Professional Documents
Culture Documents
作業2 20170323
作業2 20170323
Uploaded by
曾瑋富Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
作業2 20170323
作業2 20170323
Uploaded by
曾瑋富Copyright:
Available Formats
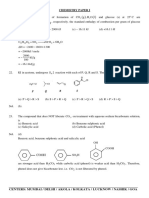
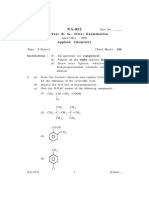
1.
A mechanism for the thermal decomposition of acetaldehyde
CH 3 CHO
k1
CH 3* CHO *
CHO *
k2
CO H *
H * CH 3 CHO
k3
CH 3 CO* H 2
CH 3* CH 3 CHO
k4
CH 4 CH 3 CO*
CH 3 CO*
k5
CH 3* CO
2CH 3*
k6
C2 H 6
Apply the steady state approximation to CH4 to obtain the rate equation.
2. For the elementary reactions in series
k1 k2
A R S
at t=0, CA=CA0, CB0=CS0=CR0=0
k3
B
(a) Plot a figure to illustrate the variation of concentration of A, B, R
and S versus reaction time t.
(b) Find the maximum concentration of R and when it’s reached.
3. The oxidation of nitrogen over a certain catalyst is found to follow the
following mechanisms:
O2 2Oads (1)
N2 + Oads N2O (2)
(a) Calculate the rate expression for N2O formation using the steady
state approximation. (Note: assume for this problem only that step
(1) is irreversible, O2 2Oads
(b) Assume that (1) in the above mechanism is the rate determining
step, and recalculate the rate expression for N2O formation.
You might also like
- Balancing Redox Equations Q & ADocument40 pagesBalancing Redox Equations Q & AEw AldoNo ratings yet
- Alkane PDFDocument5 pagesAlkane PDFRavi Kiran KoduriNo ratings yet
- Alkane Jee-Advance Level-1Document5 pagesAlkane Jee-Advance Level-1Ravi Kiran KoduriNo ratings yet
- A Level Chemistry Paper 1 Set 31marking GuideDocument14 pagesA Level Chemistry Paper 1 Set 31marking GuidekitookebarnabasNo ratings yet
- WPT Centre Xi Iit Che Key 30-1-23Document3 pagesWPT Centre Xi Iit Che Key 30-1-23pinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper1 Pre Board 2024Document3 pagesChemistry Paper1 Pre Board 2024ittefaq6053634No ratings yet
- Supporting Online Material For: Stable Prenucleation Calcium Carbonate ClustersDocument34 pagesSupporting Online Material For: Stable Prenucleation Calcium Carbonate ClustersbrianNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4Document9 pagesExercise 4Jin isnt a bed you can sleep onNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class 12th CBSE Sample PaperDocument9 pagesChemistry Class 12th CBSE Sample PaperSiddhi GoplanNo ratings yet
- 2023 H2 Chemical Equilibria Tutorial (QP)Document15 pages2023 H2 Chemical Equilibria Tutorial (QP)nivind88No ratings yet
- Revision STPM Term 1Document15 pagesRevision STPM Term 1Wong WengSiongNo ratings yet
- PH Calculation With CO2 AdditionDocument12 pagesPH Calculation With CO2 AdditionPraveen KhatriNo ratings yet
- Exercises NusDocument5 pagesExercises NusNor AzimahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Ii (Ecf 0024) Tutorial 5: CH CHCH CHCH OHDocument3 pagesChemistry Ii (Ecf 0024) Tutorial 5: CH CHCH CHCH OHutpNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry 2018Document17 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry 2018parv dhanoteNo ratings yet
- Chem15 Problem Set 4 A. Gaseous Equilibrium: 2co O 2co Co Fe Co Feo O 4H S 2so 8HDocument5 pagesChem15 Problem Set 4 A. Gaseous Equilibrium: 2co O 2co Co Fe Co Feo O 4H S 2so 8HRoxanne de RoxasNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons Work SheetDocument30 pagesHydrocarbons Work SheettarunvishalgrNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidDocument6 pagesCarboxylic Acidhareharanbt22No ratings yet
- A Level Chemistry Paper 1 Set 29 Marking GuideDocument7 pagesA Level Chemistry Paper 1 Set 29 Marking GuideSsenono AndrewNo ratings yet
- BCHCT 133Document16 pagesBCHCT 133Md YusufNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY-25-02-11th (PQRS & J) SpaceDocument18 pagesCHEMISTRY-25-02-11th (PQRS & J) SpaceRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- IB WS 4.1 (4) Mixed QuestionsDocument3 pagesIB WS 4.1 (4) Mixed QuestionsPhiri AgnesNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 2 (WK 3-4)Document5 pagesOrganic Chemistry 2 (WK 3-4)miracleobot9No ratings yet
- Alkanes: 1.1 Classification of HydrocarbonDocument33 pagesAlkanes: 1.1 Classification of HydrocarbonKhizra TehreemNo ratings yet
- CY1101Document3 pagesCY1101Anurag BaralNo ratings yet
- Introductory Organic ChemistryDocument43 pagesIntroductory Organic ChemistryCharlotte TalyorNo ratings yet
- Chem 1 Ruvuma 2023Document7 pagesChem 1 Ruvuma 2023ahmedhamadsameerNo ratings yet
- Minor IDocument2 pagesMinor Ishubham sharmaNo ratings yet
- Matriculation Chemistry (Hydrocarbon) AlkeneDocument98 pagesMatriculation Chemistry (Hydrocarbon) Alkeneridwan100% (4)
- Alkyne-Anna IN CLASS 1Document26 pagesAlkyne-Anna IN CLASS 1Siti Farhanah Mohd NasirNo ratings yet
- III Kinetics & Equilibrium-ReviewDocument3 pagesIII Kinetics & Equilibrium-ReviewChinmaya Ranjan BiswalNo ratings yet
- NSS Chemistry Part 13 Industrial Chemistry - IDocument36 pagesNSS Chemistry Part 13 Industrial Chemistry - Izwindows123456789No ratings yet
- Stereo New 2Document23 pagesStereo New 2Upendrasenareddy KunduruNo ratings yet
- Chemistry TestDocument12 pagesChemistry TestKimmy KuoNo ratings yet
- Carbondioxide in Water EquilibriumDocument7 pagesCarbondioxide in Water EquilibriumsaaroomaniNo ratings yet
- H2 Enrichment Paper 2 Chemical Eqm Gases and Atomic Structure (Ans)Document5 pagesH2 Enrichment Paper 2 Chemical Eqm Gases and Atomic Structure (Ans)Priya SivasubbramaniamNo ratings yet
- Exercises-Topic 6Document4 pagesExercises-Topic 6Arturo AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9-Alkynes 7 Unsaturations 9 Unsaturations 5 UnsaturationsDocument19 pagesChapter 9-Alkynes 7 Unsaturations 9 Unsaturations 5 Unsaturations張湧浩No ratings yet
- CU-2020 B.Sc. (General) Chemistry Semester-III Paper-CC3-GE3 QPDocument4 pagesCU-2020 B.Sc. (General) Chemistry Semester-III Paper-CC3-GE3 QPSatyajitDeyNo ratings yet
- Cherekn Problem Set 2Document5 pagesCherekn Problem Set 2Ken ColNo ratings yet
- Question Alkane and CycloalkaneDocument3 pagesQuestion Alkane and CycloalkaneFendi RohmawanNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Prelab Questions For Chemistry IDocument1 pageGas Laws Prelab Questions For Chemistry IKiionkaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Problems (Set 5)Document2 pagesTutorial Problems (Set 5)Manishaa Varatha RajuNo ratings yet
- Kj/mol Kj/mol, Respectively. The Standard Enthalpy of Combustion Per Gram of GlucoseDocument8 pagesKj/mol Kj/mol, Respectively. The Standard Enthalpy of Combustion Per Gram of GlucosekolodoloNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons 1Document3 pagesHydrocarbons 1Mahesh MedtiyaNo ratings yet
- January HW Sec 6Document3 pagesJanuary HW Sec 6Freya SawNo ratings yet
- Chem Sem 1 Q &A PDFDocument9 pagesChem Sem 1 Q &A PDFevacuate clashNo ratings yet
- Reaction Kinetics (5) : Xuan Cheng Xiamen UniversityDocument27 pagesReaction Kinetics (5) : Xuan Cheng Xiamen Universityahmadhelmiase7621No ratings yet
- CBSE 12 Chemistry Solution Term2Document5 pagesCBSE 12 Chemistry Solution Term2R roseNo ratings yet
- 2011 A Level CH H2 P3 SolnDocument11 pages2011 A Level CH H2 P3 SolnjasonwscNo ratings yet
- Class 11Document3 pagesClass 11bikasonoinam321No ratings yet
- Mock MCQ Time-TrialDocument11 pagesMock MCQ Time-Trial2022 BALAKRISHNAN ADHITHINo ratings yet
- 有機金屬 Chapter 15Document73 pages有機金屬 Chapter 15dennis980012No ratings yet
- AIEEE ChemistryDocument2 pagesAIEEE ChemistryRaja PramodNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios QO1-1Document3 pagesEjercicios QO1-1hector juarezNo ratings yet
- Stereo Chemistry I IDocument35 pagesStereo Chemistry I INikhilesh PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- Neet OrganicDocument3 pagesNeet Organicpinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- First Year B. Sc. (Fire) Examination Applied Chemistry: 3 Hours) 100 InstructionsDocument4 pagesFirst Year B. Sc. (Fire) Examination Applied Chemistry: 3 Hours) 100 InstructionsGSCSCL eAuction CellNo ratings yet
- 15-M-Chemical Engg-I (Thermodynamics & Measuring Analytical Instruments) - UpdatedDocument7 pages15-M-Chemical Engg-I (Thermodynamics & Measuring Analytical Instruments) - UpdatedSonu SinghNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)