Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Poster Marginality Tropentag
Poster Marginality Tropentag
Uploaded by
Fobe Lpt Nudalo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
100 views1 pageMarginality refers to an involuntary position at the margins of society that prevents access to resources and assets, restricts freedom of choice, and hinders capability development, ultimately leading to extreme poverty. The marginalized poor are disproportionately located in remote rural areas and often belong to ethnic or social groups facing exclusion. While global poverty has decreased, progress has been slowest for the poorest. The ultra-poor, living on less than $0.63 per day, reached 223 million in 2005, concentrated in Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia. Addressing the root causes of marginality is needed to effectively reduce extreme poverty.
Original Description:
pOST mARGINAL SECTOR
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMarginality refers to an involuntary position at the margins of society that prevents access to resources and assets, restricts freedom of choice, and hinders capability development, ultimately leading to extreme poverty. The marginalized poor are disproportionately located in remote rural areas and often belong to ethnic or social groups facing exclusion. While global poverty has decreased, progress has been slowest for the poorest. The ultra-poor, living on less than $0.63 per day, reached 223 million in 2005, concentrated in Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia. Addressing the root causes of marginality is needed to effectively reduce extreme poverty.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
100 views1 pagePoster Marginality Tropentag
Poster Marginality Tropentag
Uploaded by
Fobe Lpt NudaloMarginality refers to an involuntary position at the margins of society that prevents access to resources and assets, restricts freedom of choice, and hinders capability development, ultimately leading to extreme poverty. The marginalized poor are disproportionately located in remote rural areas and often belong to ethnic or social groups facing exclusion. While global poverty has decreased, progress has been slowest for the poorest. The ultra-poor, living on less than $0.63 per day, reached 223 million in 2005, concentrated in Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia. Addressing the root causes of marginality is needed to effectively reduce extreme poverty.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Zentrum für Entwicklungsforschung
Center for Development Research
University of Bonn
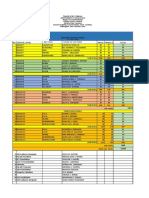
Marginality: Addressing the Root Causes
of Extreme Poverty
What is the Problem?
Although there has been progress in reducing the number of poor at the global
Poor living on less than 1.25$/day
level, especially those just below the income poverty line of about 1$/day, pro-
1,373 million in 2005
gress for the poorest has been slowest. The ultra-poor, those living from less than
63 cents/day have reached 223 million in 2005.
East Asia & Pacific Europe &
Sub- Central Asia The poorest are becoming increasingly concentrated in Sub-Saharan Africa and
23% 1%
Saharan South Asia.
Africa Latin America
& the Caribbean Poverty and widespread hunger remain even in regions that have experienced
28% 3%
rapid economic growth and substantial reductions in poverty.
Middle East &
North Africa
Whereas the number of urban poor is increasing rapidly, the poor are still predo-
South Asia
1% minantly rural.
Poverty and hunger reduction has been slower among the poorest and among
44%
excluded groups—ethnic minorities, disadvantaged people, and the disabled—
Data: Ahmed, A. 2011 causing poverty and hunger to be increasingly concentrated in these groups.
What is marginality? Who are the marginalized poor?
Marginality is an involuntary position and The marginalized poor are those
condition of an individual or group at the who are affected by both margi-
margins of social, political, economic, nalization and poverty. Findings to
ecological and biophysical systems, pre- date show that there is a correla-
venting them from access to resources, tion between remoteness, exclusi-
assets, services, restraining freedom of Poor but not Marginalized on and extreme poverty and that
Marginalized
choice, preventing the development marginalized and poor
but not poor the incidence of extreme poverty
of capabilities, and eventually causing and food insecurity is concentrated
extreme poverty. in remote rural areas. In addition,
The poorest themselves have descri- the poorest often belong to ethnic
bed their situation as being trapped in a minorities and socially excluded
“complex knot which can lead to further groups.
knots if the wrong threads are pulled.”
What can be done to reduce marginality ?
Marginality is an involuntary position and condition of an individual or group
at the margins of social, political, economic, ecological and biophysical
systems, preventing them from access to resources, assets, services, res-
training freedom of choice, preventing the development of capabilities,
and eventually causing extreme poverty.
The poorest themselves have described their situation as being trapped
in a “complex knot which can lead to further knots if the wrong threads
are pulled.”
Graw, V. et al. 2011
Learn more: Contact:
Dr. Franz W. Gatzweiler
http://www.zef.de/margip.html Center for Development Research, ZEF Bonn
Walter-Flex-Straße 3
53113 Bonn
gatzweiler@uni-bonn.de
You might also like
- Invoice 22447496600191 PDFDocument1 pageInvoice 22447496600191 PDFaqilNo ratings yet
- Intro-to-World-Religions-Belief-Systems - Q1 - Week1 For TeacherDocument21 pagesIntro-to-World-Religions-Belief-Systems - Q1 - Week1 For TeacherFobe Lpt Nudalo75% (4)
- Intro To World Religions Belief Systems Q1 Week2 For StudentDocument24 pagesIntro To World Religions Belief Systems Q1 Week2 For StudentFobe Lpt Nudalo100% (1)
- 9 Grade Social Studies Curriculum: World History Unit 1: Introduction To World History 3 Days WH9.1, WH9.8 Essential Biblical Worldview QuestionsDocument29 pages9 Grade Social Studies Curriculum: World History Unit 1: Introduction To World History 3 Days WH9.1, WH9.8 Essential Biblical Worldview QuestionsFobe Lpt NudaloNo ratings yet
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument7 pagesReview of Related LiteratureRhoxette Pedroza81% (27)
- POVERTYDocument46 pagesPOVERTYCreistel KhayNo ratings yet
- Poverty As A ChallengeDocument3 pagesPoverty As A ChallengeAdarsh Ahlawat 8D snowdropNo ratings yet
- Poverty in India: Chapter OutlineDocument8 pagesPoverty in India: Chapter OutlineRuhani AroraNo ratings yet
- Poverty in PerspectiveDocument3 pagesPoverty in PerspectiveTRI TRANNo ratings yet
- Designing Water Supply and Sanitation Projects To Meet Demand in Rural and Peri-Urban Communities, Book III Ensuring The Participation of The PoorDocument17 pagesDesigning Water Supply and Sanitation Projects To Meet Demand in Rural and Peri-Urban Communities, Book III Ensuring The Participation of The PoorSami QaddouraNo ratings yet
- SSE 208 PovertyDocument4 pagesSSE 208 PovertyjhazminlhiasNo ratings yet
- Poverty As A Challenge - Part IDocument3 pagesPoverty As A Challenge - Part ISjhababkkNo ratings yet
- WB Rural PovertyDocument4 pagesWB Rural PovertyurbanmisfitNo ratings yet
- Ethics PPT FinalsDocument10 pagesEthics PPT FinalsErica BorlagdanNo ratings yet
- Reality of PovertyDocument10 pagesReality of PovertyMuthu VezhappanNo ratings yet
- International Conference Gender, 2022Document15 pagesInternational Conference Gender, 2022Edy PurnomoNo ratings yet
- (Slideshare Downloader La) 62b699ee63400 8571656151105149Document15 pages(Slideshare Downloader La) 62b699ee63400 8571656151105149Harsh sahuNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart Chapter 3Document1 pageFlow Chart Chapter 3Dark DevilNo ratings yet
- Econdev Shit Lec5 8Document31 pagesEcondev Shit Lec5 8Franck Jeremy MoogNo ratings yet
- Poverty in AfricaDocument12 pagesPoverty in AfricaIdé Salifou AbdourahamaneNo ratings yet
- Poverty As A Challenge 9TH Class EconomicsDocument38 pagesPoverty As A Challenge 9TH Class EconomicsBlack and whiteNo ratings yet
- Midterm Religious Education B: - SJS Academic TeamDocument21 pagesMidterm Religious Education B: - SJS Academic TeamChristian Luis De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- OPHIBrief40 Africa EnglDocument8 pagesOPHIBrief40 Africa EnglMvelako StoryNo ratings yet
- Gender and PovertyDocument6 pagesGender and PovertyOxfamNo ratings yet
- Gender and PovertyDocument6 pagesGender and PovertyOxfamNo ratings yet
- Gender and PovertyDocument6 pagesGender and PovertyOxfamNo ratings yet
- Gender and PovertyDocument6 pagesGender and PovertyOxfamNo ratings yet
- Gender and PovertyDocument6 pagesGender and PovertyOxfamNo ratings yet
- Gender and PovertyDocument6 pagesGender and PovertyOxfamNo ratings yet
- Gender and PovertyDocument6 pagesGender and PovertyOxfamNo ratings yet
- Gender and PovertyDocument6 pagesGender and PovertyOxfamNo ratings yet
- Gender and PovertyDocument6 pagesGender and PovertyOxfamNo ratings yet
- Gender and PovertyDocument6 pagesGender and PovertyOxfamNo ratings yet
- Gender and PovertyDocument6 pagesGender and PovertyOxfamNo ratings yet
- Gender and PovertyDocument6 pagesGender and PovertyOxfamNo ratings yet
- Gender and PovertyDocument6 pagesGender and PovertyOxfamNo ratings yet
- Gender and PovertyDocument6 pagesGender and PovertyOxfamNo ratings yet
- Gender and PovertyDocument6 pagesGender and PovertyOxfamNo ratings yet
- Gender and PovertyDocument6 pagesGender and PovertyOxfamNo ratings yet
- Gender and PovertyDocument6 pagesGender and PovertyOxfamNo ratings yet
- Week 21: Final PR Oduct: CR Eate y Our Graphic Organiserabouttheproblem:povertyDocument2 pagesWeek 21: Final PR Oduct: CR Eate y Our Graphic Organiserabouttheproblem:povertyMaricieloNo ratings yet
- Growing Backwards: Growth in Concentrated Poverty Signals Increasing Levels of Economic, Racial Segregation PUBLISHED APRIL 13, 2018Document10 pagesGrowing Backwards: Growth in Concentrated Poverty Signals Increasing Levels of Economic, Racial Segregation PUBLISHED APRIL 13, 2018CP TewNo ratings yet
- Long Matrix Reformatted From Manifesto 16 AprilDocument18 pagesLong Matrix Reformatted From Manifesto 16 AprilAnonymous mvGv6v4QNo ratings yet
- Yecondev - Module 5Document4 pagesYecondev - Module 5wktxlsrkfNo ratings yet
- Environmental ScienceDocument18 pagesEnvironmental ScienceNeval MulchansinghNo ratings yet
- Urban Poverty and Vulnerability in Kenya: The Urgent Need For Co-Ordinated Action To Reduce Urban PovertyDocument8 pagesUrban Poverty and Vulnerability in Kenya: The Urgent Need For Co-Ordinated Action To Reduce Urban PovertyOxfamNo ratings yet
- Econdev 007Document9 pagesEcondev 007Kim Maxene GarciaNo ratings yet
- GF 643 Reducing PovertyDocument5 pagesGF 643 Reducing PovertyTowardinho14No ratings yet
- PovertyDocument19 pagesPovertyM S AthiraNo ratings yet
- The Contemporar y World: Countries ReasonsDocument3 pagesThe Contemporar y World: Countries Reasonsravelyn bresNo ratings yet
- (2015) - Most Unequal On EarthDocument3 pages(2015) - Most Unequal On Earthpeneliti danadesaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Culprits Behind Vaniashing - C - 02july2017Document32 pagesModule 4 Culprits Behind Vaniashing - C - 02july2017Elisha Anne SumilangNo ratings yet
- ASA Challenge: PovertyDocument38 pagesASA Challenge: PovertyaarghjNo ratings yet
- ISSUE BRIEF Ending Poverty by 2030Document5 pagesISSUE BRIEF Ending Poverty by 2030AKHIL H KRISHNANNo ratings yet
- Poverty in IndiaorignalDocument28 pagesPoverty in IndiaorignalShoeb IqbalNo ratings yet
- ECON POVERTY POSTER V02 LiaDocument1 pageECON POVERTY POSTER V02 LiaLia Martinez LeNo ratings yet
- ADR15 Chapter 4Document28 pagesADR15 Chapter 4Hub ErsNo ratings yet
- Lectures 5 - Dev Econ - Poverty and InequalityDocument39 pagesLectures 5 - Dev Econ - Poverty and InequalityStephen GubatanaNo ratings yet
- Poverty AsachallengeDocument3 pagesPoverty Asachallengemission.iist.1No ratings yet
- Conworld FinalsDocument4 pagesConworld FinalsRav VengerNo ratings yet
- Unmasking The Shadows of PovertyDocument11 pagesUnmasking The Shadows of Povertyaaravkumar30082010No ratings yet
- PovertyDocument12 pagesPovertyKhushal JainNo ratings yet
- Impact of Poverty On The Society - The Borgen ProjectDocument4 pagesImpact of Poverty On The Society - The Borgen ProjectjewaxaticNo ratings yet
- BC20203 - Group AssignmentDocument18 pagesBC20203 - Group AssignmentYONG LI CHANG BB20110473No ratings yet
- Cabonga An NHS - Organization of Classes S.Y. 2021 2022Document2 pagesCabonga An NHS - Organization of Classes S.Y. 2021 2022Fobe Lpt NudaloNo ratings yet
- Mount Moriah College: Mabini, Poro, Cebu 6049, PhilippinesDocument4 pagesMount Moriah College: Mabini, Poro, Cebu 6049, PhilippinesFobe Lpt NudaloNo ratings yet
- Social Science and Philosophy M6Document13 pagesSocial Science and Philosophy M6Fobe Lpt NudaloNo ratings yet
- The Problem and Its Research Design Rationale of The StudyDocument35 pagesThe Problem and Its Research Design Rationale of The StudyFobe Lpt NudaloNo ratings yet
- Social Science and Philosophy M5Document10 pagesSocial Science and Philosophy M5Fobe Lpt NudaloNo ratings yet
- AP 101 SyllabusDocument8 pagesAP 101 SyllabusFobe Lpt NudaloNo ratings yet
- Building Bridges Across Social Science Discipline 2021-2022 MIDTERM EXAMDocument2 pagesBuilding Bridges Across Social Science Discipline 2021-2022 MIDTERM EXAMFobe Lpt NudaloNo ratings yet
- Shscorephilo 1Document6 pagesShscorephilo 1Fobe Lpt NudaloNo ratings yet
- List of G12-Candidates For Graduation Sy: 2020-2021Document6 pagesList of G12-Candidates For Graduation Sy: 2020-2021Fobe Lpt NudaloNo ratings yet
- PPG La Union Module 12Document18 pagesPPG La Union Module 12Fobe Lpt NudaloNo ratings yet
- UPVM-Social Science 1Document4 pagesUPVM-Social Science 1Fobe Lpt NudaloNo ratings yet
- Philippine Politics and Governance: Quarter 2Document19 pagesPhilippine Politics and Governance: Quarter 2Fobe Lpt NudaloNo ratings yet
- PPG La Union Module 11Document15 pagesPPG La Union Module 11Fobe Lpt NudaloNo ratings yet
- University of Cebu (Main Campus) Graduate School 2020-2021 First 22 October 2021Document7 pagesUniversity of Cebu (Main Campus) Graduate School 2020-2021 First 22 October 2021Fobe Lpt NudaloNo ratings yet
- Attendance Distribution of Module 2021Document9 pagesAttendance Distribution of Module 2021Fobe Lpt NudaloNo ratings yet
- Philippine Politics and Governance: Quarter 2Document23 pagesPhilippine Politics and Governance: Quarter 2Fobe Lpt NudaloNo ratings yet
- Intro. To World Region Week 6 v1Document10 pagesIntro. To World Region Week 6 v1Fobe Lpt NudaloNo ratings yet
- Introduction To World Religion and Belief System 12Document11 pagesIntroduction To World Religion and Belief System 12Fobe Lpt NudaloNo ratings yet
- Philippine Politics and Governance: Quarter 2Document21 pagesPhilippine Politics and Governance: Quarter 2Fobe Lpt Nudalo100% (1)
- Intro T World Reigion Q3 WEEK6 V.3Document15 pagesIntro T World Reigion Q3 WEEK6 V.3Fobe Lpt NudaloNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Philippine Politics and GovernanceDocument9 pagesEvolution of Philippine Politics and GovernanceFobe Lpt NudaloNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Intro. To World Religion-1Document23 pagesWeek 2 - Intro. To World Religion-1Fobe Lpt Nudalo100% (1)
- Cgtmse (Credit Guarantee Fund Trust For Micro & Small Enterprises)Document16 pagesCgtmse (Credit Guarantee Fund Trust For Micro & Small Enterprises)Abinash MandilwarNo ratings yet
- Role of NGOs in The Promotion of EducationDocument5 pagesRole of NGOs in The Promotion of EducationnrsiddiquipkNo ratings yet
- Click On Subject & Download: 1 PUC - Commerce SolutionsDocument3 pagesClick On Subject & Download: 1 PUC - Commerce SolutionsBasavaraj GudadarNo ratings yet
- BS-EN 12504-1 Cored Specimen PDFDocument12 pagesBS-EN 12504-1 Cored Specimen PDFArisan IqmaNo ratings yet
- IDX Annually 2007 PDFDocument112 pagesIDX Annually 2007 PDFDodi HeruNo ratings yet
- Somalia FishDocument22 pagesSomalia FishOmar AwaleNo ratings yet
- David Einhorn's Greenlight Capital Q3 LetterDocument5 pagesDavid Einhorn's Greenlight Capital Q3 Lettermarketfolly.com100% (1)
- Notes For The Teacher: Chapter 4: Globalisation and The Indian EconomyDocument20 pagesNotes For The Teacher: Chapter 4: Globalisation and The Indian EconomyjoeraNo ratings yet
- This Time Is Different Eight Centuries of FinancialDocument21 pagesThis Time Is Different Eight Centuries of FinancialTanush Lokhande allmytNo ratings yet
- Play School ProposalDocument13 pagesPlay School ProposalTansen schoolNo ratings yet
- Tabela de Similaridade de Lubrificantes IndustriaisDocument2 pagesTabela de Similaridade de Lubrificantes IndustriaisSandro RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Estimated Out-of-Pocket Expenses: Mississippi State University Travel Advance RequestDocument1 pageEstimated Out-of-Pocket Expenses: Mississippi State University Travel Advance Requestuthmankheil89No ratings yet
- S1-17-Mba ZC416-L16Document43 pagesS1-17-Mba ZC416-L16AbiNo ratings yet
- Synergy International LC Partnership Proposal and Official ContractDocument6 pagesSynergy International LC Partnership Proposal and Official Contractapi-3826017100% (2)
- Basic Marketing Individual AssignmentDocument7 pagesBasic Marketing Individual Assignmentzakaria dholey100% (2)
- Imma Rswp-Final WebDocument94 pagesImma Rswp-Final WebvivekpattniNo ratings yet
- Eurekahedge Report - March 2017Document45 pagesEurekahedge Report - March 2017Mon Sour CalaunanNo ratings yet
- 30 Rules To Master Swing TradingDocument1 page30 Rules To Master Swing TradingPower of Stock MarketNo ratings yet
- Jackson Pettigrew Presentation 1221Document15 pagesJackson Pettigrew Presentation 1221SarahNo ratings yet
- TV M AssignmentDocument2 pagesTV M AssignmentAnn Marie San MiguelNo ratings yet
- ISI-Entrance Solutions: EconomicsDocument4 pagesISI-Entrance Solutions: Economicsparas hasijaNo ratings yet
- J-1203 April 2019 PDFDocument1 pageJ-1203 April 2019 PDFRohtash SinghNo ratings yet
- PrinticomDocument7 pagesPrinticomAK0% (1)
- Treasury BillsDocument11 pagesTreasury BillspoojaNo ratings yet
- Job Coaching For All MNC Caal 9908701362Document7 pagesJob Coaching For All MNC Caal 9908701362balki123No ratings yet
- DMDMDocument3 pagesDMDMclaryntafreyaaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3Document14 pagesQuiz 3Jyasmine Aura V. AgustinNo ratings yet
- Supreme Planners: Activity PlannerDocument14 pagesSupreme Planners: Activity Plannerjeffrey chua100% (1)