Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Interventions For Acute Otitis Media
Nursing Interventions For Acute Otitis Media
Uploaded by
Yousef Khalifa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views1 pageAcute otitis media is a common ear infection in young children that causes inflammation in the middle ear. Nursing interventions for acute otitis media include determining the characteristics of the child's pain, monitoring vital signs, encouraging increased fluid intake, reducing noise, and administering analgesics as ordered by the physician to relieve discomfort and pressure in the ear. Nurses also assess development at each visit and educate families on effective communication techniques to distract from pain.
Original Description:
Acute Otitis Media
Original Title
Acute Otitis Media
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAcute otitis media is a common ear infection in young children that causes inflammation in the middle ear. Nursing interventions for acute otitis media include determining the characteristics of the child's pain, monitoring vital signs, encouraging increased fluid intake, reducing noise, and administering analgesics as ordered by the physician to relieve discomfort and pressure in the ear. Nurses also assess development at each visit and educate families on effective communication techniques to distract from pain.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views1 pageNursing Interventions For Acute Otitis Media
Nursing Interventions For Acute Otitis Media
Uploaded by
Yousef KhalifaAcute otitis media is a common ear infection in young children that causes inflammation in the middle ear. Nursing interventions for acute otitis media include determining the characteristics of the child's pain, monitoring vital signs, encouraging increased fluid intake, reducing noise, and administering analgesics as ordered by the physician to relieve discomfort and pressure in the ear. Nurses also assess development at each visit and educate families on effective communication techniques to distract from pain.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
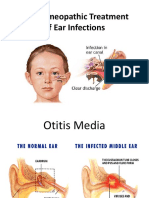
acute otitis media
In the United States, acute otitis media (AOM), defined by convention as the first 3 weeks of
a process in which the middle ear shows the signs and symptoms of acuteinflammation, is
the most common affliction necessitating medical therapy for children younger than 5 years.
Nursing Interventions for Acute Otitis Media
Determine pain characteristics through client’s description
Use pain rating scale appropriate for age
Monitor skin color and vital signs
Encourage to increase fluid intake to decrease susceptibility to infection
Reduce noise in the client environment.
Look at the client when speaking.
Speak clearly and firmly on the client without the need to shout.
Provide good lighting when the client relies on the lips.
Use the signs of non-verbal (eg facial expressions, pointing, or body movement)
and other communications.
Encourage to listen to music, have focused breathing, socializing to others or other
diversional activities
Administer analgesics as ordered by the physician
Have the child sit up, raise head on pillows, or lie on unaffected ear. Elevation
decreases pressure from fluid.
Apply heating pad or warm hot water bottle. Heat increases blood supply and
reduces discomfort.
Have the child/patient chew gum or blow on balloon to relieve pressure in ear.
Attempts to open the eustachian tube may help aerate the middle ear.
Instruct family or the people closest to the client on how techniques of effective
communication so that they can interact with clients to distract attention and reduce
tension towards pain
If the client wants, the client can use hearing aids.
Assess motor and language development at each health care visit. Early detection of
developmental delays can lead to appropriate intervention
You might also like
- NURSING and SURGICAL MANAGEMENTDocument3 pagesNURSING and SURGICAL MANAGEMENTJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Otitis MediaDocument25 pagesOtitis Mediadmmwale1995No ratings yet
- Expose On EntDocument20 pagesExpose On EntDUCHELNo ratings yet
- Om 3Document10 pagesOm 3Ma.rose AndresNo ratings yet
- Acute Ear DiesaeDocument13 pagesAcute Ear DiesaeMr FuckNo ratings yet
- How - . - I Manage Deafness in Children and Young People.Document4 pagesHow - . - I Manage Deafness in Children and Young People.Speech & Language Therapy in PracticeNo ratings yet
- Otitis MediaDocument7 pagesOtitis MediaNader Smadi67% (3)
- TLC Noah HeerDocument3 pagesTLC Noah HeerAlain SalsaMan BazilNo ratings yet
- Disease of The EarsDocument20 pagesDisease of The EarsPrecy CoNo ratings yet
- Alt To Ear Pain-1Document5 pagesAlt To Ear Pain-1nonoNo ratings yet
- Nine Effective Home Remedies For EaracheDocument1 pageNine Effective Home Remedies For EarachekaralyntNo ratings yet
- The Homeopathic Treatment of Ear Infections PDFDocument104 pagesThe Homeopathic Treatment of Ear Infections PDFdipgang7174No ratings yet
- Assessing The Ears and HearingDocument7 pagesAssessing The Ears and HearingArianne VerzolaaaNo ratings yet
- 101-114 RationaleDocument5 pages101-114 RationalecherylmbagnolNo ratings yet
- What Is An Ear InfectionDocument4 pagesWhat Is An Ear Infectionapi-236387116No ratings yet
- Otitis Media2Document5 pagesOtitis Media2Anthony LopezNo ratings yet
- Otitis MediaDocument18 pagesOtitis Mediaapi-284314498No ratings yet
- MastoiditisDocument37 pagesMastoiditisAkanksha EkkaNo ratings yet
- The Homeopathic Treatment of Ear InfectionsDocument104 pagesThe Homeopathic Treatment of Ear Infectionsdipgang7174No ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: Acute Otitis MediaDocument7 pagesAnatomy & Physiology: Acute Otitis MediaAbigael Patricia GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Manilyn B. Bagiao, MSNDocument30 pagesManilyn B. Bagiao, MSNmanilynNo ratings yet
- Ear Infections: A troubleshooting guide to common childhood ailmentsFrom EverandEar Infections: A troubleshooting guide to common childhood ailmentsNo ratings yet
- Ear ProblemDocument13 pagesEar ProblemChloe MorningstarNo ratings yet
- Child - Otitis MediaDocument2 pagesChild - Otitis MediawanyaminNo ratings yet
- Condition 136 Fever, Irritability, Ear Discharge: TasksDocument2 pagesCondition 136 Fever, Irritability, Ear Discharge: Tasksmohamed aissaNo ratings yet
- Aoe Guideline Pls FinalDocument2 pagesAoe Guideline Pls FinalJeffly Varro GilbertNo ratings yet
- Discharge Planning - AsthmaDocument1 pageDischarge Planning - Asthmayer tagalajNo ratings yet
- Otitis MediaDocument26 pagesOtitis MediaRiteka SinghNo ratings yet
- ADVANCE NURSING Ear InstillationDocument3 pagesADVANCE NURSING Ear InstillationFelix Tengan100% (1)
- Care of Hearing Aids.Document4 pagesCare of Hearing Aids.imaninjaloenkosiniNo ratings yet
- Lay Article DraftDocument3 pagesLay Article DraftMariamAlashaabNo ratings yet
- Eyes Ear Throat (New)Document19 pagesEyes Ear Throat (New)coosa liquorsNo ratings yet
- Managing Common Aches and Pains in Kids: A Parent's Handbook: Health, #9From EverandManaging Common Aches and Pains in Kids: A Parent's Handbook: Health, #9No ratings yet
- Communication With Elderly PatientsDocument10 pagesCommunication With Elderly PatientsBJ RanggaNo ratings yet
- Basog - ReportTonsillitis and EpistaxisDocument4 pagesBasog - ReportTonsillitis and EpistaxisclaribelleNo ratings yet
- 3.ENT Care - Health Promotion ENTDocument20 pages3.ENT Care - Health Promotion ENTNikkiNo ratings yet
- Dental Pediatric Behavior GuidanceDocument55 pagesDental Pediatric Behavior GuidanceAsala AbdulghaniNo ratings yet
- Pediatric DentistryDocument8 pagesPediatric DentistryPavleta RashkovaNo ratings yet
- Practical Strategies For Minimising Voice StrainDocument3 pagesPractical Strategies For Minimising Voice StrainRolo De la PiedraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 39 Pain Management in ChildrenDocument9 pagesChapter 39 Pain Management in ChildrenStephanie LeeNo ratings yet
- Asthma!!!Document18 pagesAsthma!!!Jabbamackeez50% (2)
- Your Family Health HistoryDocument9 pagesYour Family Health History308501No ratings yet
- Acute Upper Airway Obstruction in Children: Paediatric Anaesthesia Tutorial 368Document9 pagesAcute Upper Airway Obstruction in Children: Paediatric Anaesthesia Tutorial 368Fireka JuniantikaNo ratings yet
- Dental NursingDocument13 pagesDental NursingBéñtéñ BéñtéñNo ratings yet
- Ear Infection Essentials Understanding, Treating, and PreventingFrom EverandEar Infection Essentials Understanding, Treating, and PreventingNo ratings yet
- Cough Suppression - A Patients Guide PDFDocument4 pagesCough Suppression - A Patients Guide PDFEndeavor Med TutorsNo ratings yet
- Councelling-Mental HealthDocument3 pagesCouncelling-Mental Healthtracker1234No ratings yet
- Managing Otitis Media With Effusion in Young Children: Practice GuidelineDocument11 pagesManaging Otitis Media With Effusion in Young Children: Practice GuidelineJohn ThunderNo ratings yet
- Ventilation HighlightsDocument4 pagesVentilation HighlightsAndrew HippsNo ratings yet
- The Assignment For Today Are:: AnswerDocument3 pagesThe Assignment For Today Are:: AnswerAgung KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Ear Infection (Otitis Media)Document14 pagesEar Infection (Otitis Media)matushenko.n14No ratings yet
- Group 4 Grand Case Presentation 1Document43 pagesGroup 4 Grand Case Presentation 1naomie manaliliNo ratings yet
- Otitis MediaDocument5 pagesOtitis MediaRahmaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanJoshua Pascasio100% (1)
- AOEGuidelinePatientFAQFinal 0 PDFDocument2 pagesAOEGuidelinePatientFAQFinal 0 PDFMohamed JubranNo ratings yet
- IV. Activity QuestionsDocument3 pagesIV. Activity Questionspandaminion099No ratings yet
- Febrile SeizuresDocument6 pagesFebrile SeizuresKirstin del CarmenNo ratings yet
- Otitis MediaDocument6 pagesOtitis MediaAbdullah EssaNo ratings yet
- Otic Medication AdministrationDocument3 pagesOtic Medication AdministrationCardio GodNo ratings yet
- Behavior ManagementDocument2 pagesBehavior Managementابراهيم الرواشدةNo ratings yet
- Vaccination Program PDFDocument1 pageVaccination Program PDFYousef KhalifaNo ratings yet
- Health EducationDocument33 pagesHealth EducationYousef KhalifaNo ratings yet
- Health EducationDocument36 pagesHealth EducationYousef KhalifaNo ratings yet
- Breast - 4Document3 pagesBreast - 4Yousef KhalifaNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy - 1Document1 pagePregnancy - 1Yousef KhalifaNo ratings yet
- Benign Proliferative Breast Disease: The Two Most Common Types AreDocument3 pagesBenign Proliferative Breast Disease: The Two Most Common Types AreYousef KhalifaNo ratings yet
- HypothyroidismDocument1 pageHypothyroidismYousef KhalifaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostictests Laboratory Tests Nipple Discharge CytologyDocument3 pagesDiagnostictests Laboratory Tests Nipple Discharge CytologyYousef KhalifaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Breast: Subjective DataDocument2 pagesAssessment of The Breast: Subjective DataYousef KhalifaNo ratings yet
- Health Promotion - 4Document9 pagesHealth Promotion - 4Yousef KhalifaNo ratings yet
- Health Promotion - 3Document10 pagesHealth Promotion - 3Yousef KhalifaNo ratings yet
- The Rights and Responsibilities of NursesDocument2 pagesThe Rights and Responsibilities of NursesYousef KhalifaNo ratings yet
- Legal Concepts and ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesLegal Concepts and ResponsibilitiesYousef KhalifaNo ratings yet
- Home Visit - 5Document6 pagesHome Visit - 5Yousef KhalifaNo ratings yet
- Home Visi t3Document13 pagesHome Visi t3Yousef KhalifaNo ratings yet