Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eigen Decomposition 2
Eigen Decomposition 2
Uploaded by
Miguel Angel Fernandez Pinedo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageThe document defines eigenvectors and eigenvalues. An eigenvector of a matrix A is a vector u that satisfies the equation Au = λu, where λ is the scalar eigenvalue associated with that eigenvector. Put simply, an eigenvector is a vector whose length and direction are unchanged when multiplied by the matrix, except for being scaled by the eigenvalue. The document provides an example matrix and finds its eigenvectors.
Original Description:
Eigen Decomposition 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document defines eigenvectors and eigenvalues. An eigenvector of a matrix A is a vector u that satisfies the equation Au = λu, where λ is the scalar eigenvalue associated with that eigenvector. Put simply, an eigenvector is a vector whose length and direction are unchanged when multiplied by the matrix, except for being scaled by the eigenvalue. The document provides an example matrix and finds its eigenvectors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageEigen Decomposition 2
Eigen Decomposition 2
Uploaded by
Miguel Angel Fernandez PinedoThe document defines eigenvectors and eigenvalues. An eigenvector of a matrix A is a vector u that satisfies the equation Au = λu, where λ is the scalar eigenvalue associated with that eigenvector. Put simply, an eigenvector is a vector whose length and direction are unchanged when multiplied by the matrix, except for being scaled by the eigenvalue. The document provides an example matrix and finds its eigenvectors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
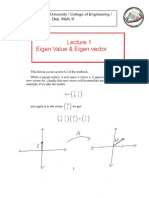
Hervé Abdi: The Eigen-Decomposition
Au 1
8
u1 u2 1
2 1
3 12 -1
-1 Au 2
a b
Figure 1: Two eigenvectors of a matrix.
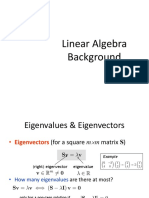
2 Notations and definition
There are several ways to define eigenvectors and eigenvalues, the
most common approach defines an eigenvector of the matrix A as
a vector u that satisfies the following equation:
Au = λu . (1)
when rewritten, the equation becomes:
(A − λI)u = 0 , (2)
where λ is a scalar called the eigenvalue associated to the eigenvec-
tor.
In a similar manner, we can also say that a vector u is an eigen-
vector of a matrix A if the length of the vector (but not its direction)
is changed when it is multiplied by A.
For example, the matrix:
· ¸
2 3
A= (3)
2 1
has the eigenvectors:
· ¸
3
u1 = with eigenvalue λ1 = 4 (4)
2
You might also like
- The Seatbelts - Sax Quartet - Cowbow Bebop-Partitura - y - Partes (Arrastrado) 3Document1 pageThe Seatbelts - Sax Quartet - Cowbow Bebop-Partitura - y - Partes (Arrastrado) 3Miguel Angel Fernandez PinedoNo ratings yet
- Eigen Decomposition 4Document1 pageEigen Decomposition 4Miguel Angel Fernandez PinedoNo ratings yet
- Dana Mackey (DIT) : Numerical Methods IIDocument30 pagesDana Mackey (DIT) : Numerical Methods IIThe Future of EthiopiaNo ratings yet
- Math 312 Supplemental Notes Finding Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors of 2 × 2 MatricesDocument3 pagesMath 312 Supplemental Notes Finding Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors of 2 × 2 MatricesAmmarNo ratings yet
- 1 Bài Tập Về Chéo Hóa Tự Đồng CấuDocument4 pages1 Bài Tập Về Chéo Hóa Tự Đồng CấuNguyễn Phương GiangNo ratings yet
- Eigenvectors AHPDocument13 pagesEigenvectors AHPAliNo ratings yet
- Module2 ADDE (MAT2002)Document27 pagesModule2 ADDE (MAT2002)GURU PRASATHNo ratings yet
- Diagonalisation: ReadingDocument15 pagesDiagonalisation: ReadingKaneNo ratings yet
- Slides7 31Document12 pagesSlides7 31Alibert Luna PalominoNo ratings yet
- TutorialMatrices3 - With AnswersDocument3 pagesTutorialMatrices3 - With AnswersLexNo ratings yet
- Module 3 MatDocument14 pagesModule 3 MatReshmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 23Document11 pagesLecture 23filemina.gjuziNo ratings yet
- Notes On Eigenvalues 1Document9 pagesNotes On Eigenvalues 1Vivian BiryomumaishoNo ratings yet
- Changing Variables.: LS.4 Decoupling SystemsDocument5 pagesChanging Variables.: LS.4 Decoupling SystemsshankyforuNo ratings yet
- 01 SupplementDocument3 pages01 SupplementYun ShangNo ratings yet
- Mit18 06scf11 Ses2.9sumDocument4 pagesMit18 06scf11 Ses2.9sumsmithap_ullalNo ratings yet
- Lie GroupDocument5 pagesLie GroupmaplebrandishNo ratings yet
- Application of Eigen Values and Eigen VectorsDocument23 pagesApplication of Eigen Values and Eigen VectorshimanshukosliyaNo ratings yet
- Math416 SchurDecompositionDocument4 pagesMath416 SchurDecompositionJoaquimJossyNo ratings yet
- Eigenvalues and EigenvectorsDocument3 pagesEigenvalues and EigenvectorsPrithwish SahaNo ratings yet
- Eigenvalues To DiagonalizationDocument21 pagesEigenvalues To DiagonalizationMajety S LskshmiNo ratings yet
- Week 10 Lec 1Document16 pagesWeek 10 Lec 1Injamul HasanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet12 SolDocument10 pagesWorksheet12 SolOnyekachi MbajiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document2 pagesTutorial 5Prinshu RawatNo ratings yet
- La 7Document4 pagesLa 7jordan1412No ratings yet
- Eigenvalue and EigenvectorsDocument8 pagesEigenvalue and Eigenvectorsmahmood mohammadNo ratings yet
- SVD (Lecture)Document98 pagesSVD (Lecture)Tayyaba AsifNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document10 pagesChapter 5clans2806No ratings yet
- Eigenvalues-Eigenvectors 202000211Document21 pagesEigenvalues-Eigenvectors 202000211al.adi.nma.rcos.adeNo ratings yet
- Tuto3 - 2streaminstabilityDocument2 pagesTuto3 - 2streaminstabilityLiam O'LearyNo ratings yet
- A Note On Eigenvalues of Perturbed Hermitian Matrices: Chi-Kwong Li Ren-Cang Li July 2004Document8 pagesA Note On Eigenvalues of Perturbed Hermitian Matrices: Chi-Kwong Li Ren-Cang Li July 2004salehNo ratings yet
- Complex MatricesDocument13 pagesComplex Matriceschecheche24No ratings yet
- Part I - Eigenvalue ProblemDocument15 pagesPart I - Eigenvalue ProblemEndalcNo ratings yet
- Quantum Transport :atom To Transistor, Schrödinger Equation: ExamplesDocument10 pagesQuantum Transport :atom To Transistor, Schrödinger Equation: ExamplesLIAKMANNo ratings yet
- Review of The Key Ideas: 6.1. Introduction To EigenvaluesDocument1 pageReview of The Key Ideas: 6.1. Introduction To Eigenvaluessmile kmNo ratings yet
- Module 11Document7 pagesModule 11M Shahzad MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Algebraic Eigenvalue Problem: Bghiggins/Ucdavis/November - 2020Document28 pagesIntroduction To Algebraic Eigenvalue Problem: Bghiggins/Ucdavis/November - 2020Gani PurwiandonoNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra Practice Final ExamDocument5 pagesLinear Algebra Practice Final ExamahmedNo ratings yet
- Matrix EigDocument14 pagesMatrix EigОлександр РєзнікNo ratings yet
- hw1 SolutionsDocument5 pageshw1 SolutionsbennyNo ratings yet
- Representations of Clifford AlgebrasDocument8 pagesRepresentations of Clifford Algebras劉汯紳No ratings yet
- The Properties of Determinants:: 11 22 II NNDocument15 pagesThe Properties of Determinants:: 11 22 II NNVivek SinghNo ratings yet
- Ae 1Document2 pagesAe 1NameorNickNo ratings yet
- Aljabar Linear Lanjut PDFDocument57 pagesAljabar Linear Lanjut PDFFiQar Ithang RaqifNo ratings yet
- 10.3 Power Method For Approximating Eigenvalues: Definition of Dominant Eigenvalue and Dominant EigenvectorDocument9 pages10.3 Power Method For Approximating Eigenvalues: Definition of Dominant Eigenvalue and Dominant EigenvectorD.n.PrasadNo ratings yet
- 5eigenvalues and Eigenvectors #5Document32 pages5eigenvalues and Eigenvectors #5Sparky VSNo ratings yet
- 10.3 Power Method For Approximating Eigenvalues: Definition of Dominant Eigenvalue and Dominant EigenvectorDocument9 pages10.3 Power Method For Approximating Eigenvalues: Definition of Dominant Eigenvalue and Dominant EigenvectorGovind1085No ratings yet
- TA WEEK 3 CopyDocument27 pagesTA WEEK 3 Copyharjoat BhamraNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geo: Eigenvalues and EigenvectorsDocument3 pagesAnalytic Geo: Eigenvalues and Eigenvectorspooja sinhaNo ratings yet
- Aa547 Lecture Lec9XDocument12 pagesAa547 Lecture Lec9XBabiiMuffinkNo ratings yet
- Linear AlgebraDocument25 pagesLinear AlgebraMarian CatrinescuNo ratings yet
- Eigenvalues, Eigenvectors and Vector Space - SUMMER 2019-20Document14 pagesEigenvalues, Eigenvectors and Vector Space - SUMMER 2019-20tasnimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. Jordan Forms: Lecture Notes For MA1212Document26 pagesChapter 2. Jordan Forms: Lecture Notes For MA1212SameeraBharadwajaHNo ratings yet
- Abdi EVD2007 Pretty PDFDocument10 pagesAbdi EVD2007 Pretty PDFaliNo ratings yet
- Eigenvalues, Eigenvectors and Vector Space - Fall 20-21Document14 pagesEigenvalues, Eigenvectors and Vector Space - Fall 20-21RAFSUN MAHIDYNo ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Water No Get Enemy - Fela Kuti-Electric - PianoDocument2 pagesWater No Get Enemy - Fela Kuti-Electric - PianoMiguel Angel Fernandez Pinedo100% (1)
- The Seatbelts - Sax Quartet - Cowbow Bebop-Partitura - y - Partes (Arrastrado) 4Document1 pageThe Seatbelts - Sax Quartet - Cowbow Bebop-Partitura - y - Partes (Arrastrado) 4Miguel Angel Fernandez PinedoNo ratings yet
- 415187188-TheJazzStandardsPlaybookBassClef-pdf (Arrastrado) PDFDocument1 page415187188-TheJazzStandardsPlaybookBassClef-pdf (Arrastrado) PDFMiguel Angel Fernandez Pinedo0% (2)
- Workbook 2 TJSPBDocument2 pagesWorkbook 2 TJSPBMiguel Angel Fernandez Pinedo0% (1)
- The Seatbelts - Sax Quartet - Cowbow Bebop-Partitura - y - Partes (Arrastrado) PDFDocument1 pageThe Seatbelts - Sax Quartet - Cowbow Bebop-Partitura - y - Partes (Arrastrado) PDFMiguel Angel Fernandez PinedoNo ratings yet
- Caldonia - Tenor Sax Bb-Partitura - y - PartesDocument9 pagesCaldonia - Tenor Sax Bb-Partitura - y - PartesMiguel Angel Fernandez PinedoNo ratings yet
- 415187188-TheJazzStandardsPlaybookBassClef-pdf (Arrastrado) PDFDocument1 page415187188-TheJazzStandardsPlaybookBassClef-pdf (Arrastrado) PDFMiguel Angel Fernandez Pinedo0% (2)
- Caldonia - Tenor Sax BBDocument1 pageCaldonia - Tenor Sax BBMiguel Angel Fernandez PinedoNo ratings yet
- 415187188-TheJazzStandardsPlaybookBassClef-pdf (Arrastrado) PDFDocument1 page415187188-TheJazzStandardsPlaybookBassClef-pdf (Arrastrado) PDFMiguel Angel Fernandez Pinedo0% (1)
- Eigen Decomposition 4Document1 pageEigen Decomposition 4Miguel Angel Fernandez PinedoNo ratings yet
- Semi-Definite. The Eigen-Decomposition of These Matrices AlwaysDocument1 pageSemi-Definite. The Eigen-Decomposition of These Matrices AlwaysMiguel Angel Fernandez PinedoNo ratings yet
- Eigen Decomposition 1Document1 pageEigen Decomposition 1Miguel Angel Fernandez PinedoNo ratings yet