Professional Documents
Culture Documents
United States, 2018: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Centers For Disease Control and Prevention
United States, 2018: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Centers For Disease Control and Prevention
Uploaded by
Saddam HussainOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
United States, 2018: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Centers For Disease Control and Prevention
United States, 2018: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Centers For Disease Control and Prevention
Uploaded by
Saddam HussainCopyright:
Available Formats
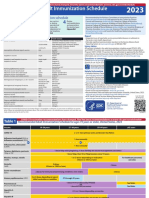
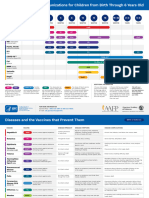
Recommended Immunization Schedule for
Children and Adolescents Aged 18 Years or Younger, UNITED STATES, 2018
• Consult relevant ACIP statements for detailed recommendations The table below shows vaccine acronyms, and brand names for vaccines routinely recommended
for children and adolescents. The use of trade names in this immunization schedule is for
(www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/index.html). identification purposes only and does not imply endorsement by the ACIP or CDC.
• When a vaccine is not administered at the recommended age, administer Vaccine type Abbreviation Brand(s)
at a subsequent visit. Diphtheria, tetanus, and acellular pertussis vaccine DTaP Daptacel
• Use combination vaccines instead of separate injections when Infanrix
Diphtheria, tetanus vaccine DT No Trade Name
appropriate.
Haemophilus influenzae type B vaccine Hib (PRP-T) ActHIB
• Report clinically significant adverse events to the Vaccine Adverse Event Hiberix
Reporting System (VAERS) online (www.vaers.hhs.gov) or by telephone Hib (PRP-OMP) PedvaxHIB
Hepatitis A vaccine HepA Havrix
(800-822-7967). Vaqta
• Report suspected cases of reportable vaccine-preventable diseases to Hepatitis B vaccine HepB Engerix-B
Recombivax HB
your state or local health department. Human papillomavirus vaccine HPV Gardasil 9
• For information about precautions and contraindications, see www.cdc. Influenza vaccine (inactivated) IIV Multiple
gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/general-recs/contraindications.html. Measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine MMR M-M-R II
Meningococcal serogroups A, C, W, Y vaccine MenACWY-D Menactra
MenACWY-CRM Menveo
Approved by the Meningococcal serogroup B vaccine MenB-4C Bexsero
MenB-FHbp Trumenba
Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices Pneumococcal 13-valent conjugate vaccine PCV13 Prevnar 13
(www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip) Pneumococcal 23-valent polysaccharide vaccine PPSV23 Pneumovax
Poliovirus vaccine (inactivated) IPV IPOL
American Academy of Pediatrics
Rotavirus vaccines RV1 Rotarix
(www.aap.org) RV5 RotaTeq
Tetanus, diphtheria, and acellular pertussis vaccine Tdap Adacel
American Academy of Family Physicians Boostrix
(www.aafp.org) Tetanus and diphtheria vaccine Td Tenivac
No Trade Name
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Varicella vaccine VAR Varivax
(www.acog.org) Combination Vaccines
DTaP, hepatitis B and inactivated poliovirus vaccine DTaP-HepB-IPV Pediarix
This schedule includes recommendations in effect as of January 1, 2018. DTaP, inactivated poliovirus and Haemophilus influenzae type DTaP-IPV/Hib Pentacel
B vaccine
DTaP and inactivated poliovirus vaccine DTaP-IPV Kinrix
Quadracel
Measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella vaccines MMRV ProQuad
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Figure 1. Recommended Immunization Schedule for Children and Adolescents Aged 18 Years or Younger—United States, 2018.
(FOR THOSE WHO FALL BEHIND OR START LATE, SEE THE CATCH-UP SCHEDULE [FIGURE 2]).
These recommendations must be read with the footnotes that follow. For those who fall behind or start late, provide catch-up vaccination at the earliest opportunity as indicated by the green bars in Figure 1.
To determine minimum intervals between doses, see the catch-up schedule (Figure 2). School entry and adolescent vaccine age groups are shaded in gray.
19-23
Vaccine Birth 1 mo 2 mos 4 mos 6 mos 9 mos 12 mos 15 mos 18 mos 2-3 yrs 4-6 yrs 7-10 yrs 11-12 yrs 13-15 yrs 16 yrs 17-18 yrs
mos
Hepatitis B1 (HepB) 1st dose 2nd dose 3rd dose
Rotavirus2 (RV) RV1 (2-dose See
1st dose 2nd dose footnote 2
series); RV5 (3-dose series)
Diphtheria, tetanus, & acellular
1st dose 2nd dose 3rd dose 4th dose 5th dose
pertussis3 (DTaP: <7 yrs)
Haemophilus influenzae type See 3rd or 4th dose,
1st dose 2nd dose footnote 4 See footnote 4
b4 (Hib)
Pneumococcal conjugate5
1st dose 2nd dose 3rd dose 4th dose
(PCV13)
Inactivated poliovirus6
1st dose 2nd dose 3rd dose 4th dose
(IPV: <18 yrs)
Annual vaccination (IIV)
Influenza7 (IIV) Annual vaccination (IIV) 1 or 2 doses 1 dose only
Measles, mumps, rubella8 (MMR) See footnote 8 1st dose 2nd dose
Varicella9 (VAR) 1st dose 2nd dose
Hepatitis A1 0 (HepA) 2-dose series, See footnote 10
Meningococcal1 1 (MenACWY-D
See footnote 11 1st dose 2nd dose
>9 mos; MenACWY-CRM ≥2 mos)
Tetanus, diphtheria, & acellular
Tdap
pertussis1 3 (Tdap: >7 yrs)
See footnote
Human papillomavirus1 4 (HPV) 14
See footnote 12
Meningococcal B1 2
Pneumococcal polysaccharide5
See footnote 5
(PPSV23)
Range of recommended Range of recommended ages Range of recommended ages Range of recommended ages for non-high-risk No recommendation
ages for all children for catch-up immunization for certain high-risk groups groups that may receive vaccine, subject to
individual clinical decision making
NOTE: The above recommendations must be read along with the footnotes of this schedule.
FIGURE 2. Catch-up immunization schedule for persons aged 4 months–18 years who start late or who are more than 1 month behind—United States, 2018.
The figure below provides catch-up schedules and minimum intervals between doses for children whose vaccinations have been delayed. A vaccine series does not need to be restarted, regardless of the time that has elapsed between doses. Use the
section appropriate for the child’s age. Always use this table in conjunction with Figure 1 and the footnotes that follow.
Children age 4 months through 6 years
Minimum Minimum Interval Between Doses
Vaccine Age for
Dose 1 Dose 1 to Dose 2 Dose 2 to Dose 3 Dose 3 to Dose 4 Dose 4 to Dose 5
Hepatitis B1 Birth 4 weeks 8 weeks and at least 16 weeks after first dose.
Minimum age for the final dose is 24 weeks.
6 weeks
Rotavirus2 Maximum age for 4 weeks 4 weeks2
first dose is Maximum age for final dose is 8 months, 0 days.
14 weeks, 6 days
Diphtheria, tetanus, and 6 weeks 4 weeks 4 weeks 6 months 6 months3
acellular pertussis3
4 weeks4
if current age is younger than 12 months and first dose was administered at younger than age 7 months,
4 weeks and at least 1 previous dose was PRP-T (ActHib, Pentacel, Hiberix) or unknown.
if first dose was administered before the 8 weeks and age 12 through 59 months (as final dose)4
1st birthday. 8 weeks (as final dose)
• if current age is younger than 12 months and first dose was administered at age 7 through 11 months; This dose only necessary for
Haemophilus influenzae 6 weeks 8 weeks (as final dose) OR children age 12 through 59 months
type b4 if first dose was administered at age 12 who received 3 doses before the
through 14 months. • if current age is 12 through 59 months and first dose was administered before the 1st birthday, and
second dose administered at younger than 15 months; 1st birthday.
No further doses needed if first dose was OR
administered at age 15 months or older.
• if both doses were PRP-OMP (PedvaxHIB; Comvax) and were administered before the 1st birthday.
No further doses needed if previous dose was administered at age 15 months or older.
4 weeks
if first dose administered before the 1st 4 weeks
birthday. 8 weeks (as final dose)
if current age is younger than 12 months and previous dose given at <7 months old. This dose only necessary for
8 weeks (as final dose for healthy 8 weeks (as final dose for healthy children) children aged 12 through 59
Pneumococcal children)
conjugate5 6 weeks if first dose was administered at the 1st if previous dose given between 7-11 months (wait until at least 12 months old); months who received 3 doses
OR before age 12 months or for
birthday or after.
if current age is 12 months or older and at least 1 dose was given before age 12 months. children at high risk who received 3
No further doses needed doses at any age.
No further doses needed for healthy children if previous dose administered at age 24 months or older.
for healthy children if first dose was
administered at age 24 months or older.
4 weeks6 if current age is < 4 years 6 months6 (minimum age 4 years for
Inactivated poliovirus6 6 weeks 4 weeks6
6 months (as final dose) if current age is 4 years or older final dose).
Measles, mumps, rubella8 12 months 4 weeks
Varicella9 12 months 3 months
Hepatitis A10 12 months 6 months
Meningococcal11
(MenACWY-D ≥9 mos; 6 weeks 8 weeks11 See footnote 11 See footnote 11
MenACWY-CRM ≥2 mos)
Children and adolescents age 7 through 18 years
Meningococcal11
Not Applicable
(MenACWY-D ≥9 mos; (N/A) 8 weeks11
MenACWY-CRM ≥2 mos)
4 weeks
Tetanus, diphtheria; if first dose of DTaP/DT was administered before the 1st birthday. 6 months if first dose of DTaP/
tetanus, diphtheria, and 7 years13 4 weeks DT was administered before the
acellular pertussis13 6 months (as final dose) 1st birthday.
if first dose of DTaP/DT or Tdap/Td was administered at or after the 1st birthday.
Human papillomavirus14 9 years Routine dosing intervals are recommended.14
Hepatitis A10 N/A 6 months
Hepatitis B1 N/A 4 weeks 8 weeks and at least 16 weeks after first dose.
A fourth dose of IPV is indicated if all
6 months6 previous doses were administered
Inactivated poliovirus6 N/A 4 weeks A fourth dose is not necessary if the third dose was administered at age 4 years or older and at least 6 months at <4 years or if the third dose was
after the previous dose. administered <6 months after the
second dose.
Measles, mumps, rubella8 N/A 4 weeks
Varicella9 N/A 3 months if younger than age 13 years.
4 weeks if age 13 years or older.
NOTE: The above recommendations must be read along with the footnotes of this schedule.
Figure 3. Vaccines that might be indicated for children and adolescents aged 18 years or younger based on medical indications
HIV infection
CD4+ count†
<15% or ≥15% or
total CD4 total CD4
Immunocompromised cell count cell count Kidney failure, end- CSF leaks/ Asplenia and persistent Chronic
status (excluding HIV of <200/ of ≥200/ stage renal disease, on Heart disease, cochlear complement component liver
VACCINE INDICATION Pregnancy infection) mm3 mm3 hemodialysis chronic lung disease implants deficiencies disease Diabetes
Hepatitis B 1
Rotavirus2
SCID*
Diphtheria, tetanus, & acellular pertussis3
(DTaP)
Haemophilus influenzae type b4
Pneumococcal conjugate5
Inactivated poliovirus6
Influenza7
Measles, mumps, rubella8
Varicella9
Hepatitis A1 0
Meningococcal ACWY1 1
Tetanus, diphtheria, & acellular pertussis1 3
(Tdap)
Human papillomavirus1 4
Meningococcal B1 2
Pneumococcal polysaccharide5
Recommended for persons with Vaccination is recommended,
Vaccination according to the and additional doses may be
an additional risk factor for which No recommendation Contraindicated Precaution for vaccination
routine schedule recommended necessary based on medical
the vaccine would be indicated condition. See footnotes.
*Severe Combined Immunodeficiency
†
For additional information regarding HIV laboratory parameters and use of live vaccines; see the General Best Practice Guidelines for Immunization “Altered Immunocompetence” at: www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/gener-
al-recs/immunocompetence.html; and Table 4-1 (footnote D) at: www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/general-recs/contraindications.html.
NOTE: The above recommendations must be read along with the footnotes of this schedule.
Footnotes — Recommended Immunization Schedule for Children and Adolescents Aged 18 Years or Younger, UNITED STATES, 2018
For further guidance on the use of the vaccines mentioned below, see: www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/index.html.
For vaccine recommendations for persons 19 years of age and older, see the Adult Immunization Schedule.
Additional information
• For information on contraindications and precautions for the use of a vaccine, consult the General Best Practice Guidelines for Immunization and relevant ACIP
statements, at www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/index.html.
• For calculating intervals between doses, 4 weeks = 28 days. Intervals of >4 months are determined by calendar months.
• Within a number range (e.g., 12–18), a dash (–) should be read as “through.”
• Vaccine doses administered ≤4 days before the minimum age or interval are considered valid. Doses of any vaccine administered ≥5 days earlier than the minimum
interval or minimum age should not be counted as valid and should be repeated as age-appropriate. The repeat dose should be spaced after the invalid dose by
the recommended minimum interval. For further details, see Table 3-1, Recommended and minimum ages and intervals between vaccine doses, in General Best Practice
Guidelines for Immunization at www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/general-recs/timing.html.
• Information on travel vaccine requirements and recommendations is available at wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/.
• For vaccination of persons with immunodeficiencies, see Table 8-1, Vaccination of persons with primary and secondary immunodeficiencies, in General Best Practice
Guidelines for Immunization, at www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/general-recs/immunocompetence.html; and Immunization in Special Clinical Circumstances. (In:
Kimberlin DW, Brady MT, Jackson MA, Long SS, eds. Red Book: 2015 report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases. 30th ed. Elk Grove Village, IL: American Academy of
Pediatrics, 2015:68-107).
• The National Vaccine Injury Compensation Program (VICP) is a no-fault alternative to the traditional legal system for resolving vaccine injury claims. All routine child and
adolescent vaccines are covered by VICP except for pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23). For more information; see www.hrsa.gov/vaccinecompensation/
index.html.
1. Hepatitis B (HepB) vaccine. (minimum age: birth) • Infants who did not receive a birth dose should Catch-up vaccination:
Birth Dose (Monovalent HepB vaccine only): begin the series as soon as feasible (see Figure 2). • Do not start the series on or after age 15 weeks,
• Mother is HBsAg-Negative: 1 dose within 24 • Administration of 4 doses is permitted when a 0 days.
hours of birth for medically stable infants >2,000 combination vaccine containing HepB is used after • The maximum age for the final dose is 8 months,
grams. Infants <2,000 grams administer 1 dose at the birth dose. 0 days.
chronological age 1 month or hospital discharge. • Minimum age for the final (3rd or 4th) dose: 24 • For other catch-up guidance, see Figure 2.
• Mother is HBsAg-Positive: weeks.
ɱɱ Give HepB vaccine and 0.5 mL of HBIG (at • Minimum Intervals: Dose 1 to Dose 2: 4 weeks / 3. Diphtheria, tetanus, and acellular pertussis (DTaP)
separate anatomic sites) within 12 hours of Dose 2 to Dose 3: 8 weeks / Dose 1 to Dose 3: 16 vaccine. (minimum age: 6 weeks [4 years for
birth, regardless of birth weight. weeks. (When 4 doses are given, substitute “Dose Kinrix or Quadracel])
ɱɱ Test for HBsAg and anti-HBs at age 9–12 4” for “Dose 3” in these calculations.)
months. If HepB series is delayed, test 1–2 Routine vaccination:
Catch-up vaccination: • 5-dose series at 2, 4, 6, and 15–18 months, and
months after final dose.
• Unvaccinated persons should complete a 3-dose 4–6 years.
• Mother’s HBsAg status is unknown: series at 0, 1–2, and 6 months.
ɱɱ Give HepB vaccine within 12 hours of birth, ɱɱ Prospectively: A 4th dose may be given as
• Adolescents 11–15 years of age may use an early as age 12 months if at least 6 months
regardless of birth weight.
alternative 2-dose schedule, with at least 4 months
ɱɱ For infants <2,000 grams, give 0.5 mL of HBIG have elapsed since the 3rd dose.
between doses (adult formulation Recombivax
in addition to HepB vaccine within 12 hours ɱɱ Retrospectively: A 4th dose that was
HB only).
of birth. inadvertently given as early as 12 months may
• For other catch-up guidance, see Figure 2.
ɱɱ Determine mother’s HBsAg status as soon as be counted if at least 4 months have elapsed
possible. If mother is HBsAg-positive, give 0.5 2. Rotavirus vaccines. (minimum age: 6 weeks) since the 3rd dose.
mL of HBIG to infants >2,000 grams as soon as
Routine vaccination: Catch-up vaccination:
possible, but no later than 7 days of age.
Rotarix: 2-dose series at 2 and 4 months. • The 5th dose is not necessary if the 4th dose was
Routine Series:
• A complete series is 3 doses at 0, 1–2, and 6–18 RotaTeq: 3-dose series at 2, 4, and 6 months. administered at 4 years or older.
months. (Monovalent HepB vaccine should be If any dose in the series is either RotaTeq or • For other catch-up guidance, see Figure 2.
used for doses given before age 6 weeks.) unknown, default to 3-dose series.
For further guidance on the use of the vaccines mentioned below, see: www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/index.html.
4. Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) vaccine. • HIV infection Cerebrospinal fluid leak; cochlear implant:
(minimum age: 6 weeks) 12–59 months Age 2–5 years:
Routine vaccination: ɱɱ Unvaccinated or only 1 dose before 12 • Any incomplete* schedules with:
• ActHIB, Hiberix, or Pentacel: 4-dose series at 2, 4, months: Give 2 doses 8 weeks apart. ɱɱ 3 PCV13 doses: 1 dose of PCV13 (at least 8
6, and 12–15 months. ɱɱ 2 or more doses before 12 months: Give 1 weeks after any prior PCV13 dose).
• PedvaxHIB: 3-dose series at 2, 4, and 12–15 months. dose, at least 8 weeks after previous dose. ɱɱ <3 PCV13 doses: 2 doses of PCV13, 8 weeks
Catch-up vaccination: Unimmunized* persons 5–18 years after the most recent dose and given 8 weeks
• 1st dose at 7–11 months: Give 2nd dose at least 4 ɱɱ Give 1 dose apart.
weeks later and 3rd (final) dose at 12–15 months or • Immunoglobulin deficiency, early component • No history of PPSV23: 1 dose of PPSV23 (at least 8
8 weeks after 2nd dose (whichever is later). complement deficiency weeks after any prior PCV13 dose).
• 1st dose at 12–14 months: Give 2nd (final) dose at 12–59 months Age 6–18 years:
least 8 weeks after 1st dose. ɱɱ Unvaccinated or only 1 dose before 12 • No history of either PCV13 or PPSV23: 1 dose of
• 1st dose before 12 months and 2nd dose before months: Give 2 doses, 8 weeks apart. PCV13, 1 dose of PPSV23 at least 8 weeks later.
15 months: Give 3rd (final) dose 8 weeks after 2nd ɱɱ 2 or more doses before 12 months: Give 1 • Any PCV13 but no PPSV23: 1 dose of PPSV23 at
dose. dose, at least 8 weeks after previous dose. least 8 weeks after the most recent dose of PCV13
• 2 doses of PedvaxHIB before 12 months: Give 3rd • PPSV23 but no PCV13: 1 dose of PCV13 at least 8
(final) dose at 12–59 months and at least 8 weeks *Unimmunized = Less than routine series (through 14
weeks after the most recent dose of PPSV23.
after 2nd dose. months) OR no doses (14 months or older)
Sickle cell disease and other hemoglobinopathies;
• Unvaccinated at 15–59 months: 1 dose. anatomic or functional asplenia; congenital
5. Pneumococcal vaccines. (minimum age: 6 weeks
• For other catch-up guidance, see Figure 2. or acquired immunodeficiency; HIV infection;
[PCV13], 2 years [PPSV23])
Special Situations: chronic renal failure; nephrotic syndrome;
Routine vaccination with PCV13:
• Chemotherapy or radiation treatment malignant neoplasms, leukemias, lymphomas,
• 4-dose series at 2, 4, 6, and 12–15 months.
12–59 months Hodgkin disease, and other diseases associated
ɱɱ Unvaccinated or only 1 dose before 12 months: Catch-up vaccination with PCV13:
with treatment with immunosuppressive drugs
Give 2 doses, 8 weeks apart • 1 dose for healthy children aged 24–59 months
or radiation therapy; solid organ transplantation;
with any incomplete* PCV13 schedule
ɱɱ 2 or more doses before 12 months: Give 1 dose, multiple myeloma:
• For other catch-up guidance, see Figure 2.
at least 8 weeks after previous dose. Age 2–5 years:
Special situations: High-risk conditions: • Any incomplete* schedules with:
Doses given within 14 days of starting therapy or
Administer PCV13 doses before PPSV23 if ɱɱ 3 PCV13 doses: 1 dose of PCV13 (at least 8
during therapy should be repeated at least 3 months
after therapy completion. possible. weeks after any prior PCV13 dose).
• Hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) Chronic heart disease (particularly cyanotic ɱɱ <3 PCV13 doses: 2 doses of PCV13, 8 weeks
• 3-dose series with doses 4 weeks apart starting 6 to congenital heart disease and cardiac failure); after the most recent dose and given 8 weeks
12 months after successful transplant (regardless of chronic lung disease (including asthma treated apart.
Hib vaccination history). with high-dose, oral, corticosteroids); diabetes
• No history of PPSV23: 1 dose of PPSV23 (at least 8
• Anatomic or functional asplenia (including sickle mellitus:
weeks after any prior PCV13 dose) and a 2nd dose
cell disease) Age 2–5 years: of PPSV23 5 years later.
12–59 months • Any incomplete* schedules with:
Age 6–18 years:
ɱɱ Unvaccinated or only 1 dose before 12 months: ɱɱ 3 PCV13 doses: 1 dose of PCV13 (at least 8
• No history of either PCV13 or PPSV23: 1 dose of
Give 2 doses, 8 weeks apart. weeks after any prior PCV13 dose).
PCV13, 2 doses of PPSV23 (1st dose of PPSV23
ɱɱ 2 or more doses before 12 months: Give 1 dose, ɱɱ <3 PCV13 doses: 2 doses of PCV13, 8 weeks administered 8 weeks after PCV13 and 2nd dose of
at least 8 weeks after previous dose. after the most recent dose and given 8 weeks PPSV23 administered at least 5 years after the 1st
Unimmunized* persons 5 years or older apart. dose of PPSV23).
ɱɱ Give 1 dose • No history of PPSV23: 1 dose of PPSV23 (at least 8 • Any PCV13 but no PPSV23: 2 doses of PPSV23 (1st
• Elective splenectomy weeks after any prior PCV13 dose). dose of PPSV23 to be given 8 weeks after the most
Unimmunized* persons 15 months or older Age 6-18 years: recent dose of PCV13 and 2nd dose of PPSV23
ɱɱ Give 1 dose (preferably at least 14 days before • No history of PPSV23: 1 dose of PPSV23 (at least 8 administered at least 5 years after the 1st dose of
procedure). weeks after any prior PCV13 dose). PPSV23).
For further guidance on the use of the vaccines mentioned below, see: www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/index.html.
• PPSV23 but no PCV13: 1 dose of PCV13 at least 8 7. Influenza vaccines. (minimum age: 6 months) Catch-up vaccination:
weeks after the most recent PPSV23 dose and a 2nd Routine vaccination: • Ensure persons 7–18 years without evidence of
dose of PPSV23 to be given 5 years after the 1st dose • Administer an age-appropriate formulation and immunity (see MMWR 2007;56[No. RR-4], at
of PPSV23 and at least 8 weeks after a dose of PCV13. dose of influenza vaccine annually. www.cdc.gov/mmwr/pdf/rr/rr5604.pdf) have 2
Chronic liver disease, alcoholism: ɱɱ Children 6 months–8 years who did not doses of varicella vaccine:
Age 6–18 years: receive at least 2 doses of influenza vaccine ɱɱ Ages 7–12: routine interval 3 months
before July 1, 2017 should receive 2 doses (minimum interval: 4 weeks).
• No history of PPSV23: 1 dose of PPSV23 (at least 8
weeks after any prior PCV13 dose). separated by at least 4 weeks. ɱɱ Ages 13 and older: minimum interval 4 weeks.
*Incomplete schedules are any schedules where ɱɱ Persons 9 years and older 1 dose
10. Hepatitis A (HepA) vaccine. (minimum age: 12
PCV13 doses have not been completed according to • Live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV) not
months)
ACIP recommended catch-up schedules. The total recommended for the 2017–18 season.
• For additional guidance, see the 2017–18 ACIP Routine vaccination:
number and timing of doses for complete PCV13
influenza vaccine recommendations (MMWR • 2 doses, separated by 6-18 months, between the
series are dictated by the age at first vaccination. See
August 25, 2017;66(2):1-20: www.cdc.gov/mmwr/ 1st and 2nd birthdays. (A series begun before the
Tables 8 and 9 in the ACIP pneumococcal vaccine
2nd birthday should be completed even if the child
recommendations (www.cdc.gov/mmwr/pdf/rr/ volumes/66/rr/pdfs/rr6602.pdf).
turns 2 before the second dose is given.)
rr5911.pdf ) for complete schedule details. (For the 2018–19 season, see the 2018–19 ACIP
influenza vaccine recommendations.) Catch-up vaccination:
6. Inactivated poliovirus vaccine (IPV). (minimum • Anyone 2 years of age or older may receive HepA
age: 6 weeks) 8. Measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine. vaccine if desired. Minimum interval between
Routine vaccination: (minimum age: 12 months for routine vaccination) doses is 6 months.
• 4-dose series at ages 2, 4, 6–18 months, and 4–6 years. Routine vaccination: Special populations:
Administer the final dose on or after the 4th birthday • 2-dose series at 12–15 months and 4–6 years. Previously unvaccinated persons who should be
and at least 6 months after the previous dose. • The 2nd dose may be given as early as 4 weeks after vaccinated:
the 1st dose. • Persons traveling to or working in countries with
Catch-up vaccination:
Catch-up vaccination: high or intermediate endemicity
• In the first 6 months of life, use minimum ages and • Men who have sex with men
intervals only for travel to a polio-endemic region or • Unvaccinated children and adolescents: 2 doses at
• Users of injection and non-injection drugs
during an outbreak. least 4 weeks apart.
• Persons who work with hepatitis A virus in a
• If 4 or more doses were given before the 4th birthday, International travel: research laboratory or with non-human primates
give 1 more dose at age 4–6 years and at least 6 • Infants 6–11 months: 1 dose before departure. • Persons with clotting-factor disorders
months after the previous dose. Revaccinate with 2 doses at 12–15 months (12 • Persons with chronic liver disease
• A 4th dose is not necessary if the 3rd dose was given months for children in high-risk areas) and 2nd dose • Persons who anticipate close, personal contact
on or after the 4th birthday and at least 6 months as early as 4 weeks later. (e.g., household or regular babysitting) with an
after the previous dose. • Unvaccinated children 12 months and older: international adoptee during the first 60 days after
• IPV is not routinely recommended for U.S. residents 2 doses at least 4 weeks apart before departure. arrival in the United States from a country with high
18 years and older. Mumps outbreak: or intermediate endemicity (administer the 1st dose
Series Containing Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV), either • Persons ≥12 months who previously received as soon as the adoption is planned—ideally at least
mixed OPV-IPV or OPV-only series: ≤2 doses of mumps-containing vaccine and are 2 weeks before the adoptee’s arrival).
• Total number of doses needed to complete the series identified by public health authorities to be at
is the same as that recommended for the U.S. IPV increased risk during a mumps outbreak should 11. Serogroup A, C, W, Y meningococcal vaccines.
schedule. See www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/66/wr/ receive a dose of mumps-virus containing vaccine. (Minimum age: 2 months [Menveo], 9 months
mm6601a6.htm?s_cid=mm6601a6_w. [Menactra].
• Only trivalent OPV (tOPV) counts toward the 9. Varicella (VAR) vaccine. (minimum age: 12 months) Routine:
U.S. vaccination requirements. For guidance to Routine vaccination: • 2-dose series: 11-12 years and 16 years.
assess doses documented as “OPV” see www. • 2-dose series: 12–15 months and 4–6 years. Catch-Up:
cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/66/wr/mm6606a7. • The 2nd dose may be given as early as 3 months • Age 13-15 years: 1 dose now and booster at age
htm?s_cid=mm6606a7_w. after the 1st dose (a dose given after a 4-week 16-18 years. Minimum interval 8 weeks.
• For other catch-up guidance, see Figure 2. interval may be counted). • Age 16-18 years: 1 dose.
For further guidance on the use of the vaccines mentioned below, see: www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/index.html.
Special populations and situations: 12. Serogroup B meningococcal vaccines (minimum • Children 7–10 years who receive Tdap
Anatomic or functional asplenia, sickle cell disease, age: 10 years [Bexsero, Trumenba]. inadvertently or as part of the catch-up series may
HIV infection, persistent complement component Clinical discretion: Adolescents not at increased receive the routine Tdap dose at 11–12 years.
deficiency (including eculizumab use): risk for meningococcal B infection who want • DTaP inadvertently given after the 7th birthday:
• Menveo ɱɱ Child 7–10: DTaP may count as part of
ɱɱ 1st dose at 8 weeks: 4-dose series at 2, 4, 6, and MenB vaccine.
catch-up series. Routine Tdap dose at 11-12
12 months. MenB vaccines may be given at clinical discretion to
may be given.
ɱɱ 1st dose at 7–23 months: 2 doses (2nd dose at adolescents 16–23 years (preferred age 16–18 years)
ɱɱ Adolescent 11–18: Count dose of DTaP as the
least 12 weeks after the 1st dose and after the 1st who are not at increased risk.
adolescent Tdap booster.
birthday). • Bexsero: 2 doses at least 1 month apart.
• For other catch-up guidance, see Figure 2.
ɱɱ 1st dose at 24 months or older: 2 doses at least 8 • Trumenba: 2 doses at least 6 months apart. If the
weeks apart. 2nd dose is given earlier than 6 months, give a 3rd 14. Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine (minimum
• Menactra dose at least 4 months after the 2nd. age: 9 years)
ɱɱ Persistent complement component deficiency: Special populations and situations: Routine and catch-up vaccination:
ʲʲ9–23 months: 2 doses at least 12 weeks apart Anatomic or functional asplenia, sickle cell • Routine vaccination for all adolescents at 11–12
ʲʲ24 months or older: 2 doses at least 8 weeks disease, persistent complement component years (can start at age 9) and through age 18 if not
apart deficiency (including eculizumab use), serogroup previously adequately vaccinated. Number of doses
ɱɱ Anatomic or functional asplenia, sickle cell B meningococcal disease outbreak dependent on age at initial vaccination:
disease, or HIV infection: • Bexsero: 2-dose series at least 1 month apart. ɱɱ Age 9–14 years at initiation: 2-dose series at 0
ʲʲ24 months or older: 2 doses at least 8 weeks • Trumenba: 3-dose series at 0, 1-2, and 6 months. and 6–12 months. Minimum interval: 5 months
apart. (repeat a dose given too soon at least 12 weeks
Note: Bexsero and Trumenba are not after the invalid dose and at least 5 months
ʲʲMenactra must be administered at least 4
weeks after completion of PCV13 series. interchangeable. after the 1st dose).
For additional meningococcal vaccination ɱɱ Age 15 years or older at initiation: 3-dose
Children who travel to or live in countries where
meningococcal disease is hyperendemic or information, see meningococcal MMWR publications series at 0, 1–2 months, and 6 months.
epidemic, including countries in the African at: www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/vacc- Minimum intervals: 4 weeks between 1st and
meningitis belt or during the Hajj, or exposure to an specific/mening.html. 2nd dose; 12 weeks between 2nd and 3rd
outbreak attributable to a vaccine serogroup: dose; 5 months between 1st and 3rd dose
• Children <24 months of age: 13. Tetanus, diphtheria, and acellular pertussis (repeat dose(s) given too soon at or after the
ɱɱ Menveo (2-23 months): (Tdap) vaccine. (minimum age: 11 years for minimum interval since the most recent dose).
ʲʲ1st dose at 8 weeks: 4-dose series at 2, 4, 6, and routine vaccinations, 7 years for catch-up • Persons who have completed a valid series with any
12 months. vaccination) HPV vaccine do not need any additional doses.
ʲʲ1st dose at 7-23 months: 2 doses (2nd dose at Routine vaccination: Special situations:
least 12 weeks after the 1st dose and after the • Adolescents 11–12 years of age: 1 dose. • History of sexual abuse or assault: Begin series at
1st birthday). • Pregnant adolescents: 1 dose during each age 9 years.
ɱɱ Menactra (9-23 months): pregnancy (preferably during the early part of • Immunocompromised* (including HIV) aged
ʲʲ2 doses (2nd dose at least 12 weeks after the gestational weeks 27–36). 9–26 years: 3-dose series at 0, 1–2 months, and 6
1st dose. 2nd dose may be administered as • Tdap may be administered regardless of the months.
early as 8 weeks after the 1st dose in travelers). interval since the last tetanus- and diphtheria- • Pregnancy: Vaccination not recommended,
• Children 2 years or older: 1 dose of Menveo or toxoid-containing vaccine. but there is no evidence the vaccine is harmful.
Menactra. No intervention is needed for women who
Catch-up vaccination: inadvertently received a dose of HPV vaccine
Note: Menactra should be given either before or at
• Adolescents 13–18 who have not received Tdap: while pregnant. Delay remaining doses until after
the same time as DTaP. For MenACWY booster dose
recommendations for groups listed under “Special 1 dose, followed by a Td booster every 10 years. pregnancy. Pregnancy testing not needed before
populations and situations” above, and additional • Persons aged 7–18 years not fully immunized vaccination.
meningococcal vaccination information, see with DTaP: 1 dose of Tdap as part of the catch-up *See MMWR, December 16, 2016;65(49):1405–1408,
meningococcal MMWR publications at: www.cdc.gov/ series (preferably the first dose). If additional doses at www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/65/wr/pdfs/
vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/vacc-specific/mening.html. are needed, use Td. mm6549a5.pdf. CS270457-F
You might also like
- Trifold Vaccine Card ENGLISHDocument2 pagesTrifold Vaccine Card ENGLISHGarrett GoldwaiteNo ratings yet
- Walter Kaufmann Ac 2012 SymposiumDocument41 pagesWalter Kaufmann Ac 2012 SymposiumErwin SyahNo ratings yet
- Adult Combined Schedule BWDocument6 pagesAdult Combined Schedule BWalbatros4816No ratings yet
- Adult Combined ScheduleDocument6 pagesAdult Combined SchedulesharvaniNo ratings yet
- Adult Combined ScheduleDocument6 pagesAdult Combined Scheduleice teeNo ratings yet
- 0 To 18yrs Combined Immunization ScheduleDocument8 pages0 To 18yrs Combined Immunization ScheduleNurses CommunityNo ratings yet
- 0 18yrs Child Combined ScheduleDocument14 pages0 18yrs Child Combined ScheduleEphrem LemmaNo ratings yet
- Recommended Adult Immunization Schedule: For Ages 19 Years or OlderDocument6 pagesRecommended Adult Immunization Schedule: For Ages 19 Years or OlderBhargavNo ratings yet
- Notification of VaccinationDocument1 pageNotification of VaccinationklinikputrasimpangampatNo ratings yet
- Immunization RecordDocument4 pagesImmunization RecordVin BitzNo ratings yet
- Vaccine Project - FinalDocument2 pagesVaccine Project - Finalchelsea garzaNo ratings yet
- Immunization Record: Haemophilus InfluenzaeDocument2 pagesImmunization Record: Haemophilus InfluenzaeApshar MunnaNo ratings yet
- Adult Combined ScheduleDocument10 pagesAdult Combined ScheduleTadilakshmikiranNo ratings yet
- Anne Lise Becker Sanofi Pasteur MSD 2Document10 pagesAnne Lise Becker Sanofi Pasteur MSD 2SRARNo ratings yet
- Notification of Vaccination Letter Template: Vaccines AdministeredDocument1 pageNotification of Vaccination Letter Template: Vaccines AdministeredJacob BuckNo ratings yet
- Vaccine Administration Record For Children and TeensDocument2 pagesVaccine Administration Record For Children and TeensGian Franco ApesNo ratings yet
- Adult Combined ScheduleDocument6 pagesAdult Combined ScheduleAstrid Elaine RosalesNo ratings yet
- Adult Combined Schedule VaccineDocument33 pagesAdult Combined Schedule VaccinehatsuneNo ratings yet
- Vesikari Comparison of Hexavalent VaccinesDocument31 pagesVesikari Comparison of Hexavalent VaccinesdragondostNo ratings yet
- Adult Combined ScheduleDocument10 pagesAdult Combined ScheduledrabdulrabbNo ratings yet
- 0 18yrs Child Combined ScheduleDocument14 pages0 18yrs Child Combined ScheduleMohemma Ibrahim AsaramNo ratings yet
- 2010 Adolescent Immunization Schedule Final 121709Document1 page2010 Adolescent Immunization Schedule Final 121709Dustin Van WilkesNo ratings yet
- Panorama of Immunization in The Americas: Webinar: Covering COVID-19 Vaccines in A Responsible and Evidence-Based MannerDocument61 pagesPanorama of Immunization in The Americas: Webinar: Covering COVID-19 Vaccines in A Responsible and Evidence-Based MannerM. RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Health Care Professionals Refusal To Vaccinate Form English 3Document1 pageHealth Care Professionals Refusal To Vaccinate Form English 3Marshall FeatherNo ratings yet
- Links To Clinical Info About The VaccineDocument9 pagesLinks To Clinical Info About The VaccinekarunaNo ratings yet
- Immunization Child2005 EnglDocument4 pagesImmunization Child2005 EnglGanesh BabuNo ratings yet
- (LIST) Adult VaccinationsDocument4 pages(LIST) Adult VaccinationsLeslie MartinezNo ratings yet
- PHE Complete Immunisation Schedule Jan2020 PDFDocument2 pagesPHE Complete Immunisation Schedule Jan2020 PDFJyotirmaya RajaNo ratings yet
- PHE Complete Immunisation ScheduDocument2 pagesPHE Complete Immunisation ScheduJasminewai927No ratings yet
- Vaccine Administration Record For AdultsDocument2 pagesVaccine Administration Record For AdultsAlfonso VincentNo ratings yet
- National Immunisation Program: Queensland ScheduleDocument1 pageNational Immunisation Program: Queensland ScheduleHarshpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Vaccine NamesDocument4 pagesVaccine NamesRima Carolina Bahsas ZakyNo ratings yet
- Immunizations Preg ChartDocument2 pagesImmunizations Preg ChartPutri MahacakriNo ratings yet
- Vaccination of HIV Infected Children 2018Document4 pagesVaccination of HIV Infected Children 2018alpha.blocker11No ratings yet
- Adult Schedule Easy ReadDocument2 pagesAdult Schedule Easy Read12345zolyNo ratings yet
- Immunization Rec RDDocument1 pageImmunization Rec RDmail2saeedisNo ratings yet
- Multisystem & Genetic - BoardsDocument10 pagesMultisystem & Genetic - BoardsSoojung NamNo ratings yet
- UKHSA 12706 Complete Immunisation Schedule September2023Document2 pagesUKHSA 12706 Complete Immunisation Schedule September2023Ebuwa AmadasunNo ratings yet
- JabsDocument1 pageJabsgvswainNo ratings yet
- Upload 7Document10 pagesUpload 7zendah123No ratings yet
- Vaccine Injury Infographic 2017Document1 pageVaccine Injury Infographic 2017paulNo ratings yet
- 0 18yrs Child Combined ScheduleDocument10 pages0 18yrs Child Combined ScheduleMGKNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Hepatitis B VaccineDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Hepatitis B VaccineJustin AncogNo ratings yet
- Helminth Vaccines in RuminantsDocument13 pagesHelminth Vaccines in RuminantsAntonio Márquez LaraNo ratings yet
- PHE Complete Immunisation Schedule Jun2020 05Document2 pagesPHE Complete Immunisation Schedule Jun2020 05GAnnNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication / Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities Indications: CnsDocument1 pageDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication / Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities Indications: CnsSeno HyeonNo ratings yet
- National Immunisation Program ScheduleDocument2 pagesNational Immunisation Program Schedulesophile660No ratings yet
- Parent Ver SCH 0 6yrsDocument2 pagesParent Ver SCH 0 6yrsunmundoextranopodcastNo ratings yet
- For Those Who Fall Behind or Start Late, See The Catch-Up ScheduleDocument4 pagesFor Those Who Fall Behind or Start Late, See The Catch-Up ScheduleTony MichelNo ratings yet
- Ant Vaccines WRF Hepatitis B FinalDocument6 pagesAnt Vaccines WRF Hepatitis B FinalRidhi MurarkaNo ratings yet
- Vaccines in DermatologyDocument31 pagesVaccines in Dermatologydr.aparajitaghoshNo ratings yet
- BscNR20 - Topic 8 - VaccinesDocument6 pagesBscNR20 - Topic 8 - Vaccinesakoeljames8543No ratings yet
- Davao Doctors College: Community Health NursingDocument5 pagesDavao Doctors College: Community Health NursingEllyn Rose Cardente ManiwangNo ratings yet
- HEPAB Vax DSDocument3 pagesHEPAB Vax DSSheena Marie M. TarleNo ratings yet
- National Immunisation ScheduleDocument2 pagesNational Immunisation SchedulegreatvedasNo ratings yet
- Immunization: For C-1 Med Student DR Muluken JAN/2018Document71 pagesImmunization: For C-1 Med Student DR Muluken JAN/2018Yemata HailuNo ratings yet
- GSK Vaccines in USADocument6 pagesGSK Vaccines in USAmrinal agarwalNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyyyyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyyyyNathalie kate petallarNo ratings yet
- HIV Vaccines Overview: Shaleena TheophilusDocument34 pagesHIV Vaccines Overview: Shaleena TheophilusREETHUNo ratings yet
- Good Health in the Tropics: Advice to Travellers and SettlersFrom EverandGood Health in the Tropics: Advice to Travellers and SettlersNo ratings yet
- PLC Based Motor StartingDocument5 pagesPLC Based Motor StartingSaddam HussainNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Utm AttachedDocument2 pagesSchedule of Utm AttachedSaddam HussainNo ratings yet
- Higher Educa (On Commission, Pakistan: List of UniversitiesDocument4 pagesHigher Educa (On Commission, Pakistan: List of UniversitiesSaddam HussainNo ratings yet
- Each Teacher To Submit Course Plan IndividuallyDocument1 pageEach Teacher To Submit Course Plan IndividuallySaddam HussainNo ratings yet
- USA Fulbright and Direct AdmissionsDocument19 pagesUSA Fulbright and Direct AdmissionsSaddam HussainNo ratings yet
- Get File - Etap Training Manual PDFDocument2 pagesGet File - Etap Training Manual PDFSaddam Hussain0% (1)
- Impact of Distributed Generation On Radial Distribution Network With Various Load ModelsDocument5 pagesImpact of Distributed Generation On Radial Distribution Network With Various Load ModelsSaddam HussainNo ratings yet
- Call Letter For TestDocument1 pageCall Letter For TestSaddam HussainNo ratings yet
- (Electrical Machines) CLOSDocument3 pages(Electrical Machines) CLOSSaddam HussainNo ratings yet
- Shah Nawaz: Personal DataDocument2 pagesShah Nawaz: Personal DataSaddam Hussain50% (2)
- Ned University of Engineering & Technology, University Road, Karachi-75270Document3 pagesNed University of Engineering & Technology, University Road, Karachi-75270Saddam HussainNo ratings yet
- Basic CircuitDocument31 pagesBasic CircuitSaddam HussainNo ratings yet
- Deposit ID: Deposit ID:: Applicant Signature Cashier Officer Applicant Signature Cashier OfficerDocument1 pageDeposit ID: Deposit ID:: Applicant Signature Cashier Officer Applicant Signature Cashier OfficerSaddam HussainNo ratings yet
- Understanding Viruses Video SheetDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Viruses Video Sheetapi-264004571No ratings yet
- Hubungan Perilaku Petugas Dan Perlengkapan Peralatan Dengan Potensi Vaksin Pada Sistem Rantai Dingin Vaksin DI Seluruh Puskesmas Kota CimahiDocument12 pagesHubungan Perilaku Petugas Dan Perlengkapan Peralatan Dengan Potensi Vaksin Pada Sistem Rantai Dingin Vaksin DI Seluruh Puskesmas Kota CimahiElsa Putri AgustinNo ratings yet
- AE Poxine Product ProfileDocument2 pagesAE Poxine Product Profileikram chohanNo ratings yet
- Vikram Covid Vaccine Certificate1666801329239Document1 pageVikram Covid Vaccine Certificate1666801329239DR nagar gamerNo ratings yet
- Vaccination 881031355529 PDFDocument1 pageVaccination 881031355529 PDFNuh NuhaNo ratings yet
- B2.3 How Can We Prevent The Spread of Infections (F) - 3Document12 pagesB2.3 How Can We Prevent The Spread of Infections (F) - 3dreamvision710No ratings yet
- Mandatory VaccinationsDocument7 pagesMandatory Vaccinationsapi-487208181No ratings yet
- Pre-Placement Immunization Form (June 2017) BrockDocument2 pagesPre-Placement Immunization Form (June 2017) BrockroldinpgNo ratings yet
- Vaccination 810423045070Document1 pageVaccination 810423045070yasiniNo ratings yet
- Daftar Obat Poli AnakDocument3 pagesDaftar Obat Poli AnakSyftr AbdnNo ratings yet
- Northern Police District District Medical and Dental UnitDocument3 pagesNorthern Police District District Medical and Dental UnitTon LeidrajNo ratings yet
- Merged File - HLTH 101Document14 pagesMerged File - HLTH 101Harshana Sandaruwan SomarathneNo ratings yet
- ImmunizationDocument28 pagesImmunizationTusvendran Pillai100% (1)
- Dataset On Child Vaccination in Brazil From 1996 To 2021: Data DescriptorDocument9 pagesDataset On Child Vaccination in Brazil From 1996 To 2021: Data DescriptorlaireneNo ratings yet
- FDA To Authorize New Covid Boosters Without Trials in PeopleDocument3 pagesFDA To Authorize New Covid Boosters Without Trials in PeopleZsi GaNo ratings yet
- Sabarimala: Virtual-Q Booking CouponDocument2 pagesSabarimala: Virtual-Q Booking CouponST COMMNICATIONNo ratings yet
- CertificateDocument1 pageCertificateHimanshu maulekhiNo ratings yet
- APA DSM 5 Somatic Symptom DisorderDocument2 pagesAPA DSM 5 Somatic Symptom DisordermargauxNo ratings yet
- Certificate For COVID-19 Vaccination: Beneficiary DetailsDocument1 pageCertificate For COVID-19 Vaccination: Beneficiary Detailsuday xeroxNo ratings yet
- B. Schedule of Vaccination: A. Different Important VaccinesDocument4 pagesB. Schedule of Vaccination: A. Different Important VaccinesJane LappaoNo ratings yet
- Epi Cold Chain and LogisticsDocument28 pagesEpi Cold Chain and LogisticsPEDRO M. MAGADANNo ratings yet
- Vaccination CentersDocument4 pagesVaccination CentersdmonlinelkNo ratings yet
- Certificate For COVID-19 Vaccination: Beneficiary DetailsDocument1 pageCertificate For COVID-19 Vaccination: Beneficiary DetailsNis DisNo ratings yet
- VACCINATION Monitoring Report For StudentsDocument3 pagesVACCINATION Monitoring Report For StudentsMj ManuelNo ratings yet
- 4790 9576 1 SMDocument5 pages4790 9576 1 SMNs. ANITA SUKARNO, S.Kep., M.Sc.� 7884�No ratings yet
- Daftar Pemberian Vaksinasi Covid-19 14-02-2022Document6 pagesDaftar Pemberian Vaksinasi Covid-19 14-02-2022jeketimbilNo ratings yet
- Id AssignmentDocument4 pagesId AssignmentAmutuhaire JudithNo ratings yet
- ExcelDocument2 pagesExcelNur YahmanNo ratings yet
- AAEP Core Vaccinations For Adult HorsesDocument1 pageAAEP Core Vaccinations For Adult HorsesLauren ThompsonNo ratings yet