Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Four PROCESSES Needed For First Cells To Form:: Evolution Is The
Four PROCESSES Needed For First Cells To Form:: Evolution Is The
Uploaded by
smurplerCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Biology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandBiology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- On The Origins of Mitosing Cells - 1967 PDFDocument56 pagesOn The Origins of Mitosing Cells - 1967 PDFMartín FuentesNo ratings yet
- QA & QC Final Assignment MCSDocument36 pagesQA & QC Final Assignment MCSSadaf Sumdani NirvikNo ratings yet
- Installation of Asbestos - Cement Pressure Pipe: AWWA StandardDocument24 pagesInstallation of Asbestos - Cement Pressure Pipe: AWWA StandardJacques BlueqNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 25Document16 pagesAP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 25Shiv Ganesh100% (1)
- Heat Transfer Design Methods by John MC Ketta PDFDocument607 pagesHeat Transfer Design Methods by John MC Ketta PDFAlberto LazzarettiNo ratings yet
- Molecular EvolutionDocument21 pagesMolecular EvolutionSonu Rampal SainiNo ratings yet
- 1 - 6 - Origin of LifeDocument35 pages1 - 6 - Origin of LifeAditya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 - The Origin and Chemistry of LifeDocument10 pagesUNIT 2 - The Origin and Chemistry of LifeRachel Ae Ra JangNo ratings yet
- The Origin and Evolution of Life On EarthDocument52 pagesThe Origin and Evolution of Life On EarthTevfik DoğanNo ratings yet
- ExobiologyDocument44 pagesExobiologyJofel CañadaNo ratings yet
- Power Point in Biology 2Document25 pagesPower Point in Biology 2ROJANE FLORANo ratings yet
- A Local Ecosystem: Light Chlorophyll Uses of EnergyDocument24 pagesA Local Ecosystem: Light Chlorophyll Uses of EnergyroseNo ratings yet
- Biology (Mader) Exam Study GuideDocument8 pagesBiology (Mader) Exam Study GuidemizbigspendaNo ratings yet
- Origin of LifeDocument35 pagesOrigin of LifeNawaz SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Biology Life On Earth Dot Point SummaryDocument8 pagesPreliminary Biology Life On Earth Dot Point Summaryluke0thompsonNo ratings yet
- Life On Earth: Preliminary Biology: Topic SummaryDocument10 pagesLife On Earth: Preliminary Biology: Topic SummaryKevin KevinNo ratings yet
- B They Grow To High Cell Densities in A Short Amount of TimeDocument11 pagesB They Grow To High Cell Densities in A Short Amount of Timen karimNo ratings yet
- 1.D.1 Hypotheses of Life's OriginDocument40 pages1.D.1 Hypotheses of Life's Originapi-373344212No ratings yet
- Chapter 24: The Origin of Life: AbioticDocument5 pagesChapter 24: The Origin of Life: Abioticюрий локтионовNo ratings yet
- Origin of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument10 pagesOrigin of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cellssrisankaraglobalacademy7No ratings yet
- Chapter 25: The History of Life On EarthDocument6 pagesChapter 25: The History of Life On EarthErrol KingNo ratings yet
- Summer Assignment Scan PDFDocument58 pagesSummer Assignment Scan PDFDavid CaseyNo ratings yet
- Earth Life Science Module 4Document6 pagesEarth Life Science Module 4Rosalyn Pagatpatan BarolaNo ratings yet
- Box 1-C in The BeginningDocument1 pageBox 1-C in The BeginningRodrigo WolfordNo ratings yet
- EVOLUTION AssignmentDocument11 pagesEVOLUTION AssignmentDeana NamirembeNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slides On Cell Biology: Kedir W. (M.Sc. Molecular Biology andDocument192 pagesLecture Slides On Cell Biology: Kedir W. (M.Sc. Molecular Biology andKedir JilloNo ratings yet
- Week 11 Task Chapter 18 Origin of Life MemoDocument3 pagesWeek 11 Task Chapter 18 Origin of Life MemogladiatornthabiNo ratings yet
- Origin of The CellDocument31 pagesOrigin of The Cellbrenda.mboghoNo ratings yet
- 2 The Origin of LifeDocument39 pages2 The Origin of LifeRydel GreyNo ratings yet
- CH 26 Guided ReadingDocument3 pagesCH 26 Guided Readingblow130% (1)
- Origin of Life On EarthDocument8 pagesOrigin of Life On Earthharpal_abhNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument5 pagesBiologyLyssa LimNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiologyDocument44 pagesIntroduction To BiologyRamkiNo ratings yet
- How Life Began On EarthDocument15 pagesHow Life Began On EarthDilan9318No ratings yet
- Poster TextenglischDocument16 pagesPoster TextenglischMr UnKnOwNNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 0022519367900793 Main 1 1 25Document25 pages1 s2.0 0022519367900793 Main 1 1 25Dan Gerson Apaza AracayoNo ratings yet
- Oparin - Haldane Theory and Miller - Urey ExperimentDocument32 pagesOparin - Haldane Theory and Miller - Urey ExperimentPrayush DongolNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Ch. 28 + 29: Chapter 28: Phylogenies and The History of LifeDocument10 pagesWeek 3 - Ch. 28 + 29: Chapter 28: Phylogenies and The History of LifeHarris ChoeNo ratings yet
- Theories of OriginDocument7 pagesTheories of OriginAbby VillaNo ratings yet
- Evolution - Upto Homo and Analogous OrgansDocument7 pagesEvolution - Upto Homo and Analogous Organsshreyavjha2020No ratings yet
- Historical Development of The Concept of LifeDocument3 pagesHistorical Development of The Concept of LifeShiene MarieNo ratings yet
- Biology - 1Document26 pagesBiology - 1fiona altabanoNo ratings yet
- Origin of CellsDocument39 pagesOrigin of CellsRafael HenriqueNo ratings yet
- Cosmos 02Document3 pagesCosmos 02Shahid AnsariNo ratings yet
- Sagan, L. On The Origin of Mitosing Cells. J. Theoret. Biol. (1967) 14, 225-274Document56 pagesSagan, L. On The Origin of Mitosing Cells. J. Theoret. Biol. (1967) 14, 225-274Jéssica CristinaNo ratings yet
- General Features of The History of Life andDocument59 pagesGeneral Features of The History of Life andcatalanmariegraceNo ratings yet
- The Historical Development of The Concept of Life: Lesson 1Document43 pagesThe Historical Development of The Concept of Life: Lesson 1Ohm PawatNo ratings yet
- A1.1 The Origins of Life - 2018Document50 pagesA1.1 The Origins of Life - 2018Wayne DayataNo ratings yet
- Cellular BiologyDocument132 pagesCellular BiologyunigeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 SummaryDocument5 pagesChapter 21 SummaryJamesBlackmanNo ratings yet
- Energy - Storing Molecules: Oxidized Form Generated in Reduced Form Generated inDocument5 pagesEnergy - Storing Molecules: Oxidized Form Generated in Reduced Form Generated inelizabethmNo ratings yet
- Genbio2 ReviewerDocument3 pagesGenbio2 ReviewerkmatthewomanioNo ratings yet
- Evolution Lecture 3Document5 pagesEvolution Lecture 3Geeta DhimanNo ratings yet
- Science10 Activity 9.1Document4 pagesScience10 Activity 9.1Abigail HibayaNo ratings yet
- Bio-Chemical Evolution of LifeDocument17 pagesBio-Chemical Evolution of LifeAditi ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Cell Evolution and ExtraterrestrialsDocument4 pagesCell Evolution and ExtraterrestrialssamNo ratings yet
- Origen de La CelulaDocument3 pagesOrigen de La CelulaMildred Yaniret Guillermo ChávezNo ratings yet
- Ecology Revision ListDocument6 pagesEcology Revision ListFULYA YALDIZNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 14 History of LifeDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 14 History of LifeLaura PérezNo ratings yet
- Bio. Reviewer FinalsDocument4 pagesBio. Reviewer FinalsSTEM - Balanquit , Julianne NicoleNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus 1Document5 pagesDiabetes Mellitus 1smurplerNo ratings yet
- Cysts and TumoursDocument15 pagesCysts and TumourssmurplerNo ratings yet
- 78342a 02 Kapitola 2Document2 pages78342a 02 Kapitola 2smurplerNo ratings yet
- 78342a 02 Kapitola 2Document21 pages78342a 02 Kapitola 2smurplerNo ratings yet
- Nervous System OSCEDocument17 pagesNervous System OSCEsmurplerNo ratings yet
- Ways To Seek Help PosterDocument5 pagesWays To Seek Help PostersmurplerNo ratings yet
- Economics For DummiesDocument1 pageEconomics For DummiessmurplerNo ratings yet
- Effect FluorideVarnishApplicationDocument10 pagesEffect FluorideVarnishApplicationsmurplerNo ratings yet
- Art and Healing DraftttDocument1 pageArt and Healing DraftttsmurplerNo ratings yet
- Pulpagia - Types, Diagnosis, TreatmentDocument5 pagesPulpagia - Types, Diagnosis, TreatmentsmurplerNo ratings yet
- Properties of MetalsDocument25 pagesProperties of MetalsRegalado Cereza IIINo ratings yet
- Hardened Concrete (Lec 20)Document19 pagesHardened Concrete (Lec 20)vasu khandelwalNo ratings yet
- Membrane Stabilizing EffectsDocument5 pagesMembrane Stabilizing Effectssulthana HNo ratings yet
- Ammonium BromideDocument2 pagesAmmonium BromideInarat HussainNo ratings yet
- ERIEZ Cribas VibratoriasDocument8 pagesERIEZ Cribas VibratoriasangelsiddhartaNo ratings yet
- Erosion-Corrosion Resistant Coating For Efficiency EnhancementDocument2 pagesErosion-Corrosion Resistant Coating For Efficiency EnhancementRichard HoseNo ratings yet
- Quality Assuarance - Sop For Cleaning of Sparkler FilterDocument5 pagesQuality Assuarance - Sop For Cleaning of Sparkler FilterKrishna PalNo ratings yet
- 2-Part PUR Highly Elastic, Crack-Bridging Coating: Product DescriptionDocument7 pages2-Part PUR Highly Elastic, Crack-Bridging Coating: Product Descriptionbeck.26No ratings yet
- Percent by VolumeDocument19 pagesPercent by VolumeSabrina LavegaNo ratings yet
- Cane Sampling and AnalysisDocument13 pagesCane Sampling and AnalysisVimal WoosyeNo ratings yet
- Components of Laminated GlassDocument3 pagesComponents of Laminated GlassSarinNo ratings yet
- ONeil - 425btext Organic ReactionsDocument78 pagesONeil - 425btext Organic ReactionsnavchemNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument3 pagesProtein Synthesis WorksheetG Combalicer Bernice Darielle D.No ratings yet
- Energies: Brittleness Evaluation in Shale Gas Reservoirs and Its Influence On FracabilityDocument22 pagesEnergies: Brittleness Evaluation in Shale Gas Reservoirs and Its Influence On Fracabilityomair.latifNo ratings yet
- SCCS1624 Eng PH Salinity SodicityDocument39 pagesSCCS1624 Eng PH Salinity SodicityMenzi CekwaneNo ratings yet
- MSDS L-Ascorbic AcidDocument5 pagesMSDS L-Ascorbic Acideggy mushadiNo ratings yet
- Document 1Document38 pagesDocument 1cap40No ratings yet
- Manufacturing Cost Analysis of Novel Steel/Concrete Composite Vessel For Stationary Storage of High-Pressure HydrogenDocument25 pagesManufacturing Cost Analysis of Novel Steel/Concrete Composite Vessel For Stationary Storage of High-Pressure HydrogenGuilherme Vital MachadoNo ratings yet
- Fleta5 Usermanual Omf5pden1801Document28 pagesFleta5 Usermanual Omf5pden1801Shan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Assignment Class 12Document2 pagesAssignment Class 12mehaktyagi422No ratings yet
- Control of Substances Hazardous To Health (COSHH)Document38 pagesControl of Substances Hazardous To Health (COSHH)ghada gattouchNo ratings yet
- Synthesis Gas ReformersDocument9 pagesSynthesis Gas ReformersAlbert PowaNo ratings yet
- Mat Sci Group 3Document5 pagesMat Sci Group 3Future HazeNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - 04 - 0893 - 01 - 6RP - AFPDocument18 pagesMicrosoft Word - 04 - 0893 - 01 - 6RP - AFPNancy MohamedNo ratings yet
- 9 DNA Electrophoresis2010Document34 pages9 DNA Electrophoresis2010Hasbi Yusuf Abu ZakiNo ratings yet
- Mipa Monoisopropylamine: Safety Data SheetDocument16 pagesMipa Monoisopropylamine: Safety Data SheetVipul GandhiNo ratings yet
- Dowtherm SR-1 MSDSDocument11 pagesDowtherm SR-1 MSDSnedian_2006No ratings yet
Four PROCESSES Needed For First Cells To Form:: Evolution Is The
Four PROCESSES Needed For First Cells To Form:: Evolution Is The
Uploaded by
smurplerOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Four PROCESSES Needed For First Cells To Form:: Evolution Is The
Four PROCESSES Needed For First Cells To Form:: Evolution Is The
Uploaded by
smurplerCopyright:
Available Formats
EVOLUTION (PAPER 3, OPTION D)
Evolution is the process of cumulative change in the heritable
characteristics of a population. It is a change in the gene/allele frequencies
of a population.
Microevolution Macroevolution
Small-scale changes over Large-scale changes in form
generations. involving whole groups of
species and genera (as seen in
fossil records)
Four PROCESSES needed for first cells to form:
1. Inorganic (water, CO2, ammonia) synthesis of simple organic
molecules. Examples: amino acids, nucleotides, glucose.
2. Assembly of simple organic molecules into polymers.
Examples: Amino acids to proteins, nucleotides to nucleic acid, glucose
to starch.
3. Formation of polymers capable of self-replication, allowing
inheritance of characteristics.
Examples: RNA, DNA
4. Packaging of molecules into membranes with internal chemistry
different from surroundings.
Seven STEPS in the evolutionary process which
led to appearance of life on Earth:
1. Formation of Earth (~4600 mil. years ago) with:
Organic chemicals
High temperature
Lightning
UV light penetration
Reducing atmosphere
Water
2. Prebiotic synthesis and accumulation of amino acids, purines,
pyrimidines, lipids, sugars, and other organic molecules in the
primitive terrestrial environment.
3. Prebiotic condensation reactions synthesis of proteins and nucleic
acids with self replicating and catalytic/enzymatic abilities (RNA). First
two catalysts responsible for polymerization reactions were probably clay
minerals/metal sulfides and RNA.
4. Synthesis of lipids self-assembly into double-layered membranes.
5. Capturing of prebiotic molecules (self-replicating and catalytic) within
their boundaries.
6. Formation of protobiont. Immediate precursor to first living systems
with internal chemical environment different from surroundings.
Protobionts exhibit co-operative interactions between small catalytic
peptides, replicative molecules, proto-tRNA and protoribosomes.
7. Evolution of protobiont into a prokaryotic cell.
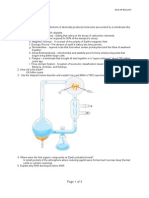
Miller and Urey Experiments
Mixture of methane, ammonia, hydrogen, steam put in reaction chamber.
Electric charges provided energy for reaction of gases.
Gases condensed and boiled.
Experiment continued for a week. After that week, samples were taken
from the collection trap for analysis.
</= 4% of carbon (methane) was converted into amino acids.
In this and subsequent experiments, it has been possible to form all 20
amino acids commonly found in organisms.
Besides that, nucleic acids, several sugars, lipids, adenine and ATP (if
phosphate added to flask) were formed.
Early atmosphere may be similar to vapors given off by modern volcanoes.
Vapors: CO, CO2, N2.
Note: lack of free atmospheric oxygen.
Three POSSIBLE THEORIES for origin of life
on Earth
The six conditions of prebiotic Earth (1. High temp, 2. Lighting, 3. UV
light, 4. Reducing atmosphere, 5. Water, 6. Organic chemicals) make the
following theories possible.
1. Ocean surface (tidal pools)
Suggests that life began in a tide pool, pond or on moist clay on
primeval Earth.
UV light or electrical discharges would have energized the gases
from volcanoes to form prebiotic molecules in froth.
2. Panspermia (cosmic ancestry)
Proposes that living organisms arrived on Earth from comets and
meteors.
The organic compounds and water on the comets may have been
delivered to early earth when heavy bombardment occurred 4000
m.y.a.
3. Undersea thermal vents
Proposes that life started at ancient volcanic vents.
Necessary gases, energy and possible source of catalysts (metal
sulfides) are provided in this environment.
Role of RNA
RNA
1. Self-replicating
2. Catalytic
Can act as both genes AND enzymes, resolving the “chicken and egg
problem” as:
Genes require enzymes to form
Enzymes require genes to form
RNA molecules performing the catalytic activities necessary to
assemble themselves from a nucleotide soup may have led to the
first stage of evolution.
(A Ribozyme is a type of RNA that catalyzes its own replication.)
RNA then began to synthesize proteins
Endosymbiotic theory for origin of
eukaryotes
It is thought that eukaryote cells evolved from the ingestion of
prokaryotes by larger prokaryote cells.
An (endo)symbiotic relationship was formed with the cells they engulfed.
The ingested prokaryotes became two types of organelles:
1. Mitochondria: for aerobic respiration
2. Chloroplasts: for photosynthesis in aerobic conditions
The state of mitochondria before/when ingested was purple bacteria.
For chloroplasts, it was cyanobacteria. (already capable of photosynthesis)
Both chloroplasts and mitochondria have a self-replicating circular
chromosome.
The chromosome uses a genetic code that contains prokaryotic features,
supporting the origins of chloroplasts and mitochondria as
endosymbionts.
The theory is further supported by the fact that both also have double
membranes (one thought to belong to their initial state before ingestion
and the other thought to belong to the host prokaryote cell).
Darwin-Wallace theory of evolution by
natural selection
They showed that species changed throughout time. They reasoned it in
this way:
1. All organisms have a high reproductive rate. But. Food supply and
other necessities limited. competition between offspring.
2. Variation in all characteristics among offspring. Some better adapted
than others. Sources: mutations and sexual reproduction.
3. Individuals possessing favourable variations survive longer in a given
environment, so more chance to pass on these characteristics to offspring.
4. The survival of the fittest – each successive generation better
adapted to environment.
5. New species evolve from old species.
-------------
Cline: variation within population of same success. (eg blue eyes)
Environmental changes select the more favourable genotype and therefore
change the gene frequency in gene pool of population.
(check emails)
* Evolution of the Horse
Fossil evidence shows a succession from the horse ancestor with four
toes to a modern horse with one toe trend towards reduced number of
toes, increase in size and durability of teeth.
You might also like
- Biology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandBiology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- On The Origins of Mitosing Cells - 1967 PDFDocument56 pagesOn The Origins of Mitosing Cells - 1967 PDFMartín FuentesNo ratings yet
- QA & QC Final Assignment MCSDocument36 pagesQA & QC Final Assignment MCSSadaf Sumdani NirvikNo ratings yet
- Installation of Asbestos - Cement Pressure Pipe: AWWA StandardDocument24 pagesInstallation of Asbestos - Cement Pressure Pipe: AWWA StandardJacques BlueqNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 25Document16 pagesAP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 25Shiv Ganesh100% (1)
- Heat Transfer Design Methods by John MC Ketta PDFDocument607 pagesHeat Transfer Design Methods by John MC Ketta PDFAlberto LazzarettiNo ratings yet
- Molecular EvolutionDocument21 pagesMolecular EvolutionSonu Rampal SainiNo ratings yet
- 1 - 6 - Origin of LifeDocument35 pages1 - 6 - Origin of LifeAditya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 - The Origin and Chemistry of LifeDocument10 pagesUNIT 2 - The Origin and Chemistry of LifeRachel Ae Ra JangNo ratings yet
- The Origin and Evolution of Life On EarthDocument52 pagesThe Origin and Evolution of Life On EarthTevfik DoğanNo ratings yet
- ExobiologyDocument44 pagesExobiologyJofel CañadaNo ratings yet
- Power Point in Biology 2Document25 pagesPower Point in Biology 2ROJANE FLORANo ratings yet
- A Local Ecosystem: Light Chlorophyll Uses of EnergyDocument24 pagesA Local Ecosystem: Light Chlorophyll Uses of EnergyroseNo ratings yet
- Biology (Mader) Exam Study GuideDocument8 pagesBiology (Mader) Exam Study GuidemizbigspendaNo ratings yet
- Origin of LifeDocument35 pagesOrigin of LifeNawaz SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Biology Life On Earth Dot Point SummaryDocument8 pagesPreliminary Biology Life On Earth Dot Point Summaryluke0thompsonNo ratings yet
- Life On Earth: Preliminary Biology: Topic SummaryDocument10 pagesLife On Earth: Preliminary Biology: Topic SummaryKevin KevinNo ratings yet
- B They Grow To High Cell Densities in A Short Amount of TimeDocument11 pagesB They Grow To High Cell Densities in A Short Amount of Timen karimNo ratings yet
- 1.D.1 Hypotheses of Life's OriginDocument40 pages1.D.1 Hypotheses of Life's Originapi-373344212No ratings yet
- Chapter 24: The Origin of Life: AbioticDocument5 pagesChapter 24: The Origin of Life: Abioticюрий локтионовNo ratings yet
- Origin of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument10 pagesOrigin of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cellssrisankaraglobalacademy7No ratings yet
- Chapter 25: The History of Life On EarthDocument6 pagesChapter 25: The History of Life On EarthErrol KingNo ratings yet
- Summer Assignment Scan PDFDocument58 pagesSummer Assignment Scan PDFDavid CaseyNo ratings yet
- Earth Life Science Module 4Document6 pagesEarth Life Science Module 4Rosalyn Pagatpatan BarolaNo ratings yet
- Box 1-C in The BeginningDocument1 pageBox 1-C in The BeginningRodrigo WolfordNo ratings yet
- EVOLUTION AssignmentDocument11 pagesEVOLUTION AssignmentDeana NamirembeNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slides On Cell Biology: Kedir W. (M.Sc. Molecular Biology andDocument192 pagesLecture Slides On Cell Biology: Kedir W. (M.Sc. Molecular Biology andKedir JilloNo ratings yet
- Week 11 Task Chapter 18 Origin of Life MemoDocument3 pagesWeek 11 Task Chapter 18 Origin of Life MemogladiatornthabiNo ratings yet
- Origin of The CellDocument31 pagesOrigin of The Cellbrenda.mboghoNo ratings yet
- 2 The Origin of LifeDocument39 pages2 The Origin of LifeRydel GreyNo ratings yet
- CH 26 Guided ReadingDocument3 pagesCH 26 Guided Readingblow130% (1)
- Origin of Life On EarthDocument8 pagesOrigin of Life On Earthharpal_abhNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument5 pagesBiologyLyssa LimNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiologyDocument44 pagesIntroduction To BiologyRamkiNo ratings yet
- How Life Began On EarthDocument15 pagesHow Life Began On EarthDilan9318No ratings yet
- Poster TextenglischDocument16 pagesPoster TextenglischMr UnKnOwNNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 0022519367900793 Main 1 1 25Document25 pages1 s2.0 0022519367900793 Main 1 1 25Dan Gerson Apaza AracayoNo ratings yet
- Oparin - Haldane Theory and Miller - Urey ExperimentDocument32 pagesOparin - Haldane Theory and Miller - Urey ExperimentPrayush DongolNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Ch. 28 + 29: Chapter 28: Phylogenies and The History of LifeDocument10 pagesWeek 3 - Ch. 28 + 29: Chapter 28: Phylogenies and The History of LifeHarris ChoeNo ratings yet
- Theories of OriginDocument7 pagesTheories of OriginAbby VillaNo ratings yet
- Evolution - Upto Homo and Analogous OrgansDocument7 pagesEvolution - Upto Homo and Analogous Organsshreyavjha2020No ratings yet
- Historical Development of The Concept of LifeDocument3 pagesHistorical Development of The Concept of LifeShiene MarieNo ratings yet
- Biology - 1Document26 pagesBiology - 1fiona altabanoNo ratings yet
- Origin of CellsDocument39 pagesOrigin of CellsRafael HenriqueNo ratings yet
- Cosmos 02Document3 pagesCosmos 02Shahid AnsariNo ratings yet
- Sagan, L. On The Origin of Mitosing Cells. J. Theoret. Biol. (1967) 14, 225-274Document56 pagesSagan, L. On The Origin of Mitosing Cells. J. Theoret. Biol. (1967) 14, 225-274Jéssica CristinaNo ratings yet
- General Features of The History of Life andDocument59 pagesGeneral Features of The History of Life andcatalanmariegraceNo ratings yet
- The Historical Development of The Concept of Life: Lesson 1Document43 pagesThe Historical Development of The Concept of Life: Lesson 1Ohm PawatNo ratings yet
- A1.1 The Origins of Life - 2018Document50 pagesA1.1 The Origins of Life - 2018Wayne DayataNo ratings yet
- Cellular BiologyDocument132 pagesCellular BiologyunigeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 SummaryDocument5 pagesChapter 21 SummaryJamesBlackmanNo ratings yet
- Energy - Storing Molecules: Oxidized Form Generated in Reduced Form Generated inDocument5 pagesEnergy - Storing Molecules: Oxidized Form Generated in Reduced Form Generated inelizabethmNo ratings yet
- Genbio2 ReviewerDocument3 pagesGenbio2 ReviewerkmatthewomanioNo ratings yet
- Evolution Lecture 3Document5 pagesEvolution Lecture 3Geeta DhimanNo ratings yet
- Science10 Activity 9.1Document4 pagesScience10 Activity 9.1Abigail HibayaNo ratings yet
- Bio-Chemical Evolution of LifeDocument17 pagesBio-Chemical Evolution of LifeAditi ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Cell Evolution and ExtraterrestrialsDocument4 pagesCell Evolution and ExtraterrestrialssamNo ratings yet
- Origen de La CelulaDocument3 pagesOrigen de La CelulaMildred Yaniret Guillermo ChávezNo ratings yet
- Ecology Revision ListDocument6 pagesEcology Revision ListFULYA YALDIZNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 14 History of LifeDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 14 History of LifeLaura PérezNo ratings yet
- Bio. Reviewer FinalsDocument4 pagesBio. Reviewer FinalsSTEM - Balanquit , Julianne NicoleNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus 1Document5 pagesDiabetes Mellitus 1smurplerNo ratings yet
- Cysts and TumoursDocument15 pagesCysts and TumourssmurplerNo ratings yet
- 78342a 02 Kapitola 2Document2 pages78342a 02 Kapitola 2smurplerNo ratings yet
- 78342a 02 Kapitola 2Document21 pages78342a 02 Kapitola 2smurplerNo ratings yet
- Nervous System OSCEDocument17 pagesNervous System OSCEsmurplerNo ratings yet
- Ways To Seek Help PosterDocument5 pagesWays To Seek Help PostersmurplerNo ratings yet
- Economics For DummiesDocument1 pageEconomics For DummiessmurplerNo ratings yet
- Effect FluorideVarnishApplicationDocument10 pagesEffect FluorideVarnishApplicationsmurplerNo ratings yet
- Art and Healing DraftttDocument1 pageArt and Healing DraftttsmurplerNo ratings yet
- Pulpagia - Types, Diagnosis, TreatmentDocument5 pagesPulpagia - Types, Diagnosis, TreatmentsmurplerNo ratings yet
- Properties of MetalsDocument25 pagesProperties of MetalsRegalado Cereza IIINo ratings yet
- Hardened Concrete (Lec 20)Document19 pagesHardened Concrete (Lec 20)vasu khandelwalNo ratings yet
- Membrane Stabilizing EffectsDocument5 pagesMembrane Stabilizing Effectssulthana HNo ratings yet
- Ammonium BromideDocument2 pagesAmmonium BromideInarat HussainNo ratings yet
- ERIEZ Cribas VibratoriasDocument8 pagesERIEZ Cribas VibratoriasangelsiddhartaNo ratings yet
- Erosion-Corrosion Resistant Coating For Efficiency EnhancementDocument2 pagesErosion-Corrosion Resistant Coating For Efficiency EnhancementRichard HoseNo ratings yet
- Quality Assuarance - Sop For Cleaning of Sparkler FilterDocument5 pagesQuality Assuarance - Sop For Cleaning of Sparkler FilterKrishna PalNo ratings yet
- 2-Part PUR Highly Elastic, Crack-Bridging Coating: Product DescriptionDocument7 pages2-Part PUR Highly Elastic, Crack-Bridging Coating: Product Descriptionbeck.26No ratings yet
- Percent by VolumeDocument19 pagesPercent by VolumeSabrina LavegaNo ratings yet
- Cane Sampling and AnalysisDocument13 pagesCane Sampling and AnalysisVimal WoosyeNo ratings yet
- Components of Laminated GlassDocument3 pagesComponents of Laminated GlassSarinNo ratings yet
- ONeil - 425btext Organic ReactionsDocument78 pagesONeil - 425btext Organic ReactionsnavchemNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument3 pagesProtein Synthesis WorksheetG Combalicer Bernice Darielle D.No ratings yet
- Energies: Brittleness Evaluation in Shale Gas Reservoirs and Its Influence On FracabilityDocument22 pagesEnergies: Brittleness Evaluation in Shale Gas Reservoirs and Its Influence On Fracabilityomair.latifNo ratings yet
- SCCS1624 Eng PH Salinity SodicityDocument39 pagesSCCS1624 Eng PH Salinity SodicityMenzi CekwaneNo ratings yet
- MSDS L-Ascorbic AcidDocument5 pagesMSDS L-Ascorbic Acideggy mushadiNo ratings yet
- Document 1Document38 pagesDocument 1cap40No ratings yet
- Manufacturing Cost Analysis of Novel Steel/Concrete Composite Vessel For Stationary Storage of High-Pressure HydrogenDocument25 pagesManufacturing Cost Analysis of Novel Steel/Concrete Composite Vessel For Stationary Storage of High-Pressure HydrogenGuilherme Vital MachadoNo ratings yet
- Fleta5 Usermanual Omf5pden1801Document28 pagesFleta5 Usermanual Omf5pden1801Shan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Assignment Class 12Document2 pagesAssignment Class 12mehaktyagi422No ratings yet
- Control of Substances Hazardous To Health (COSHH)Document38 pagesControl of Substances Hazardous To Health (COSHH)ghada gattouchNo ratings yet
- Synthesis Gas ReformersDocument9 pagesSynthesis Gas ReformersAlbert PowaNo ratings yet
- Mat Sci Group 3Document5 pagesMat Sci Group 3Future HazeNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - 04 - 0893 - 01 - 6RP - AFPDocument18 pagesMicrosoft Word - 04 - 0893 - 01 - 6RP - AFPNancy MohamedNo ratings yet
- 9 DNA Electrophoresis2010Document34 pages9 DNA Electrophoresis2010Hasbi Yusuf Abu ZakiNo ratings yet
- Mipa Monoisopropylamine: Safety Data SheetDocument16 pagesMipa Monoisopropylamine: Safety Data SheetVipul GandhiNo ratings yet
- Dowtherm SR-1 MSDSDocument11 pagesDowtherm SR-1 MSDSnedian_2006No ratings yet