Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
90 viewsOrganization of Nervous System: Anatomic Divisions
Organization of Nervous System: Anatomic Divisions
Uploaded by
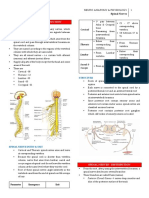
Dr P N N ReddyThe nervous system can be divided anatomically into the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS is comprised of the brain and spinal cord and contains neuronal cell bodies and processes. The PNS contains cranial and peripheral nerves and some neuronal cell bodies in ganglia as well as axonal processes and glial cells. The nervous system can also be divided functionally into sensory and motor divisions for input and output.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- 1.microbiology - Bacteriology MCQs FormattedDocument73 pages1.microbiology - Bacteriology MCQs FormattedDr P N N Reddy94% (17)
- Notes From An Alternate Universe - Introduction To A New Way of ThinkingDocument145 pagesNotes From An Alternate Universe - Introduction To A New Way of Thinkingzootsuit7100% (1)
- The Correlation of Sleep and Academic Performance: February 2021Document12 pagesThe Correlation of Sleep and Academic Performance: February 2021Kristel EyyyNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Sleep Deprivation On Decision Making - ReviewDocument14 pagesThe Impact of Sleep Deprivation On Decision Making - ReviewAna Viegas100% (1)
- The Effects of Sleep Deprivation On TheDocument7 pagesThe Effects of Sleep Deprivation On ThePrincess Martinez100% (1)
- Research Proposal Group 2Document30 pagesResearch Proposal Group 2Anthony PelayoNo ratings yet
- GegegegeDocument13 pagesGegegegeLuis CatindoyNo ratings yet
- Annotated Bibliography FinalDocument8 pagesAnnotated Bibliography Finalapi-253450997No ratings yet
- Yung Chapter 5 Nalang Tas Print NaDocument19 pagesYung Chapter 5 Nalang Tas Print NaMitchico CanonicatoNo ratings yet
- Productivity Posits That Regardless If An Individual Is Single, Living With SomeoneDocument6 pagesProductivity Posits That Regardless If An Individual Is Single, Living With Someonejankarl199160% (5)
- Synthesis PaperDocument4 pagesSynthesis PaperEthan FreemanNo ratings yet
- Nuñez Survey InstrumentDocument3 pagesNuñez Survey InstrumentAnna Carmela NuñezNo ratings yet
- 0 - Group 2 Edited FinalDocument23 pages0 - Group 2 Edited Finalana jean gamoNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Sleep Habits and Academic Performance in Dental Students in CroatiaDocument8 pagesThe Relationship Between Sleep Habits and Academic Performance in Dental Students in CroatiaBeatrizCamposNo ratings yet
- Sleep CodebookDocument6 pagesSleep CodebookJunn Ree Montilla100% (1)
- Movie Reflection On Dr. StrangeDocument4 pagesMovie Reflection On Dr. StrangefrustratedlawstudentNo ratings yet
- Final PaperDocument52 pagesFinal PaperRalph Carlos VelasNo ratings yet
- Final Research ProposalDocument14 pagesFinal Research Proposaladrian quinto100% (1)
- The ThesisDocument8 pagesThe ThesisTerraMonsta BlogspotNo ratings yet
- Sleep Deprivation and College Students 1 4Document11 pagesSleep Deprivation and College Students 1 4api-385639709No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document14 pagesChapter 3KayeJane Quiatchon-TalingtingNo ratings yet
- The Relation of Grades 9 and 10 Students' Sleeping Patterns and Their Attendance in Saint Francis of Assisi College Main CampusDocument15 pagesThe Relation of Grades 9 and 10 Students' Sleeping Patterns and Their Attendance in Saint Francis of Assisi College Main CampusJesary Marc ArnosaNo ratings yet
- Sample Qualitative Research1Document53 pagesSample Qualitative Research1AkiraNo ratings yet
- Sleep DeprivationDocument6 pagesSleep Deprivationarsh13No ratings yet
- The Impact of Sleep Deprivation To Student' Mental HealthDocument8 pagesThe Impact of Sleep Deprivation To Student' Mental HealthKrizelle LivaraNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument15 pagesAbstractDeanne Mitzi SomolloNo ratings yet
- Pe Reporting Group 1 With QuizDocument11 pagesPe Reporting Group 1 With QuizBeverly Jen Semine EnocNo ratings yet
- Sleep Deprivation Stem CaviteDocument57 pagesSleep Deprivation Stem CaviteLesley NaraNo ratings yet
- Sleep DeprivationDocument23 pagesSleep DeprivationMelody ManadongNo ratings yet
- G12RRR PR2 G1...Document18 pagesG12RRR PR2 G1...Hanny ValenciaNo ratings yet
- The Cytoskeleton Is A Network of Filament and Tubules That Extends Throughout A CellDocument9 pagesThe Cytoskeleton Is A Network of Filament and Tubules That Extends Throughout A CellHania GulNo ratings yet
- The Level of Mental and Physical Effects of Sleep Deprivation On Grade 12 StudentsDocument4 pagesThe Level of Mental and Physical Effects of Sleep Deprivation On Grade 12 StudentsAnnica Grizzel WongNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument17 pagesResearch ProposalKyle AshleyNo ratings yet
- Neuro Rehab Assignment Pt2 - Divina MahtaniDocument2 pagesNeuro Rehab Assignment Pt2 - Divina Mahtanidivina0% (1)
- Chapter 2Document4 pagesChapter 2Lawrence LuceñoNo ratings yet
- Veritas Listening QuizDocument1 pageVeritas Listening QuizMushy_ayaNo ratings yet
- Sleep Deprivation and Mental HealthDocument4 pagesSleep Deprivation and Mental Healthapi-341198049No ratings yet
- Effects of Sleep Deprivation To The Mental Health Stability of Selected G9 Students of RMCHS-with-cover-page-V2 (Appendix)Document57 pagesEffects of Sleep Deprivation To The Mental Health Stability of Selected G9 Students of RMCHS-with-cover-page-V2 (Appendix)Sebastian CrayNo ratings yet
- University of Makati Higher Schoolng UmakDocument61 pagesUniversity of Makati Higher Schoolng UmakChesca ApologistaNo ratings yet
- Review of Related Literature and StudiesDocument3 pagesReview of Related Literature and StudiesDANIELLE JOYCE BACSALNo ratings yet
- 2 - RA5527 Philippine Medical Technology Act of 1969Document4 pages2 - RA5527 Philippine Medical Technology Act of 1969Morticia VizactyhNo ratings yet
- The Problem and Its Background Introduction and BackgroundDocument17 pagesThe Problem and Its Background Introduction and Backgroundrozel jan espisoNo ratings yet
- Final Research Paper Effects of Sleep Deprivation On The Academic Performance of Senior High School StudentsDocument130 pagesFinal Research Paper Effects of Sleep Deprivation On The Academic Performance of Senior High School StudentsZyrel OtucanNo ratings yet
- Sports: Physical Education 04 2 Semester, SY 2020-2021Document23 pagesSports: Physical Education 04 2 Semester, SY 2020-2021hoohooNo ratings yet
- Effect of Sleep Deprivation On College Students' Academic PerformanceDocument10 pagesEffect of Sleep Deprivation On College Students' Academic PerformanceVirgil Viral Shah0% (1)
- HUMSS PRACTICAL RESEARCH PRDocument37 pagesHUMSS PRACTICAL RESEARCH PRyuanaaerith13No ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Nature and Scope of Physical Education, Exercise Science, and SportDocument39 pagesChapter 1: Nature and Scope of Physical Education, Exercise Science, and SportmyraturaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Student Nutrion On Academic PerformanceDocument45 pagesEffects of Student Nutrion On Academic PerformanceAbdifatah SaidNo ratings yet
- The Correlation Between Sleep Quality and Levels of Stress Among Students in Universitas IndonesiaDocument5 pagesThe Correlation Between Sleep Quality and Levels of Stress Among Students in Universitas IndonesiaKripa SriramNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - The Chemical Level of OrganizationDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - The Chemical Level of OrganizationChristina MarkwartNo ratings yet
- Formerly Ramon Magsaysay Technological UniversityDocument5 pagesFormerly Ramon Magsaysay Technological UniversityJoanne Saromo100% (1)
- Theories of Motor ControlDocument1 pageTheories of Motor ControlAqembunNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Sleep On Academic Performance and Job PerformanceDocument18 pagesThe Effects of Sleep On Academic Performance and Job PerformanceKen DobsNo ratings yet
- Students Satisfaction To The Services Rendered by The School Library of Santa. Teresita National High SchoolDocument26 pagesStudents Satisfaction To The Services Rendered by The School Library of Santa. Teresita National High SchoolLyndsey Ann BaetNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Intake Among Older People of Hermana Fausta Development Center, Lucena City and Its Relationship To Physical Health StatusDocument20 pagesNutritional Intake Among Older People of Hermana Fausta Development Center, Lucena City and Its Relationship To Physical Health StatusAngelNo ratings yet
- "Relationship With The Earth": Lesson 1: Introduction To Philosphy of The Human PersonDocument6 pages"Relationship With The Earth": Lesson 1: Introduction To Philosphy of The Human PersonMayeNo ratings yet
- Reflex ResponseDocument10 pagesReflex Responseapi-264015665No ratings yet
- Research 1-4 (gROUP 4)Document44 pagesResearch 1-4 (gROUP 4)Gly Ann Homerez LopinaNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Is Defined As "A State of Well-Being in Which Every IndividualDocument7 pagesMental Health Is Defined As "A State of Well-Being in Which Every IndividualmejulNo ratings yet
- Orientation of Central Nervous System: Neuroanatomy & Neurophysiology 1Document1 pageOrientation of Central Nervous System: Neuroanatomy & Neurophysiology 1Dr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Written Report 2Document24 pagesNervous System Written Report 2Noronisa PendalidayNo ratings yet
- DR Narendranatha Reddy Profile 15 April 2018 PDFDocument5 pagesDR Narendranatha Reddy Profile 15 April 2018 PDFDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Schedule TemplateDocument1 pageSchedule TemplateDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Test Marking (EMD) TemplateDocument1 pageTest Marking (EMD) TemplateDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Aipg 5Document64 pagesAipg 5Dr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- 1.structure of BacteriaDocument12 pages1.structure of BacteriaDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MicrobiologyDocument1 pageIntroduction To MicrobiologyDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- CNS PNS: Lipofuscin: Wear and TearDocument10 pagesCNS PNS: Lipofuscin: Wear and TearDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- General Histology FinalDocument60 pagesGeneral Histology FinalDr P N N Reddy100% (1)
- 6.nerves of Head and NeckDocument36 pages6.nerves of Head and NeckDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- 1.embryology Q ADocument11 pages1.embryology Q ADr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- 2.osteology Q ADocument11 pages2.osteology Q ADr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Aiims May 2014-QuestionsDocument7 pagesAiims May 2014-QuestionsDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Orientation of Central Nervous System: Neuroanatomy & Neurophysiology 1Document1 pageOrientation of Central Nervous System: Neuroanatomy & Neurophysiology 1Dr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Nerve Muscle PhysiologyDocument18 pagesNerve Muscle PhysiologyDr P N N Reddy100% (2)
- CNS PNS: Absent in AxonsDocument6 pagesCNS PNS: Absent in AxonsDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Embryology Synopsis-Panineeya DemoDocument13 pagesEmbryology Synopsis-Panineeya DemoDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Spinal Nerves - Introduction: Neuro Anatomy & Physiology 1Document5 pagesSpinal Nerves - Introduction: Neuro Anatomy & Physiology 1Dr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and The Somatic Nervous System PDFDocument4 pagesNeural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and The Somatic Nervous System PDFAmandaNo ratings yet
- Deepthashree K - 642153000020249 2Document1 pageDeepthashree K - 642153000020249 2Deeptha AravamudhanNo ratings yet
- Inflammation and HealingDocument15 pagesInflammation and HealingRachel Niu II100% (1)
- Review of Ayurvedic Drugs Acting On Hypothyroidism: Tarun Sharma, Malvika, Monu Gupta, Sumit NathaniDocument8 pagesReview of Ayurvedic Drugs Acting On Hypothyroidism: Tarun Sharma, Malvika, Monu Gupta, Sumit NathaniVakamalla SubbareddyNo ratings yet
- Orphan G Protein-Coupled Receptors and Novel NeuropeptidesDocument267 pagesOrphan G Protein-Coupled Receptors and Novel NeuropeptidesIsmaelVázquezEspinozaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine NotesDocument157 pagesEndocrine NotesLaila Cristine CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka TirotoksikosisDocument2 pagesDaftar Pustaka TirotoksikosisCut Mulya MutiaNo ratings yet
- David Carreras - A Cunnilinguist's Guide To Mind-Blowing Oral SexDocument6 pagesDavid Carreras - A Cunnilinguist's Guide To Mind-Blowing Oral SexKostyaNo ratings yet
- LESSON-PLAN-ON-PHYSIOLogical Changes During PregnancyDocument22 pagesLESSON-PLAN-ON-PHYSIOLogical Changes During PregnancyV.srivaniNo ratings yet
- Sinelnikov Vol IIIDocument395 pagesSinelnikov Vol IIIFlorescu Diana NicoletaNo ratings yet
- Genito Urinary TraumaDocument16 pagesGenito Urinary TraumaAjibola OlamideNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Blood Banking: Immunohaematology I (Dml405) S.Y. Pan (2009)Document15 pagesIntroduction To Blood Banking: Immunohaematology I (Dml405) S.Y. Pan (2009)shing_yiNo ratings yet
- Types of Skull FractureDocument5 pagesTypes of Skull FractureKhor Hui DiNo ratings yet
- PdfText - 2022-12-15T172553.484Document1 pagePdfText - 2022-12-15T172553.484Himanshu MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- The Complement SystemDocument9 pagesThe Complement SystemAxel RamírezNo ratings yet
- Concomitant Developmental Dental Anomalies in Chinese Children With Dens EvaginatusDocument5 pagesConcomitant Developmental Dental Anomalies in Chinese Children With Dens EvaginatusFernanda CombaNo ratings yet
- Thrombocytes (Platelets)Document13 pagesThrombocytes (Platelets)Zubda ButtNo ratings yet
- Kidney Learning Guide SeriesDocument43 pagesKidney Learning Guide SeriesRegita Indah Cahyani 7ANo ratings yet
- NCPDocument11 pagesNCPRyan Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- HypothyroidismDocument15 pagesHypothyroidismfachrulmirzaNo ratings yet
- Spermatogenesis Practical File For Clas 12THDocument7 pagesSpermatogenesis Practical File For Clas 12THSiddhartha SinghNo ratings yet
- Uro-Radiology Text and AtlassDocument257 pagesUro-Radiology Text and Atlassnancymariscal100% (1)
- Biology of ShrimpDocument12 pagesBiology of ShrimpNarasimha MurthyNo ratings yet
- Orl BR PDFDocument417 pagesOrl BR PDFAhmed Morsy100% (9)
- MalocclusionDocument60 pagesMalocclusionJeff ZachNo ratings yet
- Pain PathwayDocument6 pagesPain PathwayEynaRoslanNo ratings yet
- Botany and Zoology (Grade 12-Biology Reviewer)Document12 pagesBotany and Zoology (Grade 12-Biology Reviewer)Patricia GarciaNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic Disorders, Thromboembolic Disease, and ShockDocument87 pagesHemodynamic Disorders, Thromboembolic Disease, and Shockgifty100% (1)
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument12 pagesChemical Coordination and Integrationdlotlikar767No ratings yet
- Anatomy For The Gynecologic OncologistDocument70 pagesAnatomy For The Gynecologic OncologistjroshsperlingNo ratings yet
Organization of Nervous System: Anatomic Divisions
Organization of Nervous System: Anatomic Divisions
Uploaded by
Dr P N N Reddy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
90 views2 pagesThe nervous system can be divided anatomically into the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS is comprised of the brain and spinal cord and contains neuronal cell bodies and processes. The PNS contains cranial and peripheral nerves and some neuronal cell bodies in ganglia as well as axonal processes and glial cells. The nervous system can also be divided functionally into sensory and motor divisions for input and output.
Original Description:
Introduction to Nervous System
Original Title
Introduction to Nervous System
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe nervous system can be divided anatomically into the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS is comprised of the brain and spinal cord and contains neuronal cell bodies and processes. The PNS contains cranial and peripheral nerves and some neuronal cell bodies in ganglia as well as axonal processes and glial cells. The nervous system can also be divided functionally into sensory and motor divisions for input and output.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
90 views2 pagesOrganization of Nervous System: Anatomic Divisions
Organization of Nervous System: Anatomic Divisions
Uploaded by
Dr P N N ReddyThe nervous system can be divided anatomically into the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS is comprised of the brain and spinal cord and contains neuronal cell bodies and processes. The PNS contains cranial and peripheral nerves and some neuronal cell bodies in ganglia as well as axonal processes and glial cells. The nervous system can also be divided functionally into sensory and motor divisions for input and output.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
NEUROANATOMY 1
Introduction
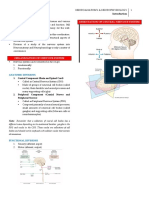
Human Body consists of abundant tissues and various ANATOMIC DIVISIONS
organs that are diverse in structure and function. Still 1. Central Component (Brain and Spinal Cord)
they function together, and in harmony, for the well- Called as Central Nervous System (CNS)
being of the body Made of groups of neuronal cell bodies (called
Nervous system plays a pivotal role in this coordination nuclei), their dendritic and axonal processes and
Neuroanatomy is the study of the structural aspects of many supporting cells (glia)
the nervous system 2. Peripheral Component (Cranial Nerves and
Division of a study of the nervous system into Peripheral Nerves)
Neuroanatomy and Neurophysiology is only a matter of Called as Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
convenience Composed primarily of axonal neural processes,
small amounts of neuronal cell bodies (called
ORGANIZATION OF NERVOUS SYSTEM ganglia) and supporting cells (Schwann cells or
neurolemmacytes)
Nervous system can be described in two ways
1. Anatomically
2. Functionally
I Brihaspathi Academy I Subscriber’s Copy I
Help Line: +91 91644 76636
www.brihaspathiacademy.com
NEUROANATOMY 2
Introduction
Note: Remember that a collection of neural cell bodies has a ORIENTATION OF CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
different name depending on its anatomical location: ganglia in the
PNS and nuclei in the CNS. These nuclei are collections of cell
bodies and should not be confused with cellular nuclei that contain
chromosomes.
FUNCTIONAL DIVISIONS
1. Sensory (afferent, input)
2. Motor (efferent, output)
I Brihaspathi Academy I Subscriber’s Copy I
Help Line: +91 91644 76636
www.brihaspathiacademy.com
You might also like
- 1.microbiology - Bacteriology MCQs FormattedDocument73 pages1.microbiology - Bacteriology MCQs FormattedDr P N N Reddy94% (17)
- Notes From An Alternate Universe - Introduction To A New Way of ThinkingDocument145 pagesNotes From An Alternate Universe - Introduction To A New Way of Thinkingzootsuit7100% (1)
- The Correlation of Sleep and Academic Performance: February 2021Document12 pagesThe Correlation of Sleep and Academic Performance: February 2021Kristel EyyyNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Sleep Deprivation On Decision Making - ReviewDocument14 pagesThe Impact of Sleep Deprivation On Decision Making - ReviewAna Viegas100% (1)
- The Effects of Sleep Deprivation On TheDocument7 pagesThe Effects of Sleep Deprivation On ThePrincess Martinez100% (1)
- Research Proposal Group 2Document30 pagesResearch Proposal Group 2Anthony PelayoNo ratings yet
- GegegegeDocument13 pagesGegegegeLuis CatindoyNo ratings yet
- Annotated Bibliography FinalDocument8 pagesAnnotated Bibliography Finalapi-253450997No ratings yet
- Yung Chapter 5 Nalang Tas Print NaDocument19 pagesYung Chapter 5 Nalang Tas Print NaMitchico CanonicatoNo ratings yet
- Productivity Posits That Regardless If An Individual Is Single, Living With SomeoneDocument6 pagesProductivity Posits That Regardless If An Individual Is Single, Living With Someonejankarl199160% (5)
- Synthesis PaperDocument4 pagesSynthesis PaperEthan FreemanNo ratings yet
- Nuñez Survey InstrumentDocument3 pagesNuñez Survey InstrumentAnna Carmela NuñezNo ratings yet
- 0 - Group 2 Edited FinalDocument23 pages0 - Group 2 Edited Finalana jean gamoNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Sleep Habits and Academic Performance in Dental Students in CroatiaDocument8 pagesThe Relationship Between Sleep Habits and Academic Performance in Dental Students in CroatiaBeatrizCamposNo ratings yet
- Sleep CodebookDocument6 pagesSleep CodebookJunn Ree Montilla100% (1)
- Movie Reflection On Dr. StrangeDocument4 pagesMovie Reflection On Dr. StrangefrustratedlawstudentNo ratings yet
- Final PaperDocument52 pagesFinal PaperRalph Carlos VelasNo ratings yet
- Final Research ProposalDocument14 pagesFinal Research Proposaladrian quinto100% (1)
- The ThesisDocument8 pagesThe ThesisTerraMonsta BlogspotNo ratings yet
- Sleep Deprivation and College Students 1 4Document11 pagesSleep Deprivation and College Students 1 4api-385639709No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document14 pagesChapter 3KayeJane Quiatchon-TalingtingNo ratings yet
- The Relation of Grades 9 and 10 Students' Sleeping Patterns and Their Attendance in Saint Francis of Assisi College Main CampusDocument15 pagesThe Relation of Grades 9 and 10 Students' Sleeping Patterns and Their Attendance in Saint Francis of Assisi College Main CampusJesary Marc ArnosaNo ratings yet
- Sample Qualitative Research1Document53 pagesSample Qualitative Research1AkiraNo ratings yet
- Sleep DeprivationDocument6 pagesSleep Deprivationarsh13No ratings yet
- The Impact of Sleep Deprivation To Student' Mental HealthDocument8 pagesThe Impact of Sleep Deprivation To Student' Mental HealthKrizelle LivaraNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument15 pagesAbstractDeanne Mitzi SomolloNo ratings yet
- Pe Reporting Group 1 With QuizDocument11 pagesPe Reporting Group 1 With QuizBeverly Jen Semine EnocNo ratings yet
- Sleep Deprivation Stem CaviteDocument57 pagesSleep Deprivation Stem CaviteLesley NaraNo ratings yet
- Sleep DeprivationDocument23 pagesSleep DeprivationMelody ManadongNo ratings yet
- G12RRR PR2 G1...Document18 pagesG12RRR PR2 G1...Hanny ValenciaNo ratings yet
- The Cytoskeleton Is A Network of Filament and Tubules That Extends Throughout A CellDocument9 pagesThe Cytoskeleton Is A Network of Filament and Tubules That Extends Throughout A CellHania GulNo ratings yet
- The Level of Mental and Physical Effects of Sleep Deprivation On Grade 12 StudentsDocument4 pagesThe Level of Mental and Physical Effects of Sleep Deprivation On Grade 12 StudentsAnnica Grizzel WongNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument17 pagesResearch ProposalKyle AshleyNo ratings yet
- Neuro Rehab Assignment Pt2 - Divina MahtaniDocument2 pagesNeuro Rehab Assignment Pt2 - Divina Mahtanidivina0% (1)
- Chapter 2Document4 pagesChapter 2Lawrence LuceñoNo ratings yet
- Veritas Listening QuizDocument1 pageVeritas Listening QuizMushy_ayaNo ratings yet
- Sleep Deprivation and Mental HealthDocument4 pagesSleep Deprivation and Mental Healthapi-341198049No ratings yet
- Effects of Sleep Deprivation To The Mental Health Stability of Selected G9 Students of RMCHS-with-cover-page-V2 (Appendix)Document57 pagesEffects of Sleep Deprivation To The Mental Health Stability of Selected G9 Students of RMCHS-with-cover-page-V2 (Appendix)Sebastian CrayNo ratings yet
- University of Makati Higher Schoolng UmakDocument61 pagesUniversity of Makati Higher Schoolng UmakChesca ApologistaNo ratings yet
- Review of Related Literature and StudiesDocument3 pagesReview of Related Literature and StudiesDANIELLE JOYCE BACSALNo ratings yet
- 2 - RA5527 Philippine Medical Technology Act of 1969Document4 pages2 - RA5527 Philippine Medical Technology Act of 1969Morticia VizactyhNo ratings yet
- The Problem and Its Background Introduction and BackgroundDocument17 pagesThe Problem and Its Background Introduction and Backgroundrozel jan espisoNo ratings yet
- Final Research Paper Effects of Sleep Deprivation On The Academic Performance of Senior High School StudentsDocument130 pagesFinal Research Paper Effects of Sleep Deprivation On The Academic Performance of Senior High School StudentsZyrel OtucanNo ratings yet
- Sports: Physical Education 04 2 Semester, SY 2020-2021Document23 pagesSports: Physical Education 04 2 Semester, SY 2020-2021hoohooNo ratings yet
- Effect of Sleep Deprivation On College Students' Academic PerformanceDocument10 pagesEffect of Sleep Deprivation On College Students' Academic PerformanceVirgil Viral Shah0% (1)
- HUMSS PRACTICAL RESEARCH PRDocument37 pagesHUMSS PRACTICAL RESEARCH PRyuanaaerith13No ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Nature and Scope of Physical Education, Exercise Science, and SportDocument39 pagesChapter 1: Nature and Scope of Physical Education, Exercise Science, and SportmyraturaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Student Nutrion On Academic PerformanceDocument45 pagesEffects of Student Nutrion On Academic PerformanceAbdifatah SaidNo ratings yet
- The Correlation Between Sleep Quality and Levels of Stress Among Students in Universitas IndonesiaDocument5 pagesThe Correlation Between Sleep Quality and Levels of Stress Among Students in Universitas IndonesiaKripa SriramNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - The Chemical Level of OrganizationDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - The Chemical Level of OrganizationChristina MarkwartNo ratings yet
- Formerly Ramon Magsaysay Technological UniversityDocument5 pagesFormerly Ramon Magsaysay Technological UniversityJoanne Saromo100% (1)
- Theories of Motor ControlDocument1 pageTheories of Motor ControlAqembunNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Sleep On Academic Performance and Job PerformanceDocument18 pagesThe Effects of Sleep On Academic Performance and Job PerformanceKen DobsNo ratings yet
- Students Satisfaction To The Services Rendered by The School Library of Santa. Teresita National High SchoolDocument26 pagesStudents Satisfaction To The Services Rendered by The School Library of Santa. Teresita National High SchoolLyndsey Ann BaetNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Intake Among Older People of Hermana Fausta Development Center, Lucena City and Its Relationship To Physical Health StatusDocument20 pagesNutritional Intake Among Older People of Hermana Fausta Development Center, Lucena City and Its Relationship To Physical Health StatusAngelNo ratings yet
- "Relationship With The Earth": Lesson 1: Introduction To Philosphy of The Human PersonDocument6 pages"Relationship With The Earth": Lesson 1: Introduction To Philosphy of The Human PersonMayeNo ratings yet
- Reflex ResponseDocument10 pagesReflex Responseapi-264015665No ratings yet
- Research 1-4 (gROUP 4)Document44 pagesResearch 1-4 (gROUP 4)Gly Ann Homerez LopinaNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Is Defined As "A State of Well-Being in Which Every IndividualDocument7 pagesMental Health Is Defined As "A State of Well-Being in Which Every IndividualmejulNo ratings yet
- Orientation of Central Nervous System: Neuroanatomy & Neurophysiology 1Document1 pageOrientation of Central Nervous System: Neuroanatomy & Neurophysiology 1Dr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Written Report 2Document24 pagesNervous System Written Report 2Noronisa PendalidayNo ratings yet
- DR Narendranatha Reddy Profile 15 April 2018 PDFDocument5 pagesDR Narendranatha Reddy Profile 15 April 2018 PDFDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Schedule TemplateDocument1 pageSchedule TemplateDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Test Marking (EMD) TemplateDocument1 pageTest Marking (EMD) TemplateDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Aipg 5Document64 pagesAipg 5Dr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- 1.structure of BacteriaDocument12 pages1.structure of BacteriaDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MicrobiologyDocument1 pageIntroduction To MicrobiologyDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- CNS PNS: Lipofuscin: Wear and TearDocument10 pagesCNS PNS: Lipofuscin: Wear and TearDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- General Histology FinalDocument60 pagesGeneral Histology FinalDr P N N Reddy100% (1)
- 6.nerves of Head and NeckDocument36 pages6.nerves of Head and NeckDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- 1.embryology Q ADocument11 pages1.embryology Q ADr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- 2.osteology Q ADocument11 pages2.osteology Q ADr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Aiims May 2014-QuestionsDocument7 pagesAiims May 2014-QuestionsDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Orientation of Central Nervous System: Neuroanatomy & Neurophysiology 1Document1 pageOrientation of Central Nervous System: Neuroanatomy & Neurophysiology 1Dr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Nerve Muscle PhysiologyDocument18 pagesNerve Muscle PhysiologyDr P N N Reddy100% (2)
- CNS PNS: Absent in AxonsDocument6 pagesCNS PNS: Absent in AxonsDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Embryology Synopsis-Panineeya DemoDocument13 pagesEmbryology Synopsis-Panineeya DemoDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Spinal Nerves - Introduction: Neuro Anatomy & Physiology 1Document5 pagesSpinal Nerves - Introduction: Neuro Anatomy & Physiology 1Dr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and The Somatic Nervous System PDFDocument4 pagesNeural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and The Somatic Nervous System PDFAmandaNo ratings yet
- Deepthashree K - 642153000020249 2Document1 pageDeepthashree K - 642153000020249 2Deeptha AravamudhanNo ratings yet
- Inflammation and HealingDocument15 pagesInflammation and HealingRachel Niu II100% (1)
- Review of Ayurvedic Drugs Acting On Hypothyroidism: Tarun Sharma, Malvika, Monu Gupta, Sumit NathaniDocument8 pagesReview of Ayurvedic Drugs Acting On Hypothyroidism: Tarun Sharma, Malvika, Monu Gupta, Sumit NathaniVakamalla SubbareddyNo ratings yet
- Orphan G Protein-Coupled Receptors and Novel NeuropeptidesDocument267 pagesOrphan G Protein-Coupled Receptors and Novel NeuropeptidesIsmaelVázquezEspinozaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine NotesDocument157 pagesEndocrine NotesLaila Cristine CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka TirotoksikosisDocument2 pagesDaftar Pustaka TirotoksikosisCut Mulya MutiaNo ratings yet
- David Carreras - A Cunnilinguist's Guide To Mind-Blowing Oral SexDocument6 pagesDavid Carreras - A Cunnilinguist's Guide To Mind-Blowing Oral SexKostyaNo ratings yet
- LESSON-PLAN-ON-PHYSIOLogical Changes During PregnancyDocument22 pagesLESSON-PLAN-ON-PHYSIOLogical Changes During PregnancyV.srivaniNo ratings yet
- Sinelnikov Vol IIIDocument395 pagesSinelnikov Vol IIIFlorescu Diana NicoletaNo ratings yet
- Genito Urinary TraumaDocument16 pagesGenito Urinary TraumaAjibola OlamideNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Blood Banking: Immunohaematology I (Dml405) S.Y. Pan (2009)Document15 pagesIntroduction To Blood Banking: Immunohaematology I (Dml405) S.Y. Pan (2009)shing_yiNo ratings yet
- Types of Skull FractureDocument5 pagesTypes of Skull FractureKhor Hui DiNo ratings yet
- PdfText - 2022-12-15T172553.484Document1 pagePdfText - 2022-12-15T172553.484Himanshu MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- The Complement SystemDocument9 pagesThe Complement SystemAxel RamírezNo ratings yet
- Concomitant Developmental Dental Anomalies in Chinese Children With Dens EvaginatusDocument5 pagesConcomitant Developmental Dental Anomalies in Chinese Children With Dens EvaginatusFernanda CombaNo ratings yet
- Thrombocytes (Platelets)Document13 pagesThrombocytes (Platelets)Zubda ButtNo ratings yet
- Kidney Learning Guide SeriesDocument43 pagesKidney Learning Guide SeriesRegita Indah Cahyani 7ANo ratings yet
- NCPDocument11 pagesNCPRyan Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- HypothyroidismDocument15 pagesHypothyroidismfachrulmirzaNo ratings yet
- Spermatogenesis Practical File For Clas 12THDocument7 pagesSpermatogenesis Practical File For Clas 12THSiddhartha SinghNo ratings yet
- Uro-Radiology Text and AtlassDocument257 pagesUro-Radiology Text and Atlassnancymariscal100% (1)
- Biology of ShrimpDocument12 pagesBiology of ShrimpNarasimha MurthyNo ratings yet
- Orl BR PDFDocument417 pagesOrl BR PDFAhmed Morsy100% (9)
- MalocclusionDocument60 pagesMalocclusionJeff ZachNo ratings yet
- Pain PathwayDocument6 pagesPain PathwayEynaRoslanNo ratings yet
- Botany and Zoology (Grade 12-Biology Reviewer)Document12 pagesBotany and Zoology (Grade 12-Biology Reviewer)Patricia GarciaNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic Disorders, Thromboembolic Disease, and ShockDocument87 pagesHemodynamic Disorders, Thromboembolic Disease, and Shockgifty100% (1)
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument12 pagesChemical Coordination and Integrationdlotlikar767No ratings yet
- Anatomy For The Gynecologic OncologistDocument70 pagesAnatomy For The Gynecologic OncologistjroshsperlingNo ratings yet