Professional Documents
Culture Documents
End of Unit Assessment
End of Unit Assessment
Uploaded by
api-395807105Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- GCSE (9-1) Y9 Science Final Exam 15 - 16 With Mark SchemeDocument31 pagesGCSE (9-1) Y9 Science Final Exam 15 - 16 With Mark SchemePaul Burgess50% (4)
- Group 7 - Halogens: Introduction & DataDocument2 pagesGroup 7 - Halogens: Introduction & DataAJ Millard0% (1)
- Web - Asgn 2Document6 pagesWeb - Asgn 2Aadesh Bagalad0% (1)
- Amount of Substance 4: © WWW - CHEMSHEETS.co - Uk 08-April-2020 Chemsheets AS 1247 1Document4 pagesAmount of Substance 4: © WWW - CHEMSHEETS.co - Uk 08-April-2020 Chemsheets AS 1247 1Ahmad RazaNo ratings yet
- RatiosendoftopictestformaDocument14 pagesRatiosendoftopictestformaapi-261894355No ratings yet
- Functions Harder Questions MMEDocument6 pagesFunctions Harder Questions MMEEffNo ratings yet
- More Group 7Document2 pagesMore Group 7AaravNo ratings yet
- Elmwood ADocument3 pagesElmwood AShwan HasanNo ratings yet
- Transformations Questions MMEDocument11 pagesTransformations Questions MMETishefunmi Ogunmoye100% (1)
- 0654 w18 QP 41Document28 pages0654 w18 QP 41EYE RIZNo ratings yet
- Inequalities Questions MMEDocument7 pagesInequalities Questions MMELoka Pavani Senthil GaneshNo ratings yet
- 8 GR Math End-Of-Module-AssessmentDocument18 pages8 GR Math End-Of-Module-AssessmentNayem Hossain Hemu100% (1)
- Topical Test 8 PDFDocument5 pagesTopical Test 8 PDFHU LEE LEE MoeNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Transformations GCSE WorksheetDocument18 pagesThird Space Learning Transformations GCSE WorksheetTishefunmi Ogunmoye100% (1)
- Corresponding Angles and Alternate Angles Questions MMEDocument7 pagesCorresponding Angles and Alternate Angles Questions MMESpyHunterNo ratings yet
- Y7 End of Year Assessment - CalculatorDocument7 pagesY7 End of Year Assessment - CalculatorKateNo ratings yet
- GIDB6651327-Unit 1 Language Worksheet 1 Class - 1.1-1.3Document1 pageGIDB6651327-Unit 1 Language Worksheet 1 Class - 1.1-1.3Nixon GrahamNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Practice Final ExamDocument11 pagesMath 9 Practice Final ExamMic CalloNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Physics Unit 1 Higher Question June 12Document20 pagesAQA GCSE Physics Unit 1 Higher Question June 12John Flores0% (1)
- AQA GCSE Maths 8300 (1 9) Topic List - HigherDocument17 pagesAQA GCSE Maths 8300 (1 9) Topic List - Higherjuke1No ratings yet
- A Practice Set 1Document5 pagesA Practice Set 1aNo ratings yet
- Solving Equations Foundation Questions MMEDocument6 pagesSolving Equations Foundation Questions MMEZoheb RehanNo ratings yet
- NS5 and Org Liv Things Worksheet 1 4Document4 pagesNS5 and Org Liv Things Worksheet 1 4Anabel Sánchez RubiaNo ratings yet
- Fidel Castro Ruz Primary SchoolDocument5 pagesFidel Castro Ruz Primary SchoolEveline Naapopye NdakoloNo ratings yet
- Pressure and Moments MarkschemeDocument1 pagePressure and Moments Markscheme박찬우No ratings yet
- Waves TestDocument4 pagesWaves TestPhilip MooreNo ratings yet
- Corresponding Angles and Alternate Angles Questions MMEDocument7 pagesCorresponding Angles and Alternate Angles Questions MMEumar tariqNo ratings yet
- Unit1 PhotosynthesisDocument7 pagesUnit1 PhotosynthesisNeetha TelkarNo ratings yet
- Stage 8 End of Unit 16 TestDocument6 pagesStage 8 End of Unit 16 Testphuongchi300523No ratings yet
- Prim Maths 3 2ed TR Unit 7 TestDocument5 pagesPrim Maths 3 2ed TR Unit 7 TestSpoken WordNo ratings yet
- 2004 May Paper 2Document12 pages2004 May Paper 2Hubbak Khan100% (3)
- Circle Sectors and Arcs Questions MMEDocument8 pagesCircle Sectors and Arcs Questions MMEAhmed NallaNo ratings yet
- S8 - Worksheets - Unit 1Document19 pagesS8 - Worksheets - Unit 1lukescienceteacherNo ratings yet
- S8 Language Worksheets Unit 6Document4 pagesS8 Language Worksheets Unit 6lukescienceteacherNo ratings yet
- Unit Test Study Guide Waves Light and Sound2Document5 pagesUnit Test Study Guide Waves Light and Sound2Aiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- End of Unit 1 Test AnswersDocument1 pageEnd of Unit 1 Test AnswershidorarobloxNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3 ReflectionDocument2 pagesExercise 3 Reflectionnoddy_noddyNo ratings yet
- Aqa Private Candidate Guide PDFDocument52 pagesAqa Private Candidate Guide PDFhello2222222No ratings yet
- F2 Mathematics Foundation Ii Mathematics Assignment 4: © Cambrilearn - All Rights ReservedDocument12 pagesF2 Mathematics Foundation Ii Mathematics Assignment 4: © Cambrilearn - All Rights ReservedlunalovegoodsNo ratings yet
- Short Y9 Algebra TestDocument4 pagesShort Y9 Algebra Testjack shanhNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 RevisionDocument3 pagesUnit 2 Revisionl wanningNo ratings yet
- Food Tests Exam QsDocument8 pagesFood Tests Exam QsAleNo ratings yet
- Past Paper1Document8 pagesPast Paper1Ne''ma Khalid Said Al HinaiNo ratings yet
- T SC 2549639 Ks3 Biology Display Posters Ver 6Document6 pagesT SC 2549639 Ks3 Biology Display Posters Ver 6Dr Ahmed Reyad100% (1)
- Year 10 Foundation Progress Practice June 222458Document16 pagesYear 10 Foundation Progress Practice June 222458MohammedNo ratings yet
- FINAL 022014 Answer KeyDocument8 pagesFINAL 022014 Answer KeyDavidNo ratings yet
- Colours and Filters WorksheetsDocument14 pagesColours and Filters WorksheetsDominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- Congruent Shapes and Triangles Third Space Learning GCSE WorksheetDocument17 pagesCongruent Shapes and Triangles Third Space Learning GCSE WorksheetForam JivrajaniNo ratings yet
- Gcse Revision 8: Atomic Structure, Structure & Bonding, Formulae & EquationsDocument2 pagesGcse Revision 8: Atomic Structure, Structure & Bonding, Formulae & EquationsWill ShuteNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Higher Progress Practice June 222459Document50 pagesYear 10 Higher Progress Practice June 222459MohammedNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 End-Of-Unit TestDocument3 pagesUnit 3 End-Of-Unit TestshamaperveenasNo ratings yet
- 0500 Example Candidate Responses Paper2 2020Document31 pages0500 Example Candidate Responses Paper2 2020waihon.pang2011No ratings yet
- SL - MathDocument2 pagesSL - MathastargroupNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade 9 June Paper (0001) Memo: Time: 2H Total: 100 MarksDocument6 pagesMathematics Grade 9 June Paper (0001) Memo: Time: 2H Total: 100 Marksknhlanhla194No ratings yet
- 7 Grade SAU 3 TermDocument4 pages7 Grade SAU 3 TermMaralNo ratings yet
- Prim Maths 3 2ed TR Unit 5 TestDocument3 pagesPrim Maths 3 2ed TR Unit 5 TestSpoken WordNo ratings yet
- DLP Math 5 Q4Document5 pagesDLP Math 5 Q4Dynah Fe Laborte TamayoNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Unit 12 ProbabilityDocument3 pagesQuiz - Unit 12 ProbabilitySusie GreenNo ratings yet
- Math 6 - Q4 - Week8Document14 pagesMath 6 - Q4 - Week8Sab Gumilao GanoticeNo ratings yet
- (Module 13) MATH 8 AssessmentDocument5 pages(Module 13) MATH 8 AssessmentDenmark SantosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 5Document5 pagesLesson 4 5Louis Miguel LauritoNo ratings yet
- Asal Sayılar Matematikteki en Gizemli RakamlarDocument291 pagesAsal Sayılar Matematikteki en Gizemli RakamlarMaji ReyhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Industrial Robot ProgrammingDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Industrial Robot ProgrammingwreathbearerNo ratings yet
- Character Datatypes: Data Type Syntax Oracle 9i Oracle 10g Oracle 11g Explanation (If Applicable)Document4 pagesCharacter Datatypes: Data Type Syntax Oracle 9i Oracle 10g Oracle 11g Explanation (If Applicable)Pankaj ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Diversity and Inclusion Survey Analysis 19th SepDocument8 pagesDiversity and Inclusion Survey Analysis 19th SepIsmail ElghoulNo ratings yet
- Lempor Ejector Calculator Beta 1.1Document21 pagesLempor Ejector Calculator Beta 1.1cristian garciaNo ratings yet
- Epilysis QADocument6 pagesEpilysis QAsamisdr3946No ratings yet
- Trigonometry ExeDocument14 pagesTrigonometry Exevimal guptaNo ratings yet
- Derivation of The Inverse Hyperbolic Trig Functions: y Sinh XDocument4 pagesDerivation of The Inverse Hyperbolic Trig Functions: y Sinh XArt Anthony Zoilo MunioNo ratings yet
- Int F (Int N) (Static Int I 1 If (N 5) Return N N N+i I++ Return F (N) )Document9 pagesInt F (Int N) (Static Int I 1 If (N 5) Return N N N+i I++ Return F (N) )rathaiNo ratings yet
- CH 9Document8 pagesCH 9Maulik ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Developing Mathematical Proficiency: Susie GrovesDocument27 pagesDeveloping Mathematical Proficiency: Susie GrovesMoh. Rizal Khaqul YaqinNo ratings yet
- Convert The Measured Units Into Three Different Units of That QuantityDocument2 pagesConvert The Measured Units Into Three Different Units of That QuantityKushal SarkarNo ratings yet
- Priestey Et Al 2007 Diseño Por DesplazamientosDocument12 pagesPriestey Et Al 2007 Diseño Por DesplazamientosUlises MendozaNo ratings yet
- PHY 413 Note Set 7Document36 pagesPHY 413 Note Set 7Ramses Jerez NicurcarNo ratings yet
- 06 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 6Document6 pages06 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 6Supreme KingNo ratings yet
- "Es - Configure.H" "Es - Framework.H" "Audioboard.H" "Shiftregisterwrite.H" "Bitdefs.H" "Definitions.H"Document4 pages"Es - Configure.H" "Es - Framework.H" "Audioboard.H" "Shiftregisterwrite.H" "Bitdefs.H" "Definitions.H"api-340769184No ratings yet
- Gravitation AssignmentDocument3 pagesGravitation AssignmentShiva Ram Prasad PulagamNo ratings yet
- 17695-Article Text-53627-1-10-20170818Document7 pages17695-Article Text-53627-1-10-20170818khansyaNo ratings yet
- STQA Imp QuesDocument3 pagesSTQA Imp QuesAnubhav SinghNo ratings yet
- ME322 Heat TransferDocument2 pagesME322 Heat TransferRagesh DuduNo ratings yet
- Patterns For Young ChildrenDocument12 pagesPatterns For Young ChildrenNicole Carait100% (1)
- Universal Wavefunction - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesUniversal Wavefunction - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaafterragnarokNo ratings yet
- Ashrae-D-86527 1Document3 pagesAshrae-D-86527 1rsahaNo ratings yet
- Ground Loop Problems With Measurement Systems and How To Avoid ThemDocument77 pagesGround Loop Problems With Measurement Systems and How To Avoid ThemAlfredo CordovaNo ratings yet
- Opencv Introduction Highgui Basic Operations Face Detection Optical Flow Template Matching Local FeatureDocument21 pagesOpencv Introduction Highgui Basic Operations Face Detection Optical Flow Template Matching Local FeatureHarish ParuchuriNo ratings yet
- CFD Test 1Document1 pageCFD Test 1MuruganNo ratings yet
- Final Exam p2 6m 2013Document7 pagesFinal Exam p2 6m 2013Shazlin SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Statistics Mean, Median, ModeDocument36 pagesStatistics Mean, Median, Moderoshni100% (1)
- (Ferreira, 2009) Matlab Codes For Finite Element AnalysisDocument249 pages(Ferreira, 2009) Matlab Codes For Finite Element Analysisakıle neseNo ratings yet
End of Unit Assessment
End of Unit Assessment
Uploaded by
api-395807105Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
End of Unit Assessment
End of Unit Assessment
Uploaded by
api-395807105Copyright:
Available Formats
GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS BY
NAME DATE PERIOD
Unit 8: End-of-Unit Assessment
Do not use a calculator. A standard number cube has the numbers 1 through 6 on its faces.
1. Elena would like to know the average height of seventh graders in her school district. She measures
the heights of everyone in a random sample of 20 students. The mean height of Elena’s sample is 61
inches, and the MAD (mean absolute deviation) is 2 inches.
Select all the true statements.
A. The median height of the sample must be between 59 and 63 inches.
B. Another random sample of 20 students is likely to have a mean between 57 and 65 inches.
C. The mean height of these 20 students is likely to be the same as the mean height of all students
in the district.
D. The mean height of these 20 students is likely to be the same as the mean height of a second
random sample of 20 students.
E. Elena would be more likely to get an accurate estimate of the mean height of the population by
sampling 40 people instead of sampling 20 people.
Unit 8: Probability and Sampling Lesson G: End-of-Unit Assessment 1
GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS BY
NAME DATE PERIOD
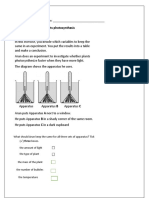
2. Below is a dot plot showing how much time customers spent in a store, rounded to the nearest five
minutes.
Which of the following is a representative sample of this population?
Unit 8: Probability and Sampling Lesson G: End-of-Unit Assessment 2
GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS BY
NAME DATE PERIOD
3. Diego predicts that his basketball team has a probability of winning each of their next 7 games.
Select all the ways Diego could accurately simulate the number of games his team will win.
A. Put the numbers 0 through 7 in a bag. Pick a number from the bag.
B. Roll a standard number cube 7 times. Count the number of twos.
C. Roll a standard number cube 7 times. Count the number of ones, twos, threes, and fours.
D. Mark a spinner with 12 equally sized sections. Write “win” on 4 of the sections. Spin the spinner 7
times and count the number of times it ends on “win.”
E. Put 10 white chips and 5 red chips in a bag. Draw a chip from the bag, record its result, and put it
back in the bag. Do this 7 times and count the total number of white chips drawn.
4. Lin is about to roll a standard number cube.
a. Describe an event that is likely to happen, but not certain, on the next roll.
b. Describe an event that is unlikely to happen, but not impossible, on the next roll.
c. Describe an event that is certain to happen on the next roll.
Unit 8: Probability and Sampling Lesson G: End-of-Unit Assessment 3
GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS BY
NAME DATE PERIOD
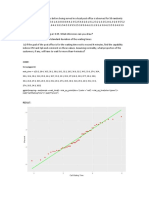
5. Two classes of students took an exam. Andre found this list of the 11 scores in Class A:
65, 70, 70, 80, 80, 85, 85, 85, 90, 90, 100
Andre’s teacher showed him this box plot of the 11 scores in Class B:
a. Which class had better overall results on the exam?
b. Which class had greater variability in the results?
6. A store owner asks each person to write “Yes” or “No” on a slip of paper as they leave, secretly writing
down whether they were happy with their experience. At the end of the day, the owner selects 12 slips
at random and looks at them. These were the results:
yes, yes, yes, no, yes, no, yes, yes, no, yes, no, yes
a. Estimate the proportion of all shoppers who were happy with their experience that day.
b. On a different day, the owner found that 25% of the 12 selected slips were marked “Yes.” Should
the store owner believe that these two results reasonably represent the overall proportion of
happy shoppers, or should the owner gather more data? Explain how you know.
Unit 8: Probability and Sampling Lesson G: End-of-Unit Assessment 4
GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS BY
NAME DATE PERIOD
7. A scientist wants to know if there is a meaningful difference between two groups of gels that grow
bacteria. He randomly selects five gels from each group, and counts the number of bacteria spots on
each gel:
Group A: 9, 12, 13, 14, 17
Group B: 6, 5, 8, 13, 8
Is there a meaningful difference between the two groups? Show all calculations that lead to your
answer.
Unit 8: Probability and Sampling Lesson G: End-of-Unit Assessment 5
You might also like
- GCSE (9-1) Y9 Science Final Exam 15 - 16 With Mark SchemeDocument31 pagesGCSE (9-1) Y9 Science Final Exam 15 - 16 With Mark SchemePaul Burgess50% (4)
- Group 7 - Halogens: Introduction & DataDocument2 pagesGroup 7 - Halogens: Introduction & DataAJ Millard0% (1)
- Web - Asgn 2Document6 pagesWeb - Asgn 2Aadesh Bagalad0% (1)
- Amount of Substance 4: © WWW - CHEMSHEETS.co - Uk 08-April-2020 Chemsheets AS 1247 1Document4 pagesAmount of Substance 4: © WWW - CHEMSHEETS.co - Uk 08-April-2020 Chemsheets AS 1247 1Ahmad RazaNo ratings yet
- RatiosendoftopictestformaDocument14 pagesRatiosendoftopictestformaapi-261894355No ratings yet
- Functions Harder Questions MMEDocument6 pagesFunctions Harder Questions MMEEffNo ratings yet
- More Group 7Document2 pagesMore Group 7AaravNo ratings yet
- Elmwood ADocument3 pagesElmwood AShwan HasanNo ratings yet
- Transformations Questions MMEDocument11 pagesTransformations Questions MMETishefunmi Ogunmoye100% (1)
- 0654 w18 QP 41Document28 pages0654 w18 QP 41EYE RIZNo ratings yet
- Inequalities Questions MMEDocument7 pagesInequalities Questions MMELoka Pavani Senthil GaneshNo ratings yet
- 8 GR Math End-Of-Module-AssessmentDocument18 pages8 GR Math End-Of-Module-AssessmentNayem Hossain Hemu100% (1)
- Topical Test 8 PDFDocument5 pagesTopical Test 8 PDFHU LEE LEE MoeNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Transformations GCSE WorksheetDocument18 pagesThird Space Learning Transformations GCSE WorksheetTishefunmi Ogunmoye100% (1)
- Corresponding Angles and Alternate Angles Questions MMEDocument7 pagesCorresponding Angles and Alternate Angles Questions MMESpyHunterNo ratings yet
- Y7 End of Year Assessment - CalculatorDocument7 pagesY7 End of Year Assessment - CalculatorKateNo ratings yet
- GIDB6651327-Unit 1 Language Worksheet 1 Class - 1.1-1.3Document1 pageGIDB6651327-Unit 1 Language Worksheet 1 Class - 1.1-1.3Nixon GrahamNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Practice Final ExamDocument11 pagesMath 9 Practice Final ExamMic CalloNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Physics Unit 1 Higher Question June 12Document20 pagesAQA GCSE Physics Unit 1 Higher Question June 12John Flores0% (1)
- AQA GCSE Maths 8300 (1 9) Topic List - HigherDocument17 pagesAQA GCSE Maths 8300 (1 9) Topic List - Higherjuke1No ratings yet
- A Practice Set 1Document5 pagesA Practice Set 1aNo ratings yet
- Solving Equations Foundation Questions MMEDocument6 pagesSolving Equations Foundation Questions MMEZoheb RehanNo ratings yet
- NS5 and Org Liv Things Worksheet 1 4Document4 pagesNS5 and Org Liv Things Worksheet 1 4Anabel Sánchez RubiaNo ratings yet
- Fidel Castro Ruz Primary SchoolDocument5 pagesFidel Castro Ruz Primary SchoolEveline Naapopye NdakoloNo ratings yet
- Pressure and Moments MarkschemeDocument1 pagePressure and Moments Markscheme박찬우No ratings yet
- Waves TestDocument4 pagesWaves TestPhilip MooreNo ratings yet
- Corresponding Angles and Alternate Angles Questions MMEDocument7 pagesCorresponding Angles and Alternate Angles Questions MMEumar tariqNo ratings yet
- Unit1 PhotosynthesisDocument7 pagesUnit1 PhotosynthesisNeetha TelkarNo ratings yet
- Stage 8 End of Unit 16 TestDocument6 pagesStage 8 End of Unit 16 Testphuongchi300523No ratings yet
- Prim Maths 3 2ed TR Unit 7 TestDocument5 pagesPrim Maths 3 2ed TR Unit 7 TestSpoken WordNo ratings yet
- 2004 May Paper 2Document12 pages2004 May Paper 2Hubbak Khan100% (3)
- Circle Sectors and Arcs Questions MMEDocument8 pagesCircle Sectors and Arcs Questions MMEAhmed NallaNo ratings yet
- S8 - Worksheets - Unit 1Document19 pagesS8 - Worksheets - Unit 1lukescienceteacherNo ratings yet
- S8 Language Worksheets Unit 6Document4 pagesS8 Language Worksheets Unit 6lukescienceteacherNo ratings yet
- Unit Test Study Guide Waves Light and Sound2Document5 pagesUnit Test Study Guide Waves Light and Sound2Aiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- End of Unit 1 Test AnswersDocument1 pageEnd of Unit 1 Test AnswershidorarobloxNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3 ReflectionDocument2 pagesExercise 3 Reflectionnoddy_noddyNo ratings yet
- Aqa Private Candidate Guide PDFDocument52 pagesAqa Private Candidate Guide PDFhello2222222No ratings yet
- F2 Mathematics Foundation Ii Mathematics Assignment 4: © Cambrilearn - All Rights ReservedDocument12 pagesF2 Mathematics Foundation Ii Mathematics Assignment 4: © Cambrilearn - All Rights ReservedlunalovegoodsNo ratings yet
- Short Y9 Algebra TestDocument4 pagesShort Y9 Algebra Testjack shanhNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 RevisionDocument3 pagesUnit 2 Revisionl wanningNo ratings yet
- Food Tests Exam QsDocument8 pagesFood Tests Exam QsAleNo ratings yet
- Past Paper1Document8 pagesPast Paper1Ne''ma Khalid Said Al HinaiNo ratings yet
- T SC 2549639 Ks3 Biology Display Posters Ver 6Document6 pagesT SC 2549639 Ks3 Biology Display Posters Ver 6Dr Ahmed Reyad100% (1)
- Year 10 Foundation Progress Practice June 222458Document16 pagesYear 10 Foundation Progress Practice June 222458MohammedNo ratings yet
- FINAL 022014 Answer KeyDocument8 pagesFINAL 022014 Answer KeyDavidNo ratings yet
- Colours and Filters WorksheetsDocument14 pagesColours and Filters WorksheetsDominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- Congruent Shapes and Triangles Third Space Learning GCSE WorksheetDocument17 pagesCongruent Shapes and Triangles Third Space Learning GCSE WorksheetForam JivrajaniNo ratings yet
- Gcse Revision 8: Atomic Structure, Structure & Bonding, Formulae & EquationsDocument2 pagesGcse Revision 8: Atomic Structure, Structure & Bonding, Formulae & EquationsWill ShuteNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Higher Progress Practice June 222459Document50 pagesYear 10 Higher Progress Practice June 222459MohammedNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 End-Of-Unit TestDocument3 pagesUnit 3 End-Of-Unit TestshamaperveenasNo ratings yet
- 0500 Example Candidate Responses Paper2 2020Document31 pages0500 Example Candidate Responses Paper2 2020waihon.pang2011No ratings yet
- SL - MathDocument2 pagesSL - MathastargroupNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade 9 June Paper (0001) Memo: Time: 2H Total: 100 MarksDocument6 pagesMathematics Grade 9 June Paper (0001) Memo: Time: 2H Total: 100 Marksknhlanhla194No ratings yet
- 7 Grade SAU 3 TermDocument4 pages7 Grade SAU 3 TermMaralNo ratings yet
- Prim Maths 3 2ed TR Unit 5 TestDocument3 pagesPrim Maths 3 2ed TR Unit 5 TestSpoken WordNo ratings yet
- DLP Math 5 Q4Document5 pagesDLP Math 5 Q4Dynah Fe Laborte TamayoNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Unit 12 ProbabilityDocument3 pagesQuiz - Unit 12 ProbabilitySusie GreenNo ratings yet
- Math 6 - Q4 - Week8Document14 pagesMath 6 - Q4 - Week8Sab Gumilao GanoticeNo ratings yet
- (Module 13) MATH 8 AssessmentDocument5 pages(Module 13) MATH 8 AssessmentDenmark SantosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 5Document5 pagesLesson 4 5Louis Miguel LauritoNo ratings yet
- Asal Sayılar Matematikteki en Gizemli RakamlarDocument291 pagesAsal Sayılar Matematikteki en Gizemli RakamlarMaji ReyhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Industrial Robot ProgrammingDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Industrial Robot ProgrammingwreathbearerNo ratings yet
- Character Datatypes: Data Type Syntax Oracle 9i Oracle 10g Oracle 11g Explanation (If Applicable)Document4 pagesCharacter Datatypes: Data Type Syntax Oracle 9i Oracle 10g Oracle 11g Explanation (If Applicable)Pankaj ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Diversity and Inclusion Survey Analysis 19th SepDocument8 pagesDiversity and Inclusion Survey Analysis 19th SepIsmail ElghoulNo ratings yet
- Lempor Ejector Calculator Beta 1.1Document21 pagesLempor Ejector Calculator Beta 1.1cristian garciaNo ratings yet
- Epilysis QADocument6 pagesEpilysis QAsamisdr3946No ratings yet
- Trigonometry ExeDocument14 pagesTrigonometry Exevimal guptaNo ratings yet
- Derivation of The Inverse Hyperbolic Trig Functions: y Sinh XDocument4 pagesDerivation of The Inverse Hyperbolic Trig Functions: y Sinh XArt Anthony Zoilo MunioNo ratings yet
- Int F (Int N) (Static Int I 1 If (N 5) Return N N N+i I++ Return F (N) )Document9 pagesInt F (Int N) (Static Int I 1 If (N 5) Return N N N+i I++ Return F (N) )rathaiNo ratings yet
- CH 9Document8 pagesCH 9Maulik ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Developing Mathematical Proficiency: Susie GrovesDocument27 pagesDeveloping Mathematical Proficiency: Susie GrovesMoh. Rizal Khaqul YaqinNo ratings yet
- Convert The Measured Units Into Three Different Units of That QuantityDocument2 pagesConvert The Measured Units Into Three Different Units of That QuantityKushal SarkarNo ratings yet
- Priestey Et Al 2007 Diseño Por DesplazamientosDocument12 pagesPriestey Et Al 2007 Diseño Por DesplazamientosUlises MendozaNo ratings yet
- PHY 413 Note Set 7Document36 pagesPHY 413 Note Set 7Ramses Jerez NicurcarNo ratings yet
- 06 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 6Document6 pages06 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 6Supreme KingNo ratings yet
- "Es - Configure.H" "Es - Framework.H" "Audioboard.H" "Shiftregisterwrite.H" "Bitdefs.H" "Definitions.H"Document4 pages"Es - Configure.H" "Es - Framework.H" "Audioboard.H" "Shiftregisterwrite.H" "Bitdefs.H" "Definitions.H"api-340769184No ratings yet
- Gravitation AssignmentDocument3 pagesGravitation AssignmentShiva Ram Prasad PulagamNo ratings yet
- 17695-Article Text-53627-1-10-20170818Document7 pages17695-Article Text-53627-1-10-20170818khansyaNo ratings yet
- STQA Imp QuesDocument3 pagesSTQA Imp QuesAnubhav SinghNo ratings yet
- ME322 Heat TransferDocument2 pagesME322 Heat TransferRagesh DuduNo ratings yet
- Patterns For Young ChildrenDocument12 pagesPatterns For Young ChildrenNicole Carait100% (1)
- Universal Wavefunction - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesUniversal Wavefunction - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaafterragnarokNo ratings yet
- Ashrae-D-86527 1Document3 pagesAshrae-D-86527 1rsahaNo ratings yet
- Ground Loop Problems With Measurement Systems and How To Avoid ThemDocument77 pagesGround Loop Problems With Measurement Systems and How To Avoid ThemAlfredo CordovaNo ratings yet
- Opencv Introduction Highgui Basic Operations Face Detection Optical Flow Template Matching Local FeatureDocument21 pagesOpencv Introduction Highgui Basic Operations Face Detection Optical Flow Template Matching Local FeatureHarish ParuchuriNo ratings yet
- CFD Test 1Document1 pageCFD Test 1MuruganNo ratings yet
- Final Exam p2 6m 2013Document7 pagesFinal Exam p2 6m 2013Shazlin SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Statistics Mean, Median, ModeDocument36 pagesStatistics Mean, Median, Moderoshni100% (1)
- (Ferreira, 2009) Matlab Codes For Finite Element AnalysisDocument249 pages(Ferreira, 2009) Matlab Codes For Finite Element Analysisakıle neseNo ratings yet