Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Parent Letter
Parent Letter
Uploaded by
api-374154554Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Parent Letter
Parent Letter
Uploaded by
api-374154554Copyright:
Available Formats
Math 6 Unit 5
Area and Volume
Volume 1 Issue 5
References Dear Parents
Helpful Links: In this unit students will learn about finding the area of polygons, the surface area of prisms and
www.khanacademy.org/ pyramids, and the volume of prisms with fractional edges.
math/basic-geo/basic-
geo-volume-surface-
area/basic-geo-
Concepts Students will Use and Understand
volume/v/volume-of-a- The area of irregular and regular polygons can be found by decomposing the polygon into
rectangular-prism-with- rectangles, triangles and other shapes.
fractional-cubes
Manipulatives and the construction of nets may be used in computing the surface area of
www.onlinemathlearning rectangular and triangular prisms, and volume of right rectangular prism.
.com/prism-surface- Formulas may be used to compute the areas of polygons, surface areas of rectangular and
area.html triangular prisms, and volumes of right rectangular prisms.
Appropriate units of measure should be used when computing the area (square units) of
www.geogebra.org/en/u
pload/files/english/Victor polygons, and surface area (square units) and volume of prisms (cubic units).
ia/TriangleArea.html Views of rectangular and triangular prisms may be interpreted and sketched to provide a 2-
dimensional representation of a three dimensional figure.
www.ixl.com/math/gra Fractional edge lengths are equivalent to the dimensions of solid figures
de-6/volume-and- The volume of a solid figure is the number of same sized cubes filling the space so that there are
surface-area
no gaps and overlaps.
http://www.learner.or
g/interactives/geometr Vocabulary
y/3d_prisms.html Area: The number of square units it takes to completely fill a space or surface.
Bases of a Prism: The two faces formed by congruent polygons that lie in parallel planes, all of the other
Georgia Math faces being parallelograms.
Textbook Connection: Cubic Units: Volume of the solids is measured in Cubic Units.
Edge: The intersection of a pair of faces in a three-dimensional figure.
Ch. 8: Lessons 1-5 Equilateral Triangle: A triangle which has all three of its sides equal in length.
Ch. 9: Lessons 1-5 Face: One of the polygons that makes up a polyhedron.
Fractional edge length: The length of each edge of the cube is a fraction.
Textbook Online: Isosceles Triangle: A triangle which has two of its sides equal in length.
Georgia Math Kite: A quadrilateral with two distinct pairs of equal adjacent sides.
http://connected.mcgr A kite-shaped figure.
aw- Lateral Faces: In a prism, a face that is not a base of the figure.
hill.com/connected/log Net: A two-dimensional figure that, when folded, forms the surfaces of a three-dimensional object.
in.do Parallelogram: A quadrilateral with both pairs of opposite sides parallel.
Polygon: A number of coplanar line segments, each connected end to end to form a closed shape. A
regular polygon has all sides equal and all interior angles equal. An irregular polygon sides are not all the
same length nor does the interior angles have the same measure.
Polyhedron: A 3-dimensional figure that has polygons as faces.
Prism: A polyhedron with two parallel and congruent faces, called bases, and all other faces that are
parallelograms.
Quadrilaterals: Four coplanar line segments linked end to end to create a closed figure.
A 4-sided polygon.
Rectangle: A 4-sided polygon where all interior angles are 90°.
Rectangular prism: A solid (3-dimensional) object which has six faces that are rectangles.
Rhombus: A quadrilateral with all four sides equal in length.
Right Triangle: A triangle where one of its interior angles is a right angle (90 degrees).
Right rectangular prism: In a right prism, the lateral faces are each perpendicular to the bases.
Scalene Triangle: A triangle where all three sides are different in length.
Square: A quadrilateral that has four right angles and four equal sides.
Surface area: The total area of the 2-dimensional surfaces that make up a 3-dimensional object.
Trapezoid: A quadrilateral which has one pair of parallel sides.
Triangles: A closed figure consisting of three line segments linked end-to-end.
A 3-sided polygon
Triangular prism: A prism whose bases are triangles. A solid (3-dimensional object what has five faces:
three rectangles and two bases.
Vertices: The common endpoint of two or more rays or line segments
Volume: The amount of space occupied by an object.
Volume of a Prism: The area of a base times the height. The number of cubic units to fill a prism.
Try http://intermath.coe.uga.edu/dictnary/homepg.asp or http://www.amathsdictionaryforkids.com/ for
further examples.
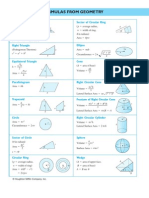
Formulas Example 1 Example 2
Area What is the area of this triangle? What is the area of this flower garden?
8 ft
28 cm
Parallelogram 8 cm
A = bh 16 cm
9 ft
Triangle
A = ½bh 13 ft
24 cm
Volume Example 3 Example 4
The net of a square pyramid is shown below.
Rectangular Prism
5 in
V = lwh
2 in
V = Bh
8 in
1 in
1½ in
What is the volume of the rectangular prism? What is the surface area of the pyramid?
Key
Example 1 Example 2
A = ½bh A = ½bh A = bh 22.5
A=½bh A=½bh A=bh + 72.0
A = ½ 24 8 A=½95 A=98 94.5
A = ½ 192 A = ½ 45 A = 72
A = 96 A = 22.5 The area of the
The area of the triangle is 96 cm2. garden is 94.5 ft2.
Example 3 Example 4
V = lwh A = b2 A = ½bh 80
V = l w h A=bb A=½bh + 64
V = 1½ 1 2 A=88 A=½85 144
V = 1½ 2 A = 64 A = ½ 40
V = 3 in3 A = 20 The surface area of
20 4 = 80 the pyramid is 144 in2.
You might also like
- 7.5.1 - Surface Area of A Prism and CylinderDocument5 pages7.5.1 - Surface Area of A Prism and CylinderGaran WisemanNo ratings yet
- Congruent Triangles Packet 2013 With Correct AnswersDocument87 pagesCongruent Triangles Packet 2013 With Correct Answersmsmmpb100% (2)
- Lecture 4 - QuadrilateralsDocument29 pagesLecture 4 - QuadrilateralsSandra Enn BahintingNo ratings yet
- Geometry EOC Review PacketDocument39 pagesGeometry EOC Review PacketVale Mejia100% (1)
- Rumus PrimoidalDocument7 pagesRumus PrimoidaltsipilNo ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument9 pagesMathematicsRachel AmairaNo ratings yet
- Math Cartoon AnimationDocument3 pagesMath Cartoon Animationapi-366304862No ratings yet
- Mathematics Note For Grade 10Document8 pagesMathematics Note For Grade 10darseziyad34No ratings yet
- Mensuration: Basic Concepts and Important Formulas Equilateral TriangleDocument5 pagesMensuration: Basic Concepts and Important Formulas Equilateral TriangleSrinu MaddikuntlaNo ratings yet
- Geometry: B. Solid/Space Geometry 1. Position of Lines in SpaceDocument9 pagesGeometry: B. Solid/Space Geometry 1. Position of Lines in SpaceBagas FajriansyahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Part 1Document16 pagesChapter 3 Part 1KokieNo ratings yet
- A About Area and PerimeterDocument11 pagesA About Area and PerimeterAmiel ColanoNo ratings yet
- Four-Side Plane FiguresDocument26 pagesFour-Side Plane FiguresFajrin Maulana Kingwijati100% (1)
- Quadrilaterals Digital TextDocument14 pagesQuadrilaterals Digital TextAmruthaNo ratings yet
- Plane Figures: Group 1Document49 pagesPlane Figures: Group 1Danielle Kate MadridNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Math Vocabulary (Gr. 8)Document3 pagesChapter 11 Math Vocabulary (Gr. 8)moona imranNo ratings yet
- Ge 4 ModuleDocument33 pagesGe 4 ModuleRenvil Igpas MompilNo ratings yet
- Heep 206Document42 pagesHeep 206Bodhisatya BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- The Volume,, of A Cube Is Determined by The Following FormulaDocument12 pagesThe Volume,, of A Cube Is Determined by The Following FormulaMolla DerbewNo ratings yet
- Nets - Volume - Surface Area of Prisms PDFDocument9 pagesNets - Volume - Surface Area of Prisms PDFTaseen TanvirNo ratings yet
- Visualizing Solid Shapes PDFDocument42 pagesVisualizing Solid Shapes PDFAshishNo ratings yet
- Geraldine Ramos - MIDTERMDocument10 pagesGeraldine Ramos - MIDTERMGeraldine RamosNo ratings yet
- Plane Figure and Their Properties A. Plane Figure Definition of Plane FigureDocument5 pagesPlane Figure and Their Properties A. Plane Figure Definition of Plane FigureKasmawati FatirNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry PrismsDocument17 pagesAnalytic Geometry PrismsCarl Kristopher Pelonia100% (1)
- Final Math PortfolioDocument32 pagesFinal Math Portfolioapi-311730016No ratings yet
- Ch8 Quadrilaterals Chapter NotesDocument5 pagesCh8 Quadrilaterals Chapter NotesMohanNayakNo ratings yet
- GEE 9 - Chapter 4 - Plane FiguresDocument23 pagesGEE 9 - Chapter 4 - Plane FiguresPREFIX THAT IS LONG - Lester LoutteNo ratings yet
- Measurement Notes For Grade 10 MathematicsDocument14 pagesMeasurement Notes For Grade 10 MathematicsBanekeNo ratings yet
- MAT14xTextbook1stEditionCh1Document38 pagesMAT14xTextbook1stEditionCh1nhlanvyNo ratings yet
- Airline Tickets: Unit SquareDocument1 pageAirline Tickets: Unit SquareCarol LizardoNo ratings yet
- Quadrilateral 2024 (1)Document41 pagesQuadrilateral 2024 (1)Yonela MquqwanaNo ratings yet
- Ariel Li Basic GeometryDocument5 pagesAriel Li Basic GeometryOmkar MandalNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3.2-MOM-1H_3.Document62 pagesChapter-3.2-MOM-1H_3.lamerez.j2004No ratings yet
- Math 5-Plane and Solid Geometry-Research - Bsed 2d-EscañoDocument35 pagesMath 5-Plane and Solid Geometry-Research - Bsed 2d-EscañoJulie Anne Ponteres EscañoNo ratings yet
- A QuadrilateralDocument64 pagesA QuadrilateralRed Dela Cruz100% (1)
- 8.1 Three-Dimensional Figures: ObjectivesDocument18 pages8.1 Three-Dimensional Figures: Objectiveszakaria shineeNo ratings yet
- 6 2 Unit 5 VocabDocument2 pages6 2 Unit 5 Vocabapi-260971765No ratings yet
- Descriptive Geometry II: Oct. 23/ 2021 Muhammed ADocument32 pagesDescriptive Geometry II: Oct. 23/ 2021 Muhammed AHULE ADDIS ENTERTAINMENTNo ratings yet
- Lesson On Solid MensurationDocument18 pagesLesson On Solid MensurationKelly Lulu100% (1)
- Chapter 3.1 Basic Concepts of SolidsDocument7 pagesChapter 3.1 Basic Concepts of SolidsSanchez Jhundell R. - BSME 2ENo ratings yet
- Area and PerimetreDocument28 pagesArea and PerimetreИакс ВбдубакировNo ratings yet
- w11 HDTBasMathDocument3 pagesw11 HDTBasMathKhaeroni KhaeroniNo ratings yet
- Solid Mensuration PDFDocument25 pagesSolid Mensuration PDFHEIDI ROSE MENDOZANo ratings yet
- MTG Handout Session9Document5 pagesMTG Handout Session9Kenzo Rafael ManaloNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment English For Basics Mathematics Solid/ Space GeometryDocument7 pagesIndividual Assignment English For Basics Mathematics Solid/ Space GeometryNadya Zahwa LuthainNo ratings yet
- 3 6webDocument18 pages3 6webJohn Nikko NicolasNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 2Document62 pagesChapter-3 2AleahNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Parallelograms and Their Properties: Lesson 1Document31 pagesKinds of Parallelograms and Their Properties: Lesson 1Ivy Mae CagandeNo ratings yet
- Cynthia Medina Salas: 25 203 Leonel CantúDocument6 pagesCynthia Medina Salas: 25 203 Leonel CantúCHOINo ratings yet
- Surface Area and VolumeDocument27 pagesSurface Area and VolumeRiNo ratings yet
- POLYGONSDocument45 pagesPOLYGONSBlessa Mae100% (1)
- ArMath1 - Presentation3Document31 pagesArMath1 - Presentation3Jayson RamirezNo ratings yet
- Triangle Square: Heptagon OctagonDocument54 pagesTriangle Square: Heptagon OctagonJyotsna Rawal100% (1)
- Module 3 - Unit 2Document16 pagesModule 3 - Unit 2ntulagan05No ratings yet
- Geometry!!!Document19 pagesGeometry!!!Jane AnonasNo ratings yet
- Measurement - Solid FiguresDocument44 pagesMeasurement - Solid FiguresFREDERICK FUENTESNo ratings yet
- SurfaceAreaandVolume TEXTDocument26 pagesSurfaceAreaandVolume TEXTprabsahiNo ratings yet
- Types Formulas Parts Special Polygons Names: What Is A Polygon?Document4 pagesTypes Formulas Parts Special Polygons Names: What Is A Polygon?Johnel AgueloNo ratings yet
- Volume FormulaDocument5 pagesVolume FormulachesteruytiepoNo ratings yet
- Area Formulas: Gemonrty FormulaDocument12 pagesArea Formulas: Gemonrty FormulaPankaj Jirafe100% (1)
- How To Find Area of A ParallelogramDocument5 pagesHow To Find Area of A Parallelogramapi-126876773No ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Three-Dimensional Figures with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Three-Dimensional Figures with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Ordered Pairs Worksheet and ActivityDocument2 pagesOrdered Pairs Worksheet and Activityapi-366304862No ratings yet
- Mathematicians Research ProjectDocument3 pagesMathematicians Research Projectapi-366304862No ratings yet
- 6th Grade Choice Board 4-17Document1 page6th Grade Choice Board 4-17api-366304862No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Study GuideDocument2 pagesUnit 2 Study Guideapi-366304862No ratings yet
- Unit 6 Study Guide Answer KeyDocument4 pagesUnit 6 Study Guide Answer Keyapi-366304862100% (1)
- Teacher For A DayDocument2 pagesTeacher For A Dayapi-366304862No ratings yet
- 1106 Am Office LensDocument1 page1106 Am Office Lensapi-366304862No ratings yet
- Name - Date - Per - Measures of Variation WorksheetDocument1 pageName - Date - Per - Measures of Variation Worksheetapi-366304862No ratings yet
- Lsga Math Mock Milestone Student VersionDocument36 pagesLsga Math Mock Milestone Student Versionapi-366304862No ratings yet
- Box and Whisker PlotsDocument20 pagesBox and Whisker Plotsapi-366304862No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Study Guide Answer KeyDocument6 pagesUnit 5 Study Guide Answer Keyapi-366304862No ratings yet
- Sqs Student WorksheetDocument2 pagesSqs Student Worksheetapi-366304862No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Study Guide Answer KeyDocument6 pagesUnit 5 Study Guide Answer Keyapi-366304862No ratings yet
- CCGPS Math 6 Grade Unit 5 Study Guide - Area & Volume FormulasDocument6 pagesCCGPS Math 6 Grade Unit 5 Study Guide - Area & Volume Formulasapi-366304862No ratings yet
- 3 5HeronFormulaDocument7 pages3 5HeronFormulaBJ ABUBONo ratings yet
- Solids For Which V (1/3) BHDocument41 pagesSolids For Which V (1/3) BHmacky02 sorenatsac100% (1)
- AGMA933Document26 pagesAGMA933Arthanari VaidyanathanNo ratings yet
- My TestDocument6 pagesMy Testenock chilufyajrNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Maths PE II PaperDocument5 pagesClass 9 Maths PE II PaperPrince PrasannanNo ratings yet
- MATH01 Answers Assignment6 PyramidDocument4 pagesMATH01 Answers Assignment6 PyramidabiNo ratings yet
- Differentiation (Maximum and Minimum Value)Document26 pagesDifferentiation (Maximum and Minimum Value)Bisma RajaNo ratings yet
- Sample Geometry QuizDocument4 pagesSample Geometry QuizJoshua MorkNo ratings yet
- 3rd ESO EnglishDocument4 pages3rd ESO EnglishDavid Bellvis EgeaNo ratings yet
- Right Triangle CongruenceDocument4 pagesRight Triangle CongruenceRoella Mae Tudias AlodNo ratings yet
- Vektor Untuk Kalkulus 2Document77 pagesVektor Untuk Kalkulus 2svitri94No ratings yet
- Q3 W2 Lesson 2 Properties of ParallelogramDocument38 pagesQ3 W2 Lesson 2 Properties of Parallelogramdeanicadelfin09No ratings yet
- Euclidean Tilings by Convex Regular PolygonsDocument20 pagesEuclidean Tilings by Convex Regular PolygonshbNo ratings yet
- Form 3 - Chapter 8Document9 pagesForm 3 - Chapter 8MARHAINI50% (2)
- 3 D Geometry MCQDocument0 pages3 D Geometry MCQVamsi VangaraNo ratings yet
- IMO Level 2 - Class 6 (2013-2014)Document13 pagesIMO Level 2 - Class 6 (2013-2014)Kushi LankaNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Mathematics 0580 Theory v6 - RemovedDocument15 pagesCaie Igcse Mathematics 0580 Theory v6 - RemovedkashishhagarwalNo ratings yet
- 14 VolumesDocument5 pages14 VolumesRosewill AlcaideNo ratings yet
- Another Name For Isosceles Right Triangle Is 45 - 45 - 90 TriangleDocument7 pagesAnother Name For Isosceles Right Triangle Is 45 - 45 - 90 TriangleLorence Atordedo TagacayNo ratings yet
- Formulas GeometryDocument1 pageFormulas Geometryguillermo franciscoNo ratings yet
- ED Acad Sheet Feb-Jun 2023Document4 pagesED Acad Sheet Feb-Jun 2023Akshita PillaiNo ratings yet
- Semi-Regular TesselationsDocument10 pagesSemi-Regular Tesselationspunjabiastonmartin95No ratings yet
- Mapeh 7 TosDocument20 pagesMapeh 7 TosBenjanNo ratings yet
- Yr11 TrigonometryDocument17 pagesYr11 Trigonometryamazingapple35No ratings yet
- q1 Precal Notes (In Progress)Document20 pagesq1 Precal Notes (In Progress)saturosjuliaclarisseNo ratings yet
- RC Sharma 6TH ClassDocument24 pagesRC Sharma 6TH ClassAnkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- PolygonsDocument18 pagesPolygonsKAVITHA CHANDRANNo ratings yet
- Volumes by Shell MethodDocument16 pagesVolumes by Shell Methodayesha noorNo ratings yet
- Lesson16 IsocelesAndEquilateralTrianglesDocument7 pagesLesson16 IsocelesAndEquilateralTrianglesJunaNo ratings yet