Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 viewsElectricity
Electricity
Uploaded by
Billy James St JohnThe document discusses several physics formulas related to electricity, energy, forces, motion, and waves. It includes equations for:
1) Power (P) equals voltage (V) multiplied by current (I).
2) Voltage equals current multiplied by resistance.
3) Charge equals current multiplied by time.
4) Energy equals voltage multiplied by charge.
5) Energy equals voltage multiplied by current multiplied by time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Igcse Physics All FormulasDocument4 pagesIgcse Physics All FormulasRichie Harvy82% (17)
- Physics-5054-All Definitions&Formulae-RevisedSyllabusDocument8 pagesPhysics-5054-All Definitions&Formulae-RevisedSyllabusSaira Kamran100% (1)
- High School Physics Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesHigh School Physics Cheat SheetM J Rhoades50% (4)
- Harmonic Analysis of p.1 of 'Im Wunderschönen Monat Mai'-2 PDFDocument1 pageHarmonic Analysis of p.1 of 'Im Wunderschönen Monat Mai'-2 PDFBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- AQA Physics Equation Sheet Triple Oct 19Document3 pagesAQA Physics Equation Sheet Triple Oct 19Ricky JacobNo ratings yet
- Bmat Physics Formula Sheet InverseDocument2 pagesBmat Physics Formula Sheet Inverseeneagu3349No ratings yet
- O Level Physics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesO Level Physics Formula SheetYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- iGCSE Physics Formula Sheet: MotionDocument4 pagesiGCSE Physics Formula Sheet: MotionCamille67% (3)
- IGCSE Physics FormulasDocument1 pageIGCSE Physics FormulasPawan Kolhe80% (30)
- Beethoven Symphony No. 5, Mvt. 1 - DevelopmentDocument8 pagesBeethoven Symphony No. 5, Mvt. 1 - DevelopmentBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Formula PHYSISCS IGCSEDocument2 pagesFormula PHYSISCS IGCSEAnita LopesNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument7 pagesPhysics FormulasCryptazNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument2 pagesPhysics FormulasBOT NigmaNo ratings yet
- Formuals 2Document1 pageFormuals 2Miranda YeungNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics EquationsDocument2 pagesIGCSE Physics EquationsMisterBlueSkyNo ratings yet
- A Level FormulaeDocument1 pageA Level FormulaeVarun PanickerNo ratings yet
- Physics equations sheet: W=mg W=Fs F=ke s=vt a = Δ v t F=ma p=mv Ek = 1 m v 2 Ep=mgh P = E T P = W tDocument2 pagesPhysics equations sheet: W=mg W=Fs F=ke s=vt a = Δ v t F=ma p=mv Ek = 1 m v 2 Ep=mgh P = E T P = W tUtkarsh IngleNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Physics IGCSE EquationsDocument1 pageEdexcel Physics IGCSE EquationsNik JonesNo ratings yet
- AS Level Equations For PhysicsDocument1 pageAS Level Equations For PhysicsAhmad MohdNo ratings yet
- AS Physics EquationsDocument1 pageAS Physics EquationsAhmad MohdNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 1 Edexcel Physics GCSEDocument3 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 1 Edexcel Physics GCSEAli AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Al PhysicsformulaeDocument2 pagesAl PhysicsformulaeMichael ScofieldNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 - Foundation Tier EquationsDocument6 pagesPhysics 1 - Foundation Tier EquationsFayzan AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1.0.8 FORMULA FOR DERIVED UNITSDocument1 page1.0.8 FORMULA FOR DERIVED UNITSmintahroland6No ratings yet
- Formulae To Study For IGCSEDocument2 pagesFormulae To Study For IGCSE2144639220No ratings yet
- Physics Formula Y9Document5 pagesPhysics Formula Y9Lim MonyratanakNo ratings yet
- Physics Equation Sheet (8464) InsertDocument2 pagesPhysics Equation Sheet (8464) Inserttzvkpbjg2yNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Formula SheetDocument1 pagePhysical Science Formula SheetglezamaeNo ratings yet
- All GCSE Physics Equations (Editable)Document3 pagesAll GCSE Physics Equations (Editable)will hayNo ratings yet
- Physics Equation SheetDocument2 pagesPhysics Equation SheetEshanB786No ratings yet
- IGCSE Formula BookletDocument4 pagesIGCSE Formula BookletNisalNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesPhysics Formula Sheetboygafadi59No ratings yet
- Physics Equation Sheet AQA 2023Document2 pagesPhysics Equation Sheet AQA 2023HazzaYT HicksNo ratings yet
- Facts and Formulas 3 RefDocument13 pagesFacts and Formulas 3 Refrania deifNo ratings yet
- iGCSE Physics Formula Sheet: MotionDocument4 pagesiGCSE Physics Formula Sheet: MotionYusuf100% (3)
- Igcse Physics All FormulasDocument4 pagesIgcse Physics All FormulasABDULLAHNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument1 pagePhysics FormulaskimblesdjNo ratings yet
- Physics Review PapersDocument18 pagesPhysics Review Papersyoonmimikyaw2008No ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics FormulaeDocument3 pagesIGCSE Physics FormulaeTanushree TapariaNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument1 pagePhysics FormulasZahid MohammadNo ratings yet
- Work Energy PowerDocument10 pagesWork Energy PowerMarvin AndradeNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument2 pagesPhysics FormulasSzraxNo ratings yet
- Physics Igcse All Imp FormulasDocument4 pagesPhysics Igcse All Imp FormulasDhruvil Desai100% (1)
- A Level FormulaeDocument2 pagesA Level FormulaeAlim EchaNo ratings yet
- Rules PhysicsDocument1 pageRules PhysicsMarwan AmirNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Mekaniks: English Swedish Symbol Units Units-Name ValueDocument10 pagesMechanics Mekaniks: English Swedish Symbol Units Units-Name ValueEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Gravitational Potential EnergyDocument2 pagesGravitational Potential EnergyHarry WangNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument2 pagesPhysics FormulasSuchetana DasNo ratings yet
- Physics Reference PDFDocument12 pagesPhysics Reference PDFRonald Chester LorenzanaNo ratings yet
- Bmat Physics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesBmat Physics Formula SheetDrAIyer90% (10)
- Physics FormulasDocument6 pagesPhysics FormulastalalrazerNo ratings yet
- Fizix FormulasDocument1 pageFizix FormulasUjjwal JainNo ratings yet
- Formula ChartDocument1 pageFormula Chartapi-87739323No ratings yet
- Paper 2 Formula Sheet 1Document1 pagePaper 2 Formula Sheet 1mochiNo ratings yet
- Work Power and EnergyDocument51 pagesWork Power and EnergyJohn Carlo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- 9203 2 INS InternationalPhysics G 16nov20!07!00 GMTDocument4 pages9203 2 INS InternationalPhysics G 16nov20!07!00 GMT王涛No ratings yet
- Work, Energy, & Power: Chapter 6 (C&J) Chapter 10 (Glencoe)Document29 pagesWork, Energy, & Power: Chapter 6 (C&J) Chapter 10 (Glencoe)Emieleah Lorenzo PauigNo ratings yet
- A Level Work Energy PowerDocument17 pagesA Level Work Energy PowerHuurun AinNo ratings yet
- Energy Work and PowerDocument35 pagesEnergy Work and PowerFabian ClarkeNo ratings yet
- MinorScalesExplanationandWorksheets 1Document49 pagesMinorScalesExplanationandWorksheets 1Billy James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Challenging Middle YearsDocument7 pagesChallenging Middle YearsBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Singing - Survey - FINAL - With CoverDocument61 pagesSinging - Survey - FINAL - With CoverBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Blue MoonDocument1 pageBlue MoonBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- 2022 Sem1 Studyplanner A3Document1 page2022 Sem1 Studyplanner A3Billy James St JohnNo ratings yet
- E737 2022 T2 Coursemap Option 2 Research PaperDocument3 pagesE737 2022 T2 Coursemap Option 2 Research PaperBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Deakin University Professional Experience Timetable MALT 2022Document1 pageDeakin University Professional Experience Timetable MALT 2022Billy James St JohnNo ratings yet
- John Cage - Experimental MusicDocument1 pageJohn Cage - Experimental MusicBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Composition AssignmentDocument2 pagesComposition AssignmentBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Michael Nyman - Experimental MusicDocument1 pageMichael Nyman - Experimental MusicBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- DFDSDDocument1 pageDFDSDBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Another Helpful Hint in My Tips and Tricks' SessionsDocument7 pagesWelcome To Another Helpful Hint in My Tips and Tricks' SessionsBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- 2020 O & R Cover Sheet PDFDocument1 page2020 O & R Cover Sheet PDFBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Simon Bolivar's Vision For South American Unity vs. Today's RealityDocument3 pagesSimon Bolivar's Vision For South American Unity vs. Today's RealityBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Lange2010 Article TheHistoryOfAttentionDeficitHy PDFDocument15 pagesLange2010 Article TheHistoryOfAttentionDeficitHy PDFBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Embellishing Notes SummaryDocument1 pageEmbellishing Notes SummaryBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- A Music Therapy Approach in Mental HealthDocument10 pagesA Music Therapy Approach in Mental HealthBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- 2019 Book VenezuelaALBAAndTheLimitsOfPosDocument226 pages2019 Book VenezuelaALBAAndTheLimitsOfPosBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- 10 1 1 738 5935Document6 pages10 1 1 738 5935Billy James St JohnNo ratings yet
- T.R.A.F.I.C. Model - 6 Cultural Tendencies: Hello MR Smith Hello John!Document1 pageT.R.A.F.I.C. Model - 6 Cultural Tendencies: Hello MR Smith Hello John!Billy James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Creativity EssayDocument7 pagesCreativity EssayBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Vice Chancellor'S Orientation Host ProgramDocument31 pagesVice Chancellor'S Orientation Host ProgramBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- ECWO Semester 1 2020 Online Mock Audition ExcerptsDocument6 pagesECWO Semester 1 2020 Online Mock Audition ExcerptsBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- ChAURALation Assessment Plan S1 2020 (FINAL - April 27)Document3 pagesChAURALation Assessment Plan S1 2020 (FINAL - April 27)Billy James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Lecture NotesDocument6 pagesWeek 7 Lecture NotesBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- 2016 Book AGirlSEducationDocument228 pages2016 Book AGirlSEducationBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
Electricity
Electricity
Uploaded by
Billy James St John0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views1 pageThe document discusses several physics formulas related to electricity, energy, forces, motion, and waves. It includes equations for:
1) Power (P) equals voltage (V) multiplied by current (I).
2) Voltage equals current multiplied by resistance.
3) Charge equals current multiplied by time.
4) Energy equals voltage multiplied by charge.
5) Energy equals voltage multiplied by current multiplied by time.
Original Description:
ghf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses several physics formulas related to electricity, energy, forces, motion, and waves. It includes equations for:
1) Power (P) equals voltage (V) multiplied by current (I).
2) Voltage equals current multiplied by resistance.
3) Charge equals current multiplied by time.
4) Energy equals voltage multiplied by charge.
5) Energy equals voltage multiplied by current multiplied by time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views1 pageElectricity
Electricity
Uploaded by
Billy James St JohnThe document discusses several physics formulas related to electricity, energy, forces, motion, and waves. It includes equations for:
1) Power (P) equals voltage (V) multiplied by current (I).
2) Voltage equals current multiplied by resistance.
3) Charge equals current multiplied by time.
4) Energy equals voltage multiplied by charge.
5) Energy equals voltage multiplied by current multiplied by time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Electricity
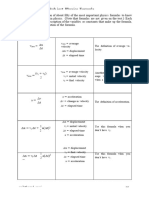
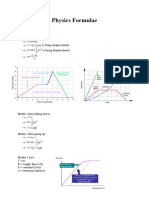
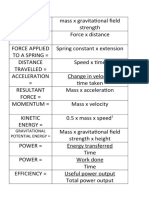
P = V x I. power = voltage x current.
V = I x R. voltage = current x resistance.
Q = I x t. charge = current x time.
E = V x Q. energy = voltage x charge.
E = V x I x t. energy = voltage x current x time.
Total cost = number of units x cost per unit.
Energy
Efficiency (%) = (useful energy out ÷ total energy in) x 100.
GPE = mgh. GPE = mass x gravity x height.
KE = ½mv . Kinetic Energy = 0·5 x mass x velocity2.
2
W = F x d. work done = force x distance.
W = E. work done = energy transferred.
P = E ÷ t. power = energy ÷ time.
E = c x m x θ. energy = specific heat
capacity x mass x change in temperature.
Forces and Motion
s = d ÷ t. speed = distance ÷ time.
a = (v-u) ÷ t. acceleration = change in velocity ÷ time.
F = m x a. Force = mass x acceleration.
w = m x g. weight = mass x gravity.
p = m x v. momentum = mass x velocity.
(mv - mu) = F x t. change in momentum = Force x time.
d = m ÷ v. density = mass ÷ volume.
p = F ÷ a. pressure = force ÷ area.
m = F x d. moment = force x perpendicular distance from pivot.
Waves
v = f x λ. velocity = frequency x wavelength.
You might also like
- Igcse Physics All FormulasDocument4 pagesIgcse Physics All FormulasRichie Harvy82% (17)
- Physics-5054-All Definitions&Formulae-RevisedSyllabusDocument8 pagesPhysics-5054-All Definitions&Formulae-RevisedSyllabusSaira Kamran100% (1)
- High School Physics Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesHigh School Physics Cheat SheetM J Rhoades50% (4)
- Harmonic Analysis of p.1 of 'Im Wunderschönen Monat Mai'-2 PDFDocument1 pageHarmonic Analysis of p.1 of 'Im Wunderschönen Monat Mai'-2 PDFBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- AQA Physics Equation Sheet Triple Oct 19Document3 pagesAQA Physics Equation Sheet Triple Oct 19Ricky JacobNo ratings yet
- Bmat Physics Formula Sheet InverseDocument2 pagesBmat Physics Formula Sheet Inverseeneagu3349No ratings yet
- O Level Physics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesO Level Physics Formula SheetYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- iGCSE Physics Formula Sheet: MotionDocument4 pagesiGCSE Physics Formula Sheet: MotionCamille67% (3)
- IGCSE Physics FormulasDocument1 pageIGCSE Physics FormulasPawan Kolhe80% (30)
- Beethoven Symphony No. 5, Mvt. 1 - DevelopmentDocument8 pagesBeethoven Symphony No. 5, Mvt. 1 - DevelopmentBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Formula PHYSISCS IGCSEDocument2 pagesFormula PHYSISCS IGCSEAnita LopesNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument7 pagesPhysics FormulasCryptazNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument2 pagesPhysics FormulasBOT NigmaNo ratings yet
- Formuals 2Document1 pageFormuals 2Miranda YeungNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics EquationsDocument2 pagesIGCSE Physics EquationsMisterBlueSkyNo ratings yet
- A Level FormulaeDocument1 pageA Level FormulaeVarun PanickerNo ratings yet
- Physics equations sheet: W=mg W=Fs F=ke s=vt a = Δ v t F=ma p=mv Ek = 1 m v 2 Ep=mgh P = E T P = W tDocument2 pagesPhysics equations sheet: W=mg W=Fs F=ke s=vt a = Δ v t F=ma p=mv Ek = 1 m v 2 Ep=mgh P = E T P = W tUtkarsh IngleNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Physics IGCSE EquationsDocument1 pageEdexcel Physics IGCSE EquationsNik JonesNo ratings yet
- AS Level Equations For PhysicsDocument1 pageAS Level Equations For PhysicsAhmad MohdNo ratings yet
- AS Physics EquationsDocument1 pageAS Physics EquationsAhmad MohdNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 1 Edexcel Physics GCSEDocument3 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 1 Edexcel Physics GCSEAli AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Al PhysicsformulaeDocument2 pagesAl PhysicsformulaeMichael ScofieldNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 - Foundation Tier EquationsDocument6 pagesPhysics 1 - Foundation Tier EquationsFayzan AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1.0.8 FORMULA FOR DERIVED UNITSDocument1 page1.0.8 FORMULA FOR DERIVED UNITSmintahroland6No ratings yet
- Formulae To Study For IGCSEDocument2 pagesFormulae To Study For IGCSE2144639220No ratings yet
- Physics Formula Y9Document5 pagesPhysics Formula Y9Lim MonyratanakNo ratings yet
- Physics Equation Sheet (8464) InsertDocument2 pagesPhysics Equation Sheet (8464) Inserttzvkpbjg2yNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Formula SheetDocument1 pagePhysical Science Formula SheetglezamaeNo ratings yet
- All GCSE Physics Equations (Editable)Document3 pagesAll GCSE Physics Equations (Editable)will hayNo ratings yet
- Physics Equation SheetDocument2 pagesPhysics Equation SheetEshanB786No ratings yet
- IGCSE Formula BookletDocument4 pagesIGCSE Formula BookletNisalNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesPhysics Formula Sheetboygafadi59No ratings yet
- Physics Equation Sheet AQA 2023Document2 pagesPhysics Equation Sheet AQA 2023HazzaYT HicksNo ratings yet
- Facts and Formulas 3 RefDocument13 pagesFacts and Formulas 3 Refrania deifNo ratings yet
- iGCSE Physics Formula Sheet: MotionDocument4 pagesiGCSE Physics Formula Sheet: MotionYusuf100% (3)
- Igcse Physics All FormulasDocument4 pagesIgcse Physics All FormulasABDULLAHNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument1 pagePhysics FormulaskimblesdjNo ratings yet
- Physics Review PapersDocument18 pagesPhysics Review Papersyoonmimikyaw2008No ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics FormulaeDocument3 pagesIGCSE Physics FormulaeTanushree TapariaNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument1 pagePhysics FormulasZahid MohammadNo ratings yet
- Work Energy PowerDocument10 pagesWork Energy PowerMarvin AndradeNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument2 pagesPhysics FormulasSzraxNo ratings yet
- Physics Igcse All Imp FormulasDocument4 pagesPhysics Igcse All Imp FormulasDhruvil Desai100% (1)
- A Level FormulaeDocument2 pagesA Level FormulaeAlim EchaNo ratings yet
- Rules PhysicsDocument1 pageRules PhysicsMarwan AmirNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Mekaniks: English Swedish Symbol Units Units-Name ValueDocument10 pagesMechanics Mekaniks: English Swedish Symbol Units Units-Name ValueEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Gravitational Potential EnergyDocument2 pagesGravitational Potential EnergyHarry WangNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument2 pagesPhysics FormulasSuchetana DasNo ratings yet
- Physics Reference PDFDocument12 pagesPhysics Reference PDFRonald Chester LorenzanaNo ratings yet
- Bmat Physics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesBmat Physics Formula SheetDrAIyer90% (10)
- Physics FormulasDocument6 pagesPhysics FormulastalalrazerNo ratings yet
- Fizix FormulasDocument1 pageFizix FormulasUjjwal JainNo ratings yet
- Formula ChartDocument1 pageFormula Chartapi-87739323No ratings yet
- Paper 2 Formula Sheet 1Document1 pagePaper 2 Formula Sheet 1mochiNo ratings yet
- Work Power and EnergyDocument51 pagesWork Power and EnergyJohn Carlo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- 9203 2 INS InternationalPhysics G 16nov20!07!00 GMTDocument4 pages9203 2 INS InternationalPhysics G 16nov20!07!00 GMT王涛No ratings yet
- Work, Energy, & Power: Chapter 6 (C&J) Chapter 10 (Glencoe)Document29 pagesWork, Energy, & Power: Chapter 6 (C&J) Chapter 10 (Glencoe)Emieleah Lorenzo PauigNo ratings yet
- A Level Work Energy PowerDocument17 pagesA Level Work Energy PowerHuurun AinNo ratings yet
- Energy Work and PowerDocument35 pagesEnergy Work and PowerFabian ClarkeNo ratings yet
- MinorScalesExplanationandWorksheets 1Document49 pagesMinorScalesExplanationandWorksheets 1Billy James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Challenging Middle YearsDocument7 pagesChallenging Middle YearsBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Singing - Survey - FINAL - With CoverDocument61 pagesSinging - Survey - FINAL - With CoverBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Blue MoonDocument1 pageBlue MoonBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- 2022 Sem1 Studyplanner A3Document1 page2022 Sem1 Studyplanner A3Billy James St JohnNo ratings yet
- E737 2022 T2 Coursemap Option 2 Research PaperDocument3 pagesE737 2022 T2 Coursemap Option 2 Research PaperBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Deakin University Professional Experience Timetable MALT 2022Document1 pageDeakin University Professional Experience Timetable MALT 2022Billy James St JohnNo ratings yet
- John Cage - Experimental MusicDocument1 pageJohn Cage - Experimental MusicBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Composition AssignmentDocument2 pagesComposition AssignmentBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Michael Nyman - Experimental MusicDocument1 pageMichael Nyman - Experimental MusicBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- DFDSDDocument1 pageDFDSDBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Another Helpful Hint in My Tips and Tricks' SessionsDocument7 pagesWelcome To Another Helpful Hint in My Tips and Tricks' SessionsBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- 2020 O & R Cover Sheet PDFDocument1 page2020 O & R Cover Sheet PDFBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Simon Bolivar's Vision For South American Unity vs. Today's RealityDocument3 pagesSimon Bolivar's Vision For South American Unity vs. Today's RealityBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Lange2010 Article TheHistoryOfAttentionDeficitHy PDFDocument15 pagesLange2010 Article TheHistoryOfAttentionDeficitHy PDFBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Embellishing Notes SummaryDocument1 pageEmbellishing Notes SummaryBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- A Music Therapy Approach in Mental HealthDocument10 pagesA Music Therapy Approach in Mental HealthBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- 2019 Book VenezuelaALBAAndTheLimitsOfPosDocument226 pages2019 Book VenezuelaALBAAndTheLimitsOfPosBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- 10 1 1 738 5935Document6 pages10 1 1 738 5935Billy James St JohnNo ratings yet
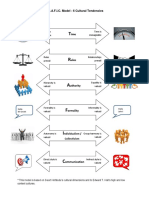
- T.R.A.F.I.C. Model - 6 Cultural Tendencies: Hello MR Smith Hello John!Document1 pageT.R.A.F.I.C. Model - 6 Cultural Tendencies: Hello MR Smith Hello John!Billy James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Creativity EssayDocument7 pagesCreativity EssayBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Vice Chancellor'S Orientation Host ProgramDocument31 pagesVice Chancellor'S Orientation Host ProgramBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- ECWO Semester 1 2020 Online Mock Audition ExcerptsDocument6 pagesECWO Semester 1 2020 Online Mock Audition ExcerptsBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- ChAURALation Assessment Plan S1 2020 (FINAL - April 27)Document3 pagesChAURALation Assessment Plan S1 2020 (FINAL - April 27)Billy James St JohnNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Lecture NotesDocument6 pagesWeek 7 Lecture NotesBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet
- 2016 Book AGirlSEducationDocument228 pages2016 Book AGirlSEducationBilly James St JohnNo ratings yet