Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsHydraulic System
Hydraulic System
Uploaded by
fildi95Defines the Hydraulic system
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Split Hydraulic SystemDocument1 pageSplit Hydraulic Systemfildi95No ratings yet
- Formula Student Racing Championship: Design and Implementation of An Automatic Localization and Trajectory Tracking SystemDocument11 pagesFormula Student Racing Championship: Design and Implementation of An Automatic Localization and Trajectory Tracking Systemfildi95No ratings yet
- LIB 18650 Cells NewDocument30 pagesLIB 18650 Cells Newfildi95No ratings yet
- Disc Brake CaliperDocument2 pagesDisc Brake Caliperfildi95No ratings yet
- Brake SystemDocument1 pageBrake Systemfildi95No ratings yet
Hydraulic System
Hydraulic System
Uploaded by
fildi950 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageDefines the Hydraulic system
Original Title
Hydraulic system
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDefines the Hydraulic system
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageHydraulic System
Hydraulic System
Uploaded by
fildi95Defines the Hydraulic system
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
You are on page 1of 1
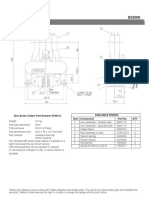
(©2004 Melir, In. Introduction to Brake Systems - Study Gulde
Hydraulic System
‘An important hydraulic principle states that fluids do not compress or produce any measurable friction.
‘Also, fluid pressure does not diminish when transferred within a closed system, That means that if there
is no leak in a system, the pressure al the wheels willbe the same as the pressure from the master
cylinder.
‘A second hydraulic principle states that a relationship exists between:
‘* Force and piston area
‘+ Piston travel and piston area
From the first principle, if a master cylinder generates 500 psi, it also transfers 500 psi to the pistons in
each wheel cylinder (remember that fluid pressure remains constant).
In the second principle (fig. 5), when pressure from a one-square-inch master cylinder piston exerts 500
psi on a wheel cylinder piston, which also has one-square-inch surface area, the wheel cylinder piston
transfers 500 pounds of force to the brake shoe (500 psi x 1 in. sq. = 500 Ibs.)
However, if the same one-square-inch master cylinder piston exerts 500 psi on a wheel cylinder piston
that has a two-square-inch area, the wheel cylinder piston will transfer 1,000 pounds of force to the
brake lining (500 psi x 2 in. sq. = 1 ,000 Ibs.)
Additionally, different piston sizes not only affect the amount of brake force applied, they also determine
the travel distance of the different pistons. For instance, if the one-square-inch master cylinder piston
moves one inch, a one-square-inch wheel cylinder piston will also move one inch (with the same force)
(fig. 5)
If that same one-square-inch master cylinder piston moves one inch, then a two-square-inch whee!
cylinder piston (twice the size) will move just one-half inch (half the distance) but with twice the force (fig
6)
(fig. 5) Piston Area and Travel (1 inch) (fig. 6) Piston Area and Travel (1/2inch)
Master Cylinder
+ Converts mechanical force from the brake pedal, power booster and push rod into hydraulic
pressure
Contain pistons, piston seals, return springs and internal brake fluid ports.
Aso has a fluid reservoir thal may either be an integral part of the unit or remotely mounted. The
reservoir itself wil have a removable cap with a rubber diaphragm seal that must be in good
condition to seal proper.
‘+ Most reservoirs also have a low brake fluid level switch to alert the driver of a low fluid condition
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Split Hydraulic SystemDocument1 pageSplit Hydraulic Systemfildi95No ratings yet
- Formula Student Racing Championship: Design and Implementation of An Automatic Localization and Trajectory Tracking SystemDocument11 pagesFormula Student Racing Championship: Design and Implementation of An Automatic Localization and Trajectory Tracking Systemfildi95No ratings yet
- LIB 18650 Cells NewDocument30 pagesLIB 18650 Cells Newfildi95No ratings yet
- Disc Brake CaliperDocument2 pagesDisc Brake Caliperfildi95No ratings yet
- Brake SystemDocument1 pageBrake Systemfildi95No ratings yet