Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Alkanes Alkenes 2
Alkanes Alkenes 2
Uploaded by
Jesseca ValenciaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Alkanes Alkenes 2
Alkanes Alkenes 2
Uploaded by
Jesseca ValenciaCopyright:
Available Formats
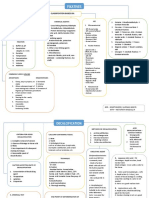
HOW ARE ALKANES AND ALKENES FACTS ABOUT
DIFFERENT? ALKANES! FACTS ABOUT
ALKENES ARE UNSATURATED ALKENES!
HYDROCARBONS. THEY CONTAIN A • any of a group of aliphatic
DOUBLE BOND, WHICH IS SHOWN hydrocarbons whose molecules • Alkenes contain contain at least
AS TWO LINES BETWEEN TWO OF contain only single bonds which is one double bond between the
THE CARBON ATOMS. THE the chemical bond. carbon atoms.
PRESENCE OF THIS DOUBLE BOND • said to have a continuous chain • Alkenes are unsaturated, as they
ALLOWS ALKENES TO REACT IN have spare bonds that they can
if each carbon atom in its
WAYS THAT ALKANES CANNOT. use. This is especially useful in
ALKANES PHYSICAL PROPERTIES molecule is joined to at most two
making polymers.
other carbon atoms
it is a saturated hydrocarbon and all of its • Alkenes decolourise bromine
• it is said to have a branched water.
bond is a complete covalent bond. chain if any of its carbon atoms is • Alkenes form polymers. This is
ALKANES CHEMICAL PROPERTIES joined to more than two other because their double bonds open
Alkanes is a covalent compound which carbon atoms up to join other monomers, but
has a relatively low boiling and melting • The first four continuous-chain this will be explained in more
alkanes are methane, CH4; ethane,
detail further down the article.
point. The more the carbon atom or the • Alkenes burn with a smoky
C2H6; propane, C3H8; and butane,
longer the chain in an alkane compound, flame. This means that is
C4H10
incomplete combustion, where
the higher its boiling and melting • alkanes with 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, and 10 not enough oxygen is getting to
point.The more the branches in the carbon atoms in their molecules the burning object, which means
are pentane, hexane, heptane, that it produces carbon dioxide,
carbon chain, the lower its boiling and
octane, nonane, and decane, carbon monoxide, water and
ALKANES &
melting point. carbon (soot).
ALKENES PHYSICAL PROPERTIES respectively
• Chemically, the alkanes are • The general formula for alkenes
The physical properties of alkenes are is CnH2n.
relatively unreactive
ALKENES
comparable with those of alkanes. The • They are obtained by fractional
physical state depends on molecular mass distillation from petroleum and
(gases from ethene to butene - liquids from are used extensively as fuels.
pentene onwards). The simplest alkenes, • sometimes referred to as the
HYDROCARBONS ARE COMPOUNDS MADE FROM
methane series (after the
ethene, propene and butene are gases. Linear CARBON AND HYDROGEN ATOMS JOINED BY
simplest alkane) or as paraffins. COVALENT BONDS.
alkenes of approximately five to sixteen • highly flammable compound at -ALKANES ARE SATURATED - THEY HAVE ONLY
carbons are liquids, and higher alkenes are high temperatures SINGLE BONDS. ALKENES HAVE A DOUBLE BOND
- THEY ARE UNSATURATED.
waxy solids. • it is a saturated hydrocarbon
ALKENES REACT WITH BROWN BROMINE WATER
ALKENES CHEMICAL PROPERTIES and all of its bond is a complete AND DECOLOURISE IT, BUT ALKANES DO NOT.
covalent bond. -ALKENES CAN ACT AS MONOMERS. UNDER HIGH
Combustion of Alkenes PRESSURE AND IN THE PRESENCE OF A
• Alkanes have lower acidity level
The alkenes are highly flammable and burn if you compare it with the acidity
CATALYST MANY MONOMER MOLECULES JOIN
TOGETHER TO MAKE POLYMER MOLECULES.
readily in air, forming carbon dioxide and level of alkenes. THESE POLYMER MOLECULES ARE SATURATED.
water
Alkene:
ETHENE (C2H4) AKA
ETHYLENE
Ethene is the smallest alkene and is a
colorless gas at room temperature. Unlike
its cousin ethane, ethane does have an odor
that is often described as “sweet and
musky.” It is sometimes called ethylene,
which is technically a misnomer, but is part
of common parlance and so remains.
USES
Ethene is a very important industrial
chemical. Its primary use is in the
production of polyethylene plastic, the
BUTANE BOTTLES ARE USED FOR A WIDE RANGE OF mostly widely-used plastic in the world.
DEVICES AND PURPOSES, INCLUDING: Polyethylene is used to make everything
• PORTABLE CAMPING STOVES from shopping bags to packing peanuts,
• OUTDOOR GRILLS lubricants, and even some detergents. More
Alkane: • PATIO HEATERS
• PORTABLE SPACE HEATERS
than half of all ethane is used to make
polyethylene
• CABINET HEATERS
Butane • CARAVAN AND MOTORHOME COOKING AND HEATING
• MOBILE CATERING
Oxidation of ethane produces various
components including ethylene glycol, the
Butane in either its refined primary ingredient in antifreeze.
• REFILLING LIGHTERS
form, n-butane, or its purer Halogenation of ethene produces a range of
WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF BUTANE? molecules such as ethyl chloride and
form, also known as ethylene dibromide. These molecules are
isobutane, is used in • Low Price
found in produces like polyvinyl chloride,
• Fast burn another widely used plastic. Finally,
industries such as plumbing,
• Ease of use alkylation of ethane (the addition of an
construction, culinary arts as alkyl group), is the first step in the
• Low toxicity
well as in jewelry making, production of styrene, which is used to
• Energy efficiency make the plastic polystyrene for insulation
glassmaking, welding, and
WHAT ARE THE BEST BUTANE BRANDS? and packaging. Ethene, without
other crafty ventures. modification, is also a plant hormone that
• Colibri
produces a number of different effects
• Newport
including ripening of fruit, pollination, leaf
• Power abscission (falling off), seed germination,
• Puretane and more.
• Vector
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Jets Quiz All QuestionsDocument70 pagesJets Quiz All QuestionsSamuel kalumba Lukwesa100% (7)
- Chemical Bonding Reading MaterialDocument6 pagesChemical Bonding Reading MaterialJohann Carlo C. AldecoaNo ratings yet
- Polysiloxane CoatingsDocument8 pagesPolysiloxane CoatingsminhnnNo ratings yet
- Ian Chow - Biology IA First DraftDocument3 pagesIan Chow - Biology IA First DraftIanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document7 pagesChapter 2Hina RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Extraction and Isolation of CaffeineDocument10 pagesExtraction and Isolation of CaffeineLucinda BricenoNo ratings yet
- High Strength ConcreteDocument6 pagesHigh Strength ConcreteOnline AdoroNo ratings yet
- SaprodgdeDocument6 pagesSaprodgdeA MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Academic Essay - ExampleDocument2 pagesAcademic Essay - ExampleEvi PartsalidiNo ratings yet
- Determination of Total Carbohydrates in Algal Biomass: Laboratory Analytical Procedure (LAP)Document17 pagesDetermination of Total Carbohydrates in Algal Biomass: Laboratory Analytical Procedure (LAP)MadhanNo ratings yet
- Pigments For Printing InksDocument49 pagesPigments For Printing Inksplast_adesh75% (4)
- Joc Noc Ssynthesis 1,3,5-TriazolesDocument3 pagesJoc Noc Ssynthesis 1,3,5-TriazolesYurelii ChiguiilsNo ratings yet
- 2010 Catholic High Chemistry PrelimDocument46 pages2010 Catholic High Chemistry PrelimSONo ratings yet
- Composite 1Document27 pagesComposite 1jenan h.albayatiiNo ratings yet
- Epithermal Quartz-Alunite Vein: Model 25e-ConDocument15 pagesEpithermal Quartz-Alunite Vein: Model 25e-ConmiguelNo ratings yet
- CSIR Test Series 2Document2 pagesCSIR Test Series 2Vasu MathuraNo ratings yet
- ICT Mumbai B.Chem - Engg SyllabusDocument41 pagesICT Mumbai B.Chem - Engg SyllabusAniruddha ShidhayeNo ratings yet
- Study of Talc Filled Polypropylene - A Concept For Improving Mechanical Properties of PolypropyleneDocument5 pagesStudy of Talc Filled Polypropylene - A Concept For Improving Mechanical Properties of PolypropyleneesatjournalsNo ratings yet
- A Literature Review On The Role of Zycotherm As An Additive Used in BitumenDocument7 pagesA Literature Review On The Role of Zycotherm As An Additive Used in BitumenEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- G8 MCQ Mid TermDocument17 pagesG8 MCQ Mid TermSaad Al Zayed JoyNo ratings yet
- Benzene WorksheetDocument7 pagesBenzene WorksheetTanzimNo ratings yet
- HISTOPATH-MODULE-4 NotesDocument7 pagesHISTOPATH-MODULE-4 NotesKaycee AyoNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: Only On @neetquestionpaperDocument14 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Only On @neetquestionpaperakenterprisesosmuzaffarpurNo ratings yet
- Non-Aqueous Titration: by Group MemberDocument10 pagesNon-Aqueous Titration: by Group MemberSiti AmirahNo ratings yet
- Sterilisation: - Define - List - Explain - Explain - Explai - Give - GiveDocument26 pagesSterilisation: - Define - List - Explain - Explain - Explai - Give - Givevalentine mhuteNo ratings yet
- Y09 PracticeDocument7 pagesY09 PracticeKissiedu YirenkyiNo ratings yet
- Material Balance PDFDocument31 pagesMaterial Balance PDFApril Joy HaroNo ratings yet
- Materials Today: Proceedings: M. Kalpana, S. MohithDocument3 pagesMaterials Today: Proceedings: M. Kalpana, S. MohithNurul muzayyanahNo ratings yet
- TDS - FlowcableDocument3 pagesTDS - FlowcableVenkata RaoNo ratings yet
- Biochem - Lec 05Document3 pagesBiochem - Lec 05Louis FortunatoNo ratings yet