Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Clinical Practice Guide On Antithrombotic Drug Dosing and Management of Antithrombotic Drug-Associated Bleeding Complications in Adults
Clinical Practice Guide On Antithrombotic Drug Dosing and Management of Antithrombotic Drug-Associated Bleeding Complications in Adults
Uploaded by
darekshepardOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Clinical Practice Guide On Antithrombotic Drug Dosing and Management of Antithrombotic Drug-Associated Bleeding Complications in Adults
Clinical Practice Guide On Antithrombotic Drug Dosing and Management of Antithrombotic Drug-Associated Bleeding Complications in Adults
Uploaded by
darekshepardCopyright:
Available Formats
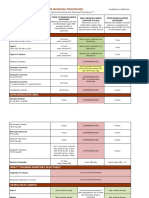
2.
Reversal of Low-Molecular-Weight Heparins [Dalteparin (Fragmin®), III. Antiplatelet Agent Reversal
QUICK REFERENCE
Enoxaparin (Lovenox®), Tinzaparin (Innohep®)] and Fondaparinux1 (Arixtra®)
Abbreviations: PCC, prothrombin complex concentrates, rFVIIa, recombinant factor VIIa Aspirin, Aspirin/Dipyridamole (Aggrenox®), Clopidogrel (Plavix®), Prasugrel (Effient®),
Non-Urgent Urgent (Not Bleeding) Urgent (Bleeding) * Commonly available tests to assess for presence of dabigatran are the aPTT and for
rivaroxaban the PT. These tests may be prolonged when dabigatran and rivaroxaban are used
Ticagrelor (Brilinta®) Clinical Practice Guide
General Considerations
• Hold day of procedure
• Once-daily regimens
• Wait 12-24 hours if possible
• Consider protamine sulfate
• HASHTI
• Protamine sulfate
at recommended doses but they do not reliably measure the anticoagulant activity. Therapeutic
levels of apixaban may not elevate the PT. To measure anticoagulant activity, the ecarin clotting
1. Plasma half-lives on Antithrombotic Drug
° ½ dose day prior
• Twice-daily regimens
if delay not possible for high
bleeding risk procedure
• Consider rVIIa
time (ECT) or dilute thrombin time for dabigatran and chromogenic anti-Factor Xa assays using
validated calibrators and controls may be used for rivaroxaban and apixaban.
a. Clopidogrel, dipyridamole, prasugrel, ticagrelor: 7-10 hours
b. Low-dose aspirin (150 mg daily): 2-4.5 hours Dosing and Management
° Hold evening dose day
prior ** Dabigatran, rivaroxaban and apixaban are excreted in the urine, therefore maintain adequate
diuresis. Rivaroxaban and apixaban are highly protein bound so dialysis is not effective.
c. Overdose aspirin (>4000 mg): 15-30 hours
2. Reversibility of antiplatelet effect of Antithrombotic Drug-
Fondaparinux has no specific antidote
1
C. Converting Between Anticoagulants1
a. Aspirin, clopidogrel,and prasugrel inhibit platelet function for lifetime of the
platelets. Inhibition takes 7-10 days to resolve as new platelets are generated. Associated Bleeding
3. Protamine Dose for Reversal of Heparin and LMWH
Agent* Half-Life Protamine Sulfate Dosing for Reversal
Current Anticoagulant
anticoagulant to be converted
Procedure
b. Ticagrelor is a reversible inhibitor, so platelet function normalizes after drug
clearance. Hold a minimum of 5 days to reverse effect. Unclear if platelet Complications in Adults
All Maximum dose is 50 mg to
transfusion will be effective in reversing effect if given within 5-7 days of last February 2014*
dose.
Heparin 1-2 hours • 1 mg per 90-100 units heparin given in previous 2-3 Warfarin Dabigatran or Discontinue warfarin and start dabigatran or 3. Circulating drug or active metabolites can inhibit transfused platelets. Mary Cushman1
hours (INR 2-3) Apixaban apixaban when INR <2.0 4. Must consider indication for use in decision to reverse Wendy Lim2
a. Risk of coronary stent occlusion (which can be fatal) within 3 months of bare Neil A Zakai1
° e.g., 25-35 mg if 1000-1250 units/hour heparin infusion Warfarin Rivaroxaban Discontinue warfarin and start rivaroxaban when
metal stent implantation; period of risk is likely longer for drug-eluting stents.
Enoxaparin 4.5 hours • 1 mg per 1 mg Enoxaparin in previous 8 hours (INR 2-3) INR <3.0
b. Consult cardiologist or current guideline recommendations if uncertain. 1
University of Vermont
Dalteparin 2.2 hours • 1 mg per 100 units Dalteparin in previous 8 hours LMWH or Dabigatran Start dabigatran 0-2 hours before administration
Reversal of Antiplatelet Agents
2
McMaster University
Heparin of last LMWH/Heparin dose, or at same time as
Tinzaparin 3.9 hours • 1 mg per 100 units Tinzaparin in previous 8 hours discontinuation of infusional heparin. Non-Urgent Urgent (Not Bleeding) Urgent (Bleeding)
*Half-life is longer with subcutaneous administration for all agents so may require monitoring LMWH or Rivaroxaban or Discontinue LMWH or heparin and initiate • Discontinue agent 5-10 • Consider platelet • HASHTI
with PTT (heparin) or anti-Xa level (LMWH) every 3 hours with repeat protamine (0.5 mg per Heparin Apixaban rivaroxaban or apixaban 0-2 hours prior to next days prior to procedure transfusion prior to high • Consider platelet
indicated amount of LMWH or heparin) if bleeding continues. scheduled LMWH/Heparin dose. risk bleeding procedures transfusion
4. Reversal of Dabigatran, Rivaroxaban or Apixaban Dabigatran LMWH or Heparin CrCl ≥ 30 ml/min: start 12 hours after last dose of This document summarizes selected recommendations from the: American College of Chest
Non-urgent: Hold further doses (refer to table for recommended duration). Con- dabigatran Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guideline on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic
sider longer times for major surgery, placement of spinal or epidural catheter or port. CrCl < 30 ml/min: start 24 hours after last dose of Therapy (9th Edition).
dabigatran
Dabigatran Rivaroxaban Apixaban This guide is intended to provide the practitioner with clear principles and strategies for quality
Rivaroxaban Warfarin -US: Initiate warfarin and a parental anticoagulant patient care and does not establish a fixed set of rules that preempt physician judgment.
CrCl > 50 ml/min: Hold 1-2 Hold at least 24 hours Hold 24 to 48 hours (INR 2-3) 24 hours after discontinuation of rivaroxaban
days Half Life: 5-9 hours Half Life: 8-15 hours. Drug -Canada: Continue rivaroxaban concomitantly For further information, please see the complete guidelines on the Chest Website at
CrCl < 50 ml/min: Hold 3-5 (with normal renal presence may be assessed by with warfarin until INR ≥2.0 and then discontinue http://journal.publications.chestnet.org/issue.aspx?journalid=99&issueid=23443 or refer to
days or longer. function). Drug anti-Xa assay. rivaroxaban2 the Practice Guidelines section of the ASH website at www.hematology.org/practiceguidelines.
Half Life: 12-14 hours presence may be You may also contact the ASH Department of Quality Improvement Programs at 202-776-0544.
Drug presence may be assessed by anti-Xa Rivaroxaban or LMWH or Heparin Initiate LMWH/Heparin 24 hours after
Apixaban discontinuation of Rivaroxaban or Apixaban. © 2014 by the American Society of Hematology. All rights reserved.
assessed by thrombin time. assay.
Images courtesy of Kenneth Mann, PhD, and Matthew Whelihan, MS.
Apixaban Warfarin Discontinue Apixaban and start warfarin 24 hours
Urgent: Hold further doses of dabigatran, rivaroxaban, or apixaban later3. If continuous anticoagulation desired, initiate
alternative anticoagulant while starting warfarin. Presented by the American Society of Hematology,
Draw baseline coagulation tests* Canada: Continue apixaban concomitantly with adapted in part from the American College of
Activated charcoal if recent ingestion: warfarin until INR ≥2.0 and then discontinue Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice
Apixaban: <6 hours • Dabigatran: <2 hours • Rivaroxaban: <8 hours apixaban1
Guideline on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic
Abbreviations: CrCl, creatinine clearance; INR, international normalized ratio; LMWH, low Therapy (9th Edition).
Normal aPTT—Unlikely dabigatran Prolonged aPTT—Dabigatran present molecular weight heparin
is contributing to bleeding and may be contributing to bleeding Conversion to and from rivaroxaban based on 20 mg daily dose for non-valvular atrial fibrillation. *This pocket guide is a revision of the 2011 Clinical
Normal PT—Unlikely rivaroxaban Prolonged PT—Rivaroxaban 1
Pradaxa® product monograph 2010, Xarelto® product monograph 2011, Eliquis® product Practice Guide on Anticoagulant Dosing and Management
is contributing to bleeding if last present and may be contributing to bleeding monograph 2012 of Anticoagulant-Associated Bleeding Complications in
ingestion >24 hours prior 2
Rivaroxaban affects INR, so INR measurements made during coadministration with Adults
No antidote available warfarin may not be useful for determining the appropriate dose of warfarin. To minimize this
For bleeding consider: phenomenon, measure INR at rivaroxaban trough. If continuous anticoagulation desired, stop American Society of Hematology Look for this pocket guide as a
HASHTI** PCC • activated PCC (FEIBA) • rFVIIa rivaroxaban and initiate alternative anticoagulant while starting warfarin. Xarelto® product 2021 L Street NW, Suite 900 downloadable app by searching
hemodialysis for dabigatran monograph 2011
Washington, DC 20036 for “ASH Guides” in the iTunes
(if patient has renal failure) 3
Apixaban affects INR, so INR measurements made during coadministration with warfarin store or Android market.
may not be useful for determining appropriate dose of warfarin. To minimize this phenomenon,
measure INR at apixaban trough.
www.hematology.org
Reassess patient Repeat abnormal coagulation tests*
2. Reversal of Low-Molecular-Weight Heparins [Dalteparin (Fragmin®), III. Antiplatelet Agent Reversal
QUICK REFERENCE
Enoxaparin (Lovenox®), Tinzaparin (Innohep®)] and Fondaparinux1 (Arixtra®)
Abbreviations: PCC, prothrombin complex concentrates, rFVIIa, recombinant factor VIIa Aspirin, Aspirin/Dipyridamole (Aggrenox®), Clopidogrel (Plavix®), Prasugrel (Effient®),
Non-Urgent Urgent (Not Bleeding) Urgent (Bleeding) * Commonly available tests to assess for presence of dabigatran are the aPTT and for
rivaroxaban the PT. These tests may be prolonged when dabigatran and rivaroxaban are used
Ticagrelor (Brilinta®) Clinical Practice Guide
General Considerations
• Hold day of procedure
• Once-daily regimens
• Wait 12-24 hours if possible
• Consider protamine sulfate
• HASHTI
• Protamine sulfate
at recommended doses but they do not reliably measure the anticoagulant activity. Therapeutic
levels of apixaban may not elevate the PT. To measure anticoagulant activity, the ecarin clotting
1. Plasma half-lives on Antithrombotic Drug
° ½ dose day prior
• Twice-daily regimens
if delay not possible for high
bleeding risk procedure
• Consider rVIIa
time (ECT) or dilute thrombin time for dabigatran and chromogenic anti-Factor Xa assays using
validated calibrators and controls may be used for rivaroxaban and apixaban.
a. Clopidogrel, dipyridamole, prasugrel, ticagrelor: 7-10 hours
b. Low-dose aspirin (150 mg daily): 2-4.5 hours Dosing and Management
° Hold evening dose day
prior ** Dabigatran, rivaroxaban and apixaban are excreted in the urine, therefore maintain adequate
diuresis. Rivaroxaban and apixaban are highly protein bound so dialysis is not effective.
c. Overdose aspirin (>4000 mg): 15-30 hours
2. Reversibility of antiplatelet effect of Antithrombotic Drug-
Fondaparinux has no specific antidote
1
C. Converting Between Anticoagulants1
a. Aspirin, clopidogrel,and prasugrel inhibit platelet function for lifetime of the
platelets. Inhibition takes 7-10 days to resolve as new platelets are generated. Associated Bleeding
3. Protamine Dose for Reversal of Heparin and LMWH
Agent* Half-Life Protamine Sulfate Dosing for Reversal
Current Anticoagulant
anticoagulant to be converted
Procedure
b. Ticagrelor is a reversible inhibitor, so platelet function normalizes after drug
clearance. Hold a minimum of 5 days to reverse effect. Unclear if platelet Complications in Adults
All Maximum dose is 50 mg to
transfusion will be effective in reversing effect if given within 5-7 days of last February 2014*
dose.
Heparin 1-2 hours • 1 mg per 90-100 units heparin given in previous 2-3 Warfarin Dabigatran or Discontinue warfarin and start dabigatran or 3. Circulating drug or active metabolites can inhibit transfused platelets. Mary Cushman1
hours (INR 2-3) Apixaban apixaban when INR <2.0 4. Must consider indication for use in decision to reverse Wendy Lim2
a. Risk of coronary stent occlusion (which can be fatal) within 3 months of bare Neil A Zakai1
° e.g., 25-35 mg if 1000-1250 units/hour heparin infusion Warfarin Rivaroxaban Discontinue warfarin and start rivaroxaban when
metal stent implantation; period of risk is likely longer for drug-eluting stents.
Enoxaparin 4.5 hours • 1 mg per 1 mg Enoxaparin in previous 8 hours (INR 2-3) INR <3.0
b. Consult cardiologist or current guideline recommendations if uncertain. 1
University of Vermont
Dalteparin 2.2 hours • 1 mg per 100 units Dalteparin in previous 8 hours LMWH or Dabigatran Start dabigatran 0-2 hours before administration
Reversal of Antiplatelet Agents
2
McMaster University
Heparin of last LMWH/Heparin dose, or at same time as
Tinzaparin 3.9 hours • 1 mg per 100 units Tinzaparin in previous 8 hours discontinuation of infusional heparin. Non-Urgent Urgent (Not Bleeding) Urgent (Bleeding)
*Half-life is longer with subcutaneous administration for all agents so may require monitoring LMWH or Rivaroxaban or Discontinue LMWH or heparin and initiate • Discontinue agent 5-10 • Consider platelet • HASHTI
with PTT (heparin) or anti-Xa level (LMWH) every 3 hours with repeat protamine (0.5 mg per Heparin Apixaban rivaroxaban or apixaban 0-2 hours prior to next days prior to procedure transfusion prior to high • Consider platelet
indicated amount of LMWH or heparin) if bleeding continues. scheduled LMWH/Heparin dose. risk bleeding procedures transfusion
4. Reversal of Dabigatran, Rivaroxaban or Apixaban Dabigatran LMWH or Heparin CrCl ≥ 30 ml/min: start 12 hours after last dose of This document summarizes selected recommendations from the: American College of Chest
Non-urgent: Hold further doses (refer to table for recommended duration). Con- dabigatran Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guideline on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic
sider longer times for major surgery, placement of spinal or epidural catheter or port. CrCl < 30 ml/min: start 24 hours after last dose of Therapy (9th Edition).
dabigatran
Dabigatran Rivaroxaban Apixaban This guide is intended to provide the practitioner with clear principles and strategies for quality
Rivaroxaban Warfarin -US: Initiate warfarin and a parental anticoagulant patient care and does not establish a fixed set of rules that preempt physician judgment.
CrCl > 50 ml/min: Hold 1-2 Hold at least 24 hours Hold 24 to 48 hours (INR 2-3) 24 hours after discontinuation of rivaroxaban
days Half Life: 5-9 hours Half Life: 8-15 hours. Drug -Canada: Continue rivaroxaban concomitantly For further information, please see the complete guidelines on the Chest Website at
CrCl < 50 ml/min: Hold 3-5 (with normal renal presence may be assessed by with warfarin until INR ≥2.0 and then discontinue http://journal.publications.chestnet.org/issue.aspx?journalid=99&issueid=23443 or refer to
days or longer. function). Drug anti-Xa assay. rivaroxaban2 the Practice Guidelines section of the ASH website at www.hematology.org/practiceguidelines.
Half Life: 12-14 hours presence may be You may also contact the ASH Department of Quality Improvement Programs at 202-776-0544.
Drug presence may be assessed by anti-Xa Rivaroxaban or LMWH or Heparin Initiate LMWH/Heparin 24 hours after
Apixaban discontinuation of Rivaroxaban or Apixaban. © 2014 by the American Society of Hematology. All rights reserved.
assessed by thrombin time. assay.
Images courtesy of Kenneth Mann, PhD, and Matthew Whelihan, MS.
Apixaban Warfarin Discontinue Apixaban and start warfarin 24 hours
Urgent: Hold further doses of dabigatran, rivaroxaban, or apixaban later3. If continuous anticoagulation desired, initiate
alternative anticoagulant while starting warfarin. Presented by the American Society of Hematology,
Draw baseline coagulation tests* Canada: Continue apixaban concomitantly with adapted in part from the American College of
Activated charcoal if recent ingestion: warfarin until INR ≥2.0 and then discontinue Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice
Apixaban: <6 hours • Dabigatran: <2 hours • Rivaroxaban: <8 hours apixaban1
Guideline on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic
Abbreviations: CrCl, creatinine clearance; INR, international normalized ratio; LMWH, low Therapy (9th Edition).
Normal aPTT—Unlikely dabigatran Prolonged aPTT—Dabigatran present molecular weight heparin
is contributing to bleeding and may be contributing to bleeding Conversion to and from rivaroxaban based on 20 mg daily dose for non-valvular atrial fibrillation. *This pocket guide is a revision of the 2011 Clinical
Normal PT—Unlikely rivaroxaban Prolonged PT—Rivaroxaban 1
Pradaxa® product monograph 2010, Xarelto® product monograph 2011, Eliquis® product Practice Guide on Anticoagulant Dosing and Management
is contributing to bleeding if last present and may be contributing to bleeding monograph 2012 of Anticoagulant-Associated Bleeding Complications in
ingestion >24 hours prior 2
Rivaroxaban affects INR, so INR measurements made during coadministration with Adults
No antidote available warfarin may not be useful for determining the appropriate dose of warfarin. To minimize this
For bleeding consider: phenomenon, measure INR at rivaroxaban trough. If continuous anticoagulation desired, stop American Society of Hematology Look for this pocket guide as a
HASHTI** PCC • activated PCC (FEIBA) • rFVIIa rivaroxaban and initiate alternative anticoagulant while starting warfarin. Xarelto® product 2021 L Street NW, Suite 900 downloadable app by searching
hemodialysis for dabigatran monograph 2011
Washington, DC 20036 for “ASH Guides” in the iTunes
(if patient has renal failure) 3
Apixaban affects INR, so INR measurements made during coadministration with warfarin store or Android market.
may not be useful for determining appropriate dose of warfarin. To minimize this phenomenon,
measure INR at apixaban trough.
www.hematology.org
Reassess patient Repeat abnormal coagulation tests*
2. Reversal of Low-Molecular-Weight Heparins [Dalteparin (Fragmin®), III. Antiplatelet Agent Reversal
QUICK REFERENCE
Enoxaparin (Lovenox®), Tinzaparin (Innohep®)] and Fondaparinux1 (Arixtra®)
Abbreviations: PCC, prothrombin complex concentrates, rFVIIa, recombinant factor VIIa Aspirin, Aspirin/Dipyridamole (Aggrenox®), Clopidogrel (Plavix®), Prasugrel (Effient®),
Non-Urgent Urgent (Not Bleeding) Urgent (Bleeding) * Commonly available tests to assess for presence of dabigatran are the aPTT and for
rivaroxaban the PT. These tests may be prolonged when dabigatran and rivaroxaban are used
Ticagrelor (Brilinta®) Clinical Practice Guide
General Considerations
• Hold day of procedure
• Once-daily regimens
• Wait 12-24 hours if possible
• Consider protamine sulfate
• HASHTI
• Protamine sulfate
at recommended doses but they do not reliably measure the anticoagulant activity. Therapeutic
levels of apixaban may not elevate the PT. To measure anticoagulant activity, the ecarin clotting
1. Plasma half-lives on Antithrombotic Drug
° ½ dose day prior
• Twice-daily regimens
if delay not possible for high
bleeding risk procedure
• Consider rVIIa
time (ECT) or dilute thrombin time for dabigatran and chromogenic anti-Factor Xa assays using
validated calibrators and controls may be used for rivaroxaban and apixaban.
a. Clopidogrel, dipyridamole, prasugrel, ticagrelor: 7-10 hours
b. Low-dose aspirin (150 mg daily): 2-4.5 hours Dosing and Management
° Hold evening dose day
prior ** Dabigatran, rivaroxaban and apixaban are excreted in the urine, therefore maintain adequate
diuresis. Rivaroxaban and apixaban are highly protein bound so dialysis is not effective.
c. Overdose aspirin (>4000 mg): 15-30 hours
2. Reversibility of antiplatelet effect of Antithrombotic Drug-
Fondaparinux has no specific antidote
1
C. Converting Between Anticoagulants1
a. Aspirin, clopidogrel,and prasugrel inhibit platelet function for lifetime of the
platelets. Inhibition takes 7-10 days to resolve as new platelets are generated. Associated Bleeding
3. Protamine Dose for Reversal of Heparin and LMWH
Agent* Half-Life Protamine Sulfate Dosing for Reversal
Current Anticoagulant
anticoagulant to be converted
Procedure
b. Ticagrelor is a reversible inhibitor, so platelet function normalizes after drug
clearance. Hold a minimum of 5 days to reverse effect. Unclear if platelet Complications in Adults
All Maximum dose is 50 mg to
transfusion will be effective in reversing effect if given within 5-7 days of last February 2014*
dose.
Heparin 1-2 hours • 1 mg per 90-100 units heparin given in previous 2-3 Warfarin Dabigatran or Discontinue warfarin and start dabigatran or 3. Circulating drug or active metabolites can inhibit transfused platelets. Mary Cushman1
hours (INR 2-3) Apixaban apixaban when INR <2.0 4. Must consider indication for use in decision to reverse Wendy Lim2
a. Risk of coronary stent occlusion (which can be fatal) within 3 months of bare Neil A Zakai1
° e.g., 25-35 mg if 1000-1250 units/hour heparin infusion Warfarin Rivaroxaban Discontinue warfarin and start rivaroxaban when
metal stent implantation; period of risk is likely longer for drug-eluting stents.
Enoxaparin 4.5 hours • 1 mg per 1 mg Enoxaparin in previous 8 hours (INR 2-3) INR <3.0
b. Consult cardiologist or current guideline recommendations if uncertain. 1
University of Vermont
Dalteparin 2.2 hours • 1 mg per 100 units Dalteparin in previous 8 hours LMWH or Dabigatran Start dabigatran 0-2 hours before administration
Reversal of Antiplatelet Agents
2
McMaster University
Heparin of last LMWH/Heparin dose, or at same time as
Tinzaparin 3.9 hours • 1 mg per 100 units Tinzaparin in previous 8 hours discontinuation of infusional heparin. Non-Urgent Urgent (Not Bleeding) Urgent (Bleeding)
*Half-life is longer with subcutaneous administration for all agents so may require monitoring LMWH or Rivaroxaban or Discontinue LMWH or heparin and initiate • Discontinue agent 5-10 • Consider platelet • HASHTI
with PTT (heparin) or anti-Xa level (LMWH) every 3 hours with repeat protamine (0.5 mg per Heparin Apixaban rivaroxaban or apixaban 0-2 hours prior to next days prior to procedure transfusion prior to high • Consider platelet
indicated amount of LMWH or heparin) if bleeding continues. scheduled LMWH/Heparin dose. risk bleeding procedures transfusion
4. Reversal of Dabigatran, Rivaroxaban or Apixaban Dabigatran LMWH or Heparin CrCl ≥ 30 ml/min: start 12 hours after last dose of This document summarizes selected recommendations from the: American College of Chest
Non-urgent: Hold further doses (refer to table for recommended duration). Con- dabigatran Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guideline on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic
sider longer times for major surgery, placement of spinal or epidural catheter or port. CrCl < 30 ml/min: start 24 hours after last dose of Therapy (9th Edition).
dabigatran
Dabigatran Rivaroxaban Apixaban This guide is intended to provide the practitioner with clear principles and strategies for quality
Rivaroxaban Warfarin -US: Initiate warfarin and a parental anticoagulant patient care and does not establish a fixed set of rules that preempt physician judgment.
CrCl > 50 ml/min: Hold 1-2 Hold at least 24 hours Hold 24 to 48 hours (INR 2-3) 24 hours after discontinuation of rivaroxaban
days Half Life: 5-9 hours Half Life: 8-15 hours. Drug -Canada: Continue rivaroxaban concomitantly For further information, please see the complete guidelines on the Chest Website at
CrCl < 50 ml/min: Hold 3-5 (with normal renal presence may be assessed by with warfarin until INR ≥2.0 and then discontinue http://journal.publications.chestnet.org/issue.aspx?journalid=99&issueid=23443 or refer to
days or longer. function). Drug anti-Xa assay. rivaroxaban2 the Practice Guidelines section of the ASH website at www.hematology.org/practiceguidelines.
Half Life: 12-14 hours presence may be You may also contact the ASH Department of Quality Improvement Programs at 202-776-0544.
Drug presence may be assessed by anti-Xa Rivaroxaban or LMWH or Heparin Initiate LMWH/Heparin 24 hours after
Apixaban discontinuation of Rivaroxaban or Apixaban. © 2014 by the American Society of Hematology. All rights reserved.
assessed by thrombin time. assay.
Images courtesy of Kenneth Mann, PhD, and Matthew Whelihan, MS.
Apixaban Warfarin Discontinue Apixaban and start warfarin 24 hours
Urgent: Hold further doses of dabigatran, rivaroxaban, or apixaban later3. If continuous anticoagulation desired, initiate
alternative anticoagulant while starting warfarin. Presented by the American Society of Hematology,
Draw baseline coagulation tests* Canada: Continue apixaban concomitantly with adapted in part from the American College of
Activated charcoal if recent ingestion: warfarin until INR ≥2.0 and then discontinue Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice
Apixaban: <6 hours • Dabigatran: <2 hours • Rivaroxaban: <8 hours apixaban1
Guideline on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic
Abbreviations: CrCl, creatinine clearance; INR, international normalized ratio; LMWH, low Therapy (9th Edition).
Normal aPTT—Unlikely dabigatran Prolonged aPTT—Dabigatran present molecular weight heparin
is contributing to bleeding and may be contributing to bleeding Conversion to and from rivaroxaban based on 20 mg daily dose for non-valvular atrial fibrillation. *This pocket guide is a revision of the 2011 Clinical
Normal PT—Unlikely rivaroxaban Prolonged PT—Rivaroxaban 1
Pradaxa® product monograph 2010, Xarelto® product monograph 2011, Eliquis® product Practice Guide on Anticoagulant Dosing and Management
is contributing to bleeding if last present and may be contributing to bleeding monograph 2012 of Anticoagulant-Associated Bleeding Complications in
ingestion >24 hours prior 2
Rivaroxaban affects INR, so INR measurements made during coadministration with Adults
No antidote available warfarin may not be useful for determining the appropriate dose of warfarin. To minimize this
For bleeding consider: phenomenon, measure INR at rivaroxaban trough. If continuous anticoagulation desired, stop American Society of Hematology Look for this pocket guide as a
HASHTI** PCC • activated PCC (FEIBA) • rFVIIa rivaroxaban and initiate alternative anticoagulant while starting warfarin. Xarelto® product 2021 L Street NW, Suite 900 downloadable app by searching
hemodialysis for dabigatran monograph 2011
Washington, DC 20036 for “ASH Guides” in the iTunes
(if patient has renal failure) 3
Apixaban affects INR, so INR measurements made during coadministration with warfarin store or Android market.
may not be useful for determining appropriate dose of warfarin. To minimize this phenomenon,
measure INR at apixaban trough.
www.hematology.org
Reassess patient Repeat abnormal coagulation tests*
2. Reversal of Low-Molecular-Weight Heparins [Dalteparin (Fragmin®), III. Antiplatelet Agent Reversal
QUICK REFERENCE
Enoxaparin (Lovenox®), Tinzaparin (Innohep®)] and Fondaparinux1 (Arixtra®)
Abbreviations: PCC, prothrombin complex concentrates, rFVIIa, recombinant factor VIIa Aspirin, Aspirin/Dipyridamole (Aggrenox®), Clopidogrel (Plavix®), Prasugrel (Effient®),
Non-Urgent Urgent (Not Bleeding) Urgent (Bleeding) * Commonly available tests to assess for presence of dabigatran are the aPTT and for
rivaroxaban the PT. These tests may be prolonged when dabigatran and rivaroxaban are used
Ticagrelor (Brilinta®) Clinical Practice Guide
General Considerations
• Hold day of procedure
• Once-daily regimens
• Wait 12-24 hours if possible
• Consider protamine sulfate
• HASHTI
• Protamine sulfate
at recommended doses but they do not reliably measure the anticoagulant activity. Therapeutic
levels of apixaban may not elevate the PT. To measure anticoagulant activity, the ecarin clotting
1. Plasma half-lives on Antithrombotic Drug
° ½ dose day prior
• Twice-daily regimens
if delay not possible for high
bleeding risk procedure
• Consider rVIIa
time (ECT) or dilute thrombin time for dabigatran and chromogenic anti-Factor Xa assays using
validated calibrators and controls may be used for rivaroxaban and apixaban.
a. Clopidogrel, dipyridamole, prasugrel, ticagrelor: 7-10 hours
b. Low-dose aspirin (150 mg daily): 2-4.5 hours Dosing and Management
° Hold evening dose day
prior ** Dabigatran, rivaroxaban and apixaban are excreted in the urine, therefore maintain adequate
diuresis. Rivaroxaban and apixaban are highly protein bound so dialysis is not effective.
c. Overdose aspirin (>4000 mg): 15-30 hours
2. Reversibility of antiplatelet effect of Antithrombotic Drug-
Fondaparinux has no specific antidote
1
C. Converting Between Anticoagulants1
a. Aspirin, clopidogrel,and prasugrel inhibit platelet function for lifetime of the
platelets. Inhibition takes 7-10 days to resolve as new platelets are generated. Associated Bleeding
3. Protamine Dose for Reversal of Heparin and LMWH
Agent* Half-Life Protamine Sulfate Dosing for Reversal
Current Anticoagulant
anticoagulant to be converted
Procedure
b. Ticagrelor is a reversible inhibitor, so platelet function normalizes after drug
clearance. Hold a minimum of 5 days to reverse effect. Unclear if platelet Complications in Adults
All Maximum dose is 50 mg to
transfusion will be effective in reversing effect if given within 5-7 days of last February 2014*
dose.
Heparin 1-2 hours • 1 mg per 90-100 units heparin given in previous 2-3 Warfarin Dabigatran or Discontinue warfarin and start dabigatran or 3. Circulating drug or active metabolites can inhibit transfused platelets. Mary Cushman1
hours (INR 2-3) Apixaban apixaban when INR <2.0 4. Must consider indication for use in decision to reverse Wendy Lim2
a. Risk of coronary stent occlusion (which can be fatal) within 3 months of bare Neil A Zakai1
° e.g., 25-35 mg if 1000-1250 units/hour heparin infusion Warfarin Rivaroxaban Discontinue warfarin and start rivaroxaban when
metal stent implantation; period of risk is likely longer for drug-eluting stents.
Enoxaparin 4.5 hours • 1 mg per 1 mg Enoxaparin in previous 8 hours (INR 2-3) INR <3.0
b. Consult cardiologist or current guideline recommendations if uncertain. 1
University of Vermont
Dalteparin 2.2 hours • 1 mg per 100 units Dalteparin in previous 8 hours LMWH or Dabigatran Start dabigatran 0-2 hours before administration
Reversal of Antiplatelet Agents
2
McMaster University
Heparin of last LMWH/Heparin dose, or at same time as
Tinzaparin 3.9 hours • 1 mg per 100 units Tinzaparin in previous 8 hours discontinuation of infusional heparin. Non-Urgent Urgent (Not Bleeding) Urgent (Bleeding)
*Half-life is longer with subcutaneous administration for all agents so may require monitoring LMWH or Rivaroxaban or Discontinue LMWH or heparin and initiate • Discontinue agent 5-10 • Consider platelet • HASHTI
with PTT (heparin) or anti-Xa level (LMWH) every 3 hours with repeat protamine (0.5 mg per Heparin Apixaban rivaroxaban or apixaban 0-2 hours prior to next days prior to procedure transfusion prior to high • Consider platelet
indicated amount of LMWH or heparin) if bleeding continues. scheduled LMWH/Heparin dose. risk bleeding procedures transfusion
4. Reversal of Dabigatran, Rivaroxaban or Apixaban Dabigatran LMWH or Heparin CrCl ≥ 30 ml/min: start 12 hours after last dose of This document summarizes selected recommendations from the: American College of Chest
Non-urgent: Hold further doses (refer to table for recommended duration). Con- dabigatran Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guideline on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic
sider longer times for major surgery, placement of spinal or epidural catheter or port. CrCl < 30 ml/min: start 24 hours after last dose of Therapy (9th Edition).
dabigatran
Dabigatran Rivaroxaban Apixaban This guide is intended to provide the practitioner with clear principles and strategies for quality
Rivaroxaban Warfarin -US: Initiate warfarin and a parental anticoagulant patient care and does not establish a fixed set of rules that preempt physician judgment.
CrCl > 50 ml/min: Hold 1-2 Hold at least 24 hours Hold 24 to 48 hours (INR 2-3) 24 hours after discontinuation of rivaroxaban
days Half Life: 5-9 hours Half Life: 8-15 hours. Drug -Canada: Continue rivaroxaban concomitantly For further information, please see the complete guidelines on the Chest Website at
CrCl < 50 ml/min: Hold 3-5 (with normal renal presence may be assessed by with warfarin until INR ≥2.0 and then discontinue http://journal.publications.chestnet.org/issue.aspx?journalid=99&issueid=23443 or refer to
days or longer. function). Drug anti-Xa assay. rivaroxaban2 the Practice Guidelines section of the ASH website at www.hematology.org/practiceguidelines.
Half Life: 12-14 hours presence may be You may also contact the ASH Department of Quality Improvement Programs at 202-776-0544.
Drug presence may be assessed by anti-Xa Rivaroxaban or LMWH or Heparin Initiate LMWH/Heparin 24 hours after
Apixaban discontinuation of Rivaroxaban or Apixaban. © 2014 by the American Society of Hematology. All rights reserved.
assessed by thrombin time. assay.
Images courtesy of Kenneth Mann, PhD, and Matthew Whelihan, MS.
Apixaban Warfarin Discontinue Apixaban and start warfarin 24 hours
Urgent: Hold further doses of dabigatran, rivaroxaban, or apixaban later3. If continuous anticoagulation desired, initiate
alternative anticoagulant while starting warfarin. Presented by the American Society of Hematology,
Draw baseline coagulation tests* Canada: Continue apixaban concomitantly with adapted in part from the American College of
Activated charcoal if recent ingestion: warfarin until INR ≥2.0 and then discontinue Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice
Apixaban: <6 hours • Dabigatran: <2 hours • Rivaroxaban: <8 hours apixaban1
Guideline on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic
Abbreviations: CrCl, creatinine clearance; INR, international normalized ratio; LMWH, low Therapy (9th Edition).
Normal aPTT—Unlikely dabigatran Prolonged aPTT—Dabigatran present molecular weight heparin
is contributing to bleeding and may be contributing to bleeding Conversion to and from rivaroxaban based on 20 mg daily dose for non-valvular atrial fibrillation. *This pocket guide is a revision of the 2011 Clinical
Normal PT—Unlikely rivaroxaban Prolonged PT—Rivaroxaban 1
Pradaxa® product monograph 2010, Xarelto® product monograph 2011, Eliquis® product Practice Guide on Anticoagulant Dosing and Management
is contributing to bleeding if last present and may be contributing to bleeding monograph 2012 of Anticoagulant-Associated Bleeding Complications in
ingestion >24 hours prior 2
Rivaroxaban affects INR, so INR measurements made during coadministration with Adults
No antidote available warfarin may not be useful for determining the appropriate dose of warfarin. To minimize this
For bleeding consider: phenomenon, measure INR at rivaroxaban trough. If continuous anticoagulation desired, stop American Society of Hematology Look for this pocket guide as a
HASHTI** PCC • activated PCC (FEIBA) • rFVIIa rivaroxaban and initiate alternative anticoagulant while starting warfarin. Xarelto® product 2021 L Street NW, Suite 900 downloadable app by searching
hemodialysis for dabigatran monograph 2011
Washington, DC 20036 for “ASH Guides” in the iTunes
(if patient has renal failure) 3
Apixaban affects INR, so INR measurements made during coadministration with warfarin store or Android market.
may not be useful for determining appropriate dose of warfarin. To minimize this phenomenon,
measure INR at apixaban trough.
www.hematology.org
Reassess patient Repeat abnormal coagulation tests*
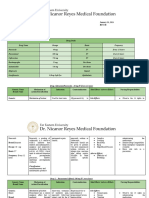
I. ANTICOAGULANT DOSING C. Chronic Warfarin Dose Adjustment in Non-Bleeding Patients E. Rivaroxaban Dosing to Prevent Stroke and Systemic Embolism B. Agents to Stop Bleeding
This nomogram is suggested for non-bleeding patients with target INR 2.0-3.0 who are in Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation and to Treat Venous
A. Subcutaneous Heparin Dosing for Treatment of Acute Venous Agent Dose Comments
out of range and who are not at high risk of bleeding. Thromboembolism
Thromboembolism Vitamin K 1-10 mg IV/ • Infusion reactions rare; administer over 20-30 min
1. If INR >3.0 confirm no bleeding. • Avoid use in patients taking strong dual inhibitors of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein PO • Takes 6 (IV) to 24 (PO) hours to reverse warfarin
General Considerations (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, ritonavir).
2. Consider noncompliance, illness, drug interaction, or dietary change as reason for • Large doses can cause warfarin resistance on
1. Round weight-based dose to nearest prefilled syringe size for LMWH. • Avoid use in patients taking strong dual inducers of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein
out-of-range INR. resumption
2. No dose cap for obesity except dalteparin in cancer patients. (e.g., rifampin, phenytoin, carbamazepine, phenobarbital, St. John’s Wort); this may
3. Clinical judgment should supersede this nomogram. • Subcutaneous or intramuscular administration not
3. Consider measuring anti-Xa heparin levels after 3rd dose for weight >120 kg or lead to reduced rivaroxaban plasma concentrations. recommended
<60 kg.
4. Repeat CBC day 7 and consider heparin-induced thrombocytopenia if platelets 1. Atrial fibrillation Protamine 12.5-50 mg IV • Full reversal of unfractionated heparin
declining. • CrCl >50 ml/min: 20 mg once daily with evening meal* sulfate • 60-80% reversal of LMWH
Target INR
• If heparin exposure in previous 3 months, CBC on day 3 rather than day 7. • CrCl 15-50 ml/min: 15 mg once daily with evening meal* • No reversal of fondaparinux
2.0–3.0
5. Use LMWH with caution if at all, and monitor anti-Xa levels if creatinine clearance • CrCl <15 ml/min: Avoid use
Platelets 1 apheresis • Used in patients receiving antiplatelet therapy
(CrCl) <30 ml/min. *US labeling: Outside US—give with a meal at same time each day; may be given with breakfast. unit • Raise platelet count by 30 x 109/L
Subcutaneous Dosing 5-8 whole • Goal platelet count 50-100 x 109/L (indication
2. Venous Thromboembolism blood units dependent)
Enoxaparin: 1 mg/kg every 12 hours or 1.5 mg/kg daily • 15 mg every 12 hours for 21 days followed by 20 mg once daily, taken with food
- For cancer patients and those at high bleeding or thrombosis • Not recommended if CrCl <30 ml/min Frozen plasma 10-30 mL/kg • Replaces all coagulation factors, but cannot fully
risk, favor twice-daily dosing INR < 2.0 INR 3.1–3.5 INR 3.6–4.0 INR 4.1–8.9 INR >9.0 (FFP) (1 unit = correct
Dalteparin: 200 IU/kg daily or 100 IU/kg every 12 hours F. Apixaban Dosing to Prevent Stroke and Systemic Embolism in ~250 ml) ° Hemostasis usually requires coagulation factor
Tinzaparin: 175 IU/kg daily Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation levels ~30%
Fondaparinux: <50 kg: 5 mg daily. 50-100 kg: 7.5 mg daily. >100 kg: 10 mg ° Factor IX may only reach 20%
Dose: 5 mg twice daily • Short half-life, may need repeat dosing after 6 hours
daily
• CrCl <15 ml/min: Avoid use • Large volume, can take hours to thaw and infuse
Unfractionated Hold 0–1 Hold 0–2 Hold 2 doses • Avoid use in patients taking strong dual inducers of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein
heparin: 333 IU/kg x 1, then 250 IU/kg every 12 hours Increase by Decrease by dose, doses, decrease decrease by (e.g., rifampin, carbamazepine, phenytoin, St. John’s Wort). Prothrombin 25-50 units/ • Rapid, complete INR correction in warfarin-treated
10–15%* 0–10% decrease by by 10–15% +/- 15–20% complex kg IV (lower patients
B. Initial Warfarin Dosing for Venous Thromboembolism or Atrial 10–15% Vit. K Dose adjustments: concentrates doses studied) • Small volume infusion over 10-30 minutes
Vit. K
Fibrillation in Ambulatory Outpatients, Target INR 2.0-3.0 2.5 mg po 2.5–5 mg po Dose 2.5 mg twice daily if: (PCC) • Risk of thrombosis 1.4%; contraindicated with history
1. Two or more of the following are present: of HIT
General Considerations
• Age ≥80 years • Short half-life, may need repeat dose after 6 hours
1. Obtain baseline PT/INR and investigate if abnormal.
• Body weight ≤60 kg • Consider concurrent FFP if 3-factor PCC used
2. Determine use of potential warfarin interacting medications.
• Serum creatinine ≥1.5 mg/dL (133 µmol/L)
3. Document target INR and prescribed warfarin tablet strength. Repeat INR Repeat INR Repeat OR
Recombinant 15-90 • Rapid infusion of small volume
Repeat INR Repeat INR factor VIIa micrograms/ • Rapid complete INR correction in warfarin patients,
4. Provide patient education on safety, monitoring, drug and food interactions. within 2 within 1 INR 2. Use of strong dual inhibitors of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein (e.g.,ketoconazole,
within 1 week in 2 days (rFVIIa) kg but may not correct bleeding because only restores
5. For acute thrombosis, overlap with heparin/LMWH/fondaparinux for 5+ days until weeks week next day itraconazole, ritonavir, clarithromycin) (lower doses FVIIa
INR therapeutic.
6. Recommend first INR check on day 3-4. Do not administer apixaban in patients with both #1 and #2. studied) • Risk of thrombosis 5-10%
*Consider 15% increase if INR ≤1.5 without explanation • Short half-life, may need repeat dose after 2 hours
7. Clinical judgment should supersede this nomogram.
II. ANTICOAGULANT REVERSAL Aminocaproic 4-5 g IV/po • May increase risk of thrombosis
D. Dabigatran Dosing to Prevent Stroke and Systemic Embolism in
Day INR DAILY DOSE acid over 1 hr, then • May accumulate in patients with renal impairment,
Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation A. General Principles of Management of Anticoagulant-Associated
1 g/hr x 8 hrs reduce loading dose or infusion rate
1-3 Not required 5 mg* Dose: Bleeding (maximum • Caution or avoid use in hematuria due to upper
1.0-1.3 7.5 mg CrCl >30 ml/min*: 150 mg orally, twice daily dose 30 g/24 urinary tract origin
HASHTI
1.4-1.5 5 mg Avoid use in patients with CrCl <30 and taking P-glycoprotein inhibitors (e.g., hrs)
1. Hold further doses of anticoagulant
dronedarone, ketoconazole)
3 or 4 1.6-1.8 5/2.5 mg alternating 2. Consider Antidote Tranexamic 1300 mg po • Labeled indication for menorrhagia
Avoid use in patients taking P-glycoprotein inducers (e.g., rifampin)
>1.9 2.5 mg 3. Supportive treatment acid q8h • Use for other indications currently off label
Dose adjustments: a. Volume resuscitation (intravenous fluids)
>2.0 Hold x 1 day, then 2.5 mg†
CrCl 15-30 ml/min*: 75 mg orally, twice daily b. Hemodynamic support (inotropes, monitoring) 1. Reversal of Warfarin (Coumadin®, Jantoven®)
< 1.5 Increase by 15% of ADD CrCl 30-50 and taking P-glycoprotein inhibitors: 75 mg orally, twice daily 4. Local or surgical Hemostatic measures
1.6-1.9 Increase by 10% of ADD a. Anti-fibrinolytic agents can be considered (aminocaproic acid, tranexamic acid) Non-Urgent Urgent (Not bleeding) Urgent (Bleeding)
No recommendation for CrCl <15 ml/min or on dialysis. Outside US—patients with CrCl
2.0-3.0 No Change 5. Transfusion • Stop 5 days prior to • If procedure can be delayed 6-24 • HASHTI
>30 ml/min and age >75 years or propensity for GI bleeding: 110 mg twice daily.
7 & 10 3.1-3.5 Decrease by 10% of ADD a. Red blood cells for severe or symptomatic anemia procedure hours, vitamin K 5-10 mg PO/IV; • Vitamin K 5-10 mg
b. Platelets if thrombocytopenia (<50 x 109/L) or patient on long-acting antiplatelet • Check INR 1-2 days otherwise: IV; repeat in 12
3.6-4.0 Decrease by 15% of ADD
agents prior ° FFP or PCC prior to procedure. hours as needed
> 4.1 Hold 1 day, decrease by 15% (or more)† • PCC or FFP;
6. Investigate for bleeding source ° If INR >1.5 administer Repeat in 6-12 hours if INR
> 6.0 Consider Vitamin K† vitamin K 1-2 mg PO >1.5 and repeat every 6
Definitions Used for Reversal Situations hours as needed
Abbreviations: ADD = average daily dose ° Vitamin K 5-10 mg PO/IV if
Non-urgent: Reversal is elective (procedures >5 days away) sustained reversal is desired
* 2.5 mg for frailty, liver disease, malnutrition, drugs that enhance warfarin activity, or Asian Urgent (without bleeding): Reversal needed within hours
ethnicity; 5-7.5 mg for young healthy patients Urgent (with bleeding): Immediate reversal
† Check INR more frequently
I. ANTICOAGULANT DOSING C. Chronic Warfarin Dose Adjustment in Non-Bleeding Patients E. Rivaroxaban Dosing to Prevent Stroke and Systemic Embolism B. Agents to Stop Bleeding
This nomogram is suggested for non-bleeding patients with target INR 2.0-3.0 who are in Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation and to Treat Venous
A. Subcutaneous Heparin Dosing for Treatment of Acute Venous Agent Dose Comments
out of range and who are not at high risk of bleeding. Thromboembolism
Thromboembolism Vitamin K 1-10 mg IV/ • Infusion reactions rare; administer over 20-30 min
1. If INR >3.0 confirm no bleeding. • Avoid use in patients taking strong dual inhibitors of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein PO • Takes 6 (IV) to 24 (PO) hours to reverse warfarin
General Considerations (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, ritonavir).
2. Consider noncompliance, illness, drug interaction, or dietary change as reason for • Large doses can cause warfarin resistance on
1. Round weight-based dose to nearest prefilled syringe size for LMWH. • Avoid use in patients taking strong dual inducers of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein
out-of-range INR. resumption
2. No dose cap for obesity except dalteparin in cancer patients. (e.g., rifampin, phenytoin, carbamazepine, phenobarbital, St. John’s Wort); this may
3. Clinical judgment should supersede this nomogram. • Subcutaneous or intramuscular administration not
3. Consider measuring anti-Xa heparin levels after 3rd dose for weight >120 kg or lead to reduced rivaroxaban plasma concentrations. recommended
<60 kg.
4. Repeat CBC day 7 and consider heparin-induced thrombocytopenia if platelets 1. Atrial fibrillation Protamine 12.5-50 mg IV • Full reversal of unfractionated heparin
declining. • CrCl >50 ml/min: 20 mg once daily with evening meal* sulfate • 60-80% reversal of LMWH
Target INR
• If heparin exposure in previous 3 months, CBC on day 3 rather than day 7. • CrCl 15-50 ml/min: 15 mg once daily with evening meal* • No reversal of fondaparinux
2.0–3.0
5. Use LMWH with caution if at all, and monitor anti-Xa levels if creatinine clearance • CrCl <15 ml/min: Avoid use
Platelets 1 apheresis • Used in patients receiving antiplatelet therapy
(CrCl) <30 ml/min. *US labeling: Outside US—give with a meal at same time each day; may be given with breakfast. unit • Raise platelet count by 30 x 109/L
Subcutaneous Dosing 5-8 whole • Goal platelet count 50-100 x 109/L (indication
2. Venous Thromboembolism blood units dependent)
Enoxaparin: 1 mg/kg every 12 hours or 1.5 mg/kg daily • 15 mg every 12 hours for 21 days followed by 20 mg once daily, taken with food
- For cancer patients and those at high bleeding or thrombosis • Not recommended if CrCl <30 ml/min Frozen plasma 10-30 mL/kg • Replaces all coagulation factors, but cannot fully
risk, favor twice-daily dosing INR < 2.0 INR 3.1–3.5 INR 3.6–4.0 INR 4.1–8.9 INR >9.0 (FFP) (1 unit = correct
Dalteparin: 200 IU/kg daily or 100 IU/kg every 12 hours F. Apixaban Dosing to Prevent Stroke and Systemic Embolism in ~250 ml) ° Hemostasis usually requires coagulation factor
Tinzaparin: 175 IU/kg daily Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation levels ~30%
Fondaparinux: <50 kg: 5 mg daily. 50-100 kg: 7.5 mg daily. >100 kg: 10 mg ° Factor IX may only reach 20%
Dose: 5 mg twice daily • Short half-life, may need repeat dosing after 6 hours
daily
• CrCl <15 ml/min: Avoid use • Large volume, can take hours to thaw and infuse
Unfractionated Hold 0–1 Hold 0–2 Hold 2 doses • Avoid use in patients taking strong dual inducers of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein
heparin: 333 IU/kg x 1, then 250 IU/kg every 12 hours Increase by Decrease by dose, doses, decrease decrease by (e.g., rifampin, carbamazepine, phenytoin, St. John’s Wort). Prothrombin 25-50 units/ • Rapid, complete INR correction in warfarin-treated
10–15%* 0–10% decrease by by 10–15% +/- 15–20% complex kg IV (lower patients
B. Initial Warfarin Dosing for Venous Thromboembolism or Atrial 10–15% Vit. K Dose adjustments: concentrates doses studied) • Small volume infusion over 10-30 minutes
Vit. K
Fibrillation in Ambulatory Outpatients, Target INR 2.0-3.0 2.5 mg po 2.5–5 mg po Dose 2.5 mg twice daily if: (PCC) • Risk of thrombosis 1.4%; contraindicated with history
1. Two or more of the following are present: of HIT
General Considerations
• Age ≥80 years • Short half-life, may need repeat dose after 6 hours
1. Obtain baseline PT/INR and investigate if abnormal.
• Body weight ≤60 kg • Consider concurrent FFP if 3-factor PCC used
2. Determine use of potential warfarin interacting medications.
• Serum creatinine ≥1.5 mg/dL (133 µmol/L)
3. Document target INR and prescribed warfarin tablet strength. Repeat INR Repeat INR Repeat OR
Recombinant 15-90 • Rapid infusion of small volume
Repeat INR Repeat INR factor VIIa micrograms/ • Rapid complete INR correction in warfarin patients,
4. Provide patient education on safety, monitoring, drug and food interactions. within 2 within 1 INR 2. Use of strong dual inhibitors of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein (e.g.,ketoconazole,
within 1 week in 2 days (rFVIIa) kg but may not correct bleeding because only restores
5. For acute thrombosis, overlap with heparin/LMWH/fondaparinux for 5+ days until weeks week next day itraconazole, ritonavir, clarithromycin) (lower doses FVIIa
INR therapeutic.
6. Recommend first INR check on day 3-4. Do not administer apixaban in patients with both #1 and #2. studied) • Risk of thrombosis 5-10%
*Consider 15% increase if INR ≤1.5 without explanation • Short half-life, may need repeat dose after 2 hours
7. Clinical judgment should supersede this nomogram.
II. ANTICOAGULANT REVERSAL Aminocaproic 4-5 g IV/po • May increase risk of thrombosis
D. Dabigatran Dosing to Prevent Stroke and Systemic Embolism in
Day INR DAILY DOSE acid over 1 hr, then • May accumulate in patients with renal impairment,
Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation A. General Principles of Management of Anticoagulant-Associated
1 g/hr x 8 hrs reduce loading dose or infusion rate
1-3 Not required 5 mg* Dose: Bleeding (maximum • Caution or avoid use in hematuria due to upper
1.0-1.3 7.5 mg CrCl >30 ml/min*: 150 mg orally, twice daily dose 30 g/24 urinary tract origin
HASHTI
1.4-1.5 5 mg Avoid use in patients with CrCl <30 and taking P-glycoprotein inhibitors (e.g., hrs)
1. Hold further doses of anticoagulant
dronedarone, ketoconazole)
3 or 4 1.6-1.8 5/2.5 mg alternating 2. Consider Antidote Tranexamic 1300 mg po • Labeled indication for menorrhagia
Avoid use in patients taking P-glycoprotein inducers (e.g., rifampin)
>1.9 2.5 mg 3. Supportive treatment acid q8h • Use for other indications currently off label
Dose adjustments: a. Volume resuscitation (intravenous fluids)
>2.0 Hold x 1 day, then 2.5 mg†
CrCl 15-30 ml/min*: 75 mg orally, twice daily b. Hemodynamic support (inotropes, monitoring) 1. Reversal of Warfarin (Coumadin®, Jantoven®)
< 1.5 Increase by 15% of ADD CrCl 30-50 and taking P-glycoprotein inhibitors: 75 mg orally, twice daily 4. Local or surgical Hemostatic measures
1.6-1.9 Increase by 10% of ADD a. Anti-fibrinolytic agents can be considered (aminocaproic acid, tranexamic acid) Non-Urgent Urgent (Not bleeding) Urgent (Bleeding)
No recommendation for CrCl <15 ml/min or on dialysis. Outside US—patients with CrCl
2.0-3.0 No Change 5. Transfusion • Stop 5 days prior to • If procedure can be delayed 6-24 • HASHTI
>30 ml/min and age >75 years or propensity for GI bleeding: 110 mg twice daily.
7 & 10 3.1-3.5 Decrease by 10% of ADD a. Red blood cells for severe or symptomatic anemia procedure hours, vitamin K 5-10 mg PO/IV; • Vitamin K 5-10 mg
b. Platelets if thrombocytopenia (<50 x 109/L) or patient on long-acting antiplatelet • Check INR 1-2 days otherwise: IV; repeat in 12
3.6-4.0 Decrease by 15% of ADD
agents prior ° FFP or PCC prior to procedure. hours as needed
> 4.1 Hold 1 day, decrease by 15% (or more)† • PCC or FFP;
6. Investigate for bleeding source ° If INR >1.5 administer Repeat in 6-12 hours if INR
> 6.0 Consider Vitamin K† vitamin K 1-2 mg PO >1.5 and repeat every 6
Definitions Used for Reversal Situations hours as needed
Abbreviations: ADD = average daily dose ° Vitamin K 5-10 mg PO/IV if
Non-urgent: Reversal is elective (procedures >5 days away) sustained reversal is desired
* 2.5 mg for frailty, liver disease, malnutrition, drugs that enhance warfarin activity, or Asian Urgent (without bleeding): Reversal needed within hours
ethnicity; 5-7.5 mg for young healthy patients Urgent (with bleeding): Immediate reversal
† Check INR more frequently
I. ANTICOAGULANT DOSING C. Chronic Warfarin Dose Adjustment in Non-Bleeding Patients E. Rivaroxaban Dosing to Prevent Stroke and Systemic Embolism B. Agents to Stop Bleeding
This nomogram is suggested for non-bleeding patients with target INR 2.0-3.0 who are in Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation and to Treat Venous
A. Subcutaneous Heparin Dosing for Treatment of Acute Venous Agent Dose Comments
out of range and who are not at high risk of bleeding. Thromboembolism
Thromboembolism Vitamin K 1-10 mg IV/ • Infusion reactions rare; administer over 20-30 min
1. If INR >3.0 confirm no bleeding. • Avoid use in patients taking strong dual inhibitors of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein PO • Takes 6 (IV) to 24 (PO) hours to reverse warfarin
General Considerations (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, ritonavir).
2. Consider noncompliance, illness, drug interaction, or dietary change as reason for • Large doses can cause warfarin resistance on
1. Round weight-based dose to nearest prefilled syringe size for LMWH. • Avoid use in patients taking strong dual inducers of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein
out-of-range INR. resumption
2. No dose cap for obesity except dalteparin in cancer patients. (e.g., rifampin, phenytoin, carbamazepine, phenobarbital, St. John’s Wort); this may
3. Clinical judgment should supersede this nomogram. • Subcutaneous or intramuscular administration not
3. Consider measuring anti-Xa heparin levels after 3rd dose for weight >120 kg or lead to reduced rivaroxaban plasma concentrations. recommended
<60 kg.
4. Repeat CBC day 7 and consider heparin-induced thrombocytopenia if platelets 1. Atrial fibrillation Protamine 12.5-50 mg IV • Full reversal of unfractionated heparin
declining. • CrCl >50 ml/min: 20 mg once daily with evening meal* sulfate • 60-80% reversal of LMWH
Target INR
• If heparin exposure in previous 3 months, CBC on day 3 rather than day 7. • CrCl 15-50 ml/min: 15 mg once daily with evening meal* • No reversal of fondaparinux
2.0–3.0
5. Use LMWH with caution if at all, and monitor anti-Xa levels if creatinine clearance • CrCl <15 ml/min: Avoid use
Platelets 1 apheresis • Used in patients receiving antiplatelet therapy
(CrCl) <30 ml/min. *US labeling: Outside US—give with a meal at same time each day; may be given with breakfast. unit • Raise platelet count by 30 x 109/L
Subcutaneous Dosing 5-8 whole • Goal platelet count 50-100 x 109/L (indication
2. Venous Thromboembolism blood units dependent)
Enoxaparin: 1 mg/kg every 12 hours or 1.5 mg/kg daily • 15 mg every 12 hours for 21 days followed by 20 mg once daily, taken with food
- For cancer patients and those at high bleeding or thrombosis • Not recommended if CrCl <30 ml/min Frozen plasma 10-30 mL/kg • Replaces all coagulation factors, but cannot fully
risk, favor twice-daily dosing INR < 2.0 INR 3.1–3.5 INR 3.6–4.0 INR 4.1–8.9 INR >9.0 (FFP) (1 unit = correct
Dalteparin: 200 IU/kg daily or 100 IU/kg every 12 hours F. Apixaban Dosing to Prevent Stroke and Systemic Embolism in ~250 ml) ° Hemostasis usually requires coagulation factor
Tinzaparin: 175 IU/kg daily Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation levels ~30%
Fondaparinux: <50 kg: 5 mg daily. 50-100 kg: 7.5 mg daily. >100 kg: 10 mg ° Factor IX may only reach 20%
Dose: 5 mg twice daily • Short half-life, may need repeat dosing after 6 hours
daily
• CrCl <15 ml/min: Avoid use • Large volume, can take hours to thaw and infuse
Unfractionated Hold 0–1 Hold 0–2 Hold 2 doses • Avoid use in patients taking strong dual inducers of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein
heparin: 333 IU/kg x 1, then 250 IU/kg every 12 hours Increase by Decrease by dose, doses, decrease decrease by (e.g., rifampin, carbamazepine, phenytoin, St. John’s Wort). Prothrombin 25-50 units/ • Rapid, complete INR correction in warfarin-treated
10–15%* 0–10% decrease by by 10–15% +/- 15–20% complex kg IV (lower patients
B. Initial Warfarin Dosing for Venous Thromboembolism or Atrial 10–15% Vit. K Dose adjustments: concentrates doses studied) • Small volume infusion over 10-30 minutes
Vit. K
Fibrillation in Ambulatory Outpatients, Target INR 2.0-3.0 2.5 mg po 2.5–5 mg po Dose 2.5 mg twice daily if: (PCC) • Risk of thrombosis 1.4%; contraindicated with history
1. Two or more of the following are present: of HIT
General Considerations
• Age ≥80 years • Short half-life, may need repeat dose after 6 hours
1. Obtain baseline PT/INR and investigate if abnormal.
• Body weight ≤60 kg • Consider concurrent FFP if 3-factor PCC used
2. Determine use of potential warfarin interacting medications.
• Serum creatinine ≥1.5 mg/dL (133 µmol/L)
3. Document target INR and prescribed warfarin tablet strength. Repeat INR Repeat INR Repeat OR
Recombinant 15-90 • Rapid infusion of small volume
Repeat INR Repeat INR factor VIIa micrograms/ • Rapid complete INR correction in warfarin patients,
4. Provide patient education on safety, monitoring, drug and food interactions. within 2 within 1 INR 2. Use of strong dual inhibitors of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein (e.g.,ketoconazole,
within 1 week in 2 days (rFVIIa) kg but may not correct bleeding because only restores
5. For acute thrombosis, overlap with heparin/LMWH/fondaparinux for 5+ days until weeks week next day itraconazole, ritonavir, clarithromycin) (lower doses FVIIa
INR therapeutic.
6. Recommend first INR check on day 3-4. Do not administer apixaban in patients with both #1 and #2. studied) • Risk of thrombosis 5-10%
*Consider 15% increase if INR ≤1.5 without explanation • Short half-life, may need repeat dose after 2 hours
7. Clinical judgment should supersede this nomogram.
II. ANTICOAGULANT REVERSAL Aminocaproic 4-5 g IV/po • May increase risk of thrombosis
D. Dabigatran Dosing to Prevent Stroke and Systemic Embolism in
Day INR DAILY DOSE acid over 1 hr, then • May accumulate in patients with renal impairment,
Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation A. General Principles of Management of Anticoagulant-Associated
1 g/hr x 8 hrs reduce loading dose or infusion rate
1-3 Not required 5 mg* Dose: Bleeding (maximum • Caution or avoid use in hematuria due to upper
1.0-1.3 7.5 mg CrCl >30 ml/min*: 150 mg orally, twice daily dose 30 g/24 urinary tract origin
HASHTI
1.4-1.5 5 mg Avoid use in patients with CrCl <30 and taking P-glycoprotein inhibitors (e.g., hrs)
1. Hold further doses of anticoagulant
dronedarone, ketoconazole)
3 or 4 1.6-1.8 5/2.5 mg alternating 2. Consider Antidote Tranexamic 1300 mg po • Labeled indication for menorrhagia
Avoid use in patients taking P-glycoprotein inducers (e.g., rifampin)
>1.9 2.5 mg 3. Supportive treatment acid q8h • Use for other indications currently off label
Dose adjustments: a. Volume resuscitation (intravenous fluids)
>2.0 Hold x 1 day, then 2.5 mg†
CrCl 15-30 ml/min*: 75 mg orally, twice daily b. Hemodynamic support (inotropes, monitoring) 1. Reversal of Warfarin (Coumadin®, Jantoven®)
< 1.5 Increase by 15% of ADD CrCl 30-50 and taking P-glycoprotein inhibitors: 75 mg orally, twice daily 4. Local or surgical Hemostatic measures
1.6-1.9 Increase by 10% of ADD a. Anti-fibrinolytic agents can be considered (aminocaproic acid, tranexamic acid) Non-Urgent Urgent (Not bleeding) Urgent (Bleeding)
No recommendation for CrCl <15 ml/min or on dialysis. Outside US—patients with CrCl
2.0-3.0 No Change 5. Transfusion • Stop 5 days prior to • If procedure can be delayed 6-24 • HASHTI
>30 ml/min and age >75 years or propensity for GI bleeding: 110 mg twice daily.
7 & 10 3.1-3.5 Decrease by 10% of ADD a. Red blood cells for severe or symptomatic anemia procedure hours, vitamin K 5-10 mg PO/IV; • Vitamin K 5-10 mg
b. Platelets if thrombocytopenia (<50 x 109/L) or patient on long-acting antiplatelet • Check INR 1-2 days otherwise: IV; repeat in 12
3.6-4.0 Decrease by 15% of ADD
agents prior ° FFP or PCC prior to procedure. hours as needed
> 4.1 Hold 1 day, decrease by 15% (or more)† • PCC or FFP;
6. Investigate for bleeding source ° If INR >1.5 administer Repeat in 6-12 hours if INR
> 6.0 Consider Vitamin K† vitamin K 1-2 mg PO >1.5 and repeat every 6
Definitions Used for Reversal Situations hours as needed
Abbreviations: ADD = average daily dose ° Vitamin K 5-10 mg PO/IV if
Non-urgent: Reversal is elective (procedures >5 days away) sustained reversal is desired
* 2.5 mg for frailty, liver disease, malnutrition, drugs that enhance warfarin activity, or Asian Urgent (without bleeding): Reversal needed within hours
ethnicity; 5-7.5 mg for young healthy patients Urgent (with bleeding): Immediate reversal
† Check INR more frequently
I. ANTICOAGULANT DOSING C. Chronic Warfarin Dose Adjustment in Non-Bleeding Patients E. Rivaroxaban Dosing to Prevent Stroke and Systemic Embolism B. Agents to Stop Bleeding
This nomogram is suggested for non-bleeding patients with target INR 2.0-3.0 who are in Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation and to Treat Venous
A. Subcutaneous Heparin Dosing for Treatment of Acute Venous Agent Dose Comments
out of range and who are not at high risk of bleeding. Thromboembolism
Thromboembolism Vitamin K 1-10 mg IV/ • Infusion reactions rare; administer over 20-30 min
1. If INR >3.0 confirm no bleeding. • Avoid use in patients taking strong dual inhibitors of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein PO • Takes 6 (IV) to 24 (PO) hours to reverse warfarin
General Considerations (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, ritonavir).
2. Consider noncompliance, illness, drug interaction, or dietary change as reason for • Large doses can cause warfarin resistance on
1. Round weight-based dose to nearest prefilled syringe size for LMWH. • Avoid use in patients taking strong dual inducers of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein
out-of-range INR. resumption
2. No dose cap for obesity except dalteparin in cancer patients. (e.g., rifampin, phenytoin, carbamazepine, phenobarbital, St. John’s Wort); this may
3. Clinical judgment should supersede this nomogram. • Subcutaneous or intramuscular administration not
3. Consider measuring anti-Xa heparin levels after 3rd dose for weight >120 kg or lead to reduced rivaroxaban plasma concentrations. recommended
<60 kg.
4. Repeat CBC day 7 and consider heparin-induced thrombocytopenia if platelets 1. Atrial fibrillation Protamine 12.5-50 mg IV • Full reversal of unfractionated heparin
declining. • CrCl >50 ml/min: 20 mg once daily with evening meal* sulfate • 60-80% reversal of LMWH
Target INR
• If heparin exposure in previous 3 months, CBC on day 3 rather than day 7. • CrCl 15-50 ml/min: 15 mg once daily with evening meal* • No reversal of fondaparinux
2.0–3.0
5. Use LMWH with caution if at all, and monitor anti-Xa levels if creatinine clearance • CrCl <15 ml/min: Avoid use
Platelets 1 apheresis • Used in patients receiving antiplatelet therapy
(CrCl) <30 ml/min. *US labeling: Outside US—give with a meal at same time each day; may be given with breakfast. unit • Raise platelet count by 30 x 109/L
Subcutaneous Dosing 5-8 whole • Goal platelet count 50-100 x 109/L (indication
2. Venous Thromboembolism blood units dependent)
Enoxaparin: 1 mg/kg every 12 hours or 1.5 mg/kg daily • 15 mg every 12 hours for 21 days followed by 20 mg once daily, taken with food
- For cancer patients and those at high bleeding or thrombosis • Not recommended if CrCl <30 ml/min Frozen plasma 10-30 mL/kg • Replaces all coagulation factors, but cannot fully
risk, favor twice-daily dosing INR < 2.0 INR 3.1–3.5 INR 3.6–4.0 INR 4.1–8.9 INR >9.0 (FFP) (1 unit = correct
Dalteparin: 200 IU/kg daily or 100 IU/kg every 12 hours F. Apixaban Dosing to Prevent Stroke and Systemic Embolism in ~250 ml) ° Hemostasis usually requires coagulation factor
Tinzaparin: 175 IU/kg daily Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation levels ~30%
Fondaparinux: <50 kg: 5 mg daily. 50-100 kg: 7.5 mg daily. >100 kg: 10 mg ° Factor IX may only reach 20%
Dose: 5 mg twice daily • Short half-life, may need repeat dosing after 6 hours
daily
• CrCl <15 ml/min: Avoid use • Large volume, can take hours to thaw and infuse
Unfractionated Hold 0–1 Hold 0–2 Hold 2 doses • Avoid use in patients taking strong dual inducers of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein
heparin: 333 IU/kg x 1, then 250 IU/kg every 12 hours Increase by Decrease by dose, doses, decrease decrease by (e.g., rifampin, carbamazepine, phenytoin, St. John’s Wort). Prothrombin 25-50 units/ • Rapid, complete INR correction in warfarin-treated
10–15%* 0–10% decrease by by 10–15% +/- 15–20% complex kg IV (lower patients
B. Initial Warfarin Dosing for Venous Thromboembolism or Atrial 10–15% Vit. K Dose adjustments: concentrates doses studied) • Small volume infusion over 10-30 minutes
Vit. K
Fibrillation in Ambulatory Outpatients, Target INR 2.0-3.0 2.5 mg po 2.5–5 mg po Dose 2.5 mg twice daily if: (PCC) • Risk of thrombosis 1.4%; contraindicated with history
1. Two or more of the following are present: of HIT
General Considerations
• Age ≥80 years • Short half-life, may need repeat dose after 6 hours
1. Obtain baseline PT/INR and investigate if abnormal.
• Body weight ≤60 kg • Consider concurrent FFP if 3-factor PCC used
2. Determine use of potential warfarin interacting medications.
• Serum creatinine ≥1.5 mg/dL (133 µmol/L)
3. Document target INR and prescribed warfarin tablet strength. Repeat INR Repeat INR Repeat OR
Recombinant 15-90 • Rapid infusion of small volume
Repeat INR Repeat INR factor VIIa micrograms/ • Rapid complete INR correction in warfarin patients,
4. Provide patient education on safety, monitoring, drug and food interactions. within 2 within 1 INR 2. Use of strong dual inhibitors of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein (e.g.,ketoconazole,
within 1 week in 2 days (rFVIIa) kg but may not correct bleeding because only restores
5. For acute thrombosis, overlap with heparin/LMWH/fondaparinux for 5+ days until weeks week next day itraconazole, ritonavir, clarithromycin) (lower doses FVIIa
INR therapeutic.
6. Recommend first INR check on day 3-4. Do not administer apixaban in patients with both #1 and #2. studied) • Risk of thrombosis 5-10%
*Consider 15% increase if INR ≤1.5 without explanation • Short half-life, may need repeat dose after 2 hours
7. Clinical judgment should supersede this nomogram.
II. ANTICOAGULANT REVERSAL Aminocaproic 4-5 g IV/po • May increase risk of thrombosis
D. Dabigatran Dosing to Prevent Stroke and Systemic Embolism in
Day INR DAILY DOSE acid over 1 hr, then • May accumulate in patients with renal impairment,
Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation A. General Principles of Management of Anticoagulant-Associated
1 g/hr x 8 hrs reduce loading dose or infusion rate
1-3 Not required 5 mg* Dose: Bleeding (maximum • Caution or avoid use in hematuria due to upper
1.0-1.3 7.5 mg CrCl >30 ml/min*: 150 mg orally, twice daily dose 30 g/24 urinary tract origin
HASHTI
1.4-1.5 5 mg Avoid use in patients with CrCl <30 and taking P-glycoprotein inhibitors (e.g., hrs)
1. Hold further doses of anticoagulant
dronedarone, ketoconazole)
3 or 4 1.6-1.8 5/2.5 mg alternating 2. Consider Antidote Tranexamic 1300 mg po • Labeled indication for menorrhagia
Avoid use in patients taking P-glycoprotein inducers (e.g., rifampin)
>1.9 2.5 mg 3. Supportive treatment acid q8h • Use for other indications currently off label
Dose adjustments: a. Volume resuscitation (intravenous fluids)
>2.0 Hold x 1 day, then 2.5 mg†
CrCl 15-30 ml/min*: 75 mg orally, twice daily b. Hemodynamic support (inotropes, monitoring) 1. Reversal of Warfarin (Coumadin®, Jantoven®)
< 1.5 Increase by 15% of ADD CrCl 30-50 and taking P-glycoprotein inhibitors: 75 mg orally, twice daily 4. Local or surgical Hemostatic measures
1.6-1.9 Increase by 10% of ADD a. Anti-fibrinolytic agents can be considered (aminocaproic acid, tranexamic acid) Non-Urgent Urgent (Not bleeding) Urgent (Bleeding)
No recommendation for CrCl <15 ml/min or on dialysis. Outside US—patients with CrCl
2.0-3.0 No Change 5. Transfusion • Stop 5 days prior to • If procedure can be delayed 6-24 • HASHTI
>30 ml/min and age >75 years or propensity for GI bleeding: 110 mg twice daily.
7 & 10 3.1-3.5 Decrease by 10% of ADD a. Red blood cells for severe or symptomatic anemia procedure hours, vitamin K 5-10 mg PO/IV; • Vitamin K 5-10 mg
b. Platelets if thrombocytopenia (<50 x 109/L) or patient on long-acting antiplatelet • Check INR 1-2 days otherwise: IV; repeat in 12
3.6-4.0 Decrease by 15% of ADD
agents prior ° FFP or PCC prior to procedure. hours as needed
> 4.1 Hold 1 day, decrease by 15% (or more)† • PCC or FFP;
6. Investigate for bleeding source ° If INR >1.5 administer Repeat in 6-12 hours if INR
> 6.0 Consider Vitamin K† vitamin K 1-2 mg PO >1.5 and repeat every 6
Definitions Used for Reversal Situations hours as needed
Abbreviations: ADD = average daily dose ° Vitamin K 5-10 mg PO/IV if
Non-urgent: Reversal is elective (procedures >5 days away) sustained reversal is desired
* 2.5 mg for frailty, liver disease, malnutrition, drugs that enhance warfarin activity, or Asian Urgent (without bleeding): Reversal needed within hours
ethnicity; 5-7.5 mg for young healthy patients Urgent (with bleeding): Immediate reversal
† Check INR more frequently
You might also like
- Paracetamol (Aeknil), Metoclopramide (Plasil), Cotrimoxazole Susp. (Macromed), PedialyteDocument4 pagesParacetamol (Aeknil), Metoclopramide (Plasil), Cotrimoxazole Susp. (Macromed), PedialyteYum C100% (2)
- تجميعةDocument168 pagesتجميعةRn nadeenNo ratings yet
- Plab Emergency Medicine CompleteDocument141 pagesPlab Emergency Medicine CompleteSyedKashifAli100% (1)
- Medtech NotesDocument23 pagesMedtech NotesOnline PrometricNo ratings yet
- 1388 Cardiovascular Drugs: Interactions Units Adverse Effects, Treatment, and PrecautionsDocument2 pages1388 Cardiovascular Drugs: Interactions Units Adverse Effects, Treatment, and PrecautionsPopov VictorNo ratings yet
- NOACs DOACs Coagulation Tests 2018nov16Document5 pagesNOACs DOACs Coagulation Tests 2018nov16Agam AsikNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulation Guidelines For Neuraxial Procedures: Anticoagulants, InjectableDocument4 pagesAnticoagulation Guidelines For Neuraxial Procedures: Anticoagulants, InjectablepaulaNo ratings yet
- Acetaminophen (APAP) ToxicityDocument12 pagesAcetaminophen (APAP) ToxicityJessa MaeNo ratings yet
- RX Cheat Sheet Pharmacy CrackDocument1 pageRX Cheat Sheet Pharmacy Crackramesh kumar100% (1)
- Transition of Anticoagulants 2016: From To ActionDocument4 pagesTransition of Anticoagulants 2016: From To ActionS_XangaiNo ratings yet
- Drug Interactions ActivityDocument5 pagesDrug Interactions ActivityPatricia Camryne AmbidaNo ratings yet
- Antivirale Covid en No HospitalizadosDocument1 pageAntivirale Covid en No HospitalizadosJORGENo ratings yet
- Rivaroxaban PresentationDocument13 pagesRivaroxaban PresentationReem El-HusseinyNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Pharmacoogy Guide PDFDocument18 pagesUltimate Pharmacoogy Guide PDFElizabella Henrietta TanaquilNo ratings yet
- MILsgsdgds VDocument4 pagesMILsgsdgds Vgarywall.ukNo ratings yet
- New Oral New Oral Anticoagulants G: RB H TT MD Rebecca Hanratty, MD Denver Health April 12, 2011Document55 pagesNew Oral New Oral Anticoagulants G: RB H TT MD Rebecca Hanratty, MD Denver Health April 12, 2011andresrgomezNo ratings yet
- Psychopharmacology-Mood StabilizerDocument5 pagesPsychopharmacology-Mood StabilizerVon Hippo100% (2)
- 9 Ketamine Drug StudyDocument7 pages9 Ketamine Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Clinically Significant Drug Interactions - AAFPDocument19 pagesClinically Significant Drug Interactions - AAFPAbchoNo ratings yet
- Anti Coagulants & FibrinolyticsDocument54 pagesAnti Coagulants & FibrinolyticsSunanda mohanNo ratings yet
- DabigatranDocument25 pagesDabigatranNagesh JadavNo ratings yet
- Diphos Dihydroartemisinin+Piperaquine PhosphateDocument1 pageDiphos Dihydroartemisinin+Piperaquine PhosphateMuhammad Azhar SattarNo ratings yet
- Helicobacter Pylori Urea c14 Pi Aclmar Pat Nat 00227cDocument1 pageHelicobacter Pylori Urea c14 Pi Aclmar Pat Nat 00227cWisnu Agung WiyanggaNo ratings yet
- PRADAXA: Dosing Guide: Starting Patients On PRADAXADocument2 pagesPRADAXA: Dosing Guide: Starting Patients On PRADAXAPapp Szodorai BeátaNo ratings yet
- Clinically Significant Drug InteractionsDocument18 pagesClinically Significant Drug Interactionsmagus davilaNo ratings yet
- Magumun - 3B WARDDocument13 pagesMagumun - 3B WARDFrancesca Aurea MagumunNo ratings yet
- OET 2.0 ReadingDocument202 pagesOET 2.0 ReadingCandy Benitez100% (1)
- Deep Vein ThrombosisDocument4 pagesDeep Vein ThrombosisStefania CristinaNo ratings yet
- The ABC's of Dopamine Receptor Partial Agonists - Aripiprazole, Brexpiprazole and CariprazineDocument10 pagesThe ABC's of Dopamine Receptor Partial Agonists - Aripiprazole, Brexpiprazole and Cariprazineolivukovic100% (1)
- DRUGS2Document1 pageDRUGS2KaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- 1) Selective Serotonin Reuptic Inhepetor (SSRI) - Xetine: Fluoxetine, Paroxetine, Sertraline, DoluexitineDocument13 pages1) Selective Serotonin Reuptic Inhepetor (SSRI) - Xetine: Fluoxetine, Paroxetine, Sertraline, DoluexitineSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- 8 Drug StudyDocument9 pages8 Drug StudyJohn Michael M. RosalesNo ratings yet
- D. PharmaDocument45 pagesD. PharmaShivam Das, Tehsil KulpaharNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyDean Angelo BarrientosNo ratings yet
- DDI Booklet 2019Document88 pagesDDI Booklet 2019Nikki TranNo ratings yet
- Drug Study KidneyDocument9 pagesDrug Study Kidneymcnover22No ratings yet
- Final Haad (DOH) ExamDocument9 pagesFinal Haad (DOH) ExamsenthamizhselvanNo ratings yet
- Reversing The New AnticoagulantsDocument24 pagesReversing The New AnticoagulantsFurman BorstNo ratings yet
- Rifamycin - General InformationDocument4 pagesRifamycin - General InformationRachelle Anne LetranNo ratings yet
- Careram: Tablets 25 MGDocument6 pagesCareram: Tablets 25 MGPriya Ranjan100% (1)
- Drug Study SurgeryDocument1 pageDrug Study SurgerygorgeazNo ratings yet
- Psych Pharmacotherapy GuideDocument36 pagesPsych Pharmacotherapy Guideapi-753059042No ratings yet
- Management of Paracetamol ToxicityDocument28 pagesManagement of Paracetamol ToxicityA94-WONG JING TONGNo ratings yet
- CariprazineDocument46 pagesCariprazineRajmohan VNo ratings yet
- Reading Sample Test 2 Text Booklet Part A PDFDocument4 pagesReading Sample Test 2 Text Booklet Part A PDFAryaNo ratings yet
- Combined Alternative Meds MemoDocument62 pagesCombined Alternative Meds MemoFDRHPO North Country EMS Program AgencyNo ratings yet
- Nifedipine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesNifedipine Drug StudyCrystal Queen MarquezNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Dosage Adjustments in Renal Impairment For FormularyDocument20 pagesAntimicrobial Dosage Adjustments in Renal Impairment For Formularyangkatanjuli2019No ratings yet
- DRUG StudyDocument43 pagesDRUG StudyNathalie Faith CotengNo ratings yet
- What Diazepam Rectubes Are and What They Are Used ForDocument2 pagesWhat Diazepam Rectubes Are and What They Are Used ForsenaNo ratings yet
- Lopinavir 9Document9 pagesLopinavir 9นิวนิ่วนิ้ว ศิษย์ปตทNo ratings yet
- Sample: Reading Sub-Test - Text Booklet: Part ADocument24 pagesSample: Reading Sub-Test - Text Booklet: Part AAlwin BrightNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulant Guidelines ASHDocument8 pagesAnticoagulant Guidelines ASHmandamanda31No ratings yet
- Patient NameDocument4 pagesPatient NameCatherine MetraNo ratings yet
- Anti CoagulantsDocument37 pagesAnti CoagulantsMaria khurshidNo ratings yet
- Caripirazine Preclinical Discovery in SchizophreniaDocument13 pagesCaripirazine Preclinical Discovery in SchizophreniaEsraa SaeedNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Disease DrugsDocument6 pagesPeptic Ulcer Disease DrugsApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Medicines Management V8Document7 pagesPerioperative Medicines Management V8Waleed Ahmad.No ratings yet
- PDF Surgical Prophylaxis Poster Dec 2021Document1 pagePDF Surgical Prophylaxis Poster Dec 2021Midhun KishorNo ratings yet
- Docetaxel Carboplatin Trastuzumab T Carbo H Breast Cancer Adjuvant ProtocolDocument14 pagesDocetaxel Carboplatin Trastuzumab T Carbo H Breast Cancer Adjuvant ProtocolsmokkerNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Use of Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin During Dental Extractions in A Medicaid Population.Document6 pagesUse of Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin During Dental Extractions in A Medicaid Population.saeint.peterNo ratings yet
- HAM PresentationDocument28 pagesHAM Presentationsofiasofi191980No ratings yet
- Warfarin Q and ADocument40 pagesWarfarin Q and AAbdul-Rhman Hamdy KishkNo ratings yet
- Antiphospholipid SyndromeDocument6 pagesAntiphospholipid SyndromeOm Lakhani100% (1)
- ABUHB - Clinical - 0780 AnticoagulationForHeartValveReplacementsMarch2019 PDFDocument9 pagesABUHB - Clinical - 0780 AnticoagulationForHeartValveReplacementsMarch2019 PDFErika KennedyNo ratings yet
- Switching Between AnticoagulantsDocument2 pagesSwitching Between AnticoagulantsSylvinho46No ratings yet
- Ischemic Limb Gangrene With PulsesDocument14 pagesIschemic Limb Gangrene With PulsesJustin Ryan TanNo ratings yet
- GPHC Pre-Registration Complete Exam Question List JUNE 2017 - NOV 2021Document50 pagesGPHC Pre-Registration Complete Exam Question List JUNE 2017 - NOV 2021Summer Sunshine TVNo ratings yet
- Stroke Research Review Issue 27 PDFDocument4 pagesStroke Research Review Issue 27 PDFGhaidaa AlarajNo ratings yet
- Cardio AssignDocument13 pagesCardio AssignRhona Jade Punsalang MontalbanNo ratings yet
- Avery Franklin SummativeDocument3 pagesAvery Franklin Summativeapi-596284176No ratings yet
- HP - Supplement Guide - 9Document30 pagesHP - Supplement Guide - 9Jelena StojadinovNo ratings yet
- MCQ Bleeding Disorders 2nd Year2021Document6 pagesMCQ Bleeding Disorders 2nd Year2021sherif mamdoohNo ratings yet
- Adr Manor NotesDocument7 pagesAdr Manor NotesPNo ratings yet
- 1000 Mcqs - General Medicine & Medical Emergencies Plus September 2014 McqsDocument18 pages1000 Mcqs - General Medicine & Medical Emergencies Plus September 2014 McqsSelvaArockiamNo ratings yet
- Cardioembolic StrokeDocument13 pagesCardioembolic StrokeAzarel JimmyNo ratings yet
- Deep Vein Thrombosis: EssentialsDocument7 pagesDeep Vein Thrombosis: EssentialsLuthfia RahmaditaNo ratings yet
- Free Nclex QuestionsDocument161 pagesFree Nclex QuestionspadmaNo ratings yet
- Coronary Atery Disease-Htn-Thrombo QuestionsDocument38 pagesCoronary Atery Disease-Htn-Thrombo Questionssrivari sriniNo ratings yet
- Warfarin GuidelinesDocument9 pagesWarfarin Guidelinesmarto langNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulant DrugsDocument7 pagesAnticoagulant DrugsNadia MohammadNo ratings yet
- Mini Warfarin GuidelinesDocument2 pagesMini Warfarin GuidelinesPeunn NattaphatNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulants DaniellewelschmeyerDocument30 pagesAnticoagulants Daniellewelschmeyersumanth gowdaNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument33 pagesPharmacologyAlibasher MacalnasNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation - Diagnosis and Treatment - AAFP PDFDocument8 pagesAtrial Fibrillation - Diagnosis and Treatment - AAFP PDFNaufal AmanullahNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology 2 (Phbs 107) Midterm Examination MULTIPLE CHOICE: Each of The Questions, Statements, or Incomplete Statements Can Be CorrectlyDocument17 pagesPharmacology 2 (Phbs 107) Midterm Examination MULTIPLE CHOICE: Each of The Questions, Statements, or Incomplete Statements Can Be CorrectlyT'amo HanashNo ratings yet
- Complex Protrombina Huvh 01 10Document11 pagesComplex Protrombina Huvh 01 10Santiago Rodriguez MoralesNo ratings yet