Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MATH Forecast Fr5
MATH Forecast Fr5
Uploaded by
Patricia NobleCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Fierce Urgency of Now by Daniel FischlinDocument69 pagesThe Fierce Urgency of Now by Daniel FischlinDuke University PressNo ratings yet
- Sine Law WorksheetDocument2 pagesSine Law Worksheetapi-297847828100% (1)
- Forced Torsional Oscillations of An Elastic Half-Space. I: Articles You May Be Interested inDocument4 pagesForced Torsional Oscillations of An Elastic Half-Space. I: Articles You May Be Interested inFahim KhanNo ratings yet
- Calculus 3Document2 pagesCalculus 3Darren Troy Lingao Mayor67% (3)
- Math101 Final Summer 2022 SolutionsDocument4 pagesMath101 Final Summer 2022 SolutionsmohammadhoseinzeinaliNo ratings yet
- Mock Diagnostic TestDocument16 pagesMock Diagnostic Testalexander villamorNo ratings yet
- Examiners' Commentaries 2015 Mock: MT105a Maths 1 Comments On Specific Questions in Section ADocument10 pagesExaminers' Commentaries 2015 Mock: MT105a Maths 1 Comments On Specific Questions in Section AHa PhuongNo ratings yet
- Solutionbank C1: Edexcel Modular Mathematics For AS and A-LevelDocument53 pagesSolutionbank C1: Edexcel Modular Mathematics For AS and A-LevelMaruf_007No ratings yet
- North Sydney Boys 2015 4U HY & SolutionsDocument11 pagesNorth Sydney Boys 2015 4U HY & Solutionsz5588894No ratings yet
- MST125 201609Document13 pagesMST125 201609Iain DoranNo ratings yet
- C2 - Jan - 05 Model SolutionDocument15 pagesC2 - Jan - 05 Model SolutionAFRAH ANEESNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Graphs of FunctionsDocument10 pagesChapter 13 - Graphs of Functionsg-46005995No ratings yet
- Hssc-I (R&T) Federal Board Mathematic Test - 1 Chapter 1+2: Xiy Z Lies On. X-Axis Y-Axis XDocument2 pagesHssc-I (R&T) Federal Board Mathematic Test - 1 Chapter 1+2: Xiy Z Lies On. X-Axis Y-Axis XAL-Rayyan PoultryNo ratings yet
- Sem 1 2015 Math TestDocument9 pagesSem 1 2015 Math TestdNo ratings yet
- Ujian Feb f5 2011Document8 pagesUjian Feb f5 2011Hunkok TanNo ratings yet
- MATH2201 Assignment 1Document3 pagesMATH2201 Assignment 1Jesse Waechter-CornwillNo ratings yet
- Calculus Practice # 5b: Differentiating A Sum: DX DV DX Du DX DyDocument2 pagesCalculus Practice # 5b: Differentiating A Sum: DX DV DX Du DX Dygusvani aulia putriNo ratings yet
- C.maths First TermDocument1 pageC.maths First Termkrish benoitNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning HomeworkDocument8 pagesMachine Learning HomeworkWessel van DamNo ratings yet
- General Maths Unit 2 - Topic 1 Linear Equations & Graphs HomeworkDocument3 pagesGeneral Maths Unit 2 - Topic 1 Linear Equations & Graphs HomeworkSam PITSONNo ratings yet
- (1A) Math 1A - Math RefDocument7 pages(1A) Math 1A - Math RefJake Floyd G. FabianNo ratings yet
- HwsolnsDocument16 pagesHwsolnsPARAMITA DUTTANo ratings yet
- Samplefinal ADocument11 pagesSamplefinal A2kt2j5dwy6No ratings yet
- 2024 - 12MAT - Term 2 Assessment - Bank of QuestionsDocument12 pages2024 - 12MAT - Term 2 Assessment - Bank of QuestionsPurnima Sidhant BabbarNo ratings yet
- Solution P 1 Jan 19Document16 pagesSolution P 1 Jan 19hasan zaidiNo ratings yet
- Coordinate GeometryDocument33 pagesCoordinate GeometryvenkatachalampreethaNo ratings yet
- Homework 0: Mathematical Background For Machine LearningDocument11 pagesHomework 0: Mathematical Background For Machine Learninganwer fadelNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-01-25 at 11.26.23 AMDocument16 pagesScreenshot 2023-01-25 at 11.26.23 AMRajeev RastogiNo ratings yet
- Pre-Assignment For L1: Limit of A FunctionDocument6 pagesPre-Assignment For L1: Limit of A FunctionJordane McCallaNo ratings yet
- Backpropagation ExercisesDocument7 pagesBackpropagation ExercisesSiriusNo ratings yet
- Ss - Vtamps 2024 4Document13 pagesSs - Vtamps 2024 4KIRSTEL JOY PICARNo ratings yet
- S03C01 5.5 Teorema Fundamental Del CálculoDocument13 pagesS03C01 5.5 Teorema Fundamental Del Cálculogabriel cervinoNo ratings yet
- Itute 2007 Mathematical Methods Examination 2 SolutionsDocument3 pagesItute 2007 Mathematical Methods Examination 2 SolutionsnochnochNo ratings yet
- North Sydney Boys 2014 2U HY & Solutions PDFDocument12 pagesNorth Sydney Boys 2014 2U HY & Solutions PDFfbjsjdfhNo ratings yet
- UACE MathematicsDocument4 pagesUACE MathematicsTusiime RobertNo ratings yet
- 2021 F5 T2 Paper 1 Secction A1 MSDocument4 pages2021 F5 T2 Paper 1 Secction A1 MSTai Yin LAMNo ratings yet
- Manifolds, Tensor Analysis and Applications 3rd Ed. - Marsden, Ratiu and AbrahamDocument21 pagesManifolds, Tensor Analysis and Applications 3rd Ed. - Marsden, Ratiu and AbrahamSreerag S KumarNo ratings yet
- 35 (Pengantar Diferensiasi)Document16 pages35 (Pengantar Diferensiasi)Muh fadel alqurtubiNo ratings yet
- Fall 2021Document11 pagesFall 2021JanviNo ratings yet
- January 2008 6665 Core Mathematics C3 Mark Scheme: X X X X X X X X XDocument6 pagesJanuary 2008 6665 Core Mathematics C3 Mark Scheme: X X X X X X X X XMichael 黃建峰 HoangNo ratings yet
- Lecture NotesDocument90 pagesLecture NotesSharad RaykhereNo ratings yet
- Sample 2Document12 pagesSample 2exhasbeenslainNo ratings yet
- Sydney Grammar 2014 3U Prelim Yearly & SolutionsDocument22 pagesSydney Grammar 2014 3U Prelim Yearly & SolutionsgeeeelooNo ratings yet
- Graphs of Functions IIDocument17 pagesGraphs of Functions IIVisnuVaratanNo ratings yet
- CLS JEEAD-19-20 XI Mat Target-4 Level-2 Chapter-12Document41 pagesCLS JEEAD-19-20 XI Mat Target-4 Level-2 Chapter-12Awan DubeyNo ratings yet
- Test 17Document9 pagesTest 17Saad HasanNo ratings yet
- Solutions & Answers For Kerala Engineering Entrance Examination-2011 - Paper Ii Version - B1Document11 pagesSolutions & Answers For Kerala Engineering Entrance Examination-2011 - Paper Ii Version - B1ArgoNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced 2024 Complete SolutionDocument84 pagesJEE Advanced 2024 Complete Solutionamrocker080No ratings yet
- Quadratic Functions Practice Test BDocument3 pagesQuadratic Functions Practice Test ByourmomsdadsfriendNo ratings yet
- 3b. Coordinate Geometry Further Questions AnswersDocument2 pages3b. Coordinate Geometry Further Questions AnswerslaavanyasathyvellNo ratings yet
- 2023 HSC Maths Ext 1Document20 pages2023 HSC Maths Ext 1n4eel3shNo ratings yet
- CCH 13Document21 pagesCCH 13navinavinaviNo ratings yet
- CLS JEEAD-19-20 XI Mat Target-4 Level-2 Chapter-13 PDFDocument54 pagesCLS JEEAD-19-20 XI Mat Target-4 Level-2 Chapter-13 PDFAniNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 1 Spring 2015Document5 pagesAssignment No 1 Spring 2015shahinaaslam938No ratings yet
- Definition Basic Formula and PrinciplesDocument5 pagesDefinition Basic Formula and PrinciplesJhoan Cinco VelardeNo ratings yet
- Finalf 04Document10 pagesFinalf 04vimashaanimalloverNo ratings yet
- MTH501 Practice Question Lecture 1 To 18-MergedDocument76 pagesMTH501 Practice Question Lecture 1 To 18-MergedomersaleemNo ratings yet
- C2 May 05 Model SolutionDocument22 pagesC2 May 05 Model SolutionAFRAH ANEESNo ratings yet
- Solve The ODE by Integration or by Remembering A Differentia - QuizletDocument4 pagesSolve The ODE by Integration or by Remembering A Differentia - QuizletRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 and 5Document18 pagesLec 4 and 5sehati8586No ratings yet
- Math 234 Winter 2012 FinalDocument11 pagesMath 234 Winter 2012 FinalKrage and JohnNo ratings yet
- Practice Set 3Document6 pagesPractice Set 3jordanhub05No ratings yet
- AlgebraDocument6 pagesAlgebraThein Min OoNo ratings yet
- Vectors, Spinors, and Complex Numbers in Classical and Quantum Physics David HestenesDocument23 pagesVectors, Spinors, and Complex Numbers in Classical and Quantum Physics David Hestenesosegeno654321100% (1)
- Assignment - 2 (CE 286 Survey II) Spring 2020Document2 pagesAssignment - 2 (CE 286 Survey II) Spring 2020Jawad Ahmed LeghariNo ratings yet
- Calculus I FinalDocument7 pagesCalculus I FinalRodrigo RomeroNo ratings yet
- Mainfile 1Document1 pageMainfile 1api-367252928No ratings yet
- 3.3-3.4 Centripetal Force and Rotating Frames of Reference TemplateDocument5 pages3.3-3.4 Centripetal Force and Rotating Frames of Reference TemplateAyman HalimeNo ratings yet
- Question On CFTDocument2 pagesQuestion On CFTABHINANDAN YADAVNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Reviewer For Grade 10 Q2Document2 pagesMathematics Reviewer For Grade 10 Q2martinaloreyn.delrosarioNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet SUBJECT-Maths: Chapter 5: Lines and Angles Class - ViiDocument1 pageWork Sheet SUBJECT-Maths: Chapter 5: Lines and Angles Class - ViiAnil kumarNo ratings yet
- Section 1.1-1.3 WorksheetDocument5 pagesSection 1.1-1.3 WorksheetTragic KyroNo ratings yet
- Grossberg Identity Cultural Studies Is That All There Is PDFDocument11 pagesGrossberg Identity Cultural Studies Is That All There Is PDFTias BradburyNo ratings yet
- Conic Section Maths Project PDFDocument13 pagesConic Section Maths Project PDFSiva Kumar75% (4)
- Tugas 6 - Analisa Data LapanganDocument11 pagesTugas 6 - Analisa Data LapanganRika PermataNo ratings yet
- Parts of Circles (Read) Geometry CK-12 FoundationDocument1 pageParts of Circles (Read) Geometry CK-12 FoundationJohn Thiery FedericoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2.1,2.2Document3 pagesExercise 2.1,2.2Angeline DangNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Drafting - Principles of Tangency: ObjectivesDocument7 pagesFundamentals of Drafting - Principles of Tangency: ObjectivesguyNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight-Line EndDocument10 pagesMotion in A Straight-Line EndQuynh Mai Do LeNo ratings yet
- FIZ101E TotDocument88 pagesFIZ101E TotdeniNo ratings yet
- CE 408 Module 3Document19 pagesCE 408 Module 3Janina MatanguihanNo ratings yet
- M 221Document12 pagesM 221Epic WinNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics NotesDocument6 pagesO Level Physics NotesHamza Kahemela86% (7)
- Geometry - 102714 - 4 2 Worksheet - Angles in A Triangle 1-3Document3 pagesGeometry - 102714 - 4 2 Worksheet - Angles in A Triangle 1-3api-252752147No ratings yet
- Mathematics/ Further Mathematics/ Pure Mathematics: EconomicsDocument32 pagesMathematics/ Further Mathematics/ Pure Mathematics: EconomicsBassem Khalid YasseenNo ratings yet
- Tute 1 PDFDocument2 pagesTute 1 PDFApoorv KhareNo ratings yet
- Emotion, Space and Society: John Urry, Anthony Elliott, David Radford, Nicola PittDocument8 pagesEmotion, Space and Society: John Urry, Anthony Elliott, David Radford, Nicola Pittমোঃ গোলাম কিবরিয়া রনিNo ratings yet
- Transformation RulesDocument2 pagesTransformation RulesMasterkeyNo ratings yet
- Math 2 PDFDocument1 pageMath 2 PDFJads CayabyabNo ratings yet
MATH Forecast Fr5
MATH Forecast Fr5
Uploaded by
Patricia NobleOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MATH Forecast Fr5
MATH Forecast Fr5
Uploaded by
Patricia NobleCopyright:
Available Formats
SPM FORECAST
(Fully-worked Solutions)
Form 5: Chapter 1 Number Bases
Paper 1 3 52 + 5 + 3 = 1 × 52 + 1 × 51 + 3 × 50
1 1 1 1
0 10 10 10 10
1 0 0 0 0 12 52 51 50
– 1 0 1 12 1 1 3
1 0 1 1 02
∴ 52 + 5 + 3 = 1135
Answer: D Answer: C
2 1 10 1
0 10 0 10 102
4 83 + 5 = 1 × 83 + 0 × 82 + 0 × 81 + 5 × 80
1 1 0 1 0 02
– 1 1 12 83 82 81 80
1 0 1 1 0 12 1 0 0 5
∴ 83 + 5 = 10058
Answer: C
Answer: A
5 3338
421 421 421
011 011 011
∴ 3338 = 110110112
Answer: A
Suc Math SPM (Forecast) F.indd 1 8/26/2009 10:42:29 AM
SPM FORECAST
(Fully-worked Solutions)
Form 5: Chapter 2 Graphs of Functions II
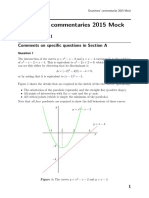
Paper 1 (c) From the graph,
1 y = ax2 (i) when x = 2.5, y = 5.
The smaller the value of ‘a’, the further the (ii) when y = –20, x = –0.6.
graph is from the y-axis.
(d) The given equation is
∴ When a = 5, it is graph I,
2x2 + 5x = 12
a = 1, it is graph II and
12
1 , it is graph III. 2x + 5 = — ..…
a=— x
2
1 The graph which is drawn is
∴ I: a = 5, II: a = 1, III: a = —
2 12
y = — ..…
x
Answer: D
– : y – (2x + 5) = 0
2 The graph shown is a graph of quadratic y = 2x + 5
function: Draw the straight line y = 2x + 5 and the
y = ax2 + b x-coordinate of the point of intersection
Since the shape of graph is , then a is of the straight line and the curve is
negative. x = 1.5.
∴ y = –x2 + 9 b is the y-intercept.
2 (a) When x = 3,
Answer: C y = 8x – 2x2
= 8(3) – 2(3)2
Paper 2 = 24 – 18
1 (a) When x = –3, =6
12 12
y=—=— = –4 When x = 4,
x –3 y = 8x – 2x2
When x = 1.5, = 8(4) – 2(4)2
12 12 = 32 – 32
y=—=— =8
x 1.5 =0
y
(b) When x = 5,
25
y = 8x – 2x2
12
y=— = 8(5) – 2(5)2
x
20 = 40 – 50
= –10
15
+5 y
2x
10 y= (b)
10
–2.5 5 7.5
–0.6 y=5
5
x 4.55
–3 –2 –1 O 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 x
–5 –2 –1 O 0.8 1 1.5 2 3 3.2 4 5 6
–5
–10
–10
–15
–15
–20 y = 8x – 2x 2
–20
–25 –25
Suc Math SPM (Forecast) F.indd 2 8/26/2009 10:42:30 AM
(c) From the graph,
(i) when x = 1.5, y = 7.5
(ii) when y = –5, x = –0.55, 4.55
(d) The given equation is
–8x + 2x2 = –5
0 = 8x – 2x2 – 5..…
The graph which is drawn is
y = 8x – 2x2 …
–:y=5
Draw the straight line y = 5 and the
x-coordinates of the points of
intersection of the straight line and the
curve are x = 0.8 and x = 3.2.
Suc Math SPM (Forecast) F.indd 3 8/26/2009 10:42:31 AM
SPM FORECAST
(Fully-worked Solutions)
Form 5: Chapter 3 Transformations III
Paper 2 (a) Draw a line segment to join the points
A and P. Construct a perpendicular
W V
1 (a) (i) H(4, 4) → H’(6, 1) → H’’(0, 1) bisector of the line segment AP..…
V W Draw a line segment to join the points
(ii) H(4, 4) → H’(2, 4) → H’’(4, 1)
B and Q. Construct a perpendicular
bisector of the line segment BQ..…
(b) X – Translation 5
3 (i) The centre of rotation is the point
Y – Anticlockwise rotation of 90°
of intersection of the perpendicular
about the point N(7, 10)
bisectors of and , i.e. (3, 5).
(ii) The angle of rotation is 90°
(c) (i) Scale factor = 2, Centre = (–1, 8)
(anticlockwise).
y
G H
(b) (i) A(1, 3) → A’(5, 0) → A’’(0, 5)
8
H G
Centre of
C
(ii) A(1, 3) → A’(3, 1) → A’’(7, –2)
B
enlargement 6 G
A (c) y
F
4
K Q′ L
2 8
E
y=6 R
x 6
–2 O 2 4 6
4
P
Q M
(ii) Area of EFG = 22 × Area of ABC 2
52 = 4 × Area of ABC
Area of ABC = 13 units2 x
O 2 4 6 8 10
∴ Area of LMN = Area of ABC
= 13 units2
(i) PQR is transformed to KQ’R
Centre of rotation under transformation V, i.e.
y
2
R reflection in the straight line
6
y = 6.
(ii) KQ’R is transformed to KLM
4
A
under transformation W, i.e.
Q
2
P enlargement with centre (5, 9)
and a scale factor of 2.
B C
x
O 2 4 6
Suc Math SPM (Forecast) F.indd 4 8/26/2009 10:42:32 AM
SPM FORECAST
(Fully-worked Solutions)
Form 5: Chapter 4 Matrices
Paper 1 2 (a) If no inverse, then determinant = 0.
∴ [2 × (–4)] – (4 × d) = 0
–2
1 (3 k) 3 = (12) –8 – 4d = 0
–4d = 8
–6 + 3k = 12 8
3k = 12 + 6 d = –—
4
3k = 18 d = –2
18
k=—
k=6
3
(b) Q = 2 –3 if d = –3
4 –4
1
Answer: A
Q = ——–————–——– –4
–1
[2 × (–4)] – (–3 × 4) –4 3
2
1
= ———– –4 3
–8 + 12 –4 2
2
1
7
+
p
3
= q
4
1
= — –4 3
1+p=4 7+3=q 4 –4 2
3
∴p=4–1
p=3
p × q = 3 × 10 = 30
∴ q = 10
=
–1 —
–1 —
4
1
2
Answer: C (c) QP = 2
6
Paper 2
1 (a) Q is the inverse matrix of P. 2 –3 a = 2
4 –4 b
6
∴ Q = P –1 =
1 –1 3
8 × (–1) – (–3) × 2 –2 8
a =—
b
1
4 –4–4 2 6
3 2
×2+3×6
=
1 –1 3
a =—
b
1
4 (–4)
(–4) × 2 + 2 × 6
–8 + 6 –2 8
1 –1 3
a =—1
–8–8 + 12
+ 18
=—
–2 –2 8 b 4
a =—1
104
1 3 b 4
— –—
= 2 2
10
—–
1 –4 = 4
1
8 –3 r –12
(b)
=
2 –1 s 4 5
—
= 2
r –1 3 –12
s = – —12 –2 8 4 5 or 2 —
1,
1
∴a=—
1 12 + 12 2 2
= –—
2 24 + 32 b=1
1 24
= –—
2 56
–12
= –28
∴ r = –12 and s = –28
Suc Math SPM (Forecast) F.indd 5 8/26/2009 10:42:32 AM
SPM FORECAST
(Fully-worked Solutions)
Form 5: Chapter 5 Variations
s2
Paper 1 3 Given that r ∝ — ,
1 t
1 Given that s ∝ —3 , ks 2
r r = ——
t
k
s = —3 When r = 8, s = 4 and t = 12,
r
k(42)
When s = 5 and r = 2, 8 = ———
12
k 8(12)
5=— k = ———
23
16
k = 40 k=6
40 6s2
∴s=— r=—
r3 t
Answer: D When r = 10, s = 5, t = u,
6(52)
2 Given that s ∝ r3, 10 = ———
u
s = kr3 10u = 150
When s = 135 and r = 3, u = 15
135 = k(33)
135 Answer: B
k = ——
27
=5
s = 5r3
When s = –40,
–40 = 5r3
r3 = –8
r = –2
Answer: B
Suc Math SPM (Forecast) F.indd 6 8/26/2009 10:42:33 AM
SPM FORECAST
(Fully-worked Solutions)
Form 5: Chapter 6 Gradient and Area Under a Graph
Paper 2
1 (a) Average speed of the lorry for the whole 10 – 0
journey from point P to point Q 18 – n 5
– ———– = – —
2
Negative gradient
Total distance travelled 5(18 – n) =
20
= ———————————
Total time taken 90 – 5n =
20
300 5n =
90 – 20
= ——
16 5n =
70
3 70
= 18 — m s–1 n = —–
4 5
(b) Speed of the car for the whole journey n = 14
= Gradient of the straight line ABC
Vertical axis (b) (i) Length of time the particle travels
= – ———————
Horizontal axis at a uniform speed
=n–7
300 – 0
= – ————
10 – 0 = 14 – 7 Horizontal part of
the graph
=7s
= –30 m s–1
(ii) Average speed in the first 7 s
Hence, the speed of the car for the
Total distance
whole journey from point Q to point P = ——————–
is 30 m s–1. Total time
(c) The point on the distance–time graph Area P + Area Q
when the lorry and the car meet is the = ——————–—
Total time
intersection point of the graph OBD and 1 1 (16 + 10)(3)
the graph ABC, i.e. point B. — (8 + 16)(4) + —
2 2
Hence, the distance from point Q when = ——————————————
7
the lorry and the car meet is 87
= —–
300 – 60 = 240 m 7
3 m s–1
= 12 —
2 Speed (m s–1) 7
16
10
8
P Q
O Time (s)
4 7 n 18
(a) Rate of change of speed from nth s to
5 m s–2
18th s = – —
2
Suc Math SPM (Forecast) F.indd 7 8/26/2009 10:42:33 AM
SPM FORECAST
(Fully-worked Solutions)
Form 5: Chapter 7 Probability II
Paper 1 3 Let
1 Let B = Event of drawing a blue ball
R = Event of obtaining a round biscuit R = Event of drawing a red ball
Sq = Event of obtaining a square biscuit S = Sample space
T = Event of obtaining a triangular biscuit
5
S = Sample space Given P(R) = — ,
8
P(T) = 1 – P(R) – P(Sq) n(R) 5
—–— = —
3 1 n(S) 8
P(T) = 1 – — – —
7 4
9 n(R) 5
P(T) = —– —–— = —
28 32 8
n(T) 9 5
—–— = —– n(R) = — × 32
n(S) 28 8
36 = —–
—–— 9 n(R) = 20
n(S) 28
9 × n(S) = 36 × 28 Let the number of blue balls added = h
36 × 28 Therefore, n(S) = 32 + h
n(S) = ———— 5
9 P(R) = — New value of P(R)
n(S) = 112 9
n(R) 5
—–— = —
n(R) + n(Sq) + n(T) = 112 n(S) 9
n(R) + n(Sq) + 36 = 112 20 5
——— = —
n(R) + n(Sq) = 112 – 36 32 + h 9
n(R) + n(Sq) = 76 5(32 + h) = 180
160 + 5h = 180
Answer: C 5h = 20
h=4
2 Let
G = Event of obtaining a green disc Hence, the number of new blue balls that
B = Event of obtaining a blue disc have to be added to the bag is 4.
S = Sample space
Answer: D
6 = —–
P(B) = 1 – P(G) = 1 – —– 5
11 11 Paper 2
n(B) 5 1 (a) P(letter M)
—–— = —–
n(S) 11 n(M)
= —–—
30 5 n(S)
—–— = —–
n(S) 11 2+5
= ——————
2+5+3+4
5 × n(S) = 30 × 11
7
= —–
30 × 11
n(S) = ———— 14
5 1
n(S) = 66 =—
2
∴ n(G) = n(S) – n(B) = 66 – 30 = 36
Answer: A
Suc Math SPM (Forecast) F.indd 8 8/26/2009 10:42:34 AM
(b) P(both the cards drawn are cards with (a) If two students are chosen at random
the letter N) from the group of boys, then
After 1 card with the letter
7 × —– 6 N is taken out, it is left with P(both students are from Form 1)
= —– 6 cards with the letter N out
14 13 8 8–1
of the balance of 13 cards. = —– × ———
32 32 – 1
8 7
Initially, there are 7 = —– × —–
cards with the letter 32 31
N out of 14 cards.
7
= ——
3 124
= —–
13
(c) P(both the cards drawn are of different (b) If two student are chosen at random
colours) from the group of girls, then
G – Green
= P(GY or YG) Y – Yellow P(both students are from the same form)
= P(GY) + P(YG) = P(both are from Form 1) +
P(both are from Form 2) +
= —–
14
5 × —–
13
9 + —– 9 × —–
14
5
13 P(both are from Form 3)
5 8 7 4 3
6 ×—
After 1 green card is taken
out, it is left with 13 cards = — + —×— + —× —
Initially, there are 5 and so there are 9 yellow 18 17 18 17 18 17
green cards out of cards out of the 13 cards. 49
14 cards. = ——
153
45
= —–
91
2 Number of students
Form Total
Boy Girl
1 8 6 14
2 10 8 18
3 14 4 18
Total 32 18 50
Suc Math SPM (Forecast) F.indd 9 8/26/2009 10:42:34 AM
SPM FORECAST
(Fully-worked Solutions)
Form 5: Chapter 8 Bearing
Paper 1 3 ∠QPR = 60° (Equilateral Δ)
1 ∠N1BA = 110° ∠NPQ = 90° – 60°
∴ Bearing of point A from point B = 30°
= 360° – 110° ∴ Bearing of Q from P = 030°
= 250°
N
N1 Bearing of
Q from P
N2 P
Q
60° 60°
110°
B
A
110° Bearing of 60°
A from B
R
Answer: D
Answer: A
180° – 110°
2 ∠FHK = ∠FKH = = 35°
2
∠N1KH = 65° + 35°
= 100°
∠WHK = 100° (Alternate angles)
∴ Bearing of K from H = 180° + 100°
= 280°
N1
F
65° N2
110°
K
Bearing of
H
K from H
Answer: C
10
Suc Math SPM (Forecast) F.indd 10 8/26/2009 10:42:35 AM
SPM FORECAST
(Fully-worked Solutions)
Form 5: Chapter 9 Earth as a Sphere
Paper 1 (a) Longitude of point P = (180 – 55)°E
1 N = 125°E
D
(b) Distance of MT
50° = (55 + 10) × 60 × cos 42°
O 40°
32° = 2898.3 n.m.
148°
(c) Distance of MQ = 4740 n.m.
148°E ∠MOQ × 60 = 4740
0°
S 4740
∠MOQ = ——— = 79°
Based on the above diagram: 60
The latitude of point D Hence, the latitude of point Q
= (90 – 50)°N = 40°N = (79 – 42)°N
The longitude of point D = 37°N
= (180 – 32)°E = 148°E Distance of MNP
(d) Time = ——————–—–
Speed ∠MOP = 180°
Hence, the location of point D is
because MP is the
(40°N, 148°E). 180 × 60 diameter of the earth.
= ————–
Answer: A 660 0.36 hours
= 0.36 × 60
= 16.36 hours = 22 minutes
2 N = 16 hours 22 minutes
0°
2 N
C J
30°N
O L
40°
50° O 30°
30°
R 80° P K
100°
S Q M
35°E
The latitude of point R = (90 – 50)°S S
= 40°S (a) The position of point Q is
The longitude of point R = (180 – 80)°W (30°S, (180 – 35)°W) = (30°S, 145°W)
= 100°W (b) (i) JK = 3300 n.m.
Hence, the position of point R is ∠JOK × 60 = 3300
(40°S, 100°W). 3300
∠JOK = ——–
60
Answer: B ∠JOK = 55°
Paper 2 30°N J
1
N
55°
Q P
Equator 0°
42° O
x°S K
M T 42°S
10°E
55°W S ∴ x = 55 – 30 = 25
11
Suc Math SPM (Forecast) F.indd 11 8/26/2009 10:42:36 AM
(ii) JL = 4936 n.m. Total distance travelled
(c) Time taken = ———————————
∠JCL × 60 × cos 30° = 4936 Speed
4936 JL + LM
∠JCL = —————– = ————
60 × cos 30° 600
∠JCL = 95° 4936 + [(30 + 40) × 60]
= ———————————
600
y°W 0° 35°E 4936 + 4200
= ——————
600
L G J
9136
= ———
95° 600
= 15.23 hours
∴ y = 95 – 35 = 60 = 15 hours 14 minutes
0.23 hours
= 0.23 × 60
= 13.8
= 14 (correct to the nearest minute)
12
Suc Math SPM (Forecast) F.indd 12 8/26/2009 10:42:36 AM
SPM FORECAST
(Fully-worked Solutions)
Form 5: Chapter 10 Plans and Elevations
Paper 2 C/D B/A
1 (a) T/S M/N J/R
2 cm 3 cm 2 cm
2 (a)
J/I
5 cm
3 cm
7 cm
K/L 4 cm F/E 3 cm G/H
Elevation as viewed from Y
U/P L/V K/Q
Plan (b) (i)
N/R/S W/Q/T
M/A/H P/B/G
(b) (i) L/A/M 3 cm B/J 1 cm 1 cm
U/T 2 cm 1 cm 3 cm
V/N
D/I/E C/J/F
6 cm
5 cm 4 cm
L 8 cm K
P/S Q/C/R Plan
Elevation as viewed from X
(ii) M N W P
(ii) 2 cm
L 3 cm B/A 4 cm J/M
R Q
1 cm D/A C/B
V/U N/T
2 cm
I J
5 cm
3 cm
1 cm 6 cm 1 cm
Q/P C R/S L/E/H S T K/F/G
Elevation as viewed from Y Elevation as viewed from X
13
Suc Math SPM (Forecast) F.indd 13 8/26/2009 10:42:38 AM
You might also like
- The Fierce Urgency of Now by Daniel FischlinDocument69 pagesThe Fierce Urgency of Now by Daniel FischlinDuke University PressNo ratings yet
- Sine Law WorksheetDocument2 pagesSine Law Worksheetapi-297847828100% (1)
- Forced Torsional Oscillations of An Elastic Half-Space. I: Articles You May Be Interested inDocument4 pagesForced Torsional Oscillations of An Elastic Half-Space. I: Articles You May Be Interested inFahim KhanNo ratings yet
- Calculus 3Document2 pagesCalculus 3Darren Troy Lingao Mayor67% (3)
- Math101 Final Summer 2022 SolutionsDocument4 pagesMath101 Final Summer 2022 SolutionsmohammadhoseinzeinaliNo ratings yet
- Mock Diagnostic TestDocument16 pagesMock Diagnostic Testalexander villamorNo ratings yet
- Examiners' Commentaries 2015 Mock: MT105a Maths 1 Comments On Specific Questions in Section ADocument10 pagesExaminers' Commentaries 2015 Mock: MT105a Maths 1 Comments On Specific Questions in Section AHa PhuongNo ratings yet
- Solutionbank C1: Edexcel Modular Mathematics For AS and A-LevelDocument53 pagesSolutionbank C1: Edexcel Modular Mathematics For AS and A-LevelMaruf_007No ratings yet
- North Sydney Boys 2015 4U HY & SolutionsDocument11 pagesNorth Sydney Boys 2015 4U HY & Solutionsz5588894No ratings yet
- MST125 201609Document13 pagesMST125 201609Iain DoranNo ratings yet
- C2 - Jan - 05 Model SolutionDocument15 pagesC2 - Jan - 05 Model SolutionAFRAH ANEESNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Graphs of FunctionsDocument10 pagesChapter 13 - Graphs of Functionsg-46005995No ratings yet
- Hssc-I (R&T) Federal Board Mathematic Test - 1 Chapter 1+2: Xiy Z Lies On. X-Axis Y-Axis XDocument2 pagesHssc-I (R&T) Federal Board Mathematic Test - 1 Chapter 1+2: Xiy Z Lies On. X-Axis Y-Axis XAL-Rayyan PoultryNo ratings yet
- Sem 1 2015 Math TestDocument9 pagesSem 1 2015 Math TestdNo ratings yet
- Ujian Feb f5 2011Document8 pagesUjian Feb f5 2011Hunkok TanNo ratings yet
- MATH2201 Assignment 1Document3 pagesMATH2201 Assignment 1Jesse Waechter-CornwillNo ratings yet
- Calculus Practice # 5b: Differentiating A Sum: DX DV DX Du DX DyDocument2 pagesCalculus Practice # 5b: Differentiating A Sum: DX DV DX Du DX Dygusvani aulia putriNo ratings yet
- C.maths First TermDocument1 pageC.maths First Termkrish benoitNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning HomeworkDocument8 pagesMachine Learning HomeworkWessel van DamNo ratings yet
- General Maths Unit 2 - Topic 1 Linear Equations & Graphs HomeworkDocument3 pagesGeneral Maths Unit 2 - Topic 1 Linear Equations & Graphs HomeworkSam PITSONNo ratings yet
- (1A) Math 1A - Math RefDocument7 pages(1A) Math 1A - Math RefJake Floyd G. FabianNo ratings yet
- HwsolnsDocument16 pagesHwsolnsPARAMITA DUTTANo ratings yet
- Samplefinal ADocument11 pagesSamplefinal A2kt2j5dwy6No ratings yet
- 2024 - 12MAT - Term 2 Assessment - Bank of QuestionsDocument12 pages2024 - 12MAT - Term 2 Assessment - Bank of QuestionsPurnima Sidhant BabbarNo ratings yet
- Solution P 1 Jan 19Document16 pagesSolution P 1 Jan 19hasan zaidiNo ratings yet
- Coordinate GeometryDocument33 pagesCoordinate GeometryvenkatachalampreethaNo ratings yet
- Homework 0: Mathematical Background For Machine LearningDocument11 pagesHomework 0: Mathematical Background For Machine Learninganwer fadelNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-01-25 at 11.26.23 AMDocument16 pagesScreenshot 2023-01-25 at 11.26.23 AMRajeev RastogiNo ratings yet
- Pre-Assignment For L1: Limit of A FunctionDocument6 pagesPre-Assignment For L1: Limit of A FunctionJordane McCallaNo ratings yet
- Backpropagation ExercisesDocument7 pagesBackpropagation ExercisesSiriusNo ratings yet
- Ss - Vtamps 2024 4Document13 pagesSs - Vtamps 2024 4KIRSTEL JOY PICARNo ratings yet
- S03C01 5.5 Teorema Fundamental Del CálculoDocument13 pagesS03C01 5.5 Teorema Fundamental Del Cálculogabriel cervinoNo ratings yet
- Itute 2007 Mathematical Methods Examination 2 SolutionsDocument3 pagesItute 2007 Mathematical Methods Examination 2 SolutionsnochnochNo ratings yet
- North Sydney Boys 2014 2U HY & Solutions PDFDocument12 pagesNorth Sydney Boys 2014 2U HY & Solutions PDFfbjsjdfhNo ratings yet
- UACE MathematicsDocument4 pagesUACE MathematicsTusiime RobertNo ratings yet
- 2021 F5 T2 Paper 1 Secction A1 MSDocument4 pages2021 F5 T2 Paper 1 Secction A1 MSTai Yin LAMNo ratings yet
- Manifolds, Tensor Analysis and Applications 3rd Ed. - Marsden, Ratiu and AbrahamDocument21 pagesManifolds, Tensor Analysis and Applications 3rd Ed. - Marsden, Ratiu and AbrahamSreerag S KumarNo ratings yet
- 35 (Pengantar Diferensiasi)Document16 pages35 (Pengantar Diferensiasi)Muh fadel alqurtubiNo ratings yet
- Fall 2021Document11 pagesFall 2021JanviNo ratings yet
- January 2008 6665 Core Mathematics C3 Mark Scheme: X X X X X X X X XDocument6 pagesJanuary 2008 6665 Core Mathematics C3 Mark Scheme: X X X X X X X X XMichael 黃建峰 HoangNo ratings yet
- Lecture NotesDocument90 pagesLecture NotesSharad RaykhereNo ratings yet
- Sample 2Document12 pagesSample 2exhasbeenslainNo ratings yet
- Sydney Grammar 2014 3U Prelim Yearly & SolutionsDocument22 pagesSydney Grammar 2014 3U Prelim Yearly & SolutionsgeeeelooNo ratings yet
- Graphs of Functions IIDocument17 pagesGraphs of Functions IIVisnuVaratanNo ratings yet
- CLS JEEAD-19-20 XI Mat Target-4 Level-2 Chapter-12Document41 pagesCLS JEEAD-19-20 XI Mat Target-4 Level-2 Chapter-12Awan DubeyNo ratings yet
- Test 17Document9 pagesTest 17Saad HasanNo ratings yet
- Solutions & Answers For Kerala Engineering Entrance Examination-2011 - Paper Ii Version - B1Document11 pagesSolutions & Answers For Kerala Engineering Entrance Examination-2011 - Paper Ii Version - B1ArgoNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced 2024 Complete SolutionDocument84 pagesJEE Advanced 2024 Complete Solutionamrocker080No ratings yet
- Quadratic Functions Practice Test BDocument3 pagesQuadratic Functions Practice Test ByourmomsdadsfriendNo ratings yet
- 3b. Coordinate Geometry Further Questions AnswersDocument2 pages3b. Coordinate Geometry Further Questions AnswerslaavanyasathyvellNo ratings yet
- 2023 HSC Maths Ext 1Document20 pages2023 HSC Maths Ext 1n4eel3shNo ratings yet
- CCH 13Document21 pagesCCH 13navinavinaviNo ratings yet
- CLS JEEAD-19-20 XI Mat Target-4 Level-2 Chapter-13 PDFDocument54 pagesCLS JEEAD-19-20 XI Mat Target-4 Level-2 Chapter-13 PDFAniNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 1 Spring 2015Document5 pagesAssignment No 1 Spring 2015shahinaaslam938No ratings yet
- Definition Basic Formula and PrinciplesDocument5 pagesDefinition Basic Formula and PrinciplesJhoan Cinco VelardeNo ratings yet
- Finalf 04Document10 pagesFinalf 04vimashaanimalloverNo ratings yet
- MTH501 Practice Question Lecture 1 To 18-MergedDocument76 pagesMTH501 Practice Question Lecture 1 To 18-MergedomersaleemNo ratings yet
- C2 May 05 Model SolutionDocument22 pagesC2 May 05 Model SolutionAFRAH ANEESNo ratings yet
- Solve The ODE by Integration or by Remembering A Differentia - QuizletDocument4 pagesSolve The ODE by Integration or by Remembering A Differentia - QuizletRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 and 5Document18 pagesLec 4 and 5sehati8586No ratings yet
- Math 234 Winter 2012 FinalDocument11 pagesMath 234 Winter 2012 FinalKrage and JohnNo ratings yet
- Practice Set 3Document6 pagesPractice Set 3jordanhub05No ratings yet
- AlgebraDocument6 pagesAlgebraThein Min OoNo ratings yet
- Vectors, Spinors, and Complex Numbers in Classical and Quantum Physics David HestenesDocument23 pagesVectors, Spinors, and Complex Numbers in Classical and Quantum Physics David Hestenesosegeno654321100% (1)
- Assignment - 2 (CE 286 Survey II) Spring 2020Document2 pagesAssignment - 2 (CE 286 Survey II) Spring 2020Jawad Ahmed LeghariNo ratings yet
- Calculus I FinalDocument7 pagesCalculus I FinalRodrigo RomeroNo ratings yet
- Mainfile 1Document1 pageMainfile 1api-367252928No ratings yet
- 3.3-3.4 Centripetal Force and Rotating Frames of Reference TemplateDocument5 pages3.3-3.4 Centripetal Force and Rotating Frames of Reference TemplateAyman HalimeNo ratings yet
- Question On CFTDocument2 pagesQuestion On CFTABHINANDAN YADAVNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Reviewer For Grade 10 Q2Document2 pagesMathematics Reviewer For Grade 10 Q2martinaloreyn.delrosarioNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet SUBJECT-Maths: Chapter 5: Lines and Angles Class - ViiDocument1 pageWork Sheet SUBJECT-Maths: Chapter 5: Lines and Angles Class - ViiAnil kumarNo ratings yet
- Section 1.1-1.3 WorksheetDocument5 pagesSection 1.1-1.3 WorksheetTragic KyroNo ratings yet
- Grossberg Identity Cultural Studies Is That All There Is PDFDocument11 pagesGrossberg Identity Cultural Studies Is That All There Is PDFTias BradburyNo ratings yet
- Conic Section Maths Project PDFDocument13 pagesConic Section Maths Project PDFSiva Kumar75% (4)
- Tugas 6 - Analisa Data LapanganDocument11 pagesTugas 6 - Analisa Data LapanganRika PermataNo ratings yet
- Parts of Circles (Read) Geometry CK-12 FoundationDocument1 pageParts of Circles (Read) Geometry CK-12 FoundationJohn Thiery FedericoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2.1,2.2Document3 pagesExercise 2.1,2.2Angeline DangNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Drafting - Principles of Tangency: ObjectivesDocument7 pagesFundamentals of Drafting - Principles of Tangency: ObjectivesguyNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight-Line EndDocument10 pagesMotion in A Straight-Line EndQuynh Mai Do LeNo ratings yet
- FIZ101E TotDocument88 pagesFIZ101E TotdeniNo ratings yet
- CE 408 Module 3Document19 pagesCE 408 Module 3Janina MatanguihanNo ratings yet
- M 221Document12 pagesM 221Epic WinNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics NotesDocument6 pagesO Level Physics NotesHamza Kahemela86% (7)
- Geometry - 102714 - 4 2 Worksheet - Angles in A Triangle 1-3Document3 pagesGeometry - 102714 - 4 2 Worksheet - Angles in A Triangle 1-3api-252752147No ratings yet
- Mathematics/ Further Mathematics/ Pure Mathematics: EconomicsDocument32 pagesMathematics/ Further Mathematics/ Pure Mathematics: EconomicsBassem Khalid YasseenNo ratings yet
- Tute 1 PDFDocument2 pagesTute 1 PDFApoorv KhareNo ratings yet
- Emotion, Space and Society: John Urry, Anthony Elliott, David Radford, Nicola PittDocument8 pagesEmotion, Space and Society: John Urry, Anthony Elliott, David Radford, Nicola Pittমোঃ গোলাম কিবরিয়া রনিNo ratings yet
- Transformation RulesDocument2 pagesTransformation RulesMasterkeyNo ratings yet
- Math 2 PDFDocument1 pageMath 2 PDFJads CayabyabNo ratings yet