Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
45 viewsUses of Quality Function Deployment
Uses of Quality Function Deployment
Uploaded by
Kavin SQuality Function Deployment (QFD) is a customer-driven approach to product planning that involves translating customer requirements into specific design requirements. It uses a cross-functional team and series of matrices called the "House of Quality" to establish customer objectives and record them throughout the development process from concept to production. QFD ensures customer desires are prioritized, translated into engineering specifications, and targets are set to meet requirements.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- G11 Lesson 02 Essay 1Document3 pagesG11 Lesson 02 Essay 1Tinet Sri UdawelaNo ratings yet
- Iec TR 62278-3-2010Document70 pagesIec TR 62278-3-2010Joanne W100% (1)
- SAP UI5 Development GuidelinesDocument20 pagesSAP UI5 Development GuidelinesVipinNo ratings yet
- What Is Quality Function DeploymentDocument6 pagesWhat Is Quality Function DeploymentAnkurNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma ExamDocument5 pagesSix Sigma Exammajid4uonly100% (5)
- QFD BriefDocument4 pagesQFD Briefronit.islwirelessNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document15 pagesAssignment 5api-652656444No ratings yet
- Quality Function DeploymentDocument13 pagesQuality Function DeploymentShafwan MuhadzdzibNo ratings yet
- QFD2 Dontqd@Comcast - Net ClausingDocument24 pagesQFD2 Dontqd@Comcast - Net ClausingGiselleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 & 9: Quality Function DeploymentDocument46 pagesChapter 8 & 9: Quality Function DeploymentAli AhmedNo ratings yet
- TQM Assignment5 TejasgDocument11 pagesTQM Assignment5 Tejasgapi-282598664No ratings yet
- Assignment: 5: Q.1 Explain What Is QFD, (Quality Function Deployment) ?Document12 pagesAssignment: 5: Q.1 Explain What Is QFD, (Quality Function Deployment) ?api-308384599No ratings yet
- House of QualityDocument18 pagesHouse of Qualityraju1112No ratings yet
- TQM Assignment-5Document16 pagesTQM Assignment-5api-546637261No ratings yet
- Quality FunctionDocument55 pagesQuality Functionyogeshkmr01No ratings yet
- SixSigma QFD MatrixDocument6 pagesSixSigma QFD MatrixAssem ElhajjNo ratings yet
- Quality Function Deployment: by Zaipul Anwar Business & Advanced Technology Centre, Universiti Teknologi MalaysiaDocument33 pagesQuality Function Deployment: by Zaipul Anwar Business & Advanced Technology Centre, Universiti Teknologi MalaysiaRian JanuarsyahNo ratings yet
- Benefits of QFD: 1-Write A Short Essay (About 500 Words) On QFD As An Approach To Requirements Development and AnalysisDocument17 pagesBenefits of QFD: 1-Write A Short Essay (About 500 Words) On QFD As An Approach To Requirements Development and AnalysisAnuj JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Quality Function DeploymentDocument32 pagesQuality Function DeploymentBittuNo ratings yet
- 1) Explain What Is QFD, (Quality Function Deployment) ? AnsDocument8 pages1) Explain What Is QFD, (Quality Function Deployment) ? Ansapi-352131221No ratings yet
- How To Build A House of Quality (QFD) : Reading Time: About 8 MinDocument14 pagesHow To Build A House of Quality (QFD) : Reading Time: About 8 MinCuenta PokemonNo ratings yet
- House of QualityDocument4 pagesHouse of Qualitybobby510No ratings yet
- A Systematic Approach To Quality Function Deployment With A Full Illustrative ExampleDocument21 pagesA Systematic Approach To Quality Function Deployment With A Full Illustrative ExampleSuman SamantaNo ratings yet
- What Are QFD and Six SigmaDocument17 pagesWhat Are QFD and Six SigmaМагистерски ТрудовиNo ratings yet
- QFD PPTDocument55 pagesQFD PPTkiollNo ratings yet
- Quality Function Deployment - A Comprehensive ReviewDocument25 pagesQuality Function Deployment - A Comprehensive ReviewgschiroNo ratings yet
- Quality Function Deployment: by Zaipul Anwar Business & Advanced Technology Centre, Universiti Teknologi MalaysiaDocument33 pagesQuality Function Deployment: by Zaipul Anwar Business & Advanced Technology Centre, Universiti Teknologi Malaysiavenkat_mie1080No ratings yet
- Quality Function DeploymentDocument10 pagesQuality Function DeploymentA DAY IN THANNINo ratings yet
- Tools and Techniques For Quality ManagementDocument48 pagesTools and Techniques For Quality ManagementSrividhya ManikandanNo ratings yet
- 10 Quality Function DeploymentDocument35 pages10 Quality Function DeploymentUmair WaqasNo ratings yet
- SixSigma QFD MatrixDocument2 pagesSixSigma QFD MatrixFaisal AnwarNo ratings yet
- Ie673 Assisngment 5Document13 pagesIe673 Assisngment 5api-348261316No ratings yet
- Quality Function DepolymentDocument13 pagesQuality Function DepolymentSakshi SinghNo ratings yet
- Quality Function Deployment (QFD)Document33 pagesQuality Function Deployment (QFD)anshuldceNo ratings yet
- Full Test 1 CO Management AccountingDocument28 pagesFull Test 1 CO Management AccountingDiana DobrescuNo ratings yet
- Individual Sabre Quiz (MKTG 6010)Document8 pagesIndividual Sabre Quiz (MKTG 6010)Veerapong Patrawanichakarn0% (3)
- Ahp Matrix TemplateDocument79 pagesAhp Matrix TemplateArun MathewNo ratings yet
- Product Planning and DevelopmentDocument38 pagesProduct Planning and DevelopmentLapi Boy Mics100% (1)
- Rating PredictionDocument20 pagesRating PredictionAnkit VermaNo ratings yet
- QFD ReportDocument18 pagesQFD ReportChintan SinghviNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis: Unit OutlineDocument15 pagesChapter One Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis: Unit OutlinebojaNo ratings yet
- What Is The House of Quality How Important Is The Voice of The Customer in Quality ManagementDocument2 pagesWhat Is The House of Quality How Important Is The Voice of The Customer in Quality ManagementAmlan MishraNo ratings yet
- Product Design and Development: Thoufiq Mohammed K Ap / MechDocument14 pagesProduct Design and Development: Thoufiq Mohammed K Ap / MechGokulCj GroveNo ratings yet
- ManagerialAccounting IndividualAssignment PGXPM152PRSDocument13 pagesManagerialAccounting IndividualAssignment PGXPM152PRSPraveen Jaganathan100% (1)
- 11th Aug 2016 4th Lecture PDFDocument10 pages11th Aug 2016 4th Lecture PDFGAURAVNo ratings yet
- Quality Function Deployment - Final ReportDocument7 pagesQuality Function Deployment - Final ReportHamza ShamsNo ratings yet
- Quality Function DeploymentDocument14 pagesQuality Function DeploymentAniketKarade100% (1)
- Welcome: in A Few WordsDocument11 pagesWelcome: in A Few WordsSasiKumar PetchiappanNo ratings yet
- Quality Function DeploymentDocument40 pagesQuality Function DeploymentVaswee Dubey100% (1)
- QM 0013Document9 pagesQM 0013Mrinal KalitaNo ratings yet
- Management System ManufactureDocument11 pagesManagement System ManufactureKanzul FadhilNo ratings yet
- Qresst: in A Few WordsDocument11 pagesQresst: in A Few WordsSasiKumar PetchiappanNo ratings yet
- Quality Function DeploymentDocument8 pagesQuality Function DeploymentNivedh VijayakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Quality Function DeploymentDocument49 pagesQuality Function DeploymentMoeshfieq WilliamsNo ratings yet
- 07 WorksheetDocument2 pages07 WorksheetAinan Cartagena100% (1)
- Quality Function Deployment (QFD)Document35 pagesQuality Function Deployment (QFD)Navendran100% (2)
- Assignment 5Document12 pagesAssignment 5api-723710078No ratings yet
- Deployment: in A Few WordsDocument11 pagesDeployment: in A Few WordsSasiKumar PetchiappanNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis: Unit OutlineDocument14 pagesChapter One Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis: Unit OutlineHussen AbdulkadirNo ratings yet
- Xilinx Zcu208 Product BriefDocument2 pagesXilinx Zcu208 Product Briefkarthikp207No ratings yet
- RBS G14 Baraka Hitachi 210 Q2023Document2 pagesRBS G14 Baraka Hitachi 210 Q2023Adeel AhsanNo ratings yet
- Novel GalaksiDocument492 pagesNovel GalaksiMarsha Nabila Marsha NabilaNo ratings yet
- C6000 Operation & Maintenance Manual: (©july, 2008)Document68 pagesC6000 Operation & Maintenance Manual: (©july, 2008)JamesNo ratings yet
- Ibsl-2 Epg q1Document4 pagesIbsl-2 Epg q1María Cecilia García ArangoNo ratings yet
- How To Use SUPA Tool For Tomcat MeasurementsDocument8 pagesHow To Use SUPA Tool For Tomcat MeasurementsGurushantha DoddamaniNo ratings yet
- VF LTE 2G & 3G - 4G Interworking - v11Document9 pagesVF LTE 2G & 3G - 4G Interworking - v11Janardan YadavNo ratings yet
- Satellite Link Budget Calculator by UsinDocument13 pagesSatellite Link Budget Calculator by Usinmouhib sanaaNo ratings yet
- Catalysts For Change: Ethics For The Information AgeDocument24 pagesCatalysts For Change: Ethics For The Information AgeJ A Y T R O NNo ratings yet
- M.Sc. Course in Applied Mathematics With Oceanology and Computer Programming Semester-IV Paper-MTM402 Unit-1Document26 pagesM.Sc. Course in Applied Mathematics With Oceanology and Computer Programming Semester-IV Paper-MTM402 Unit-1Avijit SamantaNo ratings yet
- Requirements ModelingDocument39 pagesRequirements ModelingDeshnu SudeepNo ratings yet
- LCD Interface PGMDocument4 pagesLCD Interface PGMNamrata Dhamal100% (1)
- Pediatric NursingDocument2 pagesPediatric NursingWing YenNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Technology in Action Complete 15th Edition Whats New in Information Technology 15th EditionDocument15 pagesTest Bank For Technology in Action Complete 15th Edition Whats New in Information Technology 15th EditionDebra Franken100% (30)
- Gujarat Technological University: Semester: 1Document12 pagesGujarat Technological University: Semester: 1Ha BlackNo ratings yet
- Enjoy 2 20210202Document1 pageEnjoy 2 20210202manuelc2005No ratings yet
- REDCap Training 2019 - REDCap Mobile App TrainingDocument24 pagesREDCap Training 2019 - REDCap Mobile App TrainingGeofrey BasalirwaNo ratings yet
- Gulfstream G550Document32 pagesGulfstream G550flateric74@yandex.ru100% (1)
- AWS SolutionsArchitect-Associate Version 4.0 PDFDocument8 pagesAWS SolutionsArchitect-Associate Version 4.0 PDFpuramganeshNo ratings yet
- Sia Module 1 Lesson 1Document36 pagesSia Module 1 Lesson 1Jan Mark CalugayNo ratings yet
- AI-Unit 4Document26 pagesAI-Unit 4Pranya AnejaNo ratings yet
- How To Convert Windows 10 From Legacy BIOS To UEFDocument3 pagesHow To Convert Windows 10 From Legacy BIOS To UEFBobapatatasNo ratings yet
- 02 EasyIO FC20 User Reference v1.6 PDFDocument15 pages02 EasyIO FC20 User Reference v1.6 PDFnguyendinhphuc22008No ratings yet
- PPT6 - Dynamic Programming Multistage Graph & Travelling Salesman ProblemDocument23 pagesPPT6 - Dynamic Programming Multistage Graph & Travelling Salesman ProblemAditya wahyu50% (2)
- S P Gupta Statistical Methodspdf CompressDocument2 pagesS P Gupta Statistical Methodspdf CompressArjun Anilkumar50% (2)
- Izylum: A Time-Saving, Versatile and High-Performing Road and Urban SolutionDocument35 pagesIzylum: A Time-Saving, Versatile and High-Performing Road and Urban SolutionDejan KragovicNo ratings yet
- Technical Proposal For A Multi-Vendor Ecom ApplicationDocument13 pagesTechnical Proposal For A Multi-Vendor Ecom ApplicationJVTC CorporationNo ratings yet
Uses of Quality Function Deployment
Uses of Quality Function Deployment
Uploaded by
Kavin S0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
45 views2 pagesQuality Function Deployment (QFD) is a customer-driven approach to product planning that involves translating customer requirements into specific design requirements. It uses a cross-functional team and series of matrices called the "House of Quality" to establish customer objectives and record them throughout the development process from concept to production. QFD ensures customer desires are prioritized, translated into engineering specifications, and targets are set to meet requirements.
Original Description:
QFD quality function deployement
Original Title
QFD
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentQuality Function Deployment (QFD) is a customer-driven approach to product planning that involves translating customer requirements into specific design requirements. It uses a cross-functional team and series of matrices called the "House of Quality" to establish customer objectives and record them throughout the development process from concept to production. QFD ensures customer desires are prioritized, translated into engineering specifications, and targets are set to meet requirements.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
45 views2 pagesUses of Quality Function Deployment
Uses of Quality Function Deployment
Uploaded by
Kavin SQuality Function Deployment (QFD) is a customer-driven approach to product planning that involves translating customer requirements into specific design requirements. It uses a cross-functional team and series of matrices called the "House of Quality" to establish customer objectives and record them throughout the development process from concept to production. QFD ensures customer desires are prioritized, translated into engineering specifications, and targets are set to meet requirements.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Quality Function Deployment - Definition
QFD) is a customer-driven product
planning process. It is a system for translating and deploying
customer requirements into specific company requirements at each
stage from Concept Definition to Process Engineering and
Production and into the marketplace. QFD deploys the voice of the customer through a cross-
functional team’s project management of the integrated development process. The QFD process
establishes customer objectives and measures and records them on a series of matrices.
Voice of the Customer
House of Quality
Customer-Driven Engineering
Matrix Product Planning
Uses of Quality Function Deployment
Collect customer’s requirements/desires as specified by the customers in their own
words
Prioritize these desires
Translate them into engineering/process requirements
Establish targets to meet the requirements.
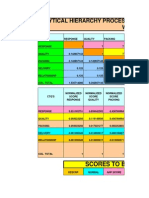
Quality Function Deployment – QFD Methodology
Identify both internal and external customers.
Create a list of customer requirements/desires (Whats) by
o Asking the customer, questions such as “What are the important features of The
Product”
o Capturing the customer’s own words or “Voice of the Customer” or VOC
o Categorizing the Whats into groups/buckets if needed.
Prioritize the above collected Whats on a scale of 1-5, with 5 being the most important. This
ranking is based on the VOC (Voice of Customer) data. The CCRs (Whats) are listed vertically
in the first column and all related CTQs (are listed horizontally across the top . In the second
column, assign 1 to 5 based on the importance of the CCRs, where 5 is the most critical to
the customer.
Score each CTQ (Hows) on how strongly it correlates to each CCR. Remember we are looking
at the absolution value of the correlation. It can have either positive correlation or negative
correlation. Use 5 for a strong correlation and 1 is a weak one. Leave it blank if there is no
correlation. Some CCRs will have few CTQs that relate and rest unrelated.
Compile list of CTQs (Hows) necessary to achieve the CCRs (Whats.)
Translate the CCRs from VOC (Whats) into CTQs (Hows)
o Arrows show direction for improvement (up for increasing, down for decreasing,
etc.)
For each What, find out the correlation with each How. If the correlation is strong use 5. If
its week use 1. If its in between, use a number 2, 3, 4 based on how strong the correlation is.
Next multiply the importance rating for the CCR by the correlation score for each CTQ.
Add up the scores vertically for each CTQ and place that value in the bottom score row.
Once you compute the score for all CTQs, the ones with the highest scores are the highest
priority Six Sigma project objectives to work on
You might also like
- G11 Lesson 02 Essay 1Document3 pagesG11 Lesson 02 Essay 1Tinet Sri UdawelaNo ratings yet
- Iec TR 62278-3-2010Document70 pagesIec TR 62278-3-2010Joanne W100% (1)
- SAP UI5 Development GuidelinesDocument20 pagesSAP UI5 Development GuidelinesVipinNo ratings yet
- What Is Quality Function DeploymentDocument6 pagesWhat Is Quality Function DeploymentAnkurNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma ExamDocument5 pagesSix Sigma Exammajid4uonly100% (5)
- QFD BriefDocument4 pagesQFD Briefronit.islwirelessNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document15 pagesAssignment 5api-652656444No ratings yet
- Quality Function DeploymentDocument13 pagesQuality Function DeploymentShafwan MuhadzdzibNo ratings yet
- QFD2 Dontqd@Comcast - Net ClausingDocument24 pagesQFD2 Dontqd@Comcast - Net ClausingGiselleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 & 9: Quality Function DeploymentDocument46 pagesChapter 8 & 9: Quality Function DeploymentAli AhmedNo ratings yet
- TQM Assignment5 TejasgDocument11 pagesTQM Assignment5 Tejasgapi-282598664No ratings yet
- Assignment: 5: Q.1 Explain What Is QFD, (Quality Function Deployment) ?Document12 pagesAssignment: 5: Q.1 Explain What Is QFD, (Quality Function Deployment) ?api-308384599No ratings yet
- House of QualityDocument18 pagesHouse of Qualityraju1112No ratings yet
- TQM Assignment-5Document16 pagesTQM Assignment-5api-546637261No ratings yet
- Quality FunctionDocument55 pagesQuality Functionyogeshkmr01No ratings yet
- SixSigma QFD MatrixDocument6 pagesSixSigma QFD MatrixAssem ElhajjNo ratings yet
- Quality Function Deployment: by Zaipul Anwar Business & Advanced Technology Centre, Universiti Teknologi MalaysiaDocument33 pagesQuality Function Deployment: by Zaipul Anwar Business & Advanced Technology Centre, Universiti Teknologi MalaysiaRian JanuarsyahNo ratings yet
- Benefits of QFD: 1-Write A Short Essay (About 500 Words) On QFD As An Approach To Requirements Development and AnalysisDocument17 pagesBenefits of QFD: 1-Write A Short Essay (About 500 Words) On QFD As An Approach To Requirements Development and AnalysisAnuj JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Quality Function DeploymentDocument32 pagesQuality Function DeploymentBittuNo ratings yet
- 1) Explain What Is QFD, (Quality Function Deployment) ? AnsDocument8 pages1) Explain What Is QFD, (Quality Function Deployment) ? Ansapi-352131221No ratings yet
- How To Build A House of Quality (QFD) : Reading Time: About 8 MinDocument14 pagesHow To Build A House of Quality (QFD) : Reading Time: About 8 MinCuenta PokemonNo ratings yet
- House of QualityDocument4 pagesHouse of Qualitybobby510No ratings yet
- A Systematic Approach To Quality Function Deployment With A Full Illustrative ExampleDocument21 pagesA Systematic Approach To Quality Function Deployment With A Full Illustrative ExampleSuman SamantaNo ratings yet
- What Are QFD and Six SigmaDocument17 pagesWhat Are QFD and Six SigmaМагистерски ТрудовиNo ratings yet
- QFD PPTDocument55 pagesQFD PPTkiollNo ratings yet
- Quality Function Deployment - A Comprehensive ReviewDocument25 pagesQuality Function Deployment - A Comprehensive ReviewgschiroNo ratings yet
- Quality Function Deployment: by Zaipul Anwar Business & Advanced Technology Centre, Universiti Teknologi MalaysiaDocument33 pagesQuality Function Deployment: by Zaipul Anwar Business & Advanced Technology Centre, Universiti Teknologi Malaysiavenkat_mie1080No ratings yet
- Quality Function DeploymentDocument10 pagesQuality Function DeploymentA DAY IN THANNINo ratings yet
- Tools and Techniques For Quality ManagementDocument48 pagesTools and Techniques For Quality ManagementSrividhya ManikandanNo ratings yet
- 10 Quality Function DeploymentDocument35 pages10 Quality Function DeploymentUmair WaqasNo ratings yet
- SixSigma QFD MatrixDocument2 pagesSixSigma QFD MatrixFaisal AnwarNo ratings yet
- Ie673 Assisngment 5Document13 pagesIe673 Assisngment 5api-348261316No ratings yet
- Quality Function DepolymentDocument13 pagesQuality Function DepolymentSakshi SinghNo ratings yet
- Quality Function Deployment (QFD)Document33 pagesQuality Function Deployment (QFD)anshuldceNo ratings yet
- Full Test 1 CO Management AccountingDocument28 pagesFull Test 1 CO Management AccountingDiana DobrescuNo ratings yet
- Individual Sabre Quiz (MKTG 6010)Document8 pagesIndividual Sabre Quiz (MKTG 6010)Veerapong Patrawanichakarn0% (3)
- Ahp Matrix TemplateDocument79 pagesAhp Matrix TemplateArun MathewNo ratings yet
- Product Planning and DevelopmentDocument38 pagesProduct Planning and DevelopmentLapi Boy Mics100% (1)
- Rating PredictionDocument20 pagesRating PredictionAnkit VermaNo ratings yet
- QFD ReportDocument18 pagesQFD ReportChintan SinghviNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis: Unit OutlineDocument15 pagesChapter One Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis: Unit OutlinebojaNo ratings yet
- What Is The House of Quality How Important Is The Voice of The Customer in Quality ManagementDocument2 pagesWhat Is The House of Quality How Important Is The Voice of The Customer in Quality ManagementAmlan MishraNo ratings yet
- Product Design and Development: Thoufiq Mohammed K Ap / MechDocument14 pagesProduct Design and Development: Thoufiq Mohammed K Ap / MechGokulCj GroveNo ratings yet
- ManagerialAccounting IndividualAssignment PGXPM152PRSDocument13 pagesManagerialAccounting IndividualAssignment PGXPM152PRSPraveen Jaganathan100% (1)
- 11th Aug 2016 4th Lecture PDFDocument10 pages11th Aug 2016 4th Lecture PDFGAURAVNo ratings yet
- Quality Function Deployment - Final ReportDocument7 pagesQuality Function Deployment - Final ReportHamza ShamsNo ratings yet
- Quality Function DeploymentDocument14 pagesQuality Function DeploymentAniketKarade100% (1)
- Welcome: in A Few WordsDocument11 pagesWelcome: in A Few WordsSasiKumar PetchiappanNo ratings yet
- Quality Function DeploymentDocument40 pagesQuality Function DeploymentVaswee Dubey100% (1)
- QM 0013Document9 pagesQM 0013Mrinal KalitaNo ratings yet
- Management System ManufactureDocument11 pagesManagement System ManufactureKanzul FadhilNo ratings yet
- Qresst: in A Few WordsDocument11 pagesQresst: in A Few WordsSasiKumar PetchiappanNo ratings yet
- Quality Function DeploymentDocument8 pagesQuality Function DeploymentNivedh VijayakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Quality Function DeploymentDocument49 pagesQuality Function DeploymentMoeshfieq WilliamsNo ratings yet
- 07 WorksheetDocument2 pages07 WorksheetAinan Cartagena100% (1)
- Quality Function Deployment (QFD)Document35 pagesQuality Function Deployment (QFD)Navendran100% (2)
- Assignment 5Document12 pagesAssignment 5api-723710078No ratings yet
- Deployment: in A Few WordsDocument11 pagesDeployment: in A Few WordsSasiKumar PetchiappanNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis: Unit OutlineDocument14 pagesChapter One Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis: Unit OutlineHussen AbdulkadirNo ratings yet
- Xilinx Zcu208 Product BriefDocument2 pagesXilinx Zcu208 Product Briefkarthikp207No ratings yet
- RBS G14 Baraka Hitachi 210 Q2023Document2 pagesRBS G14 Baraka Hitachi 210 Q2023Adeel AhsanNo ratings yet
- Novel GalaksiDocument492 pagesNovel GalaksiMarsha Nabila Marsha NabilaNo ratings yet
- C6000 Operation & Maintenance Manual: (©july, 2008)Document68 pagesC6000 Operation & Maintenance Manual: (©july, 2008)JamesNo ratings yet
- Ibsl-2 Epg q1Document4 pagesIbsl-2 Epg q1María Cecilia García ArangoNo ratings yet
- How To Use SUPA Tool For Tomcat MeasurementsDocument8 pagesHow To Use SUPA Tool For Tomcat MeasurementsGurushantha DoddamaniNo ratings yet
- VF LTE 2G & 3G - 4G Interworking - v11Document9 pagesVF LTE 2G & 3G - 4G Interworking - v11Janardan YadavNo ratings yet
- Satellite Link Budget Calculator by UsinDocument13 pagesSatellite Link Budget Calculator by Usinmouhib sanaaNo ratings yet
- Catalysts For Change: Ethics For The Information AgeDocument24 pagesCatalysts For Change: Ethics For The Information AgeJ A Y T R O NNo ratings yet
- M.Sc. Course in Applied Mathematics With Oceanology and Computer Programming Semester-IV Paper-MTM402 Unit-1Document26 pagesM.Sc. Course in Applied Mathematics With Oceanology and Computer Programming Semester-IV Paper-MTM402 Unit-1Avijit SamantaNo ratings yet
- Requirements ModelingDocument39 pagesRequirements ModelingDeshnu SudeepNo ratings yet
- LCD Interface PGMDocument4 pagesLCD Interface PGMNamrata Dhamal100% (1)
- Pediatric NursingDocument2 pagesPediatric NursingWing YenNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Technology in Action Complete 15th Edition Whats New in Information Technology 15th EditionDocument15 pagesTest Bank For Technology in Action Complete 15th Edition Whats New in Information Technology 15th EditionDebra Franken100% (30)
- Gujarat Technological University: Semester: 1Document12 pagesGujarat Technological University: Semester: 1Ha BlackNo ratings yet
- Enjoy 2 20210202Document1 pageEnjoy 2 20210202manuelc2005No ratings yet
- REDCap Training 2019 - REDCap Mobile App TrainingDocument24 pagesREDCap Training 2019 - REDCap Mobile App TrainingGeofrey BasalirwaNo ratings yet
- Gulfstream G550Document32 pagesGulfstream G550flateric74@yandex.ru100% (1)
- AWS SolutionsArchitect-Associate Version 4.0 PDFDocument8 pagesAWS SolutionsArchitect-Associate Version 4.0 PDFpuramganeshNo ratings yet
- Sia Module 1 Lesson 1Document36 pagesSia Module 1 Lesson 1Jan Mark CalugayNo ratings yet
- AI-Unit 4Document26 pagesAI-Unit 4Pranya AnejaNo ratings yet
- How To Convert Windows 10 From Legacy BIOS To UEFDocument3 pagesHow To Convert Windows 10 From Legacy BIOS To UEFBobapatatasNo ratings yet
- 02 EasyIO FC20 User Reference v1.6 PDFDocument15 pages02 EasyIO FC20 User Reference v1.6 PDFnguyendinhphuc22008No ratings yet
- PPT6 - Dynamic Programming Multistage Graph & Travelling Salesman ProblemDocument23 pagesPPT6 - Dynamic Programming Multistage Graph & Travelling Salesman ProblemAditya wahyu50% (2)
- S P Gupta Statistical Methodspdf CompressDocument2 pagesS P Gupta Statistical Methodspdf CompressArjun Anilkumar50% (2)
- Izylum: A Time-Saving, Versatile and High-Performing Road and Urban SolutionDocument35 pagesIzylum: A Time-Saving, Versatile and High-Performing Road and Urban SolutionDejan KragovicNo ratings yet
- Technical Proposal For A Multi-Vendor Ecom ApplicationDocument13 pagesTechnical Proposal For A Multi-Vendor Ecom ApplicationJVTC CorporationNo ratings yet