Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Albumin To Creatinine Ratio (ACR)
Albumin To Creatinine Ratio (ACR)
Uploaded by
Safira WasimOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Albumin To Creatinine Ratio (ACR)
Albumin To Creatinine Ratio (ACR)
Uploaded by
Safira WasimCopyright:
Available Formats
Albumin to Creatinine Ratio (ACR)
What is ACR?
Albumin to creatinine ratio is a urine test. Normal daily (24 hour) urine albumin excretion is less than 30 mg in
adults. If the 24 hour urine albumin excretion results are between 30-300 mg it becomes defined as
microalbuminuria (MAU). This may occur with kidney damage arising from diabetes mellitus. When collection
of 24 hour urine is not feasible, a random urine sample for simultaneous measurement of albumin and
creatinine can determine an albumin to creatinine ratio (ACR). This test determines whether MAU or excessive
loss of albumin is present. These results can be used to identify individuals at higher risk of developing
progressive kidney disease. In healthy adult males, ACR is less than 2.0 mg albumin/mmol creatinine, while in
healthy adult females it is less than 2.8 mg/mmol. MAU therefore refers to a specific range of ACR that
exceeds these cutoffs and lies between 2.0-20.0 mg/mmol for males and 2.8-28.0 mg/mmol for females. ACR
levels above 20.0 mg/mmol for males and 28.0 mg/mmol for females corresponds to a urine albumin level in
excess of 300 mg/day (i.e. macroalbuminuria) and are consistent with overt diabetic nephropathy. ACR can be
used to determine urine albumin loss in non diabetic kidney disease and is used instead of a total protein to
creatinine ratio on a random urine sample.
Albumin or protein in the urine is a marker of both progression of kidney disease, as well as increased risk of
cardiovascular events. Patients with diabetes should have annual random urine samples for ACR. ACR should
be repeated to determine if albumin excretion is increasing or decreasing. ACR can be ordered instead of a
24 hour urine, if routine urinalysis is positive for protein.
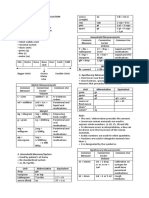
Table 1. Stages of classic diabetic nephropathy according to urinary albumin level 1
Stage of Urine dipstick for Urine ACR 24-urine collection
nephropathy protein for albumin*
(mg/mmol)
(mg/day)
Normal Negative < 2.0 (men) <30
< 2.8 (women)
Microalbuminuria Negative 2. 0 – 20.0 (men) 30-300
2.8 – 28.0 (women)
Overt nephropathy Positive > 20.0 (men) >300
(Macroalbuminuria) > 28.0 (women)
* Values are for urinary albumin, not total urinary protein, which will be higher than urinary albumin levels.
ACR results may be elevated with conditions other than diabetic nephropathy
1
Canadian Diabetes Association Clinical Practice Guidelines Expert Committee. Excerpt taken from Canadian
Diabetes Association 2008 clinical practice guidelines for the prevention and management of diabetes in
Canada. Can J Diabetes. 2008;32 (suppl1):S127.
When should an ACR be ordered?
Refer to Detection, Monitoring & Referral of Chronic Kidney Disease available from the Nova Scotia Renal
Program website: www.nsrp.gov.ns.ca.
Do all Nova Scotia laboratories offer ACR testing?
The regional laboratory sites in each District Health Authority in Nova Scotia offer ACR testing. ACR should be
ordered as a request test and the specimen will automatically be routed to the regional laboratory site in your
district.
What happens if I order Microalbuminuria (MAU)?
Microalbuminuria will be reported in addition to the ACR.
Where can I find additional information to help me understand albumin in the urine?
Refer to Detection, Monitoring & Referral of Chronic Kidney Disease available from the Nova Scotia Renal
Program website: www.nsrp.gov.ns.ca.
Canadian Diabetes Association, 2008 Clinical Practice Guidelines:
http://www.diabetes.ca/for-professionals/resources/2008-cpg/
For more information, contact:
Nova Scotia Renal Program
Bethune Building, Room 539
1276 South Park Street
Halifax, Nova Scotia B3H 2Y9
Phone: (902) 473 5656
Fax: (902) 425 1752
Email: info@nsrp.nshealth.ca
www.nsrp.gov.ns.ca
November 2009
You might also like
- Organic Chemistry Board Exam QuestionsDocument10 pagesOrganic Chemistry Board Exam QuestionsRiza Joie Versales100% (1)
- Coping With Institutional Order Flow Zicklin School of Business Financial Markets SeriesDocument208 pagesCoping With Institutional Order Flow Zicklin School of Business Financial Markets SeriesRavi Varakala100% (6)
- Injuries in Sprint Canoeists and Kayakers Etiology, Mechanisms of Injury, Treatment Options, and Practical ApplicationsDocument8 pagesInjuries in Sprint Canoeists and Kayakers Etiology, Mechanisms of Injury, Treatment Options, and Practical ApplicationsPabloAñonNo ratings yet
- Stuxnet and Its Hidden Lessons On The Ethics of CyberweaponsDocument9 pagesStuxnet and Its Hidden Lessons On The Ethics of CyberweaponsprofcameloNo ratings yet
- MRCP 2 Nephrology NOTESDocument74 pagesMRCP 2 Nephrology NOTESMuhammad HaneefNo ratings yet
- Cosmotic Surgical Center Business PlanDocument37 pagesCosmotic Surgical Center Business PlanRamchandra Cv100% (1)
- Winters PreviewDocument265 pagesWinters PreviewcqpresscustomNo ratings yet
- Aspect of CalculationDocument6 pagesAspect of CalculationdmNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument7 pagesChronic Kidney DiseasePradnya ParamitaNo ratings yet
- UACRQuick Reference SheetDocument2 pagesUACRQuick Reference SheetNixNo ratings yet
- UACR GFR QuickReference 508Document2 pagesUACR GFR QuickReference 508sarfraz_eeeNo ratings yet
- Achim Curs BRC 2014Document96 pagesAchim Curs BRC 2014Patricia IoanaNo ratings yet
- Pendukung Mikroalbuminuria, Kreatini, UcrDocument21 pagesPendukung Mikroalbuminuria, Kreatini, UcrHesty AshanNo ratings yet
- QR Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Adults (Second Edition 2018)Document8 pagesQR Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Adults (Second Edition 2018)khairulfatinNo ratings yet
- DR. Butar Butar - Diabetic Kidney Disease How To Regress (PIT MAKASAR, 23-26 Nov 06)Document42 pagesDR. Butar Butar - Diabetic Kidney Disease How To Regress (PIT MAKASAR, 23-26 Nov 06)Didi RaufNo ratings yet
- Antibiotik For Renal FailureDocument6 pagesAntibiotik For Renal FailureWidhy Joss BangetzNo ratings yet
- Clinical PathologyDocument7 pagesClinical PathologyMustafa El-saeedNo ratings yet
- Medical Check Up Standard Operating Procedure For Diagnosis 1. BMIDocument25 pagesMedical Check Up Standard Operating Procedure For Diagnosis 1. BMIlita agustinNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Therapy in The Presence of Proteinuria: ReviewDocument15 pagesAntihypertensive Therapy in The Presence of Proteinuria: ReviewMaría José GalvisNo ratings yet
- Test Normal Values Findings InterpretationDocument3 pagesTest Normal Values Findings InterpretationJohn ReyesNo ratings yet
- Blood Test of KFTDocument3 pagesBlood Test of KFTRaghvendra RathoreNo ratings yet
- Albumin Creatinine Ratio ACR 1Document3 pagesAlbumin Creatinine Ratio ACR 1quethara.photographyNo ratings yet
- Boala Renala Diabetica: Rinichi Anatomie deDocument10 pagesBoala Renala Diabetica: Rinichi Anatomie deAlexandra GheorgheNo ratings yet
- CKD Kdigo 2012Document27 pagesCKD Kdigo 2012giggs_libraNo ratings yet
- DM Algorithm Urine Alb 508cDocument1 pageDM Algorithm Urine Alb 508cArjunaPamungkasNo ratings yet
- DM Algorithm Urine Alb 508c PDFDocument1 pageDM Algorithm Urine Alb 508c PDFElang SudewaNo ratings yet
- Nephrology ?Document52 pagesNephrology ?drxghamdiNo ratings yet
- CKD 2016Document39 pagesCKD 2016husnaNo ratings yet
- TEA KIMIA Dengan SumberDocument8 pagesTEA KIMIA Dengan SumberGUSTI ADHELEIDANo ratings yet
- CKDDocument35 pagesCKDNATTAPAT SANGKAKULNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic NephropathyDocument12 pagesDiabetic Nephropathy Diabetic NephropathyKokoland KukusNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Renal Function - StudentsDocument24 pagesAssessment of Renal Function - Studentsadmiraldamian67No ratings yet
- Screening For Diabetic Nephropathy: Take Your Blinkers Off: Ahmed Eid, Shafiq Yusuff, Marie-France KongDocument2 pagesScreening For Diabetic Nephropathy: Take Your Blinkers Off: Ahmed Eid, Shafiq Yusuff, Marie-France KongRaodatul IstiharohNo ratings yet
- Nilai Normal Gula DarahDocument4 pagesNilai Normal Gula DarahNurRismaUfadillaIINo ratings yet
- CreatinineDocument8 pagesCreatinineGul RockzzNo ratings yet
- Renal Function TestDocument5 pagesRenal Function Testmitchelleizzy100% (1)
- Daftar Nilai KritisDocument2 pagesDaftar Nilai KritisNimazzBanabeautyViruzzNo ratings yet
- Kidney DiseaseDocument3 pagesKidney DiseaseHariNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument39 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseGumarbio Setiadi Zakaria100% (1)
- Renal DisordersDocument26 pagesRenal DisordersCabdalle KurbeNo ratings yet
- Lab (5) Creatinine Clearance&GFRDocument16 pagesLab (5) Creatinine Clearance&GFRAkshay Chandra Vemulapalli100% (1)
- ProtienuriaDocument12 pagesProtienuriaSobha MatthewNo ratings yet
- Protein 2Document6 pagesProtein 2soniNo ratings yet
- Slides Outcomes of Sglt2i in Diabetic Kidney Disease Is It All DiabetesDocument29 pagesSlides Outcomes of Sglt2i in Diabetic Kidney Disease Is It All DiabetesVaibhav DafaleNo ratings yet
- Diabetic NephropathyDocument14 pagesDiabetic NephropathyHasty Wahyuni50% (2)
- Kidney FunctionDocument4 pagesKidney FunctionEinah EinahNo ratings yet
- Renal Function TestsDocument36 pagesRenal Function TestsLawal Bello DanchadiNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Proteinuria Overview - Epocrates OnlineDocument4 pagesEvaluation of Proteinuria Overview - Epocrates Onlinerey_fremyNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Elevated CreatinineDocument10 pagesAssessment of Elevated CreatinineSheryl Ann PedinesNo ratings yet
- Renal FunctionsDocument30 pagesRenal FunctionsJay Andrea Vea Israel100% (1)
- HelixDocument10 pagesHelixshiv gautamNo ratings yet
- L2 InvestigationDocument14 pagesL2 InvestigationMohammed A. JameelNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Paul Cockwell Queen Elizabeth Hospital BirminghamDocument44 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: Paul Cockwell Queen Elizabeth Hospital BirminghamDhruva PatelNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease: BY Mrs. K.Shailaja., M. Pharm., Lecturer Dept of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of PharmacyDocument17 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: BY Mrs. K.Shailaja., M. Pharm., Lecturer Dept of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of PharmacyPIPER EXAMSNo ratings yet
- Patient Information Handout: Am Fam PhysicianDocument5 pagesPatient Information Handout: Am Fam PhysicianJacky Lou Tabamo LumacadNo ratings yet
- The Clinical Biochemistry of Kidney Functions: 2019 DR Boldizsár CZÉHDocument46 pagesThe Clinical Biochemistry of Kidney Functions: 2019 DR Boldizsár CZÉHJACOB FRANCISNo ratings yet
- 12B. Kuliah CKD 2017Document44 pages12B. Kuliah CKD 2017yussikafernandaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument14 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseJoel CanenciaNo ratings yet
- Gagal Ginjal Akut (GGA) : AKI (Acute Kidney Injury)Document39 pagesGagal Ginjal Akut (GGA) : AKI (Acute Kidney Injury)ratihNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) : Departemen Penyakit DalamDocument43 pagesAcute Kidney Injury (AKI) : Departemen Penyakit DalamFitria Dewi LestariNo ratings yet
- CreatinineDocument3 pagesCreatinineElixirNo ratings yet
- Kidney Disease Acute and Chronic 2019Document60 pagesKidney Disease Acute and Chronic 2019salamon2tNo ratings yet
- KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline For Acute Kidney Injury.Document18 pagesKDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline For Acute Kidney Injury.Madalina TalpauNo ratings yet
- B Rama DeviDocument10 pagesB Rama DeviBandari JanardhanNo ratings yet
- Dosage Adjustment of Cytotoxics in Renal ImpairmentDocument24 pagesDosage Adjustment of Cytotoxics in Renal ImpairmenthamzaNo ratings yet
- University of Zimbabwe B.Sc. (Engineering) Honours - Level IIDocument6 pagesUniversity of Zimbabwe B.Sc. (Engineering) Honours - Level IIkundayi shavaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Questions and Controversies Neurology 4th Edition Perlman Jeffrey M Inder Terrie Jeffrey M Perlman Terrie InderDocument70 pagesNeonatal Questions and Controversies Neurology 4th Edition Perlman Jeffrey M Inder Terrie Jeffrey M Perlman Terrie Inderclaude.moore690100% (12)
- Importing Google Earth Data Into A GISDocument15 pagesImporting Google Earth Data Into A GISJONAMNo ratings yet
- TLE DRILL 150 Items With Answer KeyDocument16 pagesTLE DRILL 150 Items With Answer KeyEd Doloriel MoralesNo ratings yet
- Wobbepresentation 2004Document43 pagesWobbepresentation 2004CARLOS SARMIENTONo ratings yet
- PSM PagewiseQuestions (Park 25th)Document12 pagesPSM PagewiseQuestions (Park 25th)JENNIFER JOHN MBBS2020No ratings yet
- TDS - Masterseal 420 HBDocument2 pagesTDS - Masterseal 420 HBVenkata RaoNo ratings yet
- Cunningworths' Checklist (1995) : Number Items YES NO A. Aims and Approaches 1 2 3 4 B. Design and Organization 5 6 7 8Document3 pagesCunningworths' Checklist (1995) : Number Items YES NO A. Aims and Approaches 1 2 3 4 B. Design and Organization 5 6 7 8Thảo NhiNo ratings yet
- 4 Types of Essay WritingDocument2 pages4 Types of Essay WritingkikiNo ratings yet
- Product Demo Feedback FormDocument1 pageProduct Demo Feedback FormVarunSharmaNo ratings yet
- QRS-CPVS 20-30 Instruction Manual 2011Document34 pagesQRS-CPVS 20-30 Instruction Manual 2011Lenin TautimezNo ratings yet
- SpaceX Response To DISH Re Mobile Platforms (6!8!22)Document6 pagesSpaceX Response To DISH Re Mobile Platforms (6!8!22)michaelkan1No ratings yet
- Metric System Common Measure Conversion Factor Common UseDocument4 pagesMetric System Common Measure Conversion Factor Common UseMarielle ChuaNo ratings yet
- Perception On CatcallingDocument19 pagesPerception On CatcallingJasmin Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- NSO Set-C Answer KeysDocument12 pagesNSO Set-C Answer KeysMota Chashma100% (1)
- Digital Media MemoryDocument10 pagesDigital Media Memorywkurlinkus7386No ratings yet
- The Concept of Developmental PsychologyDocument16 pagesThe Concept of Developmental PsychologyJulie Anne ÜNo ratings yet
- Verb Pattern in EnglishDocument4 pagesVerb Pattern in EnglishValentina Yanella Caudullo SeoaneNo ratings yet
- NIOS Class 12 Psychology Chapter 10 EmotionsDocument4 pagesNIOS Class 12 Psychology Chapter 10 Emotionsmanahil dollNo ratings yet
- SUVAT LoopDocument1 pageSUVAT LoopAhmed ZakiNo ratings yet
- Eclipse ManualDocument10 pagesEclipse ManualgiancarlohoneyNo ratings yet
- General Information: Location A Location BDocument2 pagesGeneral Information: Location A Location BNikNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument1 pageReadmedan maliwatNo ratings yet
- University of The Philippines Open University Faculty of Management and Development Studies Master of Management ProgramDocument10 pagesUniversity of The Philippines Open University Faculty of Management and Development Studies Master of Management ProgramRoldan TalaugonNo ratings yet