Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Parallel RC and RL Circuits Under Ac Excitation Objectives:: Experiment 5
Parallel RC and RL Circuits Under Ac Excitation Objectives:: Experiment 5
Uploaded by
Mohammad FaqirOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Parallel RC and RL Circuits Under Ac Excitation Objectives:: Experiment 5
Parallel RC and RL Circuits Under Ac Excitation Objectives:: Experiment 5
Uploaded by
Mohammad FaqirCopyright:
Available Formats
EXPERIMENT 5
PARALLEL RC AND RL CIRCUITS UNDER AC EXCITATION
Objectives:
To investigate the basic characteristics of parallel RL and RC circuits under
variable frequency AC excitations.
To be familiar with the oscilloscope and how to use it to measure the phase shift
between tow waveforms.
Pre-lab assignments:
show how to calculate theoretical expected values required to fill:
1. Table (1) (one frequency is enough).
2. Table (2) (one frequency is enough).
Plot BL, Z, I and θ versus frequency f for circuit of Figure (1).
Plot BC, Z, I and θ versus frequency f for circuit of Figure (2).
Draw typical impedance triangle of circuits in Figures (1) and (1).
Draw typical phasor diagram for each studied circuit.
Equipments required in the lab :
Function generator.
Oscilloscope and probes.
Digital multimeter.
Bread board.
Connecting wires.
Resistor , inductor and capacitor.
Practical procedure:
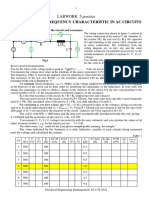
PART I: Parallel R-L circuits
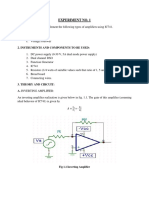
(1) Connect the circuit as shown in Figure 1 .The oscilloscope should be properly
connected as shown.
Eng. Ola Ananbeh. 1
(2) Set the first DMM to read AC voltage and the second to read the AC current.
(3) Set the function generator to be at the sinusoidal mode, and make sure that its
voltage knob is fully counter clockwise.
(4) Ask the lab instructor to check your connections.
(5) Switch ON the function generator and increase its output to (1) VRMS at 500Hz.
Use the voltmeter to measure the voltage.
(6) Record the readings of the Ammeter and the phase shift (in degrees) between V
and VRH in Table (1).
(7) Switch OFF the Function Generator.
(8) Reconnect the Ammeter to measure the RMS values of IR and record your
readings in Table (1).
(9) Switch OFF the Function Generator.
(10) Reconnect the Ammeter to measure the RMS values of IL and record your
readings in Table (1).
(11) Switch OFF the Function Generator.
(12) Reset the frequency of the input voltage signal to match the values in Table(2),
and repeat steps (6)
(13) Make sure that VS remains 1Vrms at all frequencies.
Table (1)
Frequency Current (mA) IR (mA) IL (mA) Phase shift θ Y=I/VS ( 1/Ω ) BL=IL/VS (1/Ω )
(Hz) EXP. MEAS. EXP. MEAS. EXP. MEAS. EXP. MEAS. EXP. MEAS. EXP. MEAS.
500
1000
2000
3000
5000
Eng. Ola Ananbeh. 2
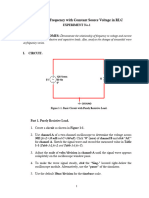
PART II: Parallel R-C circuits
(1) Connect the circuit as shown in Figure 2 . The oscilloscope should be properly
connected as shown.
(2) Connect the circuit shown in Figure (2).
(3) Repeat steps (3)-(10) as in PART I. Note that the results should be recorded in
Table (2) and IL should be replaced by IC
(5) Switch OFF the power supply.
Table (2)
BC =IC/ VC
Frequency Current (mA) IR ( mA ) IC ( mA ) Phase shift θ Y=I/VS ( 1/Ω)
(1/Ω )
(Hz)
EXP. MEAS. EXP. MEAS. EXP. MEAS. EXP. MEAS. EXP. MEAS. EXP. MEAS.
500
1000
2000
3000
5000
Eng. Ola Ananbeh. 3
You might also like
- Urdaneta City University College of Engineering and ArchitectureDocument10 pagesUrdaneta City University College of Engineering and Architecturezed cozNo ratings yet
- Common Emitter UnbypassedDocument38 pagesCommon Emitter Unbypassedaliffuden 123No ratings yet
- EEG PearlsDocument297 pagesEEG PearlsGus Alon J. Plata100% (8)
- EE201 Experiment 10Document5 pagesEE201 Experiment 10Mohammed TAOUSSINo ratings yet
- 2022 Lab 5Document3 pages2022 Lab 5Paul AndreiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4Document6 pagesExperiment 4Manar AlbarniNo ratings yet
- Part A: Resistor Networks: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesPart A: Resistor Networks: ObjectivesHAZNo ratings yet
- EEE241L - Lab 4 - Parallel RLC CircuitsDocument4 pagesEEE241L - Lab 4 - Parallel RLC CircuitsMd. Imdadul Haque Nayan 2222846643No ratings yet
- Part A: Resistor Networks: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesPart A: Resistor Networks: ObjectivesPrAnKeR GamesNo ratings yet
- 26 RC CircuitDocument6 pages26 RC CircuitsamNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 Integrator, Differentiator and Non-Linear Properties of OpampsDocument7 pagesExperiment 5 Integrator, Differentiator and Non-Linear Properties of OpampsEnes AyduranNo ratings yet
- Pre-Lab 1 - Diode v2021Document4 pagesPre-Lab 1 - Diode v2021محمد ابو جرادNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 6 Series Resistance Inductance Circuit ObjectivesDocument4 pagesActivity No. 6 Series Resistance Inductance Circuit ObjectivesJohn Paul BaquiranNo ratings yet
- Exp#5Document4 pagesExp#5Enas QtaifanNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 4-Parallel RC and RL CircuitsDocument9 pagesExperiment No. 4-Parallel RC and RL CircuitsArct John Alfante Zamora100% (1)
- EES512 Lab4Document7 pagesEES512 Lab4thetannies0613No ratings yet
- Exp 4Document5 pagesExp 4NUR AQILAH AMIRAH AIDILNo ratings yet
- AC CircuitDocument4 pagesAC CircuitJaritza DomaNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Electrical Engineering Universiti Teknologi MaraDocument5 pagesFaculty of Electrical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Maraaqil aimanNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document7 pagesLab 1Sauvegarde TackoNo ratings yet
- DC EECE1315 Lab 02 F18Document5 pagesDC EECE1315 Lab 02 F18Simon Roa (MortalSix02)No ratings yet
- EE387-V2 - Experiment No.8Document8 pagesEE387-V2 - Experiment No.8Hazel BalasbasNo ratings yet
- Yeditepe University Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Ee 232 Introduction To ElectronicsDocument5 pagesYeditepe University Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Ee 232 Introduction To Electronicstarafe5509No ratings yet
- EE1 Lab5 6 ACcircuit v2 Sept22Document7 pagesEE1 Lab5 6 ACcircuit v2 Sept22Lê Nguyễn Nguyên ThiêngNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual: EM 222 Circuit Analysis IiDocument6 pagesLaboratory Manual: EM 222 Circuit Analysis IiHarun KahramanNo ratings yet
- LRC CircuitsDocument10 pagesLRC CircuitsleisllyNo ratings yet
- Activity#1 240401 161649Document11 pagesActivity#1 240401 161649jacecarlatisNo ratings yet
- EE2CI4 Lab5 ManualDocument7 pagesEE2CI4 Lab5 Manualmoali173975No ratings yet
- Ex 1Document37 pagesEx 1Huy Lê TrườngNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Current GenerationDocument39 pagesUnit 1 Current GenerationMuse PrintingNo ratings yet
- Measurements & Electronic Instruments Laboratory Experiment ManualDocument2 pagesMeasurements & Electronic Instruments Laboratory Experiment Manualfirst lastNo ratings yet
- Integrator and orDocument2 pagesIntegrator and orAnku ParkNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Basic RL and RC DC Circuits PDFDocument32 pagesLab 1 Basic RL and RC DC Circuits PDFMarc CalilungNo ratings yet
- EEE 124 Exp5Document4 pagesEEE 124 Exp5Rakibul Hassan SajonNo ratings yet
- 2 - OhmsLawDocument8 pages2 - OhmsLawawab.hassan.eng23No ratings yet
- Inductive Reactance (In RL Circuits) : FALL2020: CNET219Document6 pagesInductive Reactance (In RL Circuits) : FALL2020: CNET219liam butlerNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifiers. Non-Linear Applications: Experiment 5Document2 pagesOperational Amplifiers. Non-Linear Applications: Experiment 5JoséAntonioNo ratings yet
- Exp 1Document8 pagesExp 1Enas QtaifanNo ratings yet
- Circuit Lab Manual Exp7 01Document9 pagesCircuit Lab Manual Exp7 01Adam AlmadhounNo ratings yet
- Advance Electrical Machine Manual 1-12Document48 pagesAdvance Electrical Machine Manual 1-12saqlainNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Laboratory 2BDocument8 pagesPower Electronics Laboratory 2Bkibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- Mamaradlo ErikaMae 2B Expt1Document6 pagesMamaradlo ErikaMae 2B Expt1Erika Mae MamaradloNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits PDFDocument6 pagesAC Circuits PDFRANDOLPHENo ratings yet
- LC C L X X Also HZ LC: EEET 1003 Electrical Circuit Theory Practical No. 4 Series Resonant Circuit AimDocument3 pagesLC C L X X Also HZ LC: EEET 1003 Electrical Circuit Theory Practical No. 4 Series Resonant Circuit AimEasy OkNo ratings yet
- A Technician Prepares To Use An Oscilloscope To Display An AC Voltage SignalDocument8 pagesA Technician Prepares To Use An Oscilloscope To Display An AC Voltage SignalgregNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment No. 3 Group 2 EE2203B 1Document20 pagesLaboratory Experiment No. 3 Group 2 EE2203B 1Alzen Galpao Enage100% (1)
- Fault Analysis of Three Phase Alternator Sequence Impedance: Apparatus RequiredDocument9 pagesFault Analysis of Three Phase Alternator Sequence Impedance: Apparatus RequiredMohan KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment No. 1Document9 pagesLaboratory Experiment No. 1JAMIR ARIOLANo ratings yet
- 18.03 Pset 5 PDFDocument23 pages18.03 Pset 5 PDFJustin CollinsNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document5 pagesExperiment 2Benedict DiwaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Basic Operational Amplifier CircuitsDocument7 pagesExperiment 2 Basic Operational Amplifier CircuitsVasursharpNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab Assignment-IV: Simulation of Full Wave Uncontrolled Ac-Dc ConverterDocument7 pagesPower Electronics Lab Assignment-IV: Simulation of Full Wave Uncontrolled Ac-Dc ConverterAurang ZaibNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - Introduction To Electronic Test Equipment: W.T. Yeung and R.T. HoweDocument14 pagesExperiment 1 - Introduction To Electronic Test Equipment: W.T. Yeung and R.T. HoweFairos ZakariahNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document3 pagesExperiment 1Akshat SharmaNo ratings yet
- 28 Alternating CurrentDocument11 pages28 Alternating CurrentRishi GovindaHarryNo ratings yet
- Lab 1-Bjt AmplifierDocument8 pagesLab 1-Bjt Amplifierhasnain3257100% (1)
- AC06-Respuesta en Frecuencia de Circuito en Serie R-LDocument13 pagesAC06-Respuesta en Frecuencia de Circuito en Serie R-LAngel Animas GNo ratings yet
- DC Lab Manual (CSE)Document26 pagesDC Lab Manual (CSE)Faisal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Ee2257 Control System Lab ManualDocument57 pagesEe2257 Control System Lab Manualchristorec100% (1)
- Lab#2 OpAmps 110420 V7Document4 pagesLab#2 OpAmps 110420 V7FrenkiNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 4Document4 pagesLab Report 4Sabbir Hasan AlexNo ratings yet
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Objective Listing - July 2009Document126 pagesObjective Listing - July 2009tallsrini100% (1)
- INDIABIX PART 2 ELEX MCQs FINAL FINAL NA PDFDocument59 pagesINDIABIX PART 2 ELEX MCQs FINAL FINAL NA PDFJehuNo ratings yet
- E40M RC Filters: M. Horowitz, J. Plummer, R. Howe 1Document22 pagesE40M RC Filters: M. Horowitz, J. Plummer, R. Howe 1luc882No ratings yet
- Problem Set No. 1Document4 pagesProblem Set No. 1Marc MathieuNo ratings yet
- SE207 Lab ManualDocument44 pagesSE207 Lab ManualchaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Circuit TheoryDocument33 pagesCircuit Theoryavi713331No ratings yet
- Electric Circuits and Electron DevicesDocument62 pagesElectric Circuits and Electron DevicesHarshaNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual PhysicsDocument56 pagesLab Manual PhysicsAnkesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Me 360 Pid ImplementationDocument3 pagesMe 360 Pid ImplementationJarfoNo ratings yet
- Frequency Response of Two Stage RC Coupled AmplifierDocument38 pagesFrequency Response of Two Stage RC Coupled AmplifierAyesha Gupta100% (2)
- Electric Circuits and FieldsDocument20 pagesElectric Circuits and Fieldssubhrajit kumar sethiNo ratings yet
- Filter Basics EbookDocument45 pagesFilter Basics Ebooknazim.cuiatdNo ratings yet
- Exp 7 - RCDocument4 pagesExp 7 - RCMonique HepburnNo ratings yet
- Ieai Lab FileDocument26 pagesIeai Lab Fileyuva5sharmaNo ratings yet
- Elecs 2008Document4 pagesElecs 2008Denaiya Watton LeehNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER17 Capacitor and Dielectrics STUDENTDocument64 pagesCHAPTER17 Capacitor and Dielectrics STUDENTNorizan HasratNo ratings yet
- Thyristor CommutationsDocument41 pagesThyristor CommutationsRohan Bose100% (1)
- Adjustable Cable Equalizer Combines Wideband Differential Receiver With Analog SwitchesDocument4 pagesAdjustable Cable Equalizer Combines Wideband Differential Receiver With Analog SwitchesAkhileshKesavanunnithanNo ratings yet
- Random Process CalculusDocument9 pagesRandom Process CalculusAjay SinghNo ratings yet
- MP1010Document10 pagesMP1010Vukica IvicNo ratings yet
- AN1048/D RC Snubber Networks For Thyristor Power Control and Transient SuppressionDocument22 pagesAN1048/D RC Snubber Networks For Thyristor Power Control and Transient Suppressionvemuri_sriNo ratings yet
- II Eie I Sem C - M Lab Manual (Ee242)Document53 pagesII Eie I Sem C - M Lab Manual (Ee242)Stishuk HFNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Noise Analysis Guide For Your Signal ChainDocument7 pagesStep by Step Noise Analysis Guide For Your Signal Chainnemarc08No ratings yet
- Mu Stage Philosophy: Alan KimmelDocument10 pagesMu Stage Philosophy: Alan KimmelbigpriapNo ratings yet
- W2016 PHYS259 Final Booklet I AnswersDocument12 pagesW2016 PHYS259 Final Booklet I AnswersYasmeenNo ratings yet
- Programacion IcspDocument8 pagesProgramacion IcspGerardo Madrigal100% (2)
- CMOS Analog IC Design - Fundamentals PDFDocument371 pagesCMOS Analog IC Design - Fundamentals PDFwicked_not_meNo ratings yet