Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reduced Blood (C0) and Its Effect On Respiration
Reduced Blood (C0) and Its Effect On Respiration
Uploaded by
Jeric Ampalaya PresasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reduced Blood (C0) and Its Effect On Respiration
Reduced Blood (C0) and Its Effect On Respiration
Uploaded by
Jeric Ampalaya PresasCopyright:
Available Formats
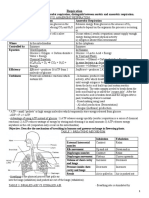
Reduced Blood [C02] and its Effect on Respiration
Table 1. Before (at rest) and After
(completed hyperventilation)
Group Before After Breathing Rate
1 24 42
2 18 38
3 20 32
4 20 28
5 18 32
In some extent, higher brain centres (e.g. cerebral cortex) consciously controlled our
breathing. It is also possible for our breathing rate to change voluntarily. A respiration rate
under 12 or over 25 breaths per minute while resting is considered abnormal. As shown in
Table 1, breathing rate after the completion of hyperventilation is much higher compared to the
breathing rate at rest. Ramgopal (2017) mentioned that, the normal breathing rate ranges from
14-18 breaths per minute. In aerobic exercise, additional carbon dioxide (CO 2) is produced
and additional oxygen (O2) is required for the muscles to work that leads to the rise in CO 2
level. The carbon dioxide acts on the brain to stimulate breathing that results to the person
who is exercising to have a faster rate of respiration. This action helps maintain the adequate
oxygenation of the blood and gets rid of the additional carbon dioxide. From the results
obtained, it showed that all the groups had the normal breathing rate and it increases after
doing a 10sec exercise for hyperventilation.
Ramgopal S. 2017. The Effects of Hyperventilation on Breathing
You might also like
- Epa+608+Technician+Training+Show 1Document183 pagesEpa+608+Technician+Training+Show 1Geo Time100% (1)
- PPL Exam Secrets Guide: Human Performance & LimitationsFrom EverandPPL Exam Secrets Guide: Human Performance & LimitationsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Exercise LabDocument3 pagesExercise LabJonatan LeflerNo ratings yet
- Physioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsDocument4 pagesPhysioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsPutri AisyahNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Exam 2 (Outline)Document9 pagesBiochemistry Exam 2 (Outline)stanly sotoNo ratings yet
- Lab 10 Exercise and Cell Respiration Data and Analysis PageDocument2 pagesLab 10 Exercise and Cell Respiration Data and Analysis Pagemackeycalvin720No ratings yet
- Homeostasis Exemplar Lab ReportDocument4 pagesHomeostasis Exemplar Lab Reportthe cornchip executionerNo ratings yet
- SPIROMETRYDocument5 pagesSPIROMETRYJayarubini JeyapalNo ratings yet
- PhysioEx Exercise 10 Activity 1 - Balamad, Maria Karla M.Document4 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 10 Activity 1 - Balamad, Maria Karla M.Maria Karla BalamadNo ratings yet
- HPL 041 Chemical Control of RespirationDocument2 pagesHPL 041 Chemical Control of Respirationhulu12No ratings yet
- Respiration 23086215D Cheung Chi MingDocument5 pagesRespiration 23086215D Cheung Chi Ming9rw9yrh6qyNo ratings yet
- LSM3212 - Lecture 10 Resp2Document29 pagesLSM3212 - Lecture 10 Resp2Abraham KangNo ratings yet
- PhysioEx Exercise 10 Activity 2 - Balamad, Maria Karla M.Document3 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 10 Activity 2 - Balamad, Maria Karla M.Maria Karla BalamadNo ratings yet
- Lab 8Document6 pagesLab 8Naz PulatNo ratings yet
- CO2 and NarcosisDocument9 pagesCO2 and NarcosisZusanna Violeta RahakbauwNo ratings yet
- Respiratory PhysiologyDocument45 pagesRespiratory PhysiologyJohn Christopher LucesNo ratings yet
- Exercise 15 - External RespirationDocument32 pagesExercise 15 - External RespirationAldrin LozanoNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument3 pagesRespirationSabita SinghNo ratings yet
- 20 Respiratory ResponseDocument7 pages20 Respiratory ResponseAmirsalar EslamiNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 2023Document7 pagesLab 4 2023api-702083722No ratings yet
- Pex 10 04Document4 pagesPex 10 04Wanda Ayuditha Noor AlifiaNo ratings yet
- Vaccari Et Al-2020-European Journal of Applied Physiology PDFDocument10 pagesVaccari Et Al-2020-European Journal of Applied Physiology PDFMarcMolNo ratings yet
- Aha Ventilación Módulo 4Document10 pagesAha Ventilación Módulo 4Juan Carlos GomezNo ratings yet
- Genbio (Peta)Document18 pagesGenbio (Peta)Pauleen IldefonsoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet-Reaction Rates: C H O (S) + 6 O (G) 6 H O (G) + 6 CO (G)Document2 pagesWorksheet-Reaction Rates: C H O (S) + 6 O (G) 6 H O (G) + 6 CO (G)rjayrjay100% (1)
- The Asphyxia ProtocolDocument3 pagesThe Asphyxia ProtocolMuhammad Octa PernadiNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument2 pagesRespirationSelena WinsborrowNo ratings yet
- Pressure Hazards at Workplace: Dryusofklia2012Document24 pagesPressure Hazards at Workplace: Dryusofklia2012Love Craft IINo ratings yet
- Patricia Shankar Jethani - A1 - PhysioEx Exercise 10, Activity 1, 3 and 4Document13 pagesPatricia Shankar Jethani - A1 - PhysioEx Exercise 10, Activity 1, 3 and 4Patricia JethaniNo ratings yet
- 125 Simple Breathing ExerciseDocument2 pages125 Simple Breathing ExerciseramamoorthyNo ratings yet
- 11 Respiratory AcidosisDocument25 pages11 Respiratory Acidosiskhadija zafarNo ratings yet
- PhysioEx Exercise 10 Activity 4Document3 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 10 Activity 4Isabel PalaciosNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Respons Op Acute Inspanning Bij Chronisch LonglijdenDocument31 pages1.4 Respons Op Acute Inspanning Bij Chronisch Longlijdensten.kuykenNo ratings yet
- Cardio Paper NewDocument24 pagesCardio Paper Newwarda abbasi100% (1)
- Physioex 9Document4 pagesPhysioex 9Dayanna MartínezNo ratings yet
- Response To Hemorrhage Worksheet 1) Immediate Effects On Mean Arterial PressureDocument3 pagesResponse To Hemorrhage Worksheet 1) Immediate Effects On Mean Arterial PressurekegwikiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Environmental Factors Influencing Human PerformanceDocument22 pagesChapter 11 - Environmental Factors Influencing Human PerformanceHyperHodgeyNo ratings yet
- Mind Booster 03 (10th)Document6 pagesMind Booster 03 (10th)bijaypdgupta30No ratings yet
- Exercise and Homeostasis Lab ReportDocument2 pagesExercise and Homeostasis Lab ReportLindsay PennNo ratings yet
- Congestif Heart Failure: Budi RaharjoDocument14 pagesCongestif Heart Failure: Budi Raharjoanisa rachmitaNo ratings yet
- Settle Out Condition EstimationDocument4 pagesSettle Out Condition Estimationnghiemta18No ratings yet
- Respiration MCQs (2016), Dr. Ahmad AlarabiDocument7 pagesRespiration MCQs (2016), Dr. Ahmad AlarabiTofik Mohammed100% (1)
- Exercise Physio MbbsDocument59 pagesExercise Physio Mbbsb0t.mc.sundayNo ratings yet
- Obat Inotropik-TitrasiDocument11 pagesObat Inotropik-TitrasijuraidahNo ratings yet
- Obat Inotropik-TitrasiDocument11 pagesObat Inotropik-TitrasijuraidahNo ratings yet
- Acid Balance Group 1Document34 pagesAcid Balance Group 1Jasper AdonisNo ratings yet
- Bio4 5Document11 pagesBio4 5HarmonyChuiNo ratings yet
- Physioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsDocument3 pagesPhysioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsYoselyn MorochoNo ratings yet
- Bio4 5Document11 pagesBio4 5ミーチェルNo ratings yet
- BIOL 2402 Lab 5 Vital Signs Lab 2Document8 pagesBIOL 2402 Lab 5 Vital Signs Lab 2William DelphNo ratings yet
- Respiration LabDocument4 pagesRespiration LabLogan Parkison100% (1)
- Lectures 54 and 55 Phys Integration LOsDocument4 pagesLectures 54 and 55 Phys Integration LOsAndrew SagalovNo ratings yet
- 循环呼吸器潜水的呼吸生理学Document14 pages循环呼吸器潜水的呼吸生理学彭亦荣No ratings yet
- Stepwise Approach To Interpreting The Arterial Blood GasDocument22 pagesStepwise Approach To Interpreting The Arterial Blood GasChuong TranNo ratings yet
- Soal QafcoDocument3 pagesSoal QafcoRatu CeliaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5 (Biology) Complete Lecture With Solution. Date:26/6/22 Contact:01715782957Document8 pagesChapter-5 (Biology) Complete Lecture With Solution. Date:26/6/22 Contact:01715782957Ahnaf Rahman RyanNo ratings yet
- BCH3120 2023 Lecture 19Document59 pagesBCH3120 2023 Lecture 19Rediet AtnafuNo ratings yet
- Równowaga Kwasowo Zasadowa 4Document4 pagesRównowaga Kwasowo Zasadowa 4nataliamagda2.1No ratings yet
- 2 Inhalational Anesthtic AgentsDocument42 pages2 Inhalational Anesthtic AgentsMoayad NawaflehNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers in Small Animal AnesthesiaFrom EverandQuestions and Answers in Small Animal AnesthesiaLesley J. SmithNo ratings yet