Professional Documents
Culture Documents
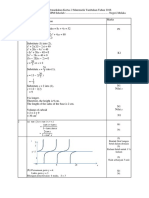
1.) 2 1 LN (Lim 1M
1.) 2 1 LN (Lim 1M
Uploaded by
ym5c2324Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1.) 2 1 LN (Lim 1M
1.) 2 1 LN (Lim 1M
Uploaded by
ym5c2324Copyright:
Available Formats
1.
1
ln(1 2 x)
lim lim ln(1 2 x) x
x 0 x x 0
1
1M
ln[ lim (1 2 x) 2 x ]2
x 0
1 1
ln[ lim (1 y ) ] y 2
[ Take y 2 x]
y 0
ln e 2
2
1
2.
Let P(n) be ‘ an 3n n 1’.
When n 1 , a1 31 1 1 3 1
P(1) is true.
Assume that P(k) is true, where k is a positive integer.
i.e. ak 3k k 1 1M+1
then ak 1 3ak 2k 3
3(3k k 1) 2k 3
3k 1 3k 3 2k 3
3k 1 k
1
3k 1 (k 1) 1
P(k 1) is true.
According to mathematical induction, P(n) is true for all positive integers n. 1
You might also like
- Master's TheoremDocument4 pagesMaster's TheoremyashdhingraNo ratings yet
- Spot Exchange Markets. Quiz QuestionsDocument14 pagesSpot Exchange Markets. Quiz Questionsym5c2324100% (1)
- Chap013 PDFDocument35 pagesChap013 PDFym5c2324No ratings yet
- PureMaths1973 Pastpaper P2Document2 pagesPureMaths1973 Pastpaper P2wltfNo ratings yet
- Q1 Soln MoodleDocument2 pagesQ1 Soln MoodleSatyamSahuNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2: Convolution: EG1110 Signals and SystemsDocument5 pagesExercise 2: Convolution: EG1110 Signals and Systemssrinvas_107796724No ratings yet
- W-13 Solving The Linear Equation Systems by Iteration MethodDocument24 pagesW-13 Solving The Linear Equation Systems by Iteration Methodumuhuza salomonNo ratings yet
- A Banach Space With A Symmetric Basis Which Is of Weak Cotype 2 But Not of Cotype 2Document17 pagesA Banach Space With A Symmetric Basis Which Is of Weak Cotype 2 But Not of Cotype 2Rakesh KhannaNo ratings yet
- The Solution of Legendre Equation Use PoDocument12 pagesThe Solution of Legendre Equation Use PoErnesto RiveraNo ratings yet
- Solutions - Principle of Mathematical Induction: Exercise # IDocument12 pagesSolutions - Principle of Mathematical Induction: Exercise # Inucleus unacademyNo ratings yet
- Math4575 - HW3Document6 pagesMath4575 - HW3jun zhaoNo ratings yet
- Modified Patankar-Runge-Kutta Schemes For The Solution Be PositiveDocument59 pagesModified Patankar-Runge-Kutta Schemes For The Solution Be PositiveBechara SaadeNo ratings yet
- 3P0 Wave Function PDFDocument30 pages3P0 Wave Function PDFMario SánchezNo ratings yet
- MT Melaka 2016 K2 ADocument10 pagesMT Melaka 2016 K2 AyenLee IOIINo ratings yet
- 2020 JC 2 H2 Math Consolidation Test II (Solutions)Document13 pages2020 JC 2 H2 Math Consolidation Test II (Solutions)Timothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Some Pascal-Like Triangles: N K K Elements WhichDocument14 pagesSome Pascal-Like Triangles: N K K Elements Whichakbar khanNo ratings yet
- Problem4 03Document2 pagesProblem4 03Fábio TakahashiNo ratings yet
- Tangent and Normal Mono - 30 Series SolDocument6 pagesTangent and Normal Mono - 30 Series SolAmiya Kumar DasNo ratings yet
- FFT (Fast Fourier Transform)Document20 pagesFFT (Fast Fourier Transform)Hemant Sudhir WavhalNo ratings yet
- Quadratic FormsDocument5 pagesQuadratic FormsMajety S LskshmiNo ratings yet
- Estimation For The Discretely Observed Cox-IngersoDocument14 pagesEstimation For The Discretely Observed Cox-IngersoLý Nguyễn Kỳ DuyênNo ratings yet
- Solutions Assignment-IiDocument5 pagesSolutions Assignment-IiARUOS SouraNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Techniques Assignment Solutions-3Document1 pageDifferentiation Techniques Assignment Solutions-3lbwnb.68868No ratings yet
- Find The N Differential Co-Efficient of The Following: MAT-101 Engineering Mathematics 1 Differential Calculus Notes 3Document12 pagesFind The N Differential Co-Efficient of The Following: MAT-101 Engineering Mathematics 1 Differential Calculus Notes 3Torcoxk NamgayNo ratings yet
- Hinyu Pm07p1sDocument20 pagesHinyu Pm07p1sapi-19834738No ratings yet
- Strong Mathematical Induction: (Proving, Validation and Verification, ETC.)Document14 pagesStrong Mathematical Induction: (Proving, Validation and Verification, ETC.)feelNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7Document4 pagesLesson 7Raheel RazzaqNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Department HKUGA College: Marking SchemeDocument7 pagesMathematics Department HKUGA College: Marking SchemeLok Hang LiNo ratings yet
- Exercises in Calculus 2Document2 pagesExercises in Calculus 2ნიკა ქურდაძეNo ratings yet
- D1 Limit of SequenceDocument14 pagesD1 Limit of Sequencescu.2022521460138No ratings yet
- EE120notesFa15 PDFDocument143 pagesEE120notesFa15 PDFnaibaf naibafNo ratings yet
- Mathematical InductionDocument17 pagesMathematical Inductionmita sari halawaNo ratings yet
- Ce 601 Num Meth Lecture 5Document18 pagesCe 601 Num Meth Lecture 5Worl BossNo ratings yet
- 1 Deterministic Quicksort: Notes Cs:5360 Randomized AlgorithmsDocument5 pages1 Deterministic Quicksort: Notes Cs:5360 Randomized AlgorithmsMirza AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Beta and Gamma FunctionDocument18 pagesBeta and Gamma FunctionPratik RaiNo ratings yet
- 2010 NJC MA H2 P1 Prelim SolnDocument30 pages2010 NJC MA H2 P1 Prelim SolnloposhNo ratings yet
- 2010 NJC MA H2 P1 Prelim SolnDocument30 pages2010 NJC MA H2 P1 Prelim SolnloposhNo ratings yet
- RandomDocument6 pagesRandomTytus MetryckiNo ratings yet
- Promo08 JJC H2 (Soln)Document10 pagesPromo08 JJC H2 (Soln)toh tim lamNo ratings yet
- Sequences (Ch.11)Document20 pagesSequences (Ch.11)wiswisnuNo ratings yet
- Sullivan 8Document6 pagesSullivan 8Satyaki BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- 2018 H2 JC1 MSM Differential Equations (Solutions)Document31 pages2018 H2 JC1 MSM Differential Equations (Solutions)VincentNo ratings yet
- 2008 2009 1 (Q+S)Document18 pages2008 2009 1 (Q+S)marwanNo ratings yet
- DSP Tutorial-1Document14 pagesDSP Tutorial-1ARUOS SouraNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1-SolutionsDocument5 pagesAssignment 1-SolutionsKaveendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Solution To The American Mathematical Monthly Problem 11989Document3 pagesSolution To The American Mathematical Monthly Problem 11989vka kudryaNo ratings yet
- ECE 301: Signals and Systems Homework Assignment #3: Professor: Aly El Gamal TA: Xianglun MaoDocument9 pagesECE 301: Signals and Systems Homework Assignment #3: Professor: Aly El Gamal TA: Xianglun Maolakshitha srimalNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Concepts of Analytic GeometryDocument11 pagesFundamental Concepts of Analytic GeometryShela RamosNo ratings yet
- Pe 588Document25 pagesPe 588sakyalolNo ratings yet
- 2021 S5 1 Exam (M2) - E SolutionDocument12 pages2021 S5 1 Exam (M2) - E SolutionAnderson LamNo ratings yet
- Solution SetDocument300 pagesSolution Setqwerty12311No ratings yet
- Legendre Polynomials PDFDocument19 pagesLegendre Polynomials PDFBappy K M BNo ratings yet
- JEE - Advance 1998-2021 - QAS PDFDocument463 pagesJEE - Advance 1998-2021 - QAS PDFArab XNo ratings yet
- Solution 3Document13 pagesSolution 3miss4200missNo ratings yet
- National Junior College 2014 - 2015 H2 Mathematics Sequences and Series Assignment SolutionsDocument3 pagesNational Junior College 2014 - 2015 H2 Mathematics Sequences and Series Assignment SolutionsYu XuanNo ratings yet
- Maths - 24-Jan-23 - Shift 1Document20 pagesMaths - 24-Jan-23 - Shift 1Uju surtNo ratings yet
- PCA Dr. Pawan Kumar TiwariDocument19 pagesPCA Dr. Pawan Kumar TiwariRudrakshitaNo ratings yet
- AnsSec3 7Document2 pagesAnsSec3 7Reginald AshongNo ratings yet
- OutputDocument5 pagesOutputnilufarkomiljonovna21No ratings yet
- Mathematical Association of AmericaDocument9 pagesMathematical Association of AmericathonguyenNo ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Pure Math Past AnswerDocument11 pagesPure Math Past Answerym5c2324No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 PPP and Fisher EffectDocument6 pagesChapter 7 PPP and Fisher Effectym5c2324No ratings yet
- S6 06-07 YearlyDocument13 pagesS6 06-07 Yearlyym5c2324No ratings yet
- Matrices and Determinants 1Document5 pagesMatrices and Determinants 1ym5c2324No ratings yet
- CM CMDocument1 pageCM CMym5c2324No ratings yet
- Hw1 2016Document5 pagesHw1 2016ym5c23240% (2)
- SolutionsDocument16 pagesSolutionsym5c2324No ratings yet
- Integration ExDocument1 pageIntegration Exym5c2324No ratings yet
- Question 1 (Section B) : 18-19/F.6/Quiz/P.1 of 1Document1 pageQuestion 1 (Section B) : 18-19/F.6/Quiz/P.1 of 1ym5c2324No ratings yet
- FalseDocument2 pagesFalseym5c2324No ratings yet
- Question 2 (Section B) : 18-19/F.6/Quiz/P.1 of 1Document1 pageQuestion 2 (Section B) : 18-19/F.6/Quiz/P.1 of 1ym5c2324No ratings yet
- Mathematics Extended Part Module 2 True Multiple Choice Test Student NameDocument2 pagesMathematics Extended Part Module 2 True Multiple Choice Test Student Nameym5c2324No ratings yet
- QB M2 E03Document46 pagesQB M2 E03ym5c2324100% (1)
- 52 CM 25 CM: D and ADCDocument1 page52 CM 25 CM: D and ADCym5c2324No ratings yet
- 3D TrigoDocument1 page3D Trigoym5c2324No ratings yet
- C of Radius R CM Touches The Larger Circle CDocument1 pageC of Radius R CM Touches The Larger Circle Cym5c2324No ratings yet
- S5 09-10 Paper I Mock ExamDocument20 pagesS5 09-10 Paper I Mock Examym5c2324No ratings yet
- AOC at ODocument1 pageAOC at Oym5c2324No ratings yet
- Formulas For ReferenceDocument1 pageFormulas For Referenceym5c2324No ratings yet
- Answers: 20 1 6 Mock Paper (Extended Part) - Module 1 (Answers)Document2 pagesAnswers: 20 1 6 Mock Paper (Extended Part) - Module 1 (Answers)ym5c2324No ratings yet
- M2 Mock 2016 AnswerDocument3 pagesM2 Mock 2016 Answerym5c2324No ratings yet
- Hkep M2-10Document24 pagesHkep M2-10ym5c2324No ratings yet
- SequenceDocument1 pageSequenceym5c2324No ratings yet
- S5 09-10 Paper I Mock Exam SolutionDocument16 pagesS5 09-10 Paper I Mock Exam Solutionym5c2324No ratings yet
- DocxDocument1 pageDocxym5c2324No ratings yet
- QB M2 E02Document40 pagesQB M2 E02ym5c23240% (1)
- QB M2 E06Document75 pagesQB M2 E06ym5c2324No ratings yet
- DocxDocument1 pageDocxym5c2324No ratings yet