Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Definition of Integration. The Operation Inverse To Differentiation Is Called Integration. by
Definition of Integration. The Operation Inverse To Differentiation Is Called Integration. by
Uploaded by
Anonymous dfvIPaYCaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Definition of Integration. The Operation Inverse To Differentiation Is Called Integration. by
Definition of Integration. The Operation Inverse To Differentiation Is Called Integration. by
Uploaded by
Anonymous dfvIPaYCaCopyright:
Available Formats
Definition of Integration. The operation inverse to differentiation is called integration.
By
differentiation we find the differential of a given function, and by integration we find the
function corresponding to a given differential. This function is called the integral of the
differential.
For instance,
since 2xdx is the differential of x2,
therefore, x2 is the integral of 2xdx.
The symbol ∫ is used to denote the integral of the expression following it.
Thus, the foregoing relations would be written,
d(x2) = 2xdx, ∫2xdx = x2
In other words, ∫ is the inverse of d.
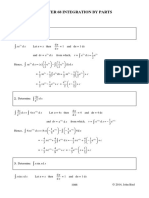
Elementary Principles
∫ (du ± dv ± dw) = ∫du ± ∫ dv ± ∫ dw
∫adu = a ∫du
Fundamental Integrals:
un+ 1 2x
1. ∫ u du= n+1 + c
n
(¿ ¿ 3−5 x 2 +3 x+ 1) dx
du ∫¿
2. ∫ u =ln u+ c
au
3. ∫ a u
du=
ln a
+c ∫ (5− √1x ) dx
4. ∫ e u du=eu +c
5. ∫ cos u du=sin u+ c ∫ 2 √4 x dx
6. ∫ sin u du=−cos u+c 2
∫ x 4 dx
7. ∫ sec u du=tan u+ c
2
8. ∫ csc2 u du=−cot u+ c 2
9. ∫ secu tan u du=secu+ c ∫ 3 x −2
√x
x +1
dx
10. ∫ csc u cot u du=−cscu+ c
11. ∫ tan u du=ln ∣ cos u ∣+c
12. ∫ cot u du=ln ∣sin u ∣+c
You might also like
- IntegralDocument5 pagesIntegralRoselyn MatienzoNo ratings yet
- Integration by PartsDocument13 pagesIntegration by PartsAbdifatah NadirNo ratings yet
- Integrals QUIZDocument3 pagesIntegrals QUIZNorma Alejandra AbrenaNo ratings yet
- Integration by PartsDocument14 pagesIntegration by PartsOuroborosKNo ratings yet
- Tugas 3 MTKDocument2 pagesTugas 3 MTKMuh IdrisNo ratings yet
- Tugas 3 MTKDocument2 pagesTugas 3 MTKMuh IdrisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Integration - Part1Document57 pagesChapter 5 Integration - Part1checekNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11Document9 pagesLecture 11muradNo ratings yet
- Common Functions Function IntegralDocument5 pagesCommon Functions Function IntegralfebriNo ratings yet
- 03 Task Performance 1 - ARGDocument2 pages03 Task Performance 1 - ARGJhan Bryan NeraNo ratings yet
- IntegrationDocument123 pagesIntegrationHari KrushnaNo ratings yet
- BACAL Integration Unit 1-2Document3 pagesBACAL Integration Unit 1-2theresaperez298No ratings yet
- Calculus Mod4 Fucking DoneDocument3 pagesCalculus Mod4 Fucking DoneAlex RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Practice Set 5Document2 pagesPractice Set 5random potatoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics 2 CMU.Document38 pagesEngineering Mathematics 2 CMU.Nyoka DunnNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument18 pagesUntitledAcebuque Arby Immanuel GopeteoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Differential Equations: Exercise 17Document9 pagesChapter 17 Differential Equations: Exercise 17ZaleNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Chapter 17 Answers PDFDocument9 pagesUnit 1 Chapter 17 Answers PDFEggBread12No ratings yet
- Further Integration TechniquesDocument39 pagesFurther Integration TechniquesReginNo ratings yet
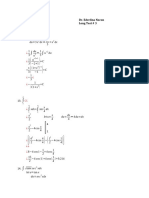
- Yao LongTest#3Document3 pagesYao LongTest#3Lester YaoNo ratings yet
- Método Por PartesDocument7 pagesMétodo Por PartesGuillermo Jesus Arce MezaNo ratings yet
- Bab 8Document2 pagesBab 8Dwi Arya permanaNo ratings yet
- MTK KlmpokDocument2 pagesMTK KlmpokDwi Arya permanaNo ratings yet
- Bab 8Document2 pagesBab 8Dwi Arya permanaNo ratings yet
- Calculus - Exercises: The Substitution Rule (代換積分法)Document3 pagesCalculus - Exercises: The Substitution Rule (代換積分法)Г. ЛувсанбатNo ratings yet
- C X G F DX X G X G F: 4.5 Integration by SubstitutionDocument11 pagesC X G F DX X G X G F: 4.5 Integration by SubstitutionAndres TorricoNo ratings yet
- 2da PC CÁLCULO DIFERENCIALDocument9 pages2da PC CÁLCULO DIFERENCIALJimena Alfaro LoyolaNo ratings yet
- INTEGRAL CALCULUS LecDocument10 pagesINTEGRAL CALCULUS LecNad DeYnNo ratings yet
- DRT 11 Neet SolDocument2 pagesDRT 11 Neet SolPRADEEP CNo ratings yet
- Differentiation C3Document16 pagesDifferentiation C3Raunaq MohamedNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 01 - Definite Integration NJ - 247Document35 pagesSheet - 01 - Definite Integration NJ - 2471qerfdNo ratings yet
- Math-3 - Module-7 Calculus Integration by PartsDocument3 pagesMath-3 - Module-7 Calculus Integration by PartsAne CalimagNo ratings yet
- Differentiation & Int All in OneDocument3 pagesDifferentiation & Int All in OneJASKIRAT GOGIANo ratings yet
- Four Step Rule and Formulas For DifferentiationDocument7 pagesFour Step Rule and Formulas For DifferentiationRosanna RosalesNo ratings yet
- Integration: Antiderivative of F or A Primitive of FDocument6 pagesIntegration: Antiderivative of F or A Primitive of Fvanesh wildNo ratings yet
- INTEGRAL FORMULAS ExponentDocument14 pagesINTEGRAL FORMULAS ExponentDina Grace MagnayeNo ratings yet
- 2da PC CálculoDocument9 pages2da PC CálculoSara Liz GutierrezNo ratings yet
- PRACTICEDocument2 pagesPRACTICEchristineNo ratings yet
- Jose Fernando Calderon ID: 353053 1.: X X X X X XDocument6 pagesJose Fernando Calderon ID: 353053 1.: X X X X X XFer CLNo ratings yet
- Differentiation and Integration FormulasDocument3 pagesDifferentiation and Integration FormulasAbell AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Differentiation and Integration FormulasDocument3 pagesDifferentiation and Integration FormulasJulius JunioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4: 4. IntegrationDocument34 pagesLesson 4: 4. IntegrationChathura LakmalNo ratings yet
- INTEGRAL35Document2 pagesINTEGRAL35Fer CLNo ratings yet
- INTEGRALDocument2 pagesINTEGRALFer CLNo ratings yet
- Properties of Indefinite IntegralsDocument10 pagesProperties of Indefinite IntegralsCarl Kristopher PeloniaNo ratings yet
- Tabela de IntegralDocument1 pageTabela de Integrallisetty1No ratings yet
- Integration by PartsDocument6 pagesIntegration by PartsLady Lee CabiganNo ratings yet
- Derivative of Some Transcendental FunctionsDocument8 pagesDerivative of Some Transcendental FunctionsAlfred BOzzNo ratings yet
- Integration Concept and FormulaDocument3 pagesIntegration Concept and FormulaVladimir Pascua CanaoNo ratings yet
- IntegralesDocument6 pagesIntegralesFer CLNo ratings yet
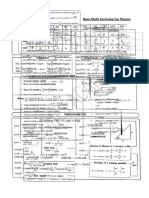
- Basic Math FormulaeDocument6 pagesBasic Math FormulaeSathya kirubaNo ratings yet
- AB Calc Solutions Manual ch6Document50 pagesAB Calc Solutions Manual ch6Joe Rowley0% (1)
- Em 2 Module 2 Lesson 4 Integration of Trigonometric FunctionsDocument9 pagesEm 2 Module 2 Lesson 4 Integration of Trigonometric FunctionsAcebuque Arby Immanuel GopeteoNo ratings yet
- Full Calculus Early Transcendentals 11Th Edition Anton Solutions Manual Online PDF All ChapterDocument76 pagesFull Calculus Early Transcendentals 11Th Edition Anton Solutions Manual Online PDF All Chaptercfrlfcfssfndrf565100% (4)
- TRABLHO DE CAL ManuelDocument6 pagesTRABLHO DE CAL Manuelvicente chocancuneneNo ratings yet
- SPM AddMath - Integration ExerciseDocument9 pagesSPM AddMath - Integration Exercisehasnitajb100% (1)
- Les01 IntegCalculusDocument52 pagesLes01 IntegCalculusPeter John ManlapigNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)