immediate effect from 26th
November 1949. Elections & fundamental rights came later on 26th January 1950.
47. Only when president’s rule is imposed, the parliament gests the exclusive authority to legislate on a
subject under state list.
48. When the three lists come in conflict, List-I has priority over both List II & List III. Further List III has
priority over List II. The expression ‘Judicial review’ is not explicitly stated in the constitution & is
implied. President of India is an integral part of the parliament.
49. The following enjoy the rank of a cabinet minister: deputy chairperson of planning commission,
Leader of opposition in Lok Sabha, Speaker of LS, and Chairman of Finance Commission. The
following are special voters in the elections to the lok sabha & the assemblies – Presidnet, VP,
Governors & Judges of the supreme court & high courts.
50. Lok Sabha enjoys the powers to pass vote on account, votes of credit & exceptional grants.
51. U.K has no written constitution. New Zealand was the first country to grant franchise to women.
Essential Extra Reference
• Important Amendments
Ghanshyam Thori 13 Indian Polity
Annexure - I
Other Articles of the Constitution
Part V The Union
Chapter I The Executive – The President & the Vice President
Article 52 The President of India
Article 53 Executive power of the Union
Article 54 Election of President
Article 55 Manner of election of President
Article 56 Term of office of President
Article 57 Eligibility for re-election
Article 58 Qualifications for election as President
Article 59 Conditions of President's office
Article 60 Oath or affirmation by the President
Article 61 Procedure for impeachment of the President
Article 62 Time of holding election to fill vacancy in the office of resident and the term of office
or person elected to fill casual vacancy
Article 63 The Vice-President Of India
Article 64 The Vice-President to be ex-officio Chairman of the Council of States
Article 65 The Vice-President to act as President or to discharge his functions during casual
vacancies in the office, or during the absence, of President
Article 66 Election of Vice-President
Article 67 Term of office of Vice-President
Article 68 Time of holding election to fill vacancy in the office of Vice-President and the term
of office of person elected to fill casual vacancy
Article 69 Oath or affirmation by the Vice-President
Article 70 Discharge of President's functions in other contingencies
Article 71 Matters relating to, or connected with, the election of a President or Vice-President
Article 72 Power of President to grant pardons, etc., and to suspend, remit or commute sentences
in certain cases
Article 73 Extent of executive power of the Union
Council of Ministers
Article 74 Council of Ministers to aid and advise President
Article 75 Other provisions as to Ministers
Attorney General of India
Article 76 Attorney-General for India
Conduct of Government Business
Article 77 Conduct of business of the Government of India
Article 78 Duties of Prime Minister as respects the furnishing of information to the President,
etc.
Chapter II Parliament
Article 79 Constitution of Parliament
Article 80 Composition of the Council of States -
Article 81 Composition of the House of the People
Article 82 Readjustment after each census
Article 83 Duration of Houses of Parliament
Article 84 Qualification for membership of Parliament
Ghanshyam Thori 14 Indian Polity
Article 85 Sessions of Parliament, prorogation and dissolution
Article 86 Right of President to address and send messages to Houses
Article 87 Special address by the President
Article 88 Rights of Ministers and Attorney-General as respects Houses
Officers of the Paliament
Article 89 The Chairman and Deputy Chairman of the Council of States
Article 90 Vacation and resignation of, and removal from, the office of Deputy Chairman
Article 91 Power of the Deputy Chairman or other person to perform the duties of the office of,
or to act as, Chairman
Article 92 The Chairman or the Deputy Chairman not to preside while a resolution for his
removal from office is under consideration
Article 93 The Speaker and Deputy Speaker of the House of the People
Article 94 Vacation and resignation of, and removal from, the offices of Speaker and Deputy
Speaker
Article 95 Power of the Deputy Speaker or other person to perform the duties of the office of, or
to act as Speaker
Article 96 The Speaker or the Deputy Speaker not to preside while a resolution for his removal
from office is under consideration
Article 97 Salaries and allowances of the Chairman and Deputy Chairman and the Speaker and
Deputy Speaker
Article 98 Secretariat of Parliament
Conduct of Business
Article 99 Oath or affirmation by members
Article 100 Voting in Houses, power of Houses to act notwithstanding vacancies and quorum
Disqualification of Members
Article 101 Vacation of seats
Article 102 Disqualifications for membership
Article 103 Decision on questions as to disqualifications of members
Article 104 Penalty for sitting and voting before making oath or affirmation under article 99 or
when not qualified or when disqualified
Powers, Priviledges & Immunities of Parliament & its Members
Article 105 Powers, Privileges, etc., of the Houses of Parliament and of the members and
committees thereof
Article 106 Salaries and allowances of members
Legislative Procedure
Article 107 Provisions as to introduction and passing of Bills
Article 108 Joint sitting of both Houses in certain cases
Article 109 Special procedure in respect of Money Bills
Article 110 Definition of "Money Bills"
Article 111 Assent to Bills
Procedure in Financial Matters
Article 112 Annual financial statement
Article 113 Procedure in Parliament with respect to estimates (1) So much of the estimates as
relates to expenditure charged upon the Consolidated Fund of India shall not be
submitted to the vote of Parliament, but nothing in this clause shall be construed as
preventing the discussion in either House of Parliament of any of those estimates.
Article 114 Appropriation Bills
Ghanshyam Thori 15 Indian Polity
Article 115 Supplementary, additional or excess grants
Article 116 Votes on account, votes of credit and exceptional grants
Article 117 Special provisions as to financial Bills
Article 118 Rules of procedure
Procedure Generally
Article 119 Regulation by law of procedure in Parliament in relation to financial business
Article 120 Language to be used in Parliament
Article 121 Restriction on discussion in Parliament
Article 122 Courts not inquire into proceedings of Parliament
Chapter III Legislative Powers of the President
Article 123 Power of President to promulgate Ordinances during recess of Parliament
Chapter IV The Union Judiciary
Article 124 Establishment and Constitution of Supreme Court
Article 125 Salaries, etc., of Judges
Article 126 Appointment of acting Chief Justice
Article 127 Appointment of ad hoc Judges
Article 128 Attendance of retired Judges at sittings of the Supreme Court
Article 129 Supreme Court to be a court of record
Article 130 Seat of Supreme Court
Article 131 Original jurisdiction of the Supreme Court
Article 131A [Repealed] Executive jurisdiction of the Supreme Court in regard to questions as to
constitutional validity of Central laws
Article 132 Appellate jurisdiction of Supreme Court in appeals from High Court in certain cases
Article 133 Appellate jurisdiction of Supreme Court in appeals from High Courts in regard to
civil matters
Article 134 Appellate jurisdiction of Supreme Court in regard to criminal matters
Article 134A Certificate for appeal to the Supreme Court
Article 135 Jurisdiction and powers of the Federal Court under existing law to be exercisable by
the Supreme Court
Article 136 Special leave to appeal by the Supreme Court
Article 137 Review of judgements or orders by the Supreme Court
Article 138 Enlargement of the jurisdiction of the Supreme Court
Article 139 Conferment on the Supreme Court of powers to issue certain writs
Article 139A Transfer of certain cases
Article 140 Ancillary powers of Supreme Court
Article 141 Law declared by Supreme Court to be binding on all courts
Article 142 Enforcement of decrees and orders of Supreme Court and orders as to discovery, etc.
Article 143 Power of President to consult Supreme Court
Article 144 Civil and judicial authorities to act in aid of the Supreme Court
Article 144A [Repealed]
Article 145 Rules of Court, etc.
Article 146A Officers and servants and the expenses of the Supreme Court
Article 147 Interpretation
Chapter V Comptroller and Auditor-General of India
Article 148 Comptroller and Auditor-General of India
Article 149 Duties and powers of the Comptroller and Auditor-General
Article 150 Form of accounts of the Union and of the States
Ghanshyam Thori 16 Indian Polity
Article 151 Audit reports
Part VI The States
Chapter I General
Article 152 Definition
Chapter II The Executive – The Governor
Article 153 Governors of States
Article 154 Executive power of State
Article 155 Appointment of Governor
Article 156 Term of office of Governor
Article 157 Qualifications for appointment as Governor
Article 158 Conditions of Governor's office
Article 159 Oath or affirmation by the Governor
Article 160 Discharge of the functions of the Governor in certain contingencies
Article 161 Power of Governor to grant pardons, etc., and to suspend, remit or commute
sentences in certain cases
Article 162 Extent of executive power of State
Council of Ministers
Article 163 Council of Ministers to aid and advise Governor
Article 164 Other provisions as to Ministers
Advocate General of the State
Article 165 Advocate-General for the State
Conduct of Government Business
Article 166 Conduct of business of the Government of a State
Article 167 Duties of Chief Minister as respects the furnishing of information to Governor, etc.
Chapter III The State Legislature
Article 168 Constitution of Legislatures in States
Article 169 Abolition or creation of Legislative Councils in States
Article 170 Composition of the Legislative Assemblies
Article 171 Composition of the Legislative Council
Article 172 Duration of States Legislatures
Article 173 Qualification for membership of the State Legislature
Article 174 Sessions of the State Legislature, prorogation and dissolution
Article 175 Right of Governor to address and send messages to the House or Houses
Article 176 Special address by the Governor
Article 177 Rights of Ministers and Advocate
Officers of the State Legislature
Article 178 The Speaker and Deputy Speaker of the Legislative Assembly
Article 179 Vacation and resignation of, and removal from, the offices of Speaker and Deputy
Speaker
Article 180 Power of the Deputy Speaker or other person to perform the duties of the office of, or
to act as, Speaker
Article 181 The Speaker or the Deputy Speaker not to preside while a resolution for his removal
from office is under consideration
Article 182 The Chairman and Deputy Chairman of the Legislative Council
Article 183 Vacation and resignation, of and removal from, the offices of Chairman and Deputy
Chairman
Article 184 Power of the Deputy Chairman or other person to perform the duties of the office of,
Ghanshyam Thori 17 Indian Polity
or to act as, Chairman
Article 185 The Chairman or the Deputy Chairman not to preside while a resolution for his
removal from office is under consideration
Article 186 Salaries and allowances of the Speaker and Deputy Speaker and the Chairman and
Deputy Chairman
Article 187 Secretariat of State Legislature
Article 188 Oath or affirmation by members
Conduct of Business
Article 189 Voting in Houses, power of Houses to act notwithstanding vacancies and quorum
Article 190 Vacation of seats
Disqualification of Members
Article 191 Disqualification for membership
Article 192 Decision on question as to disqualifications of members
Article 193 Penalty for sitting and voting before making oath or affirmation under article 188 or
when not qualified or when disqualified
Power, Privileges & Immunities of State Legislatures & their Members
Article 194 Powers, privileges, etc., of the Houses of Legislatures and of the members and
committees thereof
Article 195 Salaries and allowances of members
Legislative Procedure
Article 196 Provisions as to introduction and passing of Bills
Article 197 Restriction on powers of Legislative Council as to Bills other than Money Bills
Article 198 Special procedure in respect of Money Bills
Article 199 Definition of "Money Bills"
Article 200 Assent to Bills
Article 201 Bills reserved for consideration
Procedure in Financial Matters
Article 202 Annual financial statement
Article 203 Procedure in Legislature with respect to estimates
Article 204 Appropriation Bills
Article 205 Supplementary, additional or excess grants
Article 206 Votes on account, votes of credit and exceptional grants
Article 207 Special provisions as to financial Bills
Procedure Generally
Article 208 Rules of procedure
Article 209 Regulation by law of procedure in the Legislature of the State in relation to financial
business
Article 210 Language to be used in the Legislature
Article 211 Restriction on discussion in the Legislature
Article 212 Courts not to inquire into proceedings of the Legislature
Chapter IV Legislative Power of the Governor
Article 213 Power of Governor to promulgate Ordinances during recess of Legislature
Chapter V The High Courts in the States
Article 214 High Courts for States
Article 215 High Courts to be courts of record
Article 216 Constitution of High Courts
Article 217 Appointment and conditions of the office of a Judge of a High Court
Ghanshyam Thori 18 Indian Polity
Article 218 Application of certain provisions relating to Supreme Court to High Courts
Article 219 Oath or affirmation by Judges of High Courts
Article 220 Restriction on practice after being a permanent Judge
Article 221 Salaries, etc., of Judges
Article 222 Transfer of a Judge from one High Court to another
Article 223 Appointment of acting Chief Justice
Article 224 Appointment of additional and acting Judges
Article 224A Appointment of retired Judges at sittings of High Courts
Article 225 Jurisdiction of existing High Courts
Article 226 Power of High Courts to issue certain writs
Article 226A [Repealed] Constitutional validity of Central laws not to be considered in
proceedings under article 226
Article 227 Power of superintendence over all courts by the High Court
Article 228 Transfer of certain cases to High Court
Article 228A [Repealed] Special provisions as to disposal of questions relating to constitutional
validity of State laws
Article 229 Officers and servants and the expenses of High Courts
Article 230 Extension of jurisdiction of High Courts to Union territories
Article 231 Establishment of a common High Court for two or more States
Chapter VI Subordinate Courts
Article 233 Appointment of district judges
Article 233A Validation of appointments of, and judgments, etc. delivered by, certain district
judges
Article 234 Recruitment of persons other than district judges to the judicial service
Article 235 Control over subordinate courts
Article 236 Interpretation
Article 237 Application of the provisions of this Chapter to certain class or classes of magistrates
Part VII [Repealed] The States in Part B of the First Schedule
Part VIII The Union Territories
Article 239 Administration of Union territories
Article 239A Creation of local Legislatures or Council of Ministers or both for certain Union
territories
Article 239AA Special provisions with respect to Delhi
Article 239AB Provision in case of failure of constitutional monarchy
Article 239B Power of administrator to promulgate Ordinances during recess of Legislature
Article 240 Power of President to make regulations for certain Union territories
Article 241 High Courts for Union territories
Article 242 [Repealed]
Part IX The Panchayats
Article 243 Definitions
Article 243A Gram Sabha
Article 243B Constitution of Panchayats
Article 243C Composition of Panchayats
Article 243D Reservation of seats
Article 243E Duration of Panchayats, etc.
Article 243F Disqualifications for membership
Article 243G Powers, authority and responsibilities of Panchayats
Ghanshyam Thori 19 Indian Polity
Article 243H Powers to impose taxes by, and Funds of, the Panchayats
Article 243I Constitution of Finance Commission to review financial position
Article 243J Audit of accounts of Panchayats
Article 243K Elections to the Panchayats
Article 243L Application to Union territories
Article 243M Part not to apply to certain areas
Article 243N Continuance of existing laws and Panchayats
Article 243O Bar to interference by courts in electoral matters
Part IXA The Municipalities
Article 243P Definitions
Article 243Q Constitution of Municipalities
Article 243R Composition of Municipalities
Article 243S Constitution and composition of Wards Committees, etc.
Article 243T Reservation of seats
Article 243U Duration of Municipalities, etc.
Article 243V Disqualifications for membership
Article 243W Powers, authority and responsibilities of Municipalities etc.
Article 243X Power to impose taxes by, and Funds of, the Municipalities
Article 243Y Finance Commission
Article 243Z Audit of accounts of Municipalities
Article 243ZA Elections to the Municipalities
Article 243ZB Application to Union territories
Article 243ZC Part not to apply to certain areas
Article 243ZD Committee for district planning
Article 243ZE Committee for Metropolitan planning
Article 243ZF Continuance of existing laws and Municipalities
Article 243ZG Bar to interference by Courts in electoral matters
Part X The Scheduled and Tribal Areas
Article 244 Administration of Scheduled Areas and Tribal Areas
Article 244A Formation of an autonomous State comprising certain tribal areas in Assam and
creation of local Legislature or Council of Ministers or both therefor
Part XI Relations Between the Union and the States
Chapter I Legislative Relations
Article 245 Extent of laws made by Parliament and by the Legislatures of States
Article 246 Subject-matter of laws made by Parliament and by the Legislatures of States
Article 247 Power of Parliament to provide for the establishment of certain additional courts
Article 248 Residuary powers of legislation
Article 249 Power of Parliament to legislate with respect to a matter in the State List in the
National interest
Article 250 Power of Parliament to legislate with respect to any matter in the State List if a
Proclamation of Emergency is in operation
Article 251 Inconsistency between laws made by Parliament under articles 249 and 250 and laws
made by the legislatures of States
Article 252 Power of Parliament to legislate for two or more States by consent and adoption of
such legislation by any other State
Article 253 Legislation for giving effect to international agreements
Article 254 Inconsistency between laws made by Parliament and laws made by the Legislatures
Ghanshyam Thori 20 Indian Polity
of States
Article 255 Requirements as to recommendations and previous sanctions to be regarded as
matters of procedure only
Chapter II Administrative Relations
Article 256 Obligation of States and the Union
Article 257 Control of the Union over States in certain cases
Article 257A Assistance to States by deployment of armed forces or other forces of the Union
Article 258 Power of the Union to confer powers, etc., on States in certain cases
Article 258A Power of the States to entrust functions to the Union
Article 259 [Repealed] Armed Forces in States in Part B of the First Schedule
Article 260 Jurisdiction of the Union in relation to territories outside India
Article 261 Public acts, records and judicial proceedings
Disputes relating to Waters
Article 262 Adjudication of disputes relating to waters of inter-State rivers or river valleys
Co-ordination between States
Article 263 Provisions with respect to an inter-State Council
Part XII Finance, Property, Contracts and Suits
Chapter I Finance
Article 264 Interpretation
Article 265 Taxes not to be imposed save by authority of law
Article 266 Consolidated Funds and public accounts of India and of the States
Article 267 Contingency Fund
Article 268 Duties levied by the Union but collected and appropriated by the States
Article 269 Taxes levied and collected by the Union but assigned to the States
Article 270 Taxes levied and collected by the Union and distributed between the Union and the
States
Article 271 Surcharge on certain duties and taxes for purposes of the Union
Article 272 [Omitted]
Article 273 Grants in lieu of export duty on jute and jute products
Article 274 Prior recommendation of President require to Bills affecting taxation in which States
are interested
Article 275 Grants from the Union to certain States
Article 276 Taxes on professions, trades, callings and employments
Article 277 Savings
Article 278 [Repealed] Agreement with States in Part B of the First Schedule with regard to
certain financial matters
Article 279 Calculation of "net proceeds", etc.
Article 280 Finance Commission
Article 281 Recommendations of the Finance Commission
Miscellaneous Financial Provisions
Article 282 Expenditure defrayable by the Union or a State out of its revenues
Article 283 Custody, etc., of Consolidated Funds, Contingency Funds and moneys credited to the
public accounts
Article 284 Custody of suitors' deposits and other moneys received by public servants and courts
Article 285 Exemption of property of the Union from State taxation
Article 286 Restriction as to imposition of tax on the sale or purchase of goods
Article 287 Exemption from taxes on electricity
Ghanshyam Thori 21 Indian Polity
Article 288 Exemption from taxation by States in respect of water or electricity in certain cases
Article 289 Exemption of property and income of a State from Union taxation
Article 290 Adjustment in respect of certain expenses and pensions
Article 290A Annual payment to certain Devaswom Funds
Article 291 [Repealed]
Chapter II Borrowing
Article 292 Borrowing by the Government of India
Article 293 Borrowing by States
Chapter III Property, Contacts, Rights, Liabilities, Obligations and Suits
Article 294 Succession to property, assets, rights, liabilities and obligations in certain cases
Article 295 Succession to property, assets, rights, liabilities and obligations in other cases
Article 296 Property accruing by escheat or lapse or as Bona vacantia
Article 297 Things of value within territorial waters or continental shelf and resources of the
exclusive economic zone to vest in the Union
Article 298 Power to carry on trade, etc.
Article 299 Contracts
Article 300 Suits and proceedings
Chapter IV Right to Property
Article 300A Persons not to be deprived of property save by authority of law
Part XIII Trade, Commerce and Intercourse Within the Territory of India
Article 301 Freedom of trade, commerce and intercourse
Article 302 Power of Parliament to impose restrictions on trade, commerce and intercourse
Article 303 Restrictions on the legislative powers of the Union and of the States with regard to
trade and commerce
Article 304 Restriction on trade, commerce and intercourse among States
Article 305 Saving of existing laws and laws providing for State monopolies
Article 306 [Repealed]
Article 307 Appointment of authority for carrying out the purposes of articles 301 to 304
Part XIV Services Under the Union and the States
Chapter I Services
Article 308 Interpretation
Article 309 Recruitment and conditions of service of persons serving the Union or a State
Article 310 Tenure of office of persons serving the Union or a State
Article 311 Dismissal, removal or reduction in rank of persons employed in civil capacities under
the Union or a State
Article 312 All-India services
Article 312A Power of Parliament to vary or revoke conditions of service of officers of certain
services
Article 313 Transitional provisions
Article 314 [Repealed]
Chapter II Public Service Commissions
Article 315 Public Service Commissions for the Union and for the States
Article 316 Appointment and term of office of members
Article 317 Removal and suspension of a member of a Public Service Commission
Article 318 Power to make regulations as to conditions of service of members and staff of the
Commission
Article 319 Prohibition as to the holding of offices by members of Commission on ceasing to be
Ghanshyam Thori 22 Indian Polity
such members
Article 320 Functions of Public Service Commissions
Article 321 Power to extend functions of Public Service Commissions
Article 322 Expenses of Public Service Commissions
Article 323 Reports of Public Service Commissions
Part XIVA Tribunals
Article 323A Administrative tribunals
Article 323B Tribunals for other matters
Part XV Elections
Article 324 Superintendence, direction and control of elections to be vested in an election
commission
Article 325 No person to be ineligible for inclusion in, or to claim to be included in a special,
electoral roll on grounds of religion, race, caste or sex
Article 326 Elections to the House of the People and to the Legislative Assemblies of States to be
on the basis of adult suffrage
Article 327 Power of Parliament to make provision with respect to elections to Legislatures
Article 328 Power of Legislature of a State to make provision with respect to elections to such
Legislature
Article 329 Bar to interference by courts in electoral matters
Article 329A [Repealed
Part XVI Special Provisions Relating to Certain Classes
Article 330 Reservation of seats for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes in the House of the
People
Article 331 Representation of the Anglo-Indian community in the House of the People
Article 332 Reservation of seats for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes in the Legislative
Assemblies of the States
Article 333 Representation of the Anglo-Indian community in the Legislative Assemblies of the
States
Article 334 Reservation of seats and special representation to cease after fifty years
Article 335 Claims of Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes to services and posts
Article 336 Special provision for Anglo-Indian community in certain services
Article 337 Special provision with respect to educational grants for the benefit of Anglo-Indian
community
Article 338 National Commission for Scheduled Castes,
Article 338A National Commission for Scheduled Tribes
Article 339 Control of the Union over the administration of Scheduled Areas and the welfare of
Scheduled Tribes
Article 340 Appointment of a Commission to investigate the conditions of backward classes
Article 341 Scheduled Castes
Article 342 Scheduled Tribes
Part XVII Official Language
Chapter I Language of the Union
Article 343 Official language of the Union
Article 344 Commission and Committee of Parliament on official language
Chapter II Regional Languages
Article 345 Official language or languages of a State
Article 346 Official language for communication between one State and another or between a
Ghanshyam Thori 23 Indian Polity
State and the Union
Article 347 Special provision relating to language spoken by a section of the population of a
State
Chapter III Language of the Supreme Court, High Courts, etc.
Article 348 Language to be used in the Supreme Court and in the High Courts and for Acts,
Bills, etc.
Article 349 Special procedure for enactment of certain laws relating to language
Chapter IV Special Directives
Article 350 Language to be used in representations for redress of grievances
Article 350A Facilities for instruction in mother-tongue at primary stage
Article 350B Special Officer for linguistic minorities
Article 351 Directive for development of the Hindi language
Part XVIII Emergency Provisions
Article 352 Proclamation of National Emergency
Article 353 Effect of Proclamation of Emergency
Article 354 Application of provisions relating to distribution of revenues while a Proclamation of
Emergency is in operation
Article 355 Duty of the Union to protect States against external aggression and internal
disturbance
Article 356 Provisions in case of failure of constitutional machinery in States
Article 357 Exercise of legislative powers under Proclamation issued under article 356
Article 358 Suspension of provisions of article 19 during emergencies
Article 359 Suspension of the enforcement of the rights conferred by Part III during emergencies
Article 359A [Repealed] Application of this Part to the State of Punjab
Article 360 Provisions as to financial emergency
Part XIX Micsellaneous
Article 361 Protection of President and Governors and Rajpramukhs
Article 361A Protection of publication of proceedings of Parliament and State Legislatures
Article 362 [Repealed] Rights and privileges of Rulers of Indian States
Article 363 Bar to interference by courts in disputes arising out of certain treaties, agreements,
etc.
Article 363A Recognition granted to Rulers of Indian States to cease and Privy purses to be
abolished
Article 364 Special provisions as to major ports and aerodromes
Article 365 Effect of failure to comply with, or to give effect to, directions given by the Union
Article 366 Definitions
Article 367 Interpretation
Part XX Amendment of the Constitution
Article 368 Power of Parliament to amend the Constitution and procedure therefor
Part XXI Temporary, Transitional and Special Provisions
Article 369 Temporary power to Parliament to make laws with respect to certain matters in the
State List as if they were matters in the Concurrent List
Article 370 Temporary provisions with respect to the State of Jammu and Kashmir
Article 371 Special provision with respect to the States of Maharashtra and Gujarat
Article 371A Special provision with respect to the State of Nagaland
Article 371B Special provision with respect to the State of Assam
Article 371C Special provision with respect to the State of Manipur
Ghanshyam Thori 24 Indian Polity
Article 371D Special provisions with respect to the State of Andhra Pradesh
Article 371E Establishment of Central University in Andhra Pradesh
Article 371F Special provisions with respect to the State of Sikkim
Article 371G Special provision with respect to the State of Mizoram
Article 371H Special provision with respect to the State of Arunachal Pradesh
Article 371I Special provision with respect to the State of Goa
Article 372 Continuance in force of existing laws and their adaptation
Article 372A Power of the President to adapt laws
Article 373 Power of President to make order in respect of persons under preventive detention in
certain cases
Article 374 Provisions as to Judges of the Federal Court and proceedings pending in the Federal
Court or before His Majesty in Council
Article 375 Courts, authorities and officers to continue to function subject to the provisions of the
Constitution
Article 376 Provisions as to Judges of High Courts
Article 377 Provisions as to Comptroller and Auditor-General of India
Article 378 Provisions as to Public Commissions
Article 378A Special provisions as to duration of Andhra Pradesh Legislative Assembly
Article 379 [Article 379-391 Repealed]
Article 392 Power of the President to remove difficulties
Part XXII Short Title, Commencement, Authoritative Text in Hindu and Repeals
Article 393 Short title
Article 394 Commencement
Article 394A Authoritative text in the Hindi language
Article 395 Repeals
Ghanshyam Thori 25 Indian Polity
You might also like
- SCOTUS Question in Re: Christopher Hallett v. The Florida Department of RevenueDocument56 pagesSCOTUS Question in Re: Christopher Hallett v. The Florida Department of RevenueNacho Man50% (2)
- Attestation ON Non-Disclosure Declaration: Do Not Write On This PartDocument1 pageAttestation ON Non-Disclosure Declaration: Do Not Write On This PartTrisha Barrios100% (1)
- Indian Polity (2018)Document21 pagesIndian Polity (2018)blue azureNo ratings yet
- IMP Articles of Indian ConstitutionDocument8 pagesIMP Articles of Indian ConstitutionNandita NanditaNo ratings yet
- Polity Ready ReckonDocument57 pagesPolity Ready Reckonjijo jacobNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity Full PDF EM PDFDocument127 pagesIndian Polity Full PDF EM PDFnitshya samNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity: Presented by Bhupesh SirDocument72 pagesIndian Polity: Presented by Bhupesh SirRaju BansalNo ratings yet
- L IV E: Indian PolityDocument111 pagesL IV E: Indian PolityALLU SRISAINo ratings yet
- Polity GoveranceDocument156 pagesPolity GoveranceMohammad FareedNo ratings yet
- Newslive 23rdfeb2014 Telangana KilliDocument20 pagesNewslive 23rdfeb2014 Telangana KillideekshithNo ratings yet
- Ilp 2017 Set 2 Block 1 Polity Value Add 1Document102 pagesIlp 2017 Set 2 Block 1 Polity Value Add 1nidhi100% (1)
- Strategy To Prepare Polity For UPSC - How To Read Indian Polity Mrunal, Laxmikant For UPSCDocument9 pagesStrategy To Prepare Polity For UPSC - How To Read Indian Polity Mrunal, Laxmikant For UPSCChat GPTNo ratings yet
- 100 Pages - Prelims Booster - Indian Polity - 6194160Document101 pages100 Pages - Prelims Booster - Indian Polity - 6194160prasanti2088No ratings yet
- E Book IAS Main History Optional Papers Year 1779 2012Document51 pagesE Book IAS Main History Optional Papers Year 1779 2012annaNo ratings yet
- Modern History Question Bank 1979 2018 3Document46 pagesModern History Question Bank 1979 2018 3Master pratikNo ratings yet
- EconomyDocument138 pagesEconomyShambhavi SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Polity Laxmikant Short NotesDocument120 pagesPolity Laxmikant Short NotesKundanNo ratings yet
- Indian ConstitutionDocument54 pagesIndian Constitutionnisha dolas100% (9)
- Constitutional Bodies in IndiaDocument12 pagesConstitutional Bodies in IndiaRishabh SareenNo ratings yet
- AP White Paper On Bifurcation IssuesDocument32 pagesAP White Paper On Bifurcation IssuesharishsairamNo ratings yet
- Constitution 1500+ Q&ADocument73 pagesConstitution 1500+ Q&Aprachi singhNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity Bit BankDocument130 pagesIndian Polity Bit Banksuresh100% (4)
- POLITY 1000 MCQs With Explanatory Notes PDFDocument425 pagesPOLITY 1000 MCQs With Explanatory Notes PDFsakjdhasNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity Complete BookletDocument398 pagesIndian Polity Complete BookletAjeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Indian PolityDocument46 pagesIndian PolityAryan Raj100% (3)
- NEXT IAS UNION BUDGET 2023-24 MCQsDocument20 pagesNEXT IAS UNION BUDGET 2023-24 MCQsLBKNo ratings yet
- Geography Question BankDocument198 pagesGeography Question BankChandan NayakNo ratings yet
- Neonclassespolityenglishebook PDFDocument169 pagesNeonclassespolityenglishebook PDFkalpeshNo ratings yet
- Indian PolityDocument44 pagesIndian Politymkrao_kiranNo ratings yet
- Upsc Faqs: by Mayank Mishra (AIR-172 UPSC CSE 2019) General InformationsDocument9 pagesUpsc Faqs: by Mayank Mishra (AIR-172 UPSC CSE 2019) General InformationsARYAN PANCHOLINo ratings yet
- Indian Plity 2 EngDocument136 pagesIndian Plity 2 EngRK ENTERPRISESNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Indian ConstitutionDocument10 pagesParts of The Indian Constitutionserryserry362No ratings yet
- Polity Pages From THE MEGA YEARBOOK PDFDocument70 pagesPolity Pages From THE MEGA YEARBOOK PDFchanduNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity OnelinerDocument5 pagesIndian Polity OnelinerKiran PatilNo ratings yet
- Polity Notes For PrelimsDocument90 pagesPolity Notes For PrelimsVivekanand sahooNo ratings yet
- Modern History Revision Notes - IxambeeDocument25 pagesModern History Revision Notes - IxambeeTanish KalraNo ratings yet
- Kalyan Sir - Quick Look-2 (Indian Polity) PDFDocument10 pagesKalyan Sir - Quick Look-2 (Indian Polity) PDFR Aditya Vardhana Reddy100% (5)
- PMFIAS Environment First Vs Second EditionDocument181 pagesPMFIAS Environment First Vs Second Editionchaitanyasktp9414100% (1)
- All Important Terms History (CDS, Capf, Upsc-Cse)Document2 pagesAll Important Terms History (CDS, Capf, Upsc-Cse)Shubham KhairnarNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Econ - Van 3Document50 pagesModule 1 - Econ - Van 3Md.T. ZafarNo ratings yet
- Wbcs Indian Polity - 4edaf311 778c 4a79 Bbc2 03c140c2dc9aDocument344 pagesWbcs Indian Polity - 4edaf311 778c 4a79 Bbc2 03c140c2dc9aSubhadeep MallikNo ratings yet
- The Government of India Act, 1858Document3 pagesThe Government of India Act, 1858Sana MNo ratings yet
- Env 3Document32 pagesEnv 3Vinay GowdaNo ratings yet
- History Question Bank PDFDocument254 pagesHistory Question Bank PDFHimanshu SaxenaNo ratings yet
- UPSC Model AnswerDocument20 pagesUPSC Model AnswerFaraz AliNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity GIST of NCERTDocument26 pagesIndian Polity GIST of NCERTssingh_scribdNo ratings yet
- Indian EconomyDocument185 pagesIndian EconomyManohar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity PDFDocument25 pagesIndian Polity PDFAnonymous iQMKqMqqWNo ratings yet
- Indian PolityDocument26 pagesIndian Politymanya_borudeNo ratings yet
- Coi 1,2Document28 pagesCoi 1,2sisodiyaa853No ratings yet
- Making of The ConstitutionDocument12 pagesMaking of The ConstitutionPriyatam BolisettyNo ratings yet
- Polity 4Document10 pagesPolity 4vishalbharati10230No ratings yet
- Parliment of IndiaDocument40 pagesParliment of IndiaSandeep KattiNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity NotesDocument14 pagesIndian Polity Notesanandwe2673No ratings yet
- Parliament of IndiaDocument73 pagesParliament of IndiaKj RajuNo ratings yet
- Member of The Legislative AssemblyDocument3 pagesMember of The Legislative Assemblyಸುರೇಶ್ ಎನ್ ರಂಗನಾಥ್No ratings yet
- Making of The ConstitutionDocument10 pagesMaking of The ConstitutionRavinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Commentary On Indian ConstitutionDocument109 pagesCommentary On Indian ConstitutionDharmendra YadavNo ratings yet
- Union Executives 291674218996584Document54 pagesUnion Executives 291674218996584Andy bloaterNo ratings yet
- Persons Digests by A2016Document332 pagesPersons Digests by A2016Nikki MalferrariNo ratings yet
- Bill of Rights ScenariosDocument26 pagesBill of Rights Scenariosapi-250636862No ratings yet
- Benguet Vs FloresDocument4 pagesBenguet Vs FloresJoan MacedaNo ratings yet
- 1308 Allied Bank Vs CA - UlangkayaDocument1 page1308 Allied Bank Vs CA - UlangkayaJasielle Leigh UlangkayaNo ratings yet
- Winding Up Under Just & Equitable GroundsDocument12 pagesWinding Up Under Just & Equitable GroundsPawas SinghNo ratings yet
- Commercial Lease Agreement Template 02Document10 pagesCommercial Lease Agreement Template 02khan jeeNo ratings yet
- Civil Service Commission Res. No. 01-0940Document16 pagesCivil Service Commission Res. No. 01-0940JaneGonzalezMartinez100% (1)
- Ceat Bike TyreDocument4 pagesCeat Bike TyrenijithNo ratings yet
- Script Arraignment 1Document19 pagesScript Arraignment 1MineNo ratings yet
- P.varshini HC17144 CRPC ProjectDocument18 pagesP.varshini HC17144 CRPC ProjectVarshini PrabaharanNo ratings yet
- 18 D.K. Basu Guidelines PDFDocument2 pages18 D.K. Basu Guidelines PDFGAMING 4 FUNNo ratings yet
- Hermoso v. CADocument3 pagesHermoso v. CAClyde Tan100% (2)
- Act Justly, Love Tenderly, and Walk Humbly With God (Micah 6:8)Document35 pagesAct Justly, Love Tenderly, and Walk Humbly With God (Micah 6:8)Cry BeroNo ratings yet
- Commissioner of BIR Vs Court of Appeals GR. No. 124043 DigestDocument2 pagesCommissioner of BIR Vs Court of Appeals GR. No. 124043 DigestAmity Rose RiveroNo ratings yet
- Academic Freedom CruzDocument2 pagesAcademic Freedom CruzalmorsNo ratings yet
- Case Digest - Biraogo Vs Philippine Truth CommissionDocument3 pagesCase Digest - Biraogo Vs Philippine Truth CommissionHezro Inciso CaandoyNo ratings yet
- Buyer Agency AgreementDocument2 pagesBuyer Agency AgreementDarrylj VerduynNo ratings yet
- McPherson v. Tennessee Football, Inc. - Document No. 1Document4 pagesMcPherson v. Tennessee Football, Inc. - Document No. 1Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Gerbero DamagesDocument5 pagesGerbero DamagescarmineNo ratings yet
- Lawsuit Filed in Deadly North Myrtle Beach CrashDocument5 pagesLawsuit Filed in Deadly North Myrtle Beach CrashKristinNo ratings yet
- M. D. Transit vs. de Guzman, G.R. No. L-18810, April 23, 1963, 7 SCRA 726Document4 pagesM. D. Transit vs. de Guzman, G.R. No. L-18810, April 23, 1963, 7 SCRA 726Ivan LeeNo ratings yet
- Administrative Circular No 20-2002 - Referral of Cases For MediationDocument3 pagesAdministrative Circular No 20-2002 - Referral of Cases For MediationmarcialxNo ratings yet
- Doctrine of ElectionDocument3 pagesDoctrine of ElectionzeusapocalypseNo ratings yet
- Amatan V AujeroDocument2 pagesAmatan V AujeroJay Kent RoilesNo ratings yet
- Acacia Media Technologies Corporation v. Club Jenna, Inc. Et Al - Document No. 2Document1 pageAcacia Media Technologies Corporation v. Club Jenna, Inc. Et Al - Document No. 2Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Lucious Williams, Jr. v. Earl Butz, 843 F.2d 1335, 11th Cir. (1988)Document6 pagesLucious Williams, Jr. v. Earl Butz, 843 F.2d 1335, 11th Cir. (1988)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Heirs of Yaptinchay Vs Del RosarioDocument4 pagesHeirs of Yaptinchay Vs Del RosarioIan Van MamugayNo ratings yet
- Developmental Victimology - The Comprehensive Study of Childhood Victimizations PDFDocument26 pagesDevelopmental Victimology - The Comprehensive Study of Childhood Victimizations PDFatjoerossNo ratings yet