Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science UB1Scheme
Science UB1Scheme
Uploaded by
LEENA HingCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5824)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- NRPH AlgoDocument13 pagesNRPH AlgoJm Jm100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Anatomy and Physiology - Dengue FeverDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Dengue Feverhael yam62% (13)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Chemf 4 Chap 1Document21 pagesChemf 4 Chap 1LEENA HingNo ratings yet
- Element Fe O: Find The Empirical Formula For A Compound Containing 40.6% Carbon, 5.1% Hydrogen, and 54.2% OxygenDocument8 pagesElement Fe O: Find The Empirical Formula For A Compound Containing 40.6% Carbon, 5.1% Hydrogen, and 54.2% OxygenLEENA HingNo ratings yet
- Exercise (Chapter 7 Rate of Reaction)Document3 pagesExercise (Chapter 7 Rate of Reaction)LEENA HingNo ratings yet
- Asteroids, Meteoroids and CometsDocument4 pagesAsteroids, Meteoroids and CometsLEENA HingNo ratings yet
- 1 A.U. 1.5 X 10 KM: Solar SystemDocument8 pages1 A.U. 1.5 X 10 KM: Solar SystemLEENA HingNo ratings yet
- Crossword Puzzle GalaxiesDocument1 pageCrossword Puzzle GalaxiesLEENA HingNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM 2016 Peraturan PemarkahanDocument1 pageChemistry: Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM 2016 Peraturan PemarkahanLEENA HingNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 - Textbook ExerciseDocument8 pagesCHAPTER 1 - Textbook ExerciseLEENA HingNo ratings yet
- Quizchapter 3 Techniques of Measuring The Paramaters of Body HealthDocument1 pageQuizchapter 3 Techniques of Measuring The Paramaters of Body HealthLEENA HingNo ratings yet
- Science f3 UB1Document7 pagesScience f3 UB1LEENA HingNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Lesson Plan SCDocument5 pagesDigestive System Lesson Plan SCJustine PamaNo ratings yet
- Soal Bahasa Inggris Kelas Xi Semester 2Document9 pagesSoal Bahasa Inggris Kelas Xi Semester 2Vera NithaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System GlossaryDocument2 pagesCirculatory System Glossarykloaizar100% (1)
- TLIF6307A - Administer The Implementation of Fatigue Management Strategies - Learner GuideDocument83 pagesTLIF6307A - Administer The Implementation of Fatigue Management Strategies - Learner GuideromerofredNo ratings yet
- Tissue and Its ClassificationDocument6 pagesTissue and Its ClassificationPriyanjali Saini100% (1)
- Blood Transfusion ReactionsDocument51 pagesBlood Transfusion ReactionsIgwe SolomonNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Long Quiz 1 Resp and Circ SystemDocument2 pagesScience 9 Long Quiz 1 Resp and Circ SystemMansor P. SalikNo ratings yet
- Blood Clotting NotesDocument12 pagesBlood Clotting NotesFateh MohammadNo ratings yet
- CBC Form Neonates 2021 NewDocument1 pageCBC Form Neonates 2021 NewGCMDHNo ratings yet
- Blood Group1Document19 pagesBlood Group1hrishi rajNo ratings yet
- ApheresisDocument5 pagesApheresisGRK BIOMEDNo ratings yet
- Temperature Compensation in Ecto, Endo and HeterothermsDocument24 pagesTemperature Compensation in Ecto, Endo and HeterothermsKiran Hassan0% (1)
- Respiratory System NotesDocument6 pagesRespiratory System NotesRaduNo ratings yet
- Reflex Facilitation: Vol Control of Micturition (Corticol Areas) Control EUS & Abd MDocument1 pageReflex Facilitation: Vol Control of Micturition (Corticol Areas) Control EUS & Abd MTharani KumaraNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument6 pagesStructural Organisation in AnimalsbasheerskNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 4Document10 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 4Bella Mae Belle TaladuaNo ratings yet
- I. Attachments Worksheets Worksheet 1 How Does Blood Flow in My Body?Document8 pagesI. Attachments Worksheets Worksheet 1 How Does Blood Flow in My Body?elizalde100% (1)
- Chapter Tour 1: Chapter 1 - Introduction To Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesChapter Tour 1: Chapter 1 - Introduction To Human Anatomy and Physiologyapi-340693501No ratings yet
- (CLINPATH) 2.02 Transfusion II - Dr.-VillamayorDocument7 pages(CLINPATH) 2.02 Transfusion II - Dr.-VillamayorpasambalyrradjohndarNo ratings yet
- 21 - Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument16 pages21 - Peripheral Nervous Systembhavikrao7605No ratings yet
- BioA4 07. Gas Exchange in HumansDocument6 pagesBioA4 07. Gas Exchange in Humansthanks btNo ratings yet
- EMT Chapter 10 Vocabulary Flashcards - PT 2Document2 pagesEMT Chapter 10 Vocabulary Flashcards - PT 2Emily CallerNo ratings yet
- Local Media1995767886843754234Document10 pagesLocal Media1995767886843754234Haimen BuisanNo ratings yet
- Genito Urinary System Groupe 12Document7 pagesGenito Urinary System Groupe 12Lina BoutakakineNo ratings yet
- YogaTherapyforDigestiveHealth PDFDocument3 pagesYogaTherapyforDigestiveHealth PDFrabirm77No ratings yet
- Blood Bank SOP 2015Document52 pagesBlood Bank SOP 2015ddophlaak labdeptNo ratings yet
- 1 Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pages1 Cardiovascular SystemWaltz PadlanNo ratings yet
- Compare The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesCompare The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits of The Cardiovascular Systememanuel coatesNo ratings yet
Science UB1Scheme
Science UB1Scheme
Uploaded by
LEENA HingCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science UB1Scheme
Science UB1Scheme
Uploaded by
LEENA HingCopyright:
Available Formats
Scheme – Science F3
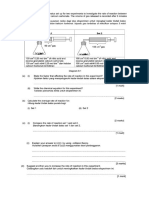
1ai Diffusion
ii Oxygen dissolves in the alveolus and diffuse into the blood capillaries.
Oxygen combine with haemoglobin in red blood cells to form oxyhaemoglobin
iii Through diffusion
Oxygen diffuse into the blood capillaries
Diffusion take place from area of high concentration to low concentration
Oxygen combine with haemoglobin to form oxyhaemoglobin and carries it around the body
cells
iv During inhalation, ribcage move up , diaphragm contract
Thoracic cavity increase, air pressure inside the lung is lowered, air is forced into the lungs
During exhalation, ribcage move down , diaphragm relax
Thoracic cavity decrease, air pressure inside the lung is higher, air is forced out of the lungs
v One cell thick wall
Moist surface
Surrounded with blood capillaries
b The amount of oxygen in exhaled air is lower than inhaled air
Oxygen is used for respiration and metabolism
The amount of carbon dioxide in exhaled air is higher than inhaled air
Carbon dioxide is eliminated as excretory product
c Tar- blacken the lung and cause lung cancer
Nicotine- cause addiction
2a S- cortex T-medulla U-pelvis
b/c Glucose and protein molecule are too big to be filtered in the kidney/ cannot pass through
the kidney
Glucose is completely reabsorbed by the kidney back to the bloodstream
d Filter blood
Regulate water and minerals
Reabsorb water or useful material
e Renal artery
Renal artery carry waste product such as urea from liver to kidney for elimination
Renal vein carry blood after waste product have been removed to the heart
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5824)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- NRPH AlgoDocument13 pagesNRPH AlgoJm Jm100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Anatomy and Physiology - Dengue FeverDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Dengue Feverhael yam62% (13)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Chemf 4 Chap 1Document21 pagesChemf 4 Chap 1LEENA HingNo ratings yet
- Element Fe O: Find The Empirical Formula For A Compound Containing 40.6% Carbon, 5.1% Hydrogen, and 54.2% OxygenDocument8 pagesElement Fe O: Find The Empirical Formula For A Compound Containing 40.6% Carbon, 5.1% Hydrogen, and 54.2% OxygenLEENA HingNo ratings yet
- Exercise (Chapter 7 Rate of Reaction)Document3 pagesExercise (Chapter 7 Rate of Reaction)LEENA HingNo ratings yet
- Asteroids, Meteoroids and CometsDocument4 pagesAsteroids, Meteoroids and CometsLEENA HingNo ratings yet
- 1 A.U. 1.5 X 10 KM: Solar SystemDocument8 pages1 A.U. 1.5 X 10 KM: Solar SystemLEENA HingNo ratings yet
- Crossword Puzzle GalaxiesDocument1 pageCrossword Puzzle GalaxiesLEENA HingNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM 2016 Peraturan PemarkahanDocument1 pageChemistry: Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM 2016 Peraturan PemarkahanLEENA HingNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 - Textbook ExerciseDocument8 pagesCHAPTER 1 - Textbook ExerciseLEENA HingNo ratings yet
- Quizchapter 3 Techniques of Measuring The Paramaters of Body HealthDocument1 pageQuizchapter 3 Techniques of Measuring The Paramaters of Body HealthLEENA HingNo ratings yet
- Science f3 UB1Document7 pagesScience f3 UB1LEENA HingNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Lesson Plan SCDocument5 pagesDigestive System Lesson Plan SCJustine PamaNo ratings yet
- Soal Bahasa Inggris Kelas Xi Semester 2Document9 pagesSoal Bahasa Inggris Kelas Xi Semester 2Vera NithaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System GlossaryDocument2 pagesCirculatory System Glossarykloaizar100% (1)
- TLIF6307A - Administer The Implementation of Fatigue Management Strategies - Learner GuideDocument83 pagesTLIF6307A - Administer The Implementation of Fatigue Management Strategies - Learner GuideromerofredNo ratings yet
- Tissue and Its ClassificationDocument6 pagesTissue and Its ClassificationPriyanjali Saini100% (1)
- Blood Transfusion ReactionsDocument51 pagesBlood Transfusion ReactionsIgwe SolomonNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Long Quiz 1 Resp and Circ SystemDocument2 pagesScience 9 Long Quiz 1 Resp and Circ SystemMansor P. SalikNo ratings yet
- Blood Clotting NotesDocument12 pagesBlood Clotting NotesFateh MohammadNo ratings yet
- CBC Form Neonates 2021 NewDocument1 pageCBC Form Neonates 2021 NewGCMDHNo ratings yet
- Blood Group1Document19 pagesBlood Group1hrishi rajNo ratings yet
- ApheresisDocument5 pagesApheresisGRK BIOMEDNo ratings yet
- Temperature Compensation in Ecto, Endo and HeterothermsDocument24 pagesTemperature Compensation in Ecto, Endo and HeterothermsKiran Hassan0% (1)
- Respiratory System NotesDocument6 pagesRespiratory System NotesRaduNo ratings yet
- Reflex Facilitation: Vol Control of Micturition (Corticol Areas) Control EUS & Abd MDocument1 pageReflex Facilitation: Vol Control of Micturition (Corticol Areas) Control EUS & Abd MTharani KumaraNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument6 pagesStructural Organisation in AnimalsbasheerskNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 4Document10 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 4Bella Mae Belle TaladuaNo ratings yet
- I. Attachments Worksheets Worksheet 1 How Does Blood Flow in My Body?Document8 pagesI. Attachments Worksheets Worksheet 1 How Does Blood Flow in My Body?elizalde100% (1)
- Chapter Tour 1: Chapter 1 - Introduction To Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesChapter Tour 1: Chapter 1 - Introduction To Human Anatomy and Physiologyapi-340693501No ratings yet
- (CLINPATH) 2.02 Transfusion II - Dr.-VillamayorDocument7 pages(CLINPATH) 2.02 Transfusion II - Dr.-VillamayorpasambalyrradjohndarNo ratings yet
- 21 - Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument16 pages21 - Peripheral Nervous Systembhavikrao7605No ratings yet
- BioA4 07. Gas Exchange in HumansDocument6 pagesBioA4 07. Gas Exchange in Humansthanks btNo ratings yet
- EMT Chapter 10 Vocabulary Flashcards - PT 2Document2 pagesEMT Chapter 10 Vocabulary Flashcards - PT 2Emily CallerNo ratings yet
- Local Media1995767886843754234Document10 pagesLocal Media1995767886843754234Haimen BuisanNo ratings yet
- Genito Urinary System Groupe 12Document7 pagesGenito Urinary System Groupe 12Lina BoutakakineNo ratings yet
- YogaTherapyforDigestiveHealth PDFDocument3 pagesYogaTherapyforDigestiveHealth PDFrabirm77No ratings yet
- Blood Bank SOP 2015Document52 pagesBlood Bank SOP 2015ddophlaak labdeptNo ratings yet
- 1 Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pages1 Cardiovascular SystemWaltz PadlanNo ratings yet
- Compare The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesCompare The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits of The Cardiovascular Systememanuel coatesNo ratings yet