Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Uspensions:) and A Heterogeneous Mixture With Properties Also Intermediate Between The
Uspensions:) and A Heterogeneous Mixture With Properties Also Intermediate Between The
Uploaded by
eswarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Uspensions:) and A Heterogeneous Mixture With Properties Also Intermediate Between The
Uspensions:) and A Heterogeneous Mixture With Properties Also Intermediate Between The
Uploaded by
eswarCopyright:
Available Formats
uspensions
A suspension is a mixture between two substances, one of which is finely divided and
dispersed in the other. Common suspensions include sand in water, dust in air, and
droplets of oil in air. Particles in a suspension are larger than those in a solutions; they
are visible under a microscope and can often be seen with the naked eye. Particles in a
suspension will settle out if the suspension is allowed to stand undisturbed. Many
particles of a suspension can be separated through a filter. An example of a simple
suspension would be flour in water, or sand in water.
Colloids
A colloid is a type of mixture intermediate between a homogeneous mixture (also called
a solution) and a heterogeneous mixture with properties also intermediate between the
two.
The particles in a colloid can be solid, liquid or bubbles of gas. The medium that they
are suspended in can be a solid, liquid or gas (although gas colloids cannot be
suspended in gas).The particles are approximately 10 to 10,000 angstroms in size and
generally cannot be filtered, or settled out in an easy manner. Colloids may be colored
or translucent because of the Tyndall effect, which is the scattering of light by particles
in the colloid. Colloid particles may be seen in a beam of light such as dust in air in a
"shaft" of sunlight.
Brownian movement may be used to distinguish between solutions and colloids.
Brownian motion is the random movement of colloidal particles suspended in a liquid or
gas, caused by collisions with molecules of the surrounding medium. The particles in
solutions and colloids are in constant motion. However colloid particles are large
enough to be observed and are small enough to still be affect by the random molecular
collisions. Colloid particles resist settling rapidly to the bottom of a vessel due to
Brownian motion.
Emulsions are a type of colloid
Emulsions are an example of colloids composed of tiny particles suspended in another
immiscible (unmixable) material. An emulsion is a suspension of two liquids that usually
do not mix together. These liquids that do not mix are said to be immiscible. An example
would be oil and water. If you mix oil and water and shake them a cloudy suspension is
formed. Let the mixture rest and the oil and water will separate.
An emulsifying agent (emulsifier) is any substance that keeps the parts of an emulsion
mixed together. For example if we mix oil and water a suspension will form that over
time separates. But now, if we add a few drops and shake the mixture the oil and water
will stay mixed much longer.
Examples of emulsions include butter and margarine, and mayonnaise.
See also HYDROCOLLOIDS
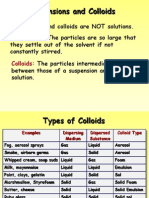
Examples of Colloids
Dispersed Medium
Gas Liquid Solid
NONE Liquid Aerosol Solid Aerosol
Gas
(All gases are soluble) Examples: Fog, Mist Examples: smoke, dust
Sol
Emulsion
Foam Examples: Paint,
Continuous Liquid Examples: Milk, Mayonnaise,
Medium
Examples: Whipped cream pigmented ink, blood, Milk
hand cream
of Magnesia
Solid Foam
Gel Solid Sol
Solid Examples: Aerogel,
Examples: Gelatin, cheese Examples: ruby glass
Styrofoam, pumice
You might also like
- Solution Manual For Introduction To MATLAB For Engineers 3rd Edition by PalmDocument41 pagesSolution Manual For Introduction To MATLAB For Engineers 3rd Edition by Palma72625014350% (6)
- Homemade Searl Effect GeneratorDocument72 pagesHomemade Searl Effect GeneratorJeffrey Farrow100% (1)
- Chemistry Grade 10 Mixtures and SeparationDocument45 pagesChemistry Grade 10 Mixtures and SeparationTrudy- Ann CaineNo ratings yet
- Siemens Valve SizingDocument32 pagesSiemens Valve SizingSteven Wei100% (2)
- Online Lesson Exemplar in Science 6 Pinky and Maribel.Document11 pagesOnline Lesson Exemplar in Science 6 Pinky and Maribel.Sonny Matias83% (6)
- WWW - Engsoft.co - KR - Es Fluegas eDocument9 pagesWWW - Engsoft.co - KR - Es Fluegas ePanosMitsopoulosNo ratings yet
- 7 Unit 3 Intro To Unit CH 7Document25 pages7 Unit 3 Intro To Unit CH 7Lorraine DonioNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem MatterDocument49 pagesGen Chem Matterzeidump18No ratings yet
- Colloids PPSXDocument6 pagesColloids PPSXPinky Caina CabotajeNo ratings yet
- Is Matter Around Us PureDocument13 pagesIs Matter Around Us PureNANDITA NAYAK BNo ratings yet
- What Is Mixture: Is Matter Around Us PureDocument19 pagesWhat Is Mixture: Is Matter Around Us PureAditya Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Colloidal State & Surface ChemistryDocument29 pagesColloidal State & Surface ChemistrydhiralNo ratings yet
- Colloids and SuspensionsDocument4 pagesColloids and SuspensionsJulius Macaballug100% (1)
- Science 6 HeterogeneousDocument73 pagesScience 6 HeterogeneousJulie Ann RaymundoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Homogeneous and Heterogeneous MixturesDocument28 pagesLesson 1 Homogeneous and Heterogeneous MixturesFlorenda Sorilla SampianoNo ratings yet
- ColloidsDocument14 pagesColloidsJulyNo ratings yet
- Suspensions and ColloidsDocument3 pagesSuspensions and Colloidsmonster40lbsNo ratings yet
- Suspensions and Colloids NotesDocument3 pagesSuspensions and Colloids Noteskallstea100% (1)
- Chapter 11 MixtureDocument12 pagesChapter 11 MixtureAbie BarceloNo ratings yet
- Pure Substances and MixturesDocument15 pagesPure Substances and MixturesChrisaundria LuceroNo ratings yet
- Mixtures CSEC LevelDocument36 pagesMixtures CSEC Levelrorlando lewisNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document30 pagesLecture 5ziaifzaNo ratings yet
- Types of Colloidal System: By: GujeldeDocument6 pagesTypes of Colloidal System: By: GujeldeJayMAX :3No ratings yet
- Is Matter Around Us PureDocument5 pagesIs Matter Around Us PureVarunagha LakshmananNo ratings yet
- C Ol Lo Id ZDocument23 pagesC Ol Lo Id ZAnnie Baloch100% (2)
- SolutionDocument3 pagesSolutionMayank PatelNo ratings yet
- Colloid: SolutionDocument4 pagesColloid: SolutionMark LuzNo ratings yet
- Introduction To General-219-225Document7 pagesIntroduction To General-219-225Andreyan PoerwonegoroNo ratings yet
- Solutions Suspensions and ColloidsDocument15 pagesSolutions Suspensions and ColloidsBernard Enriquez SorianoNo ratings yet
- Kinds of MixtureDocument42 pagesKinds of MixtureMa'am Emily RevillaNo ratings yet
- The Homogeneous Mixture of Sugar and Water Is Called True SolutionDocument3 pagesThe Homogeneous Mixture of Sugar and Water Is Called True Solutionking1qNo ratings yet
- Notes-Science-is Matter Around Us PureDocument10 pagesNotes-Science-is Matter Around Us PureHina SharmaNo ratings yet
- Matter ScienceDocument5 pagesMatter ScienceEllechir JeanneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - (I) - ColloidDocument64 pagesChapter 6 - (I) - ColloidezanaNo ratings yet
- Pure Substances, Mixtures, and SolutionsDocument19 pagesPure Substances, Mixtures, and SolutionscriselNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Matter Around Us PureDocument14 pagesChapter 2 - Matter Around Us PureSwathi KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- Mixture - WikipediaDocument5 pagesMixture - Wikipediatsvmpm1765No ratings yet
- Pure Substances and MixturesDocument18 pagesPure Substances and MixturesMariz Rivera GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Solutions Suspensions and ColloidsDocument10 pagesSolutions Suspensions and ColloidsAfesha DanielNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lesson 2.1 (Transcribed)Document4 pagesChemistry Lesson 2.1 (Transcribed)chem recordingsNo ratings yet
- Is Matter Around Us Pure NotesDocument11 pagesIs Matter Around Us Pure NotesMahima varshneyNo ratings yet
- CHM271 - Chapter 7 - Colloid - Surface ChemistryDocument45 pagesCHM271 - Chapter 7 - Colloid - Surface Chemistryhidayahtul adhaNo ratings yet
- Pure Substances Mixtures and SolutionsDocument18 pagesPure Substances Mixtures and SolutionsJoanna Angela LeeNo ratings yet
- True Solution Size 100 NMDocument12 pagesTrue Solution Size 100 NMRohit Kumar BaghelNo ratings yet
- COLLOIDS LectureDocument6 pagesCOLLOIDS LectureJeff MarianoNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Mixtures: SolutionsDocument6 pagesKinds of Mixtures: SolutionsHero MirasolNo ratings yet
- Emulsion and ColloidsDocument2 pagesEmulsion and ColloidsFazal Hussain100% (1)
- Science Lessons 3 To 6 (Autosaved)Document24 pagesScience Lessons 3 To 6 (Autosaved)Rodgen GerasolNo ratings yet
- Coll OidsDocument18 pagesColl OidsMark Albert Morales-CaacbayNo ratings yet
- Special DPP (Colloids) : Inorganic Chemistry NurtureDocument1 pageSpecial DPP (Colloids) : Inorganic Chemistry NurtureAryasingh5656No ratings yet
- Special DPP (Colloids) : Inorganic Chemistry NurtureDocument1 pageSpecial DPP (Colloids) : Inorganic Chemistry NurtureAryasingh5656No ratings yet
- CLASS 9 Chapter 2 Part 2 ChemDocument5 pagesCLASS 9 Chapter 2 Part 2 ChemRoma BohidarNo ratings yet
- Sci 6 Suspensions and ColloidsDocument29 pagesSci 6 Suspensions and ColloidsDionelyn CruzNo ratings yet
- Classes of ColloidsDocument1 pageClasses of ColloidsBritanya EastNo ratings yet
- Colloid and Surface Science: Nurul Huda BT Abu Bakar 012-7892664 Hudabakar@ump - Edu.myDocument8 pagesColloid and Surface Science: Nurul Huda BT Abu Bakar 012-7892664 Hudabakar@ump - Edu.myAlbert12346No ratings yet
- WWW Askiitians Com Revision Notes Class 9 Science Is Matter Around Us PureDocument17 pagesWWW Askiitians Com Revision Notes Class 9 Science Is Matter Around Us PureDeepak Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Disperse SystemDocument22 pagesDisperse SystemZheng JoeyNo ratings yet
- Soal Koloid English FixDocument10 pagesSoal Koloid English FixdiyahNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Module 3 ChemDocument7 pagesReviewer Module 3 Chemidieh ligNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Chemistry Notes Chapter 2 and 4Document10 pagesClass 9 Chemistry Notes Chapter 2 and 4ap4618720No ratings yet
- Chapter - 2: Is Matter Around Us PureDocument30 pagesChapter - 2: Is Matter Around Us PureKavya GoelNo ratings yet
- Solutions Booklet 2Document30 pagesSolutions Booklet 2api-546418402No ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument29 pagesChemistry Projectpintu2055No ratings yet
- Acids and Bases HandoutDocument2 pagesAcids and Bases HandoutSohid BacusNo ratings yet
- Bullies, Socialites and the Shy Ones: Exploring the Personalities of Watercolor PaintsFrom EverandBullies, Socialites and the Shy Ones: Exploring the Personalities of Watercolor PaintsNo ratings yet
- New Doc 2019-10-31 20.52.10 PDFDocument14 pagesNew Doc 2019-10-31 20.52.10 PDFeswarNo ratings yet
- Complexation Titration Department of Physical Sciences & Technology University of Sabaragamuwa Srilanka (Document33 pagesComplexation Titration Department of Physical Sciences & Technology University of Sabaragamuwa Srilanka (eswarNo ratings yet
- Posology 151223081101Document24 pagesPosology 151223081101eswarNo ratings yet
- Potentiometry 1Document39 pagesPotentiometry 1eswarNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 1Document17 pagesThermodynamics 1Wilma NaderaNo ratings yet
- Astm d2597 1994 PDFDocument12 pagesAstm d2597 1994 PDFHsaam HsaamNo ratings yet
- Paic MCQDocument12 pagesPaic MCQManish MahadevwalaNo ratings yet
- Proof of Planck Radiation Law From FirstDocument43 pagesProof of Planck Radiation Law From FirstZenegaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/42Document24 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/42Gulnur KenzheevaNo ratings yet
- Gay Lussac's LawDocument35 pagesGay Lussac's LawGarren Jude AquinoNo ratings yet
- Melc-Matrix-General Chemistry 1Document4 pagesMelc-Matrix-General Chemistry 1Ronald ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium: A2 Chemistry (Unit 4)Document9 pagesChemical Equilibrium: A2 Chemistry (Unit 4)Maliha Ishrat JarinNo ratings yet
- CCO New Moppet A4 Sales Sheet 100418Document2 pagesCCO New Moppet A4 Sales Sheet 100418Puja Ningrat WibowoNo ratings yet
- 32710-1209-Sat Old CheDocument45 pages32710-1209-Sat Old CheParesh ModiNo ratings yet
- Epm 300 Series in Situ Dilution ProbesDocument2 pagesEpm 300 Series in Situ Dilution ProbesChairil LinggabinangkitNo ratings yet
- Ato Mf5700 Digital Gas Flow Meter User ManualDocument39 pagesAto Mf5700 Digital Gas Flow Meter User ManualAnjang YudistriNo ratings yet
- Statistical Physics Solution Sheet 3: 3N 3N 3N −βH (p,q) BDocument5 pagesStatistical Physics Solution Sheet 3: 3N 3N 3N −βH (p,q) BGerman ChiappeNo ratings yet
- s120 - 4r - BR18VC Service ManDocument72 pagess120 - 4r - BR18VC Service Mantryp1perNo ratings yet
- WFSR 44004710107 PDFDocument26 pagesWFSR 44004710107 PDFAyub Anwar M-SalihNo ratings yet
- Gas Sensor On Correlated 2D Electron GasDocument7 pagesGas Sensor On Correlated 2D Electron GasShauvik BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Model 1Document68 pagesModel 1Prashanth Menon0% (1)
- Output No. 1: Bicol University Polangui CampusDocument4 pagesOutput No. 1: Bicol University Polangui CampusAlex Loma ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Worksheet-Solid Liquid and GasesDocument4 pagesWorksheet-Solid Liquid and Gasesrachna sharmaNo ratings yet
- Well Performance-3 PDFDocument33 pagesWell Performance-3 PDFWashoo Hasoo100% (3)
- Failure and Mitigation Study of Packer in The Deepwater HTHP Gas Well Considering The Temperature-Pressure Effect During Well Completion TestDocument14 pagesFailure and Mitigation Study of Packer in The Deepwater HTHP Gas Well Considering The Temperature-Pressure Effect During Well Completion TestTiannan DengNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise No. 6: Ideal Gas Law: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument3 pagesLab Exercise No. 6: Ideal Gas Law: Department of Mechanical EngineeringJino BalingNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics Eng PP 2023 24 1Document10 pages11 Physics Eng PP 2023 24 1guptadeepka168No ratings yet
- Gea17076 Encover - LRDocument1 pageGea17076 Encover - LRteedee1No ratings yet
- JEE Main Revision Plan JP ERDocument2 pagesJEE Main Revision Plan JP ERashutoshNo ratings yet