Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AU307 Vehicle Body Engineering
AU307 Vehicle Body Engineering
Uploaded by
Mathews P Reji0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
287 views2 pagesThis document outlines the course details and syllabus for the "Vehicle Body Engineering" course offered in 2016. The course aims to impart knowledge on vehicle body design for maximum passenger comfort and minimizing drag. The syllabus covers topics like vehicle body types and dimensions, aerodynamics, materials, structural analysis, stability, noise and vibration, safety, and computational fluid dynamics simulations. The course aims to enable students to design vehicle bodies for comfort and low drag. It involves both theoretical and practical modules taught through lectures and internal exams.
Original Description:
syllabus of ktu
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines the course details and syllabus for the "Vehicle Body Engineering" course offered in 2016. The course aims to impart knowledge on vehicle body design for maximum passenger comfort and minimizing drag. The syllabus covers topics like vehicle body types and dimensions, aerodynamics, materials, structural analysis, stability, noise and vibration, safety, and computational fluid dynamics simulations. The course aims to enable students to design vehicle bodies for comfort and low drag. It involves both theoretical and practical modules taught through lectures and internal exams.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
287 views2 pagesAU307 Vehicle Body Engineering
AU307 Vehicle Body Engineering
Uploaded by
Mathews P RejiThis document outlines the course details and syllabus for the "Vehicle Body Engineering" course offered in 2016. The course aims to impart knowledge on vehicle body design for maximum passenger comfort and minimizing drag. The syllabus covers topics like vehicle body types and dimensions, aerodynamics, materials, structural analysis, stability, noise and vibration, safety, and computational fluid dynamics simulations. The course aims to enable students to design vehicle bodies for comfort and low drag. It involves both theoretical and practical modules taught through lectures and internal exams.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Course Course Name L-T-P – Year of
code Credits Introduction
AU307 VEHICLE BODY ENGINEERING 3-0-0-3 2016
Prerequisite : Nil
Course Objectives
To impart knowledge on the design of vehicle body to give maximum comfort for the
passengers
To discuss the methods of stream lining vehicle body to minimize drag
Syllabus
Classification of coach work types, vehicle aerodynamics, vehicle body design parameters,
vehicle body design terms, vehicle ergonomics, body structure types, vehicle stability, and load
distribution in vehicles.
Expected outcome.
The students will be able to do vehicle body design giving maximum passenger comfort
and producing minimum drag.
Text Book:
1. Giles J Pawlowski, Vehicle body engineering Business books limited, 1989
2. Sydney F Page, “Body Engineering”’ Chapman & Hall Ltd, London, 1956
References:
1. Pope , “Wind tunnel testing” , John Wiley & Sons , 2nd edition, New York, 1974
2. Braithwaite,J.B., Vehicle Body building and drawing, Heinemann Educational Books Ltd.,
London 1977
3. Dieler Anselm., The passenger car body, SAE International, 2000
4. Giles,G.J., Body construction and design, Illiffe Books Butterworth & Co., 1971.
5. John Fenton, “Vehicle body layout and analysis”, Mechanical Engg. Publication ltd,
London.
6. Paul Browne – Auto care manual.
7. Redesign of bus bodies – Part 1 and Part 2 C. I. R. T., Pune.
Course Plan
Sem.
Module Contents Hours Exam
Marks
Classification of coachwork type: styling forms, coach and bus body style,
layout of cars, buses and coach with different seating and loading capacity,
commercial vehicle types, Vans and Pickups. Terms used in body building
construction - Angle of approach, Angle of departure, Ground clearance,
I Cross bearers, Floor longitudes, posts, seat rail, waist rail, cant rail, Roof 7 15%
stick, Roof longitude, Rub rail, skirt rail, truss panel, wheel arch structure,
wheel arch, post diagonals, gussets.
Basic dimension: Regulations as per ARAI, driver’s seat, passengers seat,
visibility.
Aerodynamics: Basics, Vehicle drag and types, Various types of forces
and moments, effects of forces and moments, various body optimization
techniques for minimum drag, Principle of wind tunnel technology, flow
visualization techniques, tests with scale models, aerodynamic study for
II heavy vehicles Interior Ergonomics: Introduction, ergonomics system 7 15%
design, Seating dimensions ,seat comfort, suspension seats, split frame
seating, back passion reducers, dash board instruments, electronic
displays, commercial vehicle cabin ergonomics, mechanical package
layout, goods vehicle layout.
FIRST INTERNAL EXAMINATION
Vehicle Body Materials: Aluminium alloys, Steel, alloy steels, plastics,
Metal matrix composites, structural timbers - properties, glass reinforced
plastics and high strength composites, thermoplastics, ABS and styrenes,
III 7 15%
load bearing plastics, semi rigid PUR foams and sandwich panel
construction. Paints adhesives and their properties, corrosion and their
prevention
Load distribution: Type of body structures, Vehicle body stress analysis,
vehicle weight distribution, Calculation for static, symmetrical,
longitudinal & side loads, stress analysis of bus body structure under
bending and torsion. Vehicle Stability: Introduction, Longitudinal, lateral
IV 7 15%
stability, vehicle on a curvilinear path, critical speed for toppling and
skidding. Effect of operating factors on lateral stability, steering geometry
and stabilization of steerable wheels, mass distribution and engine
location on stability
SECOND INTERNAL EXAMINATION
Noise and vibration: Noise characteristics, Sources of noise, noise level
measurement techniques, Body structural vibrations, chassis bearing
vibration, designing against fatigue, methods of noise suppression
V Safety: Impact protection basics, Physics of impact between deformable 7 20%
bodies, Design for crash worthiness, occupant and cargo restraint, passive
restraint systems, side impact analysis, bumper system, energy absorbent
foams, laws of mechanisms applied to safety.
Introduction to CFD technology, fluidic design considerations, effect of
air dams on front bumpers, effect of projected accessories on body, wind
tunnel testing of car body, parameters considered for wind tunnel testing,
VI 7 20%
introduction to software simulation of car body structures.
Visibility, regulations, drivers visibility, methods of improving visibility,
Window winding and seat adjustment mechanisms
END SEMESTER EXAM
Question Paper Pattern
Maximum marks: 100 Time: 3 hours
The question paper shall consist of three parts
Part A
4 questions uniformly covering modules I and II. Each question carries 10 marks
Students will have to answer any three questions out of 4 (3X10 marks =30 marks)
Part B
4 questions uniformly covering modules III and IV. Each question carries 10 marks
Students will have to answer any three questions out of 4 (3X10 marks =30 marks)
Part C
6 questions uniformly covering modules V and VI. Each question carries 10 marks
Students will have to answer any four questions out of 6 (4X10 marks =40 marks)
Note: In all parts, each question can have a maximum of four sub questions, if needed
You might also like
- Guide to Load Analysis for Durability in Vehicle EngineeringFrom EverandGuide to Load Analysis for Durability in Vehicle EngineeringP. JohannessonRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- FinkbeinerDocument38 pagesFinkbeinermordidomiNo ratings yet
- Auto Full Vehicle Durability Using Abaqus Standard 11Document4 pagesAuto Full Vehicle Durability Using Abaqus Standard 11TimNo ratings yet
- Adams Driveline Mdr3 HelpDocument326 pagesAdams Driveline Mdr3 HelpAtul DubeyNo ratings yet
- Ergonomics in The Automotive Design Process PDFDocument2 pagesErgonomics in The Automotive Design Process PDFVictorNo ratings yet
- NVH CAE Concept Modelling and Optimization at BMWDocument23 pagesNVH CAE Concept Modelling and Optimization at BMWSuyash Thorat-Gadgil100% (1)
- Automobile Chassis and Body EngineeringDocument2 pagesAutomobile Chassis and Body EngineeringcharulapNo ratings yet
- Dummies Guide To Basic Coding With NCS ExpertDocument5 pagesDummies Guide To Basic Coding With NCS Expertpatr01No ratings yet
- Biw AnalysisDocument15 pagesBiw Analysiskeepingbusy100% (1)
- Aerodynamic Drag of Car BriefDocument80 pagesAerodynamic Drag of Car Briefbhargav550850% (2)
- Hood AnalysisDocument5 pagesHood Analysisymadhu319No ratings yet
- BMW Product Design and SustainabilityDocument29 pagesBMW Product Design and SustainabilityNur Batrishya IsmailNo ratings yet
- FSAE Flex Body Tutorial (MSC ADAMS)Document22 pagesFSAE Flex Body Tutorial (MSC ADAMS)smvarunmurthy100% (1)
- 06 CFD Computational Fluid Dynamics Daimler FSG Academy Deep Dive Simulation 20201127Document28 pages06 CFD Computational Fluid Dynamics Daimler FSG Academy Deep Dive Simulation 20201127Farzad100% (1)
- Vehicle VibrationDocument61 pagesVehicle VibrationAndrew ScheichNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Ergonomics and Best Practice GuideDocument8 pagesVehicle Ergonomics and Best Practice GuideDamien ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Video Transcript:: About Us Courses Contact UsDocument13 pagesVideo Transcript:: About Us Courses Contact UsChivuAlexandruNo ratings yet
- Strength Analysis of Resistance Spot Weld-627Document10 pagesStrength Analysis of Resistance Spot Weld-627raymondNo ratings yet
- Ravi Resume PDFDocument2 pagesRavi Resume PDFRavi Prakash M PNo ratings yet
- 1 Learn German - German Speak7 Com German - ExpressionsDocument23 pages1 Learn German - German Speak7 Com German - ExpressionsGabriela DiaconuNo ratings yet
- Design and Crash Analysis of Passenger Car Frontal Bumper Beam Using Hypermesh and RadiossDocument5 pagesDesign and Crash Analysis of Passenger Car Frontal Bumper Beam Using Hypermesh and RadiossAnup M UpadhyayaNo ratings yet
- European Traffic Signs PDFDocument2 pagesEuropean Traffic Signs PDFDahndray0% (1)
- Analysis and Validation of Eicher 11.10 ChassisDocument4 pagesAnalysis and Validation of Eicher 11.10 ChassisdessaivipulNo ratings yet
- Modern Techniqes of Automotive NVHDocument7 pagesModern Techniqes of Automotive NVHatuladeupesNo ratings yet
- Automotive ErgonomicsDocument32 pagesAutomotive ErgonomicsJOSE LUIS CALPA AGUILAR100% (1)
- Automotive Special ReportDocument54 pagesAutomotive Special ReportdrypatrickNo ratings yet
- Adams Car Suspension AnalysisDocument12 pagesAdams Car Suspension Analysispeaty785No ratings yet
- Crash WorthinessDocument9 pagesCrash Worthinessgauthaman_scribidNo ratings yet
- AUDI OptimizationDocument37 pagesAUDI OptimizationKiran DamaNo ratings yet
- Auto ErgonomicDocument4 pagesAuto ErgonomicAnshul BediNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Mesh-Free Methods in LsdynaDocument91 pagesAssessment of Mesh-Free Methods in LsdynaeronelNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of An Automotive Vertical Doors Opening System AvdosDocument11 pagesDesign and Development of An Automotive Vertical Doors Opening System AvdosIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Manual of SolidWorks2003Document83 pagesManual of SolidWorks2003anurak.aun100% (5)
- BIW Structure Can Be Divided in Following SubstructuresDocument7 pagesBIW Structure Can Be Divided in Following SubstructuresJyoti KaleNo ratings yet
- Design of Hood Stiffener of A Sedan Car ForDocument7 pagesDesign of Hood Stiffener of A Sedan Car ForAli GüneşNo ratings yet
- Durability Analysis Vehicle Body Structure Using Modal TransientDocument8 pagesDurability Analysis Vehicle Body Structure Using Modal TransientBalaji KannaiyanNo ratings yet
- Ergo HF 3Document14 pagesErgo HF 3Marko BrkicNo ratings yet
- Ergonomics of Car Packaging Part 1Document2 pagesErgonomics of Car Packaging Part 1Ejan AdinNo ratings yet
- Thermal Computational Fluid Dynamic (CFD) Analysis of Automotive Lamp - Analyzer CAE Solutions Pvt. Ltd.Document3 pagesThermal Computational Fluid Dynamic (CFD) Analysis of Automotive Lamp - Analyzer CAE Solutions Pvt. Ltd.Analyzer CAE Solutions Pvt. Ltd.No ratings yet
- BIW Glossary PDFDocument2 pagesBIW Glossary PDFJessica CalvoNo ratings yet
- Unigraphics NX Interview Questions and AnswersDocument5 pagesUnigraphics NX Interview Questions and AnswersVivekPJNo ratings yet
- 1 Underbody Coating: 1.1 Modern Automotive Coating ProcessesDocument2 pages1 Underbody Coating: 1.1 Modern Automotive Coating ProcessesHari Tej100% (1)
- FFS Design ReportDocument23 pagesFFS Design ReportPranjal ShuklaNo ratings yet
- " Automatic Air Suspension System ": A Seminar ReportDocument16 pages" Automatic Air Suspension System ": A Seminar ReportUmar Hayat100% (1)
- IIHS Level 2 Autonomy ReportDocument25 pagesIIHS Level 2 Autonomy ReportSimon AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Car Msc2011Document734 pagesCar Msc2011Renan AlvimNo ratings yet
- Strength Evaluation On DoorDocument5 pagesStrength Evaluation On DoorDevendra Kumar KumawatNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Auto Mobile SeatingDocument158 pagesAnalysis of Auto Mobile Seatingkeval patel100% (1)
- Pre-Processing Tools For Interior Safety Simulation in ANSA: Physics On ScreenDocument4 pagesPre-Processing Tools For Interior Safety Simulation in ANSA: Physics On Screenபென்ஸிஹர்No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document43 pagesChapter 7Bairoju Shiva KumarNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Structure and Engines: Two Marks Questions & AnswersDocument8 pagesVehicle Structure and Engines: Two Marks Questions & AnswersThulasi RamNo ratings yet
- Automotive Proceeding First PageDocument10 pagesAutomotive Proceeding First Pageanand007krishnanNo ratings yet
- Vehicle TechnologyDocument63 pagesVehicle TechnologyAnand KumarNo ratings yet
- Ergonomics Car Design PDFDocument2 pagesErgonomics Car Design PDFRonnieNo ratings yet
- Seat Belt TypesDocument3 pagesSeat Belt TypesKrishna Kumar100% (1)
- Getting Started Using ADAMS/VibrationDocument63 pagesGetting Started Using ADAMS/VibrationvibrosticsNo ratings yet
- Automotive Safety Integrity Level A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandAutomotive Safety Integrity Level A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Body EngineeringDocument2 pagesVehicle Body EngineeringMathews P Reji100% (1)
- Gujarat Technological University: Automobile Chassis and Body Engineering 2160205 B.E. 6 SemesterDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: Automobile Chassis and Body Engineering 2160205 B.E. 6 SemesterDr. S. D. YadavNo ratings yet
- Fourth 1 PDFDocument23 pagesFourth 1 PDFMathews P RejiNo ratings yet
- AU203 Auto Chassis 3-0-0-3 2016 Prerequisite: Nil: Course Code Course Name L-T-P - Credits Year ofDocument2 pagesAU203 Auto Chassis 3-0-0-3 2016 Prerequisite: Nil: Course Code Course Name L-T-P - Credits Year ofvaisakmctNo ratings yet
- AU205 Automotive ChassisDocument2 pagesAU205 Automotive ChassisVivek Venugopal100% (1)
- Fourth 1 PDFDocument23 pagesFourth 1 PDFMathews P RejiNo ratings yet
- Basic Control ChartDocument3 pagesBasic Control ChartMathews P RejiNo ratings yet
- First PDFDocument139 pagesFirst PDFMathews P RejiNo ratings yet
- Design of Helical SpringDocument11 pagesDesign of Helical SpringMathews P RejiNo ratings yet
- Suspension &steeringDocument15 pagesSuspension &steeringMathews P RejiNo ratings yet
- Resisteance To VehicleDocument2 pagesResisteance To VehicleMathews P RejiNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Body EngineeringDocument2 pagesVehicle Body EngineeringMathews P Reji100% (1)
- Chennai Based COMPANIESDocument5 pagesChennai Based COMPANIESMathews P Reji100% (1)
- An Overview of Automobile Noise and Vibration ControlDocument11 pagesAn Overview of Automobile Noise and Vibration ControlMathews P Reji100% (1)
- EE311 Electric Drives & Control For AutomationDocument2 pagesEE311 Electric Drives & Control For AutomationMathews P RejiNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument9 pagesMCQMathews P RejiNo ratings yet
- E Baja Cost AnalysisDocument5 pagesE Baja Cost AnalysisMathews P RejiNo ratings yet
- Starting SysytemDocument12 pagesStarting SysytemMathews P RejiNo ratings yet
- Mesfin BekeleDocument56 pagesMesfin BekeleBlack AfroNo ratings yet
- Arcilla Mariel Reporting LAWSDocument9 pagesArcilla Mariel Reporting LAWSXynnia BurlatNo ratings yet
- Mazda Demio Owner's Manual (Page 348 of 358) ManualsLibDocument1 pageMazda Demio Owner's Manual (Page 348 of 358) ManualsLibNipun Mendis0% (1)
- Saudia Cargo E-Booking HandbookDocument19 pagesSaudia Cargo E-Booking HandbooktediNo ratings yet
- Limba EnglezaDocument148 pagesLimba Englezaely_flory22No ratings yet
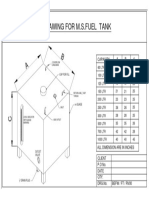
- TANK DRAWINGS-ModelDocument1 pageTANK DRAWINGS-Modelkeeprocking9777No ratings yet
- 4 FY 2023 DPWH Projects Within MHWFRDocument9 pages4 FY 2023 DPWH Projects Within MHWFRShanea Dolteo Lamsis-EliasNo ratings yet
- Air Peace Letter To New DelhiDocument4 pagesAir Peace Letter To New DelhiSahara ReportersNo ratings yet
- Clutch BoosterDocument7 pagesClutch Boosterdmitry esaulkovNo ratings yet
- GRNDocument74 pagesGRNAvinashNo ratings yet
- Fiat 500 SpecificationsDocument2 pagesFiat 500 SpecificationsFiat500USANo ratings yet
- Door Module Repair Golf MK 5Document20 pagesDoor Module Repair Golf MK 5Anonymous mEU3GDIQDNo ratings yet
- Steering System: Introduction: This System Provides The Directional ChangeDocument14 pagesSteering System: Introduction: This System Provides The Directional ChangeAkash Sood100% (1)
- Spicer Off-Highway, Agriculture Steering Components For All Makes OHST-ALLMKS-01 PDFDocument106 pagesSpicer Off-Highway, Agriculture Steering Components For All Makes OHST-ALLMKS-01 PDFviemey1952No ratings yet
- ICAO Flight Plan PresentationDocument15 pagesICAO Flight Plan PresentationJose Luis Oliveros100% (1)
- Astm D1196Document2 pagesAstm D1196David Sta Rosa100% (1)
- Airport Code SummaryDocument1 pageAirport Code SummarySinan İcikNo ratings yet
- Catálogo de Conceptos Aero VallartaDocument54 pagesCatálogo de Conceptos Aero Vallartaderrick Torres0% (1)
- 整改质量问题跟进 安派尔 nextDocument16 pages整改质量问题跟进 安派尔 nextMazheidy Mat DarusNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12.Document19 pagesChapter 12.Chirag ThadodaNo ratings yet
- PCT 304414 PDFDocument36 pagesPCT 304414 PDFNugrawan SatriaNo ratings yet
- Sep 2019Document1 pageSep 2019PraveenkumarNo ratings yet
- Net Horsepower 101 HP (76 KW) Operating Weight 20,348 LB (9230 KG) STD 20,598 LB (9343 KG) LGP Blade Capacity 2.81 Yd (2.15 M) 2.89 Yd (2.21 M)Document4 pagesNet Horsepower 101 HP (76 KW) Operating Weight 20,348 LB (9230 KG) STD 20,598 LB (9343 KG) LGP Blade Capacity 2.81 Yd (2.15 M) 2.89 Yd (2.21 M)Người Chiến Sĩ ẤyNo ratings yet
- LaufennDocument10 pagesLaufennHennyNo ratings yet
- THC 101 Prelim - M1Document8 pagesTHC 101 Prelim - M1Santana ShaneNo ratings yet
- PDF Swagata Dasgupta 93 104 Roomghata Dewan Bazar Chittagong Mobile 01749550640 Career ObjectiveDocument3 pagesPDF Swagata Dasgupta 93 104 Roomghata Dewan Bazar Chittagong Mobile 01749550640 Career ObjectiveShayan AbagnaleNo ratings yet
- Site of The First Mass-Lesson 3.1Document23 pagesSite of The First Mass-Lesson 3.1Emmanuel El Gibor AlmarioNo ratings yet
- COF069115 05 Systemlosungen Broschure en RZ WebDocument11 pagesCOF069115 05 Systemlosungen Broschure en RZ WebAnonymous TThmYKFpNo ratings yet