Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bacterial Morphology, Physiology, Metabolism & Genetics
Bacterial Morphology, Physiology, Metabolism & Genetics
Uploaded by
Gail HamtigOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bacterial Morphology, Physiology, Metabolism & Genetics
Bacterial Morphology, Physiology, Metabolism & Genetics
Uploaded by
Gail HamtigCopyright:
Available Formats
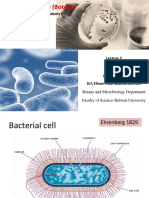
BACTERIAL MORPHOLOGY, PHYSIOLOGY, METABOLISM & GENETICS
Shape
1. Cocci – spherical
a. Diplococci – pair
b. Streptococci - chains
c. Staphylococci – clusters
d. Sarcina – tetrads
2. Bacilli – rod-shaped
a. Coccobacilli – short (e.g Escherichia coli)
b. Palisades – side by side
There’s no bacilli in chains in gram negative
3. Spirochetes – spiral
4. Others
a. Fusobacterium – enlarged rod
b. Vibrio – comma form
c. Bdellovibrio – comma s form
d. Corynebacteriaceae – club rod
e. Helicobacter pylori – helical form
f. Borrelia burgdorferi – corkscrew s form
g. Filamentous
Common stains
1. Acridine orange
- Fluorochrome dye that stains both gram (+) and gram (-) bacteria, living or dead
- Binds the nucleic acid of cell and fluoresces as bright orange
- Used to locate bacteria in blood cultures and other specimens where discerning bacteria
might be difficult
2. Calcofluor white
- Fluorchrome that binds to chitin in fungal cell walls
- Fluoresces as bright apple-green or blue-white
- The original blueing agent used in high-volume laundries to whiten yellow-appearing white
cotton or other fabrics
3. Methylene blue
- Traditionally used to stain Corynebacterium diphtheriae for observation of metachromatic
granules (combination of dark and light)
- Used as counterstain in acid-fast staining
4. Lactophenol cotton blue
- Used to stain the cell walls of medically important fungi grown in slide culture
5. India ink
- Negative stain
- Used to visualize the capsule surrounding the yeast, eg. Cryptococcus spp.
- Fine ink particles are excluded from the capsule, leaving a dark background and a clear
capsule surrounding the yeasts.
MICROBIAL GROWTH AND NUTRITION
All bacteria require the following:
1. Carbon source – synthesis of cell components
Autotroph – require carbon dioxide to grow
Heterotroph – require organic compounds
2. Nitrogen source – for protein synthesis
3. Water
4. Energy source
Phototroph – uses light for energy
Chemotroph – uses chemical energy
Organotroph – uses organic compounds
Lithotroph – inorganic compounds
5. Metallic elements – for enzyme activation
6. Organic substances
7. High osmotic pressure – archaebacteria
You might also like
- Chapter 2Document9 pagesChapter 2jjumlaboratoryNo ratings yet
- How Are Chromobionta Different From The Other Stramenopiles?Document19 pagesHow Are Chromobionta Different From The Other Stramenopiles?sheilaNo ratings yet
- Classification of OrganismsDocument35 pagesClassification of OrganismsABEL JEDIDIAHNo ratings yet
- MLT 415 Lab Report Innoculation of CultuDocument23 pagesMLT 415 Lab Report Innoculation of CultuTrishNo ratings yet
- BacteriologyDocument75 pagesBacteriologyHoward BarlomentoNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Morphology Stains Growth and NutritionDocument51 pagesBacterial Morphology Stains Growth and NutritionCelestine MarivelezNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3: Plant Kingdom: One Mark QuestionsDocument6 pagesChapter-3: Plant Kingdom: One Mark QuestionsMonica BaiNo ratings yet
- BIOL 324 Introduction To MicroBDocument5 pagesBIOL 324 Introduction To MicroBKargboNo ratings yet
- Biology 2005 Nabteb Past QuestionDocument6 pagesBiology 2005 Nabteb Past Questionidrisfaridat06No ratings yet
- Bacteriology - AmjedDocument135 pagesBacteriology - AmjedLola KhatimNo ratings yet
- 2729 (2 Files Merged)Document51 pages2729 (2 Files Merged)taufiq islamNo ratings yet
- 0969d5da 1619498709723Document6 pages0969d5da 1619498709723AGNo ratings yet
- L-1 Nutrition in PlantsDocument7 pagesL-1 Nutrition in Plantsyajatbhavsar8No ratings yet
- Class 11 Bacteria PDFDocument32 pagesClass 11 Bacteria PDFSachin PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and Parasitology1Document249 pagesMicrobiology and Parasitology1Keshi Wo100% (3)
- GS 7Document32 pagesGS 7prabhatNo ratings yet
- BIology SeminarDocument26 pagesBIology Seminarm.m.giridharavel2196vmjschoolNo ratings yet
- Classification of AlgaeDocument10 pagesClassification of AlgaeKrishna Santhosh SanthoshNo ratings yet
- Science Class Viii Chap 2 MicroorganismsDocument5 pagesScience Class Viii Chap 2 MicroorganismsAbhaygyan SinghNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Science Chapter 1 PDFDocument20 pagesForm 5 Science Chapter 1 PDFfrez_kingdom100% (1)
- Nutrients in PlantsDocument6 pagesNutrients in PlantsYesha Shah CherubsNo ratings yet
- VIRUSESDocument6 pagesVIRUSESJoanna Carla Marmonejo Estorninos-WalkerNo ratings yet
- All Mycoses SGDDocument140 pagesAll Mycoses SGDkashan100% (1)
- Growth, Survival and Death of MicroorganismsDocument15 pagesGrowth, Survival and Death of MicroorganismsLidi SofyNo ratings yet
- G7 L-1 Nutrition in Plants - Worksheet - 230520 - 115119Document3 pagesG7 L-1 Nutrition in Plants - Worksheet - 230520 - 115119ohiobossNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Bacteria G Biology ES1Document27 pagesLecture 3 Bacteria G Biology ES1nourhan yousefNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Microbial World AND YOUDocument18 pagesChapter 1 Microbial World AND YOUChristian AbordoNo ratings yet
- Bridge CourseDocument158 pagesBridge Coursehjg234937No ratings yet
- Division: Cyanobacteria: - Single Class: Cyanophyceae - 150 Genera - 4037 SpeciesDocument10 pagesDivision: Cyanobacteria: - Single Class: Cyanophyceae - 150 Genera - 4037 SpeciesKavisa GhoshNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document25 pagesPresentation 1Saurav Suman100% (1)
- People To Observe and Describe Microorganisms Generation: LivingDocument7 pagesPeople To Observe and Describe Microorganisms Generation: LivingSabnin SoroniNo ratings yet
- G12 1st Sem FinalsDocument22 pagesG12 1st Sem FinalsTolentino, Ma. LykaNo ratings yet
- Cbse - Grade 7 - Science - CH-1 - Nutrition in PlantsDocument5 pagesCbse - Grade 7 - Science - CH-1 - Nutrition in PlantsjayeshmananiNo ratings yet
- EM - Bio - G13 - T2 - I, II PP - 2020Document18 pagesEM - Bio - G13 - T2 - I, II PP - 2020Sumaiya RizanNo ratings yet
- General Characters of MicroorganismsDocument3 pagesGeneral Characters of MicroorganismssadafNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27 Protists I. Evolution of EukaryotesDocument7 pagesChapter 27 Protists I. Evolution of EukaryotesNadeem IqbalNo ratings yet
- Flashcards - MicrobiologyDocument26 pagesFlashcards - MicrobiologyAngela Carrillo TrianoNo ratings yet
- Ncert Page Wise Q Plant KingdomDocument17 pagesNcert Page Wise Q Plant KingdomSagarNo ratings yet
- An Introduction: Marx P. Catalan, RMTDocument48 pagesAn Introduction: Marx P. Catalan, RMTstoopiidgurl91% (11)
- 1 IntroDocument5 pages1 IntroJeanjayannseptoeman100% (1)
- (L-5) - Cell - The Unit of Life - 31 ST MarDocument38 pages(L-5) - Cell - The Unit of Life - 31 ST Marpuneetlokwani04No ratings yet
- Biology ReviewDocument197 pagesBiology ReviewEden Lucas Ginez PitpitanNo ratings yet
- Intro & Hist of MicrobiologyDocument21 pagesIntro & Hist of MicrobiologyKumkum CrNo ratings yet
- LIFE PROCESSESDocument49 pagesLIFE PROCESSESJaimukeshNo ratings yet
- Naming, Classifying, and Identifying Microorganisms: Taxonomic Ranks Formal Ranks ExampleDocument6 pagesNaming, Classifying, and Identifying Microorganisms: Taxonomic Ranks Formal Ranks ExampleNano KaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition - Food SupplyingsystemDocument29 pagesNutrition - Food SupplyingsystemRavi KiranNo ratings yet
- AP Science 7 AnswerDocument80 pagesAP Science 7 AnswerSakshat KaleNo ratings yet
- Introduction On Biodiversity: Kingdom ArcheabacteriaDocument3 pagesIntroduction On Biodiversity: Kingdom ArcheabacteriaRyzaRosalesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6Document4 pagesLesson 6Shaina LimNo ratings yet
- Laporan Media Jamur NurulDocument13 pagesLaporan Media Jamur NurulNur HikmaNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Formation ClassificationDocument9 pagesBacteria Formation Classificationfurqanbaig8No ratings yet
- Microbial Nutrition and GrowthDocument14 pagesMicrobial Nutrition and GrowthsanmathiNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Workshop QuestionsDocument9 pagesWeek 1 Workshop QuestionsshlokNo ratings yet
- WK - 4 Bacterial Classification-IDocument39 pagesWK - 4 Bacterial Classification-IBakhtawarNo ratings yet
- Lab. TechniquesDocument31 pagesLab. TechniquesBlessy MartinNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument52 pagesChapter Threemseid678No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Biological Classification: K C MeenaDocument5 pagesChapter 2 - Biological Classification: K C MeenaZainab UsmanNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Respiration 1 Rge4g4e2g4Document53 pagesNutrition and Respiration 1 Rge4g4e2g4T3X1CNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideFrom EverandMicrobiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideNo ratings yet