Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Brain Computer Interface
Brain Computer Interface
Uploaded by
Md Moshiur RahmanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Brain-Computer Interface (Bci) : Shaik - Khaja Mohiuddin 10MSE0050Document13 pagesBrain-Computer Interface (Bci) : Shaik - Khaja Mohiuddin 10MSE0050Sujitha ChaituNo ratings yet
- Brain Computer InterfacesDocument1 pageBrain Computer InterfacesCarmella Mae QuidiligNo ratings yet
- Brain Machine Interface (BMI) : Pradeep Kumar. P 1DA10EC408Document6 pagesBrain Machine Interface (BMI) : Pradeep Kumar. P 1DA10EC408Pradeep Kumar PaladiNo ratings yet
- Brain Computer Interface: Interface (MMI), or Sometimes Called A Direct Neural Interface orDocument2 pagesBrain Computer Interface: Interface (MMI), or Sometimes Called A Direct Neural Interface orRaksha RanganathNo ratings yet
- Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) : Raghuvarma BasavarajuDocument11 pagesBrain-Computer Interface (BCI) : Raghuvarma BasavarajuanidcrustNo ratings yet
- Brain-Computer Interface: Presented By:-Priya Mittal Shailly Verma Msc. (CS) - RD Sem Supervised By: - Mr. Narendra SirDocument31 pagesBrain-Computer Interface: Presented By:-Priya Mittal Shailly Verma Msc. (CS) - RD Sem Supervised By: - Mr. Narendra SirKundanSinghNo ratings yet
- Slideshare Brain-Computer InterfaceDocument29 pagesSlideshare Brain-Computer InterfaceGold AugustNo ratings yet
- Revolutionizing Military Operations: The Neurotech Race For Brain-Computer Interfaces To Control Multiple Robots With The Speed of ThoughtDocument15 pagesRevolutionizing Military Operations: The Neurotech Race For Brain-Computer Interfaces To Control Multiple Robots With The Speed of ThoughtGeneration GenerationNo ratings yet
- Bci AbstractDocument3 pagesBci AbstractsofiaNo ratings yet
- NeuroscienceDocument1 pageNeuroscienceshildrendelumiereNo ratings yet
- Brain Computer InterfaceDocument6 pagesBrain Computer InterfaceVanga PrathyushaNo ratings yet
- Saisreeravuri DocumentationDocument29 pagesSaisreeravuri DocumentationupendarraoNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument17 pagesSeminar Reportsudhir_raja_1No ratings yet
- Ain Computer InterfaceDocument26 pagesAin Computer Interfaceapocalypto524No ratings yet
- Brain Machine Interface BMIDocument15 pagesBrain Machine Interface BMIaj3751425No ratings yet
- Brain Machine Interface: Anup WadhekarDocument19 pagesBrain Machine Interface: Anup WadhekarArjun S NairNo ratings yet
- BiswaDocument1 pageBiswaSatish PadheeNo ratings yet
- Ranjith SeminarDocument31 pagesRanjith SeminarSAMI.E. SNo ratings yet
- Brain Gate LibreDocument3 pagesBrain Gate Libreanks1605No ratings yet
- Brain GateDocument35 pagesBrain GateAarthi Balasubramanian80% (5)
- Brain Microcircuits For Neuro Impaired PatientsDocument19 pagesBrain Microcircuits For Neuro Impaired Patientsaniljoseph007No ratings yet
- PDFenDocument45 pagesPDFenshaik roshanNo ratings yet
- Brain Sig AbsDocument1 pageBrain Sig AbssharanshabarishNo ratings yet
- Brain Machine InterfaceDocument26 pagesBrain Machine InterfaceMettu Balanandu100% (3)
- Ranjith SeminarDocument31 pagesRanjith SeminarSAMI.E. SNo ratings yet
- EEG-Based Brain-Computer Interfaces BCIs A Survey of Recent Studies On Signal Sensing Technologies and Computational Intelligence Approaches and Their Applications PDFDocument22 pagesEEG-Based Brain-Computer Interfaces BCIs A Survey of Recent Studies On Signal Sensing Technologies and Computational Intelligence Approaches and Their Applications PDFdaytdeenNo ratings yet
- Brain Computer InterfaceDocument21 pagesBrain Computer Interfaceeager_learner67% (3)
- A SeminarDocument18 pagesA SeminarVinjamuri Joshi ManoharNo ratings yet
- Brain Chip: Presented byDocument28 pagesBrain Chip: Presented byCélia OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Brain Computer Interface DissertationDocument7 pagesBrain Computer Interface DissertationPaperWritersAlbuquerque100% (1)
- Ranjith SeminarDocument32 pagesRanjith SeminarSAMI.E. SNo ratings yet
- (IJETA-V11I3P14) :ms. Manju Mathur Aman Agarwal, Hardik Soni, Kushal Mathur, Raghav ChandiwalDocument6 pages(IJETA-V11I3P14) :ms. Manju Mathur Aman Agarwal, Hardik Soni, Kushal Mathur, Raghav ChandiwaleditorijetaNo ratings yet
- Brain ComputerDocument1 pageBrain ComputerNicey CmNo ratings yet
- Jyoti SeminarDocument37 pagesJyoti Seminarjyotigupta.maitNo ratings yet
- History of BCIDocument2 pagesHistory of BCIaj3751425No ratings yet
- Seminar BrainGateDocument34 pagesSeminar BrainGatesorathiyasmruti26No ratings yet
- A Brain-Machine Interface Is A: Scribd Upload A Document Search Documents Explore Sign Up Log inDocument75 pagesA Brain-Machine Interface Is A: Scribd Upload A Document Search Documents Explore Sign Up Log insudhakarsssNo ratings yet
- Seminor On Brainchip TechnologyDocument1 pageSeminor On Brainchip TechnologyRajashekharNo ratings yet
- A Survey of Interactive Systems Based On Brain-Computer InterfacesDocument11 pagesA Survey of Interactive Systems Based On Brain-Computer InterfacesPanos LionasNo ratings yet
- Brain Computing InterfaceDocument3 pagesBrain Computing InterfaceK SaiNo ratings yet
- Synopsis BMIDocument4 pagesSynopsis BMIHina JoshiNo ratings yet
- Brain Computer Interface Seminar ReportDocument17 pagesBrain Computer Interface Seminar ReportRavi Chandra100% (3)
- Brain Computer InterfaceDocument8 pagesBrain Computer InterfaceswethaharithaNo ratings yet
- Brain Computer InterfaceDocument7 pagesBrain Computer InterfaceRAJKUMAR .BNo ratings yet
- Journal Pre-Proof: Informatics in Medicine UnlockedDocument31 pagesJournal Pre-Proof: Informatics in Medicine Unlockedpimpo_glamar100% (1)
- Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI)Document9 pagesBrain-Computer Interfaces (BCI)mayyamdjdhjkNo ratings yet
- SeminarDocument22 pagesSeminarVinay JoisNo ratings yet
- VTH VsemDocument30 pagesVTH VsemVinay MathadNo ratings yet
- A Beginner's Guide To Brain-Computer Interface and Convolutional Neural NetworksDocument14 pagesA Beginner's Guide To Brain-Computer Interface and Convolutional Neural NetworksafaqunaNo ratings yet
- BY-Abhishek Verma 3 Year IT DEPDocument24 pagesBY-Abhishek Verma 3 Year IT DEPlidhisijuNo ratings yet
- TopicDocument2 pagesTopicAshwani GuptaNo ratings yet
- Brain-Machine Interfac E: Seminar Report OnDocument21 pagesBrain-Machine Interfac E: Seminar Report OnAbhisek JenaNo ratings yet
- Final Signature Assignment 1Document2 pagesFinal Signature Assignment 1api-648869457No ratings yet
- Intro 03Document9 pagesIntro 03PoojaNo ratings yet
- Brain Computer Interface: HCI ReportDocument17 pagesBrain Computer Interface: HCI ReportNeha ArifNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument2 pagesBrainArunkumaran KeNo ratings yet
- Brain Computer Interface BCI PDFDocument12 pagesBrain Computer Interface BCI PDFSalih AnwarNo ratings yet
- Advancements in Neuroscience: Modern Tools and Techniques Fueling Thrilling Discoveries in the 21st Century (Neuroscience in the 21st Century: New Tools and Techniques Driving Exciting Discoveries 2)From EverandAdvancements in Neuroscience: Modern Tools and Techniques Fueling Thrilling Discoveries in the 21st Century (Neuroscience in the 21st Century: New Tools and Techniques Driving Exciting Discoveries 2)No ratings yet
- Cyborg Mind: What Brain–Computer and Mind–Cyberspace Interfaces Mean for CyberneuroethicsFrom EverandCyborg Mind: What Brain–Computer and Mind–Cyberspace Interfaces Mean for CyberneuroethicsNo ratings yet
- Course Code: CSE 2203 Course Title: Digital TechniquesDocument14 pagesCourse Code: CSE 2203 Course Title: Digital TechniquesMd Moshiur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Math Ques 2213Document8 pagesMath Ques 2213Md Moshiur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Bin PackingDocument10 pagesBin PackingMd Moshiur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Algorithm and Programming Technique ListDocument17 pagesAlgorithm and Programming Technique ListMd Moshiur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Salasar ProfileDocument58 pagesSalasar ProfilePANKAJ KUMARNo ratings yet
- RAZOAN Service Marketing Term-PaperDocument10 pagesRAZOAN Service Marketing Term-PaperRAZOAN HOSSAINNo ratings yet
- F 2100 BDocument83 pagesF 2100 BYolan Lopez100% (1)
- Virtual Poster-Making Contest: Tiktok Dance ChallengeDocument4 pagesVirtual Poster-Making Contest: Tiktok Dance ChallengeAbimia SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Visible Surface Detection Algorithms-Cg Unit 7Document12 pagesVisible Surface Detection Algorithms-Cg Unit 7Charles Sanders100% (1)
- Conversion Us Uk Metric Si Units For Thermal EngineersDocument1 pageConversion Us Uk Metric Si Units For Thermal EngineersMuhammad AslamNo ratings yet
- Library Management System (LMS) : Software Requirements SpecificationDocument22 pagesLibrary Management System (LMS) : Software Requirements SpecificationRohit DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Industrial Safety Systems: Flexi Soft Designer - Release NotesDocument23 pagesIndustrial Safety Systems: Flexi Soft Designer - Release Notesgerardo floresNo ratings yet
- Project Experience: Pt. Bukaka Teknik Utama Business Tower UnitDocument22 pagesProject Experience: Pt. Bukaka Teknik Utama Business Tower UnitMaulana Loem BizkitsNo ratings yet
- Ad Agency Proposal TemplateDocument7 pagesAd Agency Proposal TemplateBib EkNo ratings yet
- Network Install Guide: For The Enterprise Version of Nuance PDF ProductsDocument23 pagesNetwork Install Guide: For The Enterprise Version of Nuance PDF ProductsAduvier AlexNo ratings yet
- Format of Bridge Report Dated 29.08.2020Document8 pagesFormat of Bridge Report Dated 29.08.2020lenkapradipta2011No ratings yet
- Sabrent USB-SND8 - Manual PDFDocument12 pagesSabrent USB-SND8 - Manual PDFMatias OrtizNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Statistics ReviewerDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Statistics ReviewerVianne TabiqueNo ratings yet
- Tecnam P2006T: Aircraft Flight ManualDocument866 pagesTecnam P2006T: Aircraft Flight ManualAlejandro RamosNo ratings yet
- NAAC SSR Vol IIDocument407 pagesNAAC SSR Vol IIsummerstoryNo ratings yet
- Process Costing-FifoDocument8 pagesProcess Costing-FifoMang OlehNo ratings yet
- Signing Naturally Homework Answers Unit 2Document5 pagesSigning Naturally Homework Answers Unit 2h40n7bjd100% (1)
- UFS-Podni RazvodDocument300 pagesUFS-Podni RazvodDEJAN SRECKOVICNo ratings yet
- AXON Energy Products - Bop Controls Brochure v2015.04.28 Mts 1Document16 pagesAXON Energy Products - Bop Controls Brochure v2015.04.28 Mts 1leoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Installation and Configuration of AndroidDocument23 pagesUnit 2 Installation and Configuration of AndroidAtharv KadamNo ratings yet
- Wall Mounted: Split Type Room Air Conditioner TypeDocument18 pagesWall Mounted: Split Type Room Air Conditioner TypeDavid Lemos Sanchez100% (1)
- Kick-Ass Customer Service-Part 1Document3 pagesKick-Ass Customer Service-Part 1Mahfuzul Haque SujanNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 ICT Worksheet1Document5 pagesGrade 9 ICT Worksheet1SOLONo ratings yet
- Preventative: Maintenance ClinicDocument3 pagesPreventative: Maintenance ClinicPurnama AbhieNo ratings yet
- Computer Operator Practical Paper 2071Document4 pagesComputer Operator Practical Paper 2071amitNo ratings yet
- La Faute Et Le Divorce DissertationDocument6 pagesLa Faute Et Le Divorce DissertationPaySomeoneToWriteAPaperSingapore100% (1)
- Single Piston 8-500-1Document4 pagesSingle Piston 8-500-1TowerNo ratings yet
- Automating Migration To Webex CallingDocument32 pagesAutomating Migration To Webex CallingInfomedia supportNo ratings yet
- Nomi CVDocument2 pagesNomi CVFozia AnsariNo ratings yet
Brain Computer Interface
Brain Computer Interface
Uploaded by
Md Moshiur RahmanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Brain Computer Interface
Brain Computer Interface
Uploaded by
Md Moshiur RahmanCopyright:
Available Formats
Brain–computer Interface
Description: A brain–computer interface (BCI), sometimes called a neural-
control interface (NCI), mind-machine interface (MMI), direct neural
interface (DNI), or brain–machine interface (BMI), is a direct communication pathway
between an enhanced or wired brainand an external device. BCI differs
from neuromodulation in that it allows for bidirectional information flow. BCIs are
often directed at researching, mapping, assisting, augmenting, or repairing human
cognitive or sensory-motor functions.1
Technology has made it possible to make use of computers as a replacement for the
brain. Many kinds of research are going on to reduce the human work. The world is
marching towards the automation in order to reduce the complexity in the work,
speed up the process and at the same time to provide a relaxed life to all mankind.
Some of the technologies involving human brain are the blue brain project, the blue
eyes technology.
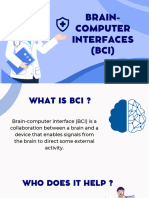
Brain-computer interface (BCI) is a collaboration between a brain and a device that
enables signals from the brain to direct some external activity, such as control of a
cursor or a prosthetic limb the interface enables the direct communications pathway
between the brain and object to be controlled.2
In this report we want to elaborate that how does the brain-computer interface work?
We will focus on animal BCI research and human BCI research, future about BCI
etc.
References
1
Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brain%E2%80%93computer_interface
2
WhatIs.com : http://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/brain-computer-interface-BCI
You might also like
- Brain-Computer Interface (Bci) : Shaik - Khaja Mohiuddin 10MSE0050Document13 pagesBrain-Computer Interface (Bci) : Shaik - Khaja Mohiuddin 10MSE0050Sujitha ChaituNo ratings yet
- Brain Computer InterfacesDocument1 pageBrain Computer InterfacesCarmella Mae QuidiligNo ratings yet
- Brain Machine Interface (BMI) : Pradeep Kumar. P 1DA10EC408Document6 pagesBrain Machine Interface (BMI) : Pradeep Kumar. P 1DA10EC408Pradeep Kumar PaladiNo ratings yet
- Brain Computer Interface: Interface (MMI), or Sometimes Called A Direct Neural Interface orDocument2 pagesBrain Computer Interface: Interface (MMI), or Sometimes Called A Direct Neural Interface orRaksha RanganathNo ratings yet
- Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) : Raghuvarma BasavarajuDocument11 pagesBrain-Computer Interface (BCI) : Raghuvarma BasavarajuanidcrustNo ratings yet
- Brain-Computer Interface: Presented By:-Priya Mittal Shailly Verma Msc. (CS) - RD Sem Supervised By: - Mr. Narendra SirDocument31 pagesBrain-Computer Interface: Presented By:-Priya Mittal Shailly Verma Msc. (CS) - RD Sem Supervised By: - Mr. Narendra SirKundanSinghNo ratings yet
- Slideshare Brain-Computer InterfaceDocument29 pagesSlideshare Brain-Computer InterfaceGold AugustNo ratings yet
- Revolutionizing Military Operations: The Neurotech Race For Brain-Computer Interfaces To Control Multiple Robots With The Speed of ThoughtDocument15 pagesRevolutionizing Military Operations: The Neurotech Race For Brain-Computer Interfaces To Control Multiple Robots With The Speed of ThoughtGeneration GenerationNo ratings yet
- Bci AbstractDocument3 pagesBci AbstractsofiaNo ratings yet
- NeuroscienceDocument1 pageNeuroscienceshildrendelumiereNo ratings yet
- Brain Computer InterfaceDocument6 pagesBrain Computer InterfaceVanga PrathyushaNo ratings yet
- Saisreeravuri DocumentationDocument29 pagesSaisreeravuri DocumentationupendarraoNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument17 pagesSeminar Reportsudhir_raja_1No ratings yet
- Ain Computer InterfaceDocument26 pagesAin Computer Interfaceapocalypto524No ratings yet
- Brain Machine Interface BMIDocument15 pagesBrain Machine Interface BMIaj3751425No ratings yet
- Brain Machine Interface: Anup WadhekarDocument19 pagesBrain Machine Interface: Anup WadhekarArjun S NairNo ratings yet
- BiswaDocument1 pageBiswaSatish PadheeNo ratings yet
- Ranjith SeminarDocument31 pagesRanjith SeminarSAMI.E. SNo ratings yet
- Brain Gate LibreDocument3 pagesBrain Gate Libreanks1605No ratings yet
- Brain GateDocument35 pagesBrain GateAarthi Balasubramanian80% (5)
- Brain Microcircuits For Neuro Impaired PatientsDocument19 pagesBrain Microcircuits For Neuro Impaired Patientsaniljoseph007No ratings yet
- PDFenDocument45 pagesPDFenshaik roshanNo ratings yet
- Brain Sig AbsDocument1 pageBrain Sig AbssharanshabarishNo ratings yet
- Brain Machine InterfaceDocument26 pagesBrain Machine InterfaceMettu Balanandu100% (3)
- Ranjith SeminarDocument31 pagesRanjith SeminarSAMI.E. SNo ratings yet
- EEG-Based Brain-Computer Interfaces BCIs A Survey of Recent Studies On Signal Sensing Technologies and Computational Intelligence Approaches and Their Applications PDFDocument22 pagesEEG-Based Brain-Computer Interfaces BCIs A Survey of Recent Studies On Signal Sensing Technologies and Computational Intelligence Approaches and Their Applications PDFdaytdeenNo ratings yet
- Brain Computer InterfaceDocument21 pagesBrain Computer Interfaceeager_learner67% (3)
- A SeminarDocument18 pagesA SeminarVinjamuri Joshi ManoharNo ratings yet
- Brain Chip: Presented byDocument28 pagesBrain Chip: Presented byCélia OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Brain Computer Interface DissertationDocument7 pagesBrain Computer Interface DissertationPaperWritersAlbuquerque100% (1)
- Ranjith SeminarDocument32 pagesRanjith SeminarSAMI.E. SNo ratings yet
- (IJETA-V11I3P14) :ms. Manju Mathur Aman Agarwal, Hardik Soni, Kushal Mathur, Raghav ChandiwalDocument6 pages(IJETA-V11I3P14) :ms. Manju Mathur Aman Agarwal, Hardik Soni, Kushal Mathur, Raghav ChandiwaleditorijetaNo ratings yet
- Brain ComputerDocument1 pageBrain ComputerNicey CmNo ratings yet
- Jyoti SeminarDocument37 pagesJyoti Seminarjyotigupta.maitNo ratings yet
- History of BCIDocument2 pagesHistory of BCIaj3751425No ratings yet
- Seminar BrainGateDocument34 pagesSeminar BrainGatesorathiyasmruti26No ratings yet
- A Brain-Machine Interface Is A: Scribd Upload A Document Search Documents Explore Sign Up Log inDocument75 pagesA Brain-Machine Interface Is A: Scribd Upload A Document Search Documents Explore Sign Up Log insudhakarsssNo ratings yet
- Seminor On Brainchip TechnologyDocument1 pageSeminor On Brainchip TechnologyRajashekharNo ratings yet
- A Survey of Interactive Systems Based On Brain-Computer InterfacesDocument11 pagesA Survey of Interactive Systems Based On Brain-Computer InterfacesPanos LionasNo ratings yet
- Brain Computing InterfaceDocument3 pagesBrain Computing InterfaceK SaiNo ratings yet
- Synopsis BMIDocument4 pagesSynopsis BMIHina JoshiNo ratings yet
- Brain Computer Interface Seminar ReportDocument17 pagesBrain Computer Interface Seminar ReportRavi Chandra100% (3)
- Brain Computer InterfaceDocument8 pagesBrain Computer InterfaceswethaharithaNo ratings yet
- Brain Computer InterfaceDocument7 pagesBrain Computer InterfaceRAJKUMAR .BNo ratings yet
- Journal Pre-Proof: Informatics in Medicine UnlockedDocument31 pagesJournal Pre-Proof: Informatics in Medicine Unlockedpimpo_glamar100% (1)
- Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI)Document9 pagesBrain-Computer Interfaces (BCI)mayyamdjdhjkNo ratings yet
- SeminarDocument22 pagesSeminarVinay JoisNo ratings yet
- VTH VsemDocument30 pagesVTH VsemVinay MathadNo ratings yet
- A Beginner's Guide To Brain-Computer Interface and Convolutional Neural NetworksDocument14 pagesA Beginner's Guide To Brain-Computer Interface and Convolutional Neural NetworksafaqunaNo ratings yet
- BY-Abhishek Verma 3 Year IT DEPDocument24 pagesBY-Abhishek Verma 3 Year IT DEPlidhisijuNo ratings yet
- TopicDocument2 pagesTopicAshwani GuptaNo ratings yet
- Brain-Machine Interfac E: Seminar Report OnDocument21 pagesBrain-Machine Interfac E: Seminar Report OnAbhisek JenaNo ratings yet
- Final Signature Assignment 1Document2 pagesFinal Signature Assignment 1api-648869457No ratings yet
- Intro 03Document9 pagesIntro 03PoojaNo ratings yet
- Brain Computer Interface: HCI ReportDocument17 pagesBrain Computer Interface: HCI ReportNeha ArifNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument2 pagesBrainArunkumaran KeNo ratings yet
- Brain Computer Interface BCI PDFDocument12 pagesBrain Computer Interface BCI PDFSalih AnwarNo ratings yet
- Advancements in Neuroscience: Modern Tools and Techniques Fueling Thrilling Discoveries in the 21st Century (Neuroscience in the 21st Century: New Tools and Techniques Driving Exciting Discoveries 2)From EverandAdvancements in Neuroscience: Modern Tools and Techniques Fueling Thrilling Discoveries in the 21st Century (Neuroscience in the 21st Century: New Tools and Techniques Driving Exciting Discoveries 2)No ratings yet
- Cyborg Mind: What Brain–Computer and Mind–Cyberspace Interfaces Mean for CyberneuroethicsFrom EverandCyborg Mind: What Brain–Computer and Mind–Cyberspace Interfaces Mean for CyberneuroethicsNo ratings yet
- Course Code: CSE 2203 Course Title: Digital TechniquesDocument14 pagesCourse Code: CSE 2203 Course Title: Digital TechniquesMd Moshiur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Math Ques 2213Document8 pagesMath Ques 2213Md Moshiur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Bin PackingDocument10 pagesBin PackingMd Moshiur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Algorithm and Programming Technique ListDocument17 pagesAlgorithm and Programming Technique ListMd Moshiur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Salasar ProfileDocument58 pagesSalasar ProfilePANKAJ KUMARNo ratings yet
- RAZOAN Service Marketing Term-PaperDocument10 pagesRAZOAN Service Marketing Term-PaperRAZOAN HOSSAINNo ratings yet
- F 2100 BDocument83 pagesF 2100 BYolan Lopez100% (1)
- Virtual Poster-Making Contest: Tiktok Dance ChallengeDocument4 pagesVirtual Poster-Making Contest: Tiktok Dance ChallengeAbimia SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Visible Surface Detection Algorithms-Cg Unit 7Document12 pagesVisible Surface Detection Algorithms-Cg Unit 7Charles Sanders100% (1)
- Conversion Us Uk Metric Si Units For Thermal EngineersDocument1 pageConversion Us Uk Metric Si Units For Thermal EngineersMuhammad AslamNo ratings yet
- Library Management System (LMS) : Software Requirements SpecificationDocument22 pagesLibrary Management System (LMS) : Software Requirements SpecificationRohit DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Industrial Safety Systems: Flexi Soft Designer - Release NotesDocument23 pagesIndustrial Safety Systems: Flexi Soft Designer - Release Notesgerardo floresNo ratings yet
- Project Experience: Pt. Bukaka Teknik Utama Business Tower UnitDocument22 pagesProject Experience: Pt. Bukaka Teknik Utama Business Tower UnitMaulana Loem BizkitsNo ratings yet
- Ad Agency Proposal TemplateDocument7 pagesAd Agency Proposal TemplateBib EkNo ratings yet
- Network Install Guide: For The Enterprise Version of Nuance PDF ProductsDocument23 pagesNetwork Install Guide: For The Enterprise Version of Nuance PDF ProductsAduvier AlexNo ratings yet
- Format of Bridge Report Dated 29.08.2020Document8 pagesFormat of Bridge Report Dated 29.08.2020lenkapradipta2011No ratings yet
- Sabrent USB-SND8 - Manual PDFDocument12 pagesSabrent USB-SND8 - Manual PDFMatias OrtizNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Statistics ReviewerDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Statistics ReviewerVianne TabiqueNo ratings yet
- Tecnam P2006T: Aircraft Flight ManualDocument866 pagesTecnam P2006T: Aircraft Flight ManualAlejandro RamosNo ratings yet
- NAAC SSR Vol IIDocument407 pagesNAAC SSR Vol IIsummerstoryNo ratings yet
- Process Costing-FifoDocument8 pagesProcess Costing-FifoMang OlehNo ratings yet
- Signing Naturally Homework Answers Unit 2Document5 pagesSigning Naturally Homework Answers Unit 2h40n7bjd100% (1)
- UFS-Podni RazvodDocument300 pagesUFS-Podni RazvodDEJAN SRECKOVICNo ratings yet
- AXON Energy Products - Bop Controls Brochure v2015.04.28 Mts 1Document16 pagesAXON Energy Products - Bop Controls Brochure v2015.04.28 Mts 1leoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Installation and Configuration of AndroidDocument23 pagesUnit 2 Installation and Configuration of AndroidAtharv KadamNo ratings yet
- Wall Mounted: Split Type Room Air Conditioner TypeDocument18 pagesWall Mounted: Split Type Room Air Conditioner TypeDavid Lemos Sanchez100% (1)
- Kick-Ass Customer Service-Part 1Document3 pagesKick-Ass Customer Service-Part 1Mahfuzul Haque SujanNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 ICT Worksheet1Document5 pagesGrade 9 ICT Worksheet1SOLONo ratings yet
- Preventative: Maintenance ClinicDocument3 pagesPreventative: Maintenance ClinicPurnama AbhieNo ratings yet
- Computer Operator Practical Paper 2071Document4 pagesComputer Operator Practical Paper 2071amitNo ratings yet
- La Faute Et Le Divorce DissertationDocument6 pagesLa Faute Et Le Divorce DissertationPaySomeoneToWriteAPaperSingapore100% (1)
- Single Piston 8-500-1Document4 pagesSingle Piston 8-500-1TowerNo ratings yet
- Automating Migration To Webex CallingDocument32 pagesAutomating Migration To Webex CallingInfomedia supportNo ratings yet
- Nomi CVDocument2 pagesNomi CVFozia AnsariNo ratings yet