Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Seed Flowering Plants Ovary Flowering Seeds Symbiotic Relationship Seed Dispersal Nutrition Agricultural Apple Pomegranate
Seed Flowering Plants Ovary Flowering Seeds Symbiotic Relationship Seed Dispersal Nutrition Agricultural Apple Pomegranate
Uploaded by
Jeje0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
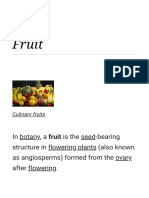
9 views1 pageFruits develop from the ovary of flowering plants and serve to disseminate seeds. Many edible fruits have evolved alongside human and animal consumption as a means of seed dispersal and nutrition, making fruits an important global agricultural product. While commonly referring to sweet and sour fleshy plant structures like apples and oranges, the botanical definition of a fruit is broader and includes seeds and grains contained within pods, kernels, tomatoes, and fungal spore-producing structures.
Original Description:
Fruits -Definition
Original Title
Fruit
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFruits develop from the ovary of flowering plants and serve to disseminate seeds. Many edible fruits have evolved alongside human and animal consumption as a means of seed dispersal and nutrition, making fruits an important global agricultural product. While commonly referring to sweet and sour fleshy plant structures like apples and oranges, the botanical definition of a fruit is broader and includes seeds and grains contained within pods, kernels, tomatoes, and fungal spore-producing structures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageSeed Flowering Plants Ovary Flowering Seeds Symbiotic Relationship Seed Dispersal Nutrition Agricultural Apple Pomegranate
Seed Flowering Plants Ovary Flowering Seeds Symbiotic Relationship Seed Dispersal Nutrition Agricultural Apple Pomegranate
Uploaded by
JejeFruits develop from the ovary of flowering plants and serve to disseminate seeds. Many edible fruits have evolved alongside human and animal consumption as a means of seed dispersal and nutrition, making fruits an important global agricultural product. While commonly referring to sweet and sour fleshy plant structures like apples and oranges, the botanical definition of a fruit is broader and includes seeds and grains contained within pods, kernels, tomatoes, and fungal spore-producing structures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (also known as angiosperms) formed from
the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate seeds. Edible fruits, in particular, have
propagated with the movements of humans and animals in a symbiotic relationship as a means
for seed dispersal and nutrition; in fact, humans and many animals have become dependent on fruits
as a source of food.[1] Accordingly, fruits account for a substantial fraction of the
world's agricultural output, and some (such as the apple and the pomegranate) have acquired
extensive cultural and symbolic meanings.
In common language usage, "fruit" normally means the fleshy seed-associated structures of a plant
that are sweet or sour, and edible in the raw state, such
as apples, bananas, grapes, lemons, oranges, and strawberries. On the other hand, in botanical
usage, "fruit" includes many structures that are not commonly called "fruits", such
as bean pods, corn kernels, tomatoes, and wheat grains.[2][3] The section of a fungusthat
produces spores is also called a fruiting body.[4]
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fruit
You might also like
- Botany Seed Flowering Plants Ovary Flowering Seeds Symbiotic Relationship Seed Dispersal Nutrition Agricultural Apple PomegranateDocument1 pageBotany Seed Flowering Plants Ovary Flowering Seeds Symbiotic Relationship Seed Dispersal Nutrition Agricultural Apple PomegranateRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Botany Seed Flowering Plants Ovary Flowering Seeds Symbiotic Relationship Seed Dispersal Nutrition Agricultural Apple PomegranateDocument1 pageBotany Seed Flowering Plants Ovary Flowering Seeds Symbiotic Relationship Seed Dispersal Nutrition Agricultural Apple PomegranateshobhrajNo ratings yet
- Botany Seed Flowering Plants Ovary Flowering Seeds Symbiotic Relationship Seed Dispersal Nutrition Agricultural Apple PomegranateDocument1 pageBotany Seed Flowering Plants Ovary Flowering Seeds Symbiotic Relationship Seed Dispersal Nutrition Agricultural Apple Pomegranatesujit21in4376No ratings yet
- FruitsDocument1 pageFruitsBaleña AselNo ratings yet
- For Other Uses, See .: Fruit (Disambiguation)Document1 pageFor Other Uses, See .: Fruit (Disambiguation)dariokNo ratings yet
- Fruit: Navigation Search Fruit (Disambiguation)Document6 pagesFruit: Navigation Search Fruit (Disambiguation)devakikris1985No ratings yet
- Fruit - WikipediaDocument27 pagesFruit - WikipediaVider AscarNo ratings yet
- Fruit - WikipediaDocument62 pagesFruit - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- Fruit - WikipediaDocument53 pagesFruit - WikipediaOrigami toturial by AbhijeetNo ratings yet
- Information of Food: Download Image.... Cereals Dairy Prducts Edible Plants Edible Nuts and SeedsDocument2 pagesInformation of Food: Download Image.... Cereals Dairy Prducts Edible Plants Edible Nuts and SeedsManish VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- FruitDocument13 pagesFruitKristoff Bryan BermacheaNo ratings yet
- Fruit - WikipediaDocument87 pagesFruit - WikipediaBiology ChemistryNo ratings yet
- VegetableDocument2 pagesVegetableSergio Rios CNo ratings yet
- Berry: For Botanical Usage, See - For Other Uses, SeeDocument13 pagesBerry: For Botanical Usage, See - For Other Uses, SeeEirojram MarjorieNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Meaning of Vegetables and Vegetable GardeningDocument6 pagesGroup 5 Meaning of Vegetables and Vegetable GardeningJAY MARIE PRESBITERONo ratings yet
- AngiospermsDocument12 pagesAngiospermsShivam Pratap Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Apple FruitDocument2 pagesApple Fruitrajeshjain90No ratings yet
- Semener ReportDocument17 pagesSemener ReportHUSSAINI SANI KANKIANo ratings yet
- All About Fruits: NutritionDocument2 pagesAll About Fruits: NutritionDharmendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Botany AssignmentDocument4 pagesBotany AssignmentAntonneth batislaongNo ratings yet
- Fruit Versus VegetableDocument4 pagesFruit Versus VegetableReezvee Sultana EvaNo ratings yet
- Anglais L2Document6 pagesAnglais L24f4d8b84jmNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument12 pagesLab ReportValentinoDullSatinNo ratings yet
- Apple The Tasty FruitDocument2 pagesApple The Tasty FruitlololoNo ratings yet
- Bees The ImportanceDocument1 pageBees The ImportanceYnranNo ratings yet
- BDocument1 pageBEthan GuoNo ratings yet
- Assign # 2Document2 pagesAssign # 2Christian Carl RecedeNo ratings yet
- Apple: Apple Inc. Apple (Disambiguation)Document2 pagesApple: Apple Inc. Apple (Disambiguation)Anonymous MqF7u3uNo ratings yet
- What Is A Pollen AllergyDocument13 pagesWhat Is A Pollen AllergyHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- Flower EssayDocument5 pagesFlower EssayallthingswaltNo ratings yet
- Classification of Crop DetailedDocument11 pagesClassification of Crop DetailedRahulNo ratings yet
- PiA1 11Document52 pagesPiA1 11Paulino mariak AtemNo ratings yet
- Biology RealDocument15 pagesBiology Reallodhishivansh2567No ratings yet
- Group 1 Chapter 1PDFDocument24 pagesGroup 1 Chapter 1PDFRai-Dale Lorence L. ArrofoNo ratings yet
- Adv Sci G7Document22 pagesAdv Sci G7Ezequiel ManluluNo ratings yet
- About PlantsDocument8 pagesAbout PlantsOana100% (1)
- An Accessory FruitDocument24 pagesAn Accessory FruitPutu Novi KurniawatiNo ratings yet
- Fruit: Botanic Fruit and Culinary FruitDocument5 pagesFruit: Botanic Fruit and Culinary FruitGrety IancuNo ratings yet
- Dr. David Iluz Is A Lecturer in Bar Ilan University, Ramat Gan, Israel. He ObtainedDocument15 pagesDr. David Iluz Is A Lecturer in Bar Ilan University, Ramat Gan, Israel. He ObtainedGabriel Miguel S CNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity PDFDocument67 pagesBiodiversity PDFTanaya BorseNo ratings yet
- Made by Azka NoorDocument8 pagesMade by Azka NoorazkanoorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4.variety of Liv. Nat. The W. of Plants.Document3 pagesLecture 4.variety of Liv. Nat. The W. of Plants.SabinaNo ratings yet
- Fungus: 1 EtymologyDocument28 pagesFungus: 1 EtymologyJohnNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument5 pagesSexual Reproduction in PlantsAbbie Hyacinth GetalagaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Crop Production CRPT 102: BS Agriculture 1 A.Y. 2021-2022 Second SemesterDocument49 pagesPrinciples of Crop Production CRPT 102: BS Agriculture 1 A.Y. 2021-2022 Second SemesterAllena VillarinNo ratings yet
- ApricotsDocument2 pagesApricotsArriane Joy Yturalde InsularNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 Pharma. BotanyDocument3 pagesQuiz 1 Pharma. BotanyKate MendozaNo ratings yet
- Docs 10Document5 pagesDocs 10Jobelle RafaelNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plants Classification Grade 5 6Document7 pagesKingdom Plants Classification Grade 5 6Anam ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Name - Class - Xi Roll No. - Subject - Biology: TOPIC - Dispersal of Seeds by Various Agencies..Document23 pagesName - Class - Xi Roll No. - Subject - Biology: TOPIC - Dispersal of Seeds by Various Agencies..RaJdEeP BiSwAsNo ratings yet
- KivasokimejalalimojavidDocument2 pagesKivasokimejalalimojavidThe Reactant GroupNo ratings yet
- ApplesDocument1 pageApplesPip JohnsonNo ratings yet
- EpiphyteDocument1 pageEpiphyteAbdulaziz AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Name - Arun.S CLASS - 12th Roll No. - 05 Subject - Biology TOPIC - Dispersal of Seeds by Various Agencies..Document22 pagesName - Arun.S CLASS - 12th Roll No. - 05 Subject - Biology TOPIC - Dispersal of Seeds by Various Agencies..LokeshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Plant Growth and DevelopmentDocument6 pagesChapter 1. Plant Growth and Developmentkangethemoses371No ratings yet
- Biology Project PDF - MergedDocument19 pagesBiology Project PDF - Mergedᴀᴅᴡᴀɪᴛʜ ʀᴀᴊNo ratings yet
- B L R D P: F, F, S: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesB L R D P: F, F, S: ObjectivesJorelyn Giron NaniongNo ratings yet
- Dispersal of Seeds by AnimalsDocument15 pagesDispersal of Seeds by AnimalsDevika Midha100% (1)
- Lecture 13 Notes 2013Document4 pagesLecture 13 Notes 2013Richard HampsonNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory States That The Cell Is The Fundamental Unit of Life, That All Living Things Are Composed ofDocument1 pageCell Theory States That The Cell Is The Fundamental Unit of Life, That All Living Things Are Composed ofJejeNo ratings yet
- Biology Is The Natural Science That Involves The Study of Life and Living Organisms, IncludingDocument1 pageBiology Is The Natural Science That Involves The Study of Life and Living Organisms, IncludingJejeNo ratings yet
- Parts of Bodies, and The Relation of Heat To Electrical Agency."Document1 pageParts of Bodies, and The Relation of Heat To Electrical Agency."JejeNo ratings yet
- Non FoodDocument1 pageNon FoodJejeNo ratings yet
- European Union Multilateral Agreement On Information Exchange Local Taxation Tax EvasionDocument1 pageEuropean Union Multilateral Agreement On Information Exchange Local Taxation Tax EvasionJejeNo ratings yet
- Income Taxes Asset Capital Taxes Financial Transaction Sales TaxesDocument1 pageIncome Taxes Asset Capital Taxes Financial Transaction Sales TaxesJejeNo ratings yet
- RytDocument1 pageRytJejeNo ratings yet
- Design 1Document21 pagesDesign 1JejeNo ratings yet
- Latin Legal Entity Direct Indirect TaxesDocument1 pageLatin Legal Entity Direct Indirect TaxesJejeNo ratings yet
- RightsDocument1 pageRightsJejeNo ratings yet
- Please Print Name: - Student #Document2 pagesPlease Print Name: - Student #JejeNo ratings yet
- RightsDocument1 pageRightsJejeNo ratings yet
- Legal Ethical Principles Freedom Entitlement Normative Law Ethics Justice Deontology Civilization Society Culture Social Conflicts Governments Laws MoralityDocument1 pageLegal Ethical Principles Freedom Entitlement Normative Law Ethics Justice Deontology Civilization Society Culture Social Conflicts Governments Laws MoralityJejeNo ratings yet
- Solutions Notetaking GuideDocument9 pagesSolutions Notetaking GuideJejeNo ratings yet
- PD Sources in LiteratureDocument3 pagesPD Sources in LiteratureJejeNo ratings yet