Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Handouts (Jean Piaget) (Personal Development)
Handouts (Jean Piaget) (Personal Development)
Uploaded by
CyberR.DomingoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Handouts (Jean Piaget) (Personal Development)
Handouts (Jean Piaget) (Personal Development)
Uploaded by
CyberR.DomingoCopyright:
Available Formats
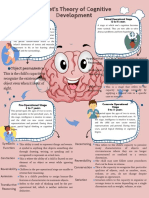
Jean Piaget’s Cognitive Theory of Development understand or
know something
Three Basic Components of Piaget's Cognitive Theory: without any
1. Schema/s reasoning process)
2. Adaptation Processes (equilibration, assimilation, and
Symbolic
accommodation)
3. Stages of Cognitive Development Thinking is the use
of words, gestures,
Schema/s 1. an organized pattern of thoughts that pictures, or actions
establishes a mental framework that represents some to represent ideas,
aspect of the world. things, or
-We develop schemas for all types of items and activities. behaviors.
From simple items such as a chair, a car, fish, bird or Intellectual
house. To complex like the chemical bonds between development in
atoms or the seating in the House of Representatives. this stage is
-also called as “unit of knowledge”. demonstrated
through the use of
Adaptation Processes: Concrete- logical and
Operational 7 to 11 years systematic
Assimilation 1. Using an existing schema to deal with a Stage manipulation of
new object or situation. Your knowledge about the world symbols, which
or general knowledge. are related to
concrete objects.
Accommodation 2. Happens when the existing schema or Thinking becomes
knowledge does not work, so you need to changed it to less ego-centric.
deal with a new object or situation. The period from
2 Parts of Equilibration adolescence
Equilibrium occurs when a child’s schemas can deal with through adulthood
most new information through assimilation. While The child is no
Disequilibrium occurs when new information cannot be longer dependent
filled with existing schemas. on concrete
personal
experiences in the
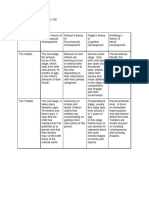
Stages of Cognitive Development present. In dealing
with situations, the
Stages Period Descriptions
past or the future
Knowledge is Starts to
can be a reference
limited Formal emerge
to know what to do.
Infants cannot Operational between 11
Able to analyze
predict reaction, Stage to 15 years
problems, and
they must learn of age
consider different
through trial and
ways of solving it
error.
in a systematic
The main way.
development
Can deal with
Sensorimotor From birth during this stage is
abstract or
Stage to 2 years the understanding
hypothetical
that objects exist
situations and
and events occur
generate ideas
in the world
about it through
independently of
logical thinking.
one's own actions.
Criticisms:
Object
Permanence means Piaget underestimated the abilities of children
knowing that an because his tests were confusing or difficult to
object still exists, understand. He failed to distinguish between
even if it is hidden. competence (what a child is capable of doing) and
In this stage, the performance (what a child can show when given a
children’s way of particular task) When tasks were altered,
thinking and performance (and therefore competence) was
intelligence is affected.
egocentric
Sensorimotor From 2 to 7
(thinking only of
Stage years
oneself) It is all
about him or
herself.
Intuition (having
the ability to
You might also like
- HX-2600 Manual ENDocument16 pagesHX-2600 Manual ENJosé PérezNo ratings yet
- "2040" Documentary Name: - : Viewing QuestionsDocument3 pages"2040" Documentary Name: - : Viewing Questionsapi-562285277No ratings yet
- Dimitra Fimi. Tolkien, Race and Cultural History From Fairies ToDocument4 pagesDimitra Fimi. Tolkien, Race and Cultural History From Fairies Tomadeehamaqbool736250% (4)
- SAP BW Business Blueprint Step by Step GuideDocument33 pagesSAP BW Business Blueprint Step by Step Guidekavya.nori0% (1)
- Network Security - 3.4) The Following Ciphertext Wa...Document3 pagesNetwork Security - 3.4) The Following Ciphertext Wa...Zeeshan Khan100% (1)
- Piaget's Theory of Cognitive Development TasksDocument2 pagesPiaget's Theory of Cognitive Development TasksRozechele LlandelarNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Development TheoryDocument31 pagesCognitive Development TheorychionNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Developmental TheoryDocument3 pagesCognitive Developmental TheoryMaribel Pascual FloresNo ratings yet
- Blue Main Idea Graphic Organizer (21 X 27.94 CM)Document1 pageBlue Main Idea Graphic Organizer (21 X 27.94 CM)jasmin agaranNo ratings yet
- ESD 1100 Topic 3 Online Lecture 2018Document46 pagesESD 1100 Topic 3 Online Lecture 2018murse101No ratings yet
- Stages of DevelopmentDocument3 pagesStages of Developmentmaria mercedesNo ratings yet
- Theory ToolkitDocument20 pagesTheory ToolkitAngel TNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Part 2 Learning GuideDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Part 2 Learning GuideXzandria WellsNo ratings yet
- Didactics ExamDocument11 pagesDidactics Exammaria fernanada GiraldoNo ratings yet
- Piaget's Theory of Cognitive DevelopmentDocument12 pagesPiaget's Theory of Cognitive DevelopmentAlisya Saraswati SjamtotoNo ratings yet
- COGNITIVE DevelopmentDocument4 pagesCOGNITIVE DevelopmentvanmusiciantvNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Facilitating Learner-Centered TeachingDocument5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Facilitating Learner-Centered TeachingRuchee PolsNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 ReviewDocument19 pagesUnit 6 Reviewsindhuja.sajjaNo ratings yet
- Educ 1Document3 pagesEduc 1John Carl AparicioNo ratings yet
- Development Stages of One's LifeDocument15 pagesDevelopment Stages of One's LifeJenny CariagaNo ratings yet
- Quiz Kay PiagetDocument2 pagesQuiz Kay PiagetGene Lloyd NacorNo ratings yet
- Milestone of Child Development PiagetDocument1 pageMilestone of Child Development PiagetTheva TharshiniNo ratings yet
- PiagetDocument5 pagesPiagetMhoer CoertibNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - PiagetDocument43 pagesLecture 2 - PiagetsofiaNo ratings yet
- GE 1 - 7 - Cognitive Development Theory X Personality Traits TheoryDocument3 pagesGE 1 - 7 - Cognitive Development Theory X Personality Traits TheoryJarixa BalbuenaNo ratings yet
- Piaget Psychology Assignmet Alomo GataDocument31 pagesPiaget Psychology Assignmet Alomo GataYussif AyikuNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 PART 2 Cognitive DevelopmentDocument30 pagesMODULE 2 PART 2 Cognitive DevelopmentJohn Brad Angelo LacuataNo ratings yet
- Cognitive DevelopmentDocument11 pagesCognitive Developmentgiadocallas24No ratings yet
- Piaget and NeoPiagetianDocument5 pagesPiaget and NeoPiagetianRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Appendix CDocument2 pagesAppendix CTimothy CochranNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: Topic: Piaget's Stages of Cognitive DevelopmentDocument2 pagesActivity 1: Topic: Piaget's Stages of Cognitive DevelopmentCrislie CaibiganNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Development: Reporter: Jelina C. SodosoDocument8 pagesCognitive Development: Reporter: Jelina C. SodosoAngelica Sulay BalaodNo ratings yet
- Jean Piaget's Cognitive Developmental StageDocument17 pagesJean Piaget's Cognitive Developmental Stagejohn kevin laurenoNo ratings yet
- Piaget Vygotsky TheoryDocument50 pagesPiaget Vygotsky TheoryJenniemaepudangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2EP 4-2020Document64 pagesChapter 2EP 4-2020Thư Nguyễn AnhNo ratings yet
- Piaget's Theory of Cognitive DevelopmentDocument32 pagesPiaget's Theory of Cognitive DevelopmentrheburgessNo ratings yet
- Theories of Cognitive Development Jean PiagetDocument6 pagesTheories of Cognitive Development Jean PiagetArtclaude AquinoNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged (1) MergedDocument126 pagesIlovepdf Merged (1) Mergedlaia bustamanteNo ratings yet
- Note That The Notebook Includes Active Links To Some of The Resources, I.E. Videos, Graphic Organizers, Practice QuestionsDocument5 pagesNote That The Notebook Includes Active Links To Some of The Resources, I.E. Videos, Graphic Organizers, Practice QuestionsMichaelNo ratings yet
- Cpe100 - XX Group 2 (Handouts)Document3 pagesCpe100 - XX Group 2 (Handouts)Hazema Gaguil Amid CamamaNo ratings yet
- COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT JEAN PIAGET by Edrica PascualDocument16 pagesCOGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT JEAN PIAGET by Edrica PascualEdrica Pascual100% (1)
- Document 6Document4 pagesDocument 6Sumbal MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Name of Theory and Its ProponentDocument25 pagesName of Theory and Its ProponentJohnwel Magpayo AñabezaNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Development TheoriesDocument50 pagesCognitive Development TheoriesNatcon ProductionsNo ratings yet
- Group 3 (Jean Piaget's Cognitive Developmental Theory)Document16 pagesGroup 3 (Jean Piaget's Cognitive Developmental Theory)Jasmine LopezNo ratings yet
- Development Psychology - Chapter 5 (Santrock)Document88 pagesDevelopment Psychology - Chapter 5 (Santrock)Shaine C.No ratings yet
- Educ 311: Facilitating Learner-Centered Teaching: Piaget'S Cognitive Development TheoryDocument44 pagesEduc 311: Facilitating Learner-Centered Teaching: Piaget'S Cognitive Development TheoryLeah Lorenzana MalabananNo ratings yet
- FL Module - Cognitive Learning Theories - PIAGET ContentDocument5 pagesFL Module - Cognitive Learning Theories - PIAGET ContentJeyden BaguiNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Piagets Cognitive DevelopmentDocument17 pagesModule 6 Piagets Cognitive DevelopmentLeonard JohnNo ratings yet
- Management and Learning ProcessDocument11 pagesManagement and Learning Processcarlos hernan ramirez poloNo ratings yet
- Piaget's Stages of Cognitive Development: EquilibrationDocument2 pagesPiaget's Stages of Cognitive Development: EquilibrationJohn Harold CastroNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Child and AdolescentsDocument27 pagesModule 6 - Child and AdolescentsPing Garcia Arandia100% (1)
- Developmental PsychologyDocument3 pagesDevelopmental PsychologyMae OponNo ratings yet
- PL100 Block 2 Study GuideDocument17 pagesPL100 Block 2 Study GuidepwoerNo ratings yet
- Piaget'sDocument9 pagesPiaget'spedelalpandey90No ratings yet
- Perspective Theories Proponents Key Concepts Strengths WeaknessDocument4 pagesPerspective Theories Proponents Key Concepts Strengths WeaknessMiles NawalNo ratings yet
- Module 8-Piaget's Stages of Cognitive DevelopmentDocument11 pagesModule 8-Piaget's Stages of Cognitive Developmentrushy121100% (1)
- Axia College Material: Appendix CDocument4 pagesAxia College Material: Appendix CCHAKCHACKNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument4 pagesUntitled DocumentsustiguerchristianpaulNo ratings yet
- HCI Assignment 2 Divyashree Jadeja AU2040261 PDFDocument5 pagesHCI Assignment 2 Divyashree Jadeja AU2040261 PDFdivyashree jadejaNo ratings yet
- Physical, Cognitive, and Psychosocial Development in Young AdulthoddDocument3 pagesPhysical, Cognitive, and Psychosocial Development in Young AdulthoddideonellathebacteriaNo ratings yet
- Piaget'S Stages of Cognitive DevelopmentDocument34 pagesPiaget'S Stages of Cognitive DevelopmentChristyMae DelaCruzNo ratings yet
- How to Study and Understand Anything: Discovering The Secrets of the Greatest Geniuses in HistoryFrom EverandHow to Study and Understand Anything: Discovering The Secrets of the Greatest Geniuses in HistoryRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Peer Evaluation - PS 1 - Res 1Document1 pagePeer Evaluation - PS 1 - Res 1CyberR.DomingoNo ratings yet
- Why Study Structure of Crystalline SolidsDocument1 pageWhy Study Structure of Crystalline SolidsCyberR.DomingoNo ratings yet
- Materials Around Me (Write Up)Document9 pagesMaterials Around Me (Write Up)CyberR.DomingoNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Output Waves of The Voltages (SERIES) Series Voltage Schematic GraphDocument2 pagesDiscuss The Output Waves of The Voltages (SERIES) Series Voltage Schematic GraphCyberR.DomingoNo ratings yet
- Exp5 The Green Minded 3735Document16 pagesExp5 The Green Minded 3735CyberR.DomingoNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Introduction To Process Safety EngineeringDocument33 pagesMODULE 1 Introduction To Process Safety EngineeringCyberR.DomingoNo ratings yet
- Che3261 - Domingo, Duran, Fernandez - Midterm-AssignmentDocument5 pagesChe3261 - Domingo, Duran, Fernandez - Midterm-AssignmentCyberR.DomingoNo ratings yet
- Che3261 Duran Midterm-AssignmentDocument5 pagesChe3261 Duran Midterm-AssignmentCyberR.DomingoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - Fluid Mechanics: Thursday, March 24Document19 pagesChapter 15 - Fluid Mechanics: Thursday, March 24CyberR.DomingoNo ratings yet
- September, 06 2020 QR Code: Egov:Baguio - Health Declaration Form Egov:Baguio - HDFDocument1 pageSeptember, 06 2020 QR Code: Egov:Baguio - Health Declaration Form Egov:Baguio - HDFCyberR.DomingoNo ratings yet
- Domingo, Cyber R. (Evaluate 1)Document1 pageDomingo, Cyber R. (Evaluate 1)CyberR.DomingoNo ratings yet
- Butane:: It Is A Mixture of Different ChemicalsDocument4 pagesButane:: It Is A Mixture of Different ChemicalsCyberR.DomingoNo ratings yet
- CFE NotesDocument2 pagesCFE NotesCyberR.DomingoNo ratings yet
- GlobalizationDocument1 pageGlobalizationCyberR.DomingoNo ratings yet
- Pol 1101 Syllabus Spring 2020Document11 pagesPol 1101 Syllabus Spring 2020bennyNo ratings yet
- Microwave: LAB ReportDocument14 pagesMicrowave: LAB Reportmakhzom alshhumiNo ratings yet
- Thesis Statement Cafeteria FoodDocument7 pagesThesis Statement Cafeteria Foodafbwszvft100% (1)
- Fbidoj ComplaintDocument7 pagesFbidoj ComplaintPennLiveNo ratings yet
- Songs To Practice Advent SG Masses 2013Document4 pagesSongs To Practice Advent SG Masses 2013Ronaldo BulanNo ratings yet
- Oracle® Territory Manager: User Guide Release 12.1Document80 pagesOracle® Territory Manager: User Guide Release 12.1Marcelo MestiNo ratings yet
- Perception of Hostel StudentsDocument6 pagesPerception of Hostel StudentsKhairul Hazwan100% (3)
- Le CorbusierDocument21 pagesLe CorbusierAbhishek GandhiNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test Untuk Siswa Baru Kelas ViiDocument2 pagesDiagnostic Test Untuk Siswa Baru Kelas ViiZendy PradiktaNo ratings yet
- Final Asian StudiesDocument9 pagesFinal Asian StudiesRazel G. TaquisoNo ratings yet
- APS ThinsulatorsDocument3 pagesAPS ThinsulatorsBobbie RuckNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence in The Insurance SectorDocument13 pagesArtificial Intelligence in The Insurance SectorSupratim DattaNo ratings yet
- Private Complaint - 498aDocument37 pagesPrivate Complaint - 498aVijay Vardhan Kudari100% (1)
- Pile CapDocument44 pagesPile Capbhavik modiNo ratings yet
- Absolute AdvantageDocument3 pagesAbsolute AdvantageSana KaNo ratings yet
- Panda by Svetlana Maksimenko EngDocument12 pagesPanda by Svetlana Maksimenko Engcarolina MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Scientific Method Test Study Guide2Document4 pagesScientific Method Test Study Guide2Gabriel TaylorNo ratings yet
- Siva Stuti SanskritDocument374 pagesSiva Stuti SanskritDurgavenkat LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Anang Yanuar Ramadhan - B1B015015 - Acara 2 (Prelab) - Identifikasi Karakter Taksonomi VertebrataDocument9 pagesAnang Yanuar Ramadhan - B1B015015 - Acara 2 (Prelab) - Identifikasi Karakter Taksonomi VertebrataAnang Yanuar RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Classroom Ppa MathDocument2 pagesClassroom Ppa MathJaime DailegNo ratings yet
- Defining The Parameters of Loading of Concrete BridgesDocument8 pagesDefining The Parameters of Loading of Concrete BridgesAmy Aidara JahNo ratings yet
- Production Planning and Control (Uninterruptable Power Supply)Document6 pagesProduction Planning and Control (Uninterruptable Power Supply)zesleyNo ratings yet
- Critical Book Report Written Language SkillDocument13 pagesCritical Book Report Written Language SkillMeysy Silvia SembiringNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Bonding Powerpoint AP ChemDocument68 pagesChapter 8 Bonding Powerpoint AP ChemAbdul jan sultaniNo ratings yet
- PM Debug InfoDocument88 pagesPM Debug InfoanaguadalupemendozaortizNo ratings yet